基础语法构成:
查询一般有四个组成部分:
- 查询内容
- 查询对象
- 过滤条件
- 结果排序
举例如下:
select StudentId, StudentName, Gender
from Students
where Gender = '男'
order by StudentId DESC
基本查询语法框架:
- select <列明>
- from <表名>
- where <查询条件表达式>
- order by <排序的列名><升序/降序>
升序:ASC
降序:DESC
前面两条必须有,后面两条可选!
各列之间用逗号分隔!
特殊:查询全部列:select * from <表名>
多个查询条件,用and连接:
举例如下:
select StudentId, Gender, Age
from Students
where Gender = '男' and Age > 22
查询过程重命名:
as 举例如下:
select StudentId as 学号, StudentName as 姓名, Gender as 性别
from Students
where Gender = '男'
order by StudentId DESC
= 举例如下
select 学号 = StudentId, 姓名 = StudentName, 性别 = Gender
from Students
where Gender = '男'
order by StudentId DESC
特殊:+ 的使用,合并的效果
举例如下:
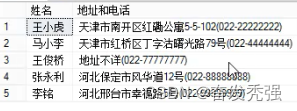
select 姓名 = StudentName, 地址和电话 = StudentAdress + '(' + PhoneNumber + ')'
from Students
--where Gender = '男'
--order by StudentId DESC
运行结果:
使用常量列

查询空列

限制固定行数
select top 5 StudentName, StudentAdress --前五
--select top 20 percent StudentName, StudentAdress --前20%
from Students
--where Gender = '男'
--order by StudentId DESC
总结
简单查询:
一、投影
select * from 表名
select 列1,列2... from 表名
select distinct 列名 from 表名二、筛选
select top 数字 列|* from 表名
(一)等值与不等值
select * from 表名 where 列名=值
select * from 表名 where 列名!=值
select * from 表名 where 列名>值
select * from 表名 where 列名<值
select * from 表名 where 列名>=值
select * from 表名 where 列名<=值(二)多条件与范围
select * from 表名 where 条件1 and|or 条件2 ...
select * from 表名 where between ... and ...
select * from 表名 where 列 in (值列表)(三)模糊查询 like % _
select * from 表名 where 列 like '%_....'三、排序
select * from 表名 where 条件 order by 列名 ASC|DESC,列名 ASC|DESC
四、分组:
统计函数(聚合函数)
count(), max(), min(), sum(), avg()count()统计总行数
count()得到所有的行数
count(列)得到该列中所有非null个数。
select COUNT() from car where Brand='b003'max(列) 这一列的最大,min(列)这一列的最小
select min(price) from carsum(列)这一列的和,avg(列)这一列的平均
select AVG(price) from cargroup by ...having...
1.group by后面跟的是列名。
2.一旦使用group by分组了,则select和from中间就不能用,只能包含两类东西一类是:group by 后面的列名,另一类是统计函数
select Oil,avg(price) from Car group by oil
对于统计函数生成的列,默认是无列名,可以通过下面的方法指定列名。
select Oil as 油耗,COUNT() as 数量,avg(price) 均价 from Car group by oilhaving后面一般跟得是统计函数。它用来对分组后的数据进一步筛选。
版权归原作者 奋发秃强 所有, 如有侵权,请联系我们删除。