文章目录
行转列
测试数据:
DROPTABLEIFEXISTS student_scores;CREATETABLE student_scores (
student_id INT,
subject STRING,
score INT);INSERTINTO student_scores (student_id, subject, score)VALUES(1,'Math',85),(1,'English',78),(1,'Science',92),(2,'Math',88),(2,'English',76),(2,'Science',81),(3,'Math',90),(3,'English',82),(3,'Science',89);
表的结构以及数据展示如下:
student_idsubjectscore1Math851English781Science922Math882English762Science813Math903English823Science89
根据上面的学生成绩表,将其中的行转换成列进行展示,如下所示:
student_idmathenglishscience18578922887681…………
这个需求主要从两个方面切入:
- 因为是统计每名学生的成绩,所以按学生进行分组。
- 行转列操作,其实就是将行数据通过列的方式进行查询展示而已,这里将行转为列的数据共有
3列,分别代表每名同学各科的成绩,我们只需要在统计时加入判断条件即可,每列固定求某科的成绩,如果不是该科则用0或者空值替代,这样就可以轻松完成需求啦。
select
student_id,sum(if(subject="Math",score,0)) math,sum(if(subject="English",score,0)) english,sum(if(subject="Science",score,0)) science
from
student_scores
groupby
student_id;
输出结果如下:

列传行
现在变换一下需求,将学生成绩表中的数据列转换为行,测试数据:
DROPTABLEIFEXISTS student_scores_pivoted;CREATETABLE student_scores_pivoted (
student_id INT,
math INT,
english INT,
science INT);INSERTINTO student_scores_pivoted VALUES(1,85,78,92),(2,88,76,81),(3,90,82,89);
表的结构以及数据展示如下:
student_idMathEnglishScience185789228876813908289
我们需要将其转换为如下结构:
student_idsubjectscore1Math851English781Science922Math882English762Science813Math903English823Science89
这里使用到了
lateral view + posexplode
的方式,将表的一列扩展到多行,从而完成列转行的需求。
相较于传统的
lateral view + explode
扩展方式,
posexplode
会返回两个参数,其中第一个参数表示索引,第二个参数才是其对应的值。
select
student_id,
subject_name_list,
subject_list
from(select
student_id,
concat_ws(',',"Math","English","Science") subject_name,
concat_ws(',',cast(math as string),cast(english as string),cast(science as string)) subject
from
student_scores_pivoted)t1
lateral view posexplode(split(subject,",")) tmp1 as pos1,subject_list
lateral view posexplode(split(subject_name,",")) tmp2 as pos2,subject_name_list
where
tmp1.pos1 = tmp2.pos2;
输出结果如下:

explode
和
posexplode
的区别:
-- explode 主要用于将一个包含多个元素的列转换为多行,每行对应一个元素。SELECT explode(array(1,2,3));-- 结果为:123-- posexplode 与 explode 类似,但它不仅返回数组中的值,还返回值在数组中的位置(索引)。SELECT posexplode(array(1,2,3));-- 结果为:011223
那么这里为什么使用
posexplode
而不是
explode
呢?
如果在这里使用
explode
,那么会导致扩张多次(因为在这里使用了两次
explode
,
3*3
最终会将每行扩张
9
次,形成笛卡尔积),变成如下所示的结果:

所以在这里并不使用
explode
,推荐使用另一个函数
posexplode
,虽然它也会导致笛卡尔积,但可以根据索引设置条件进行过滤:
下面将来讲述这些笛卡尔积数据产生的原因,以及过滤条件该如何设置。
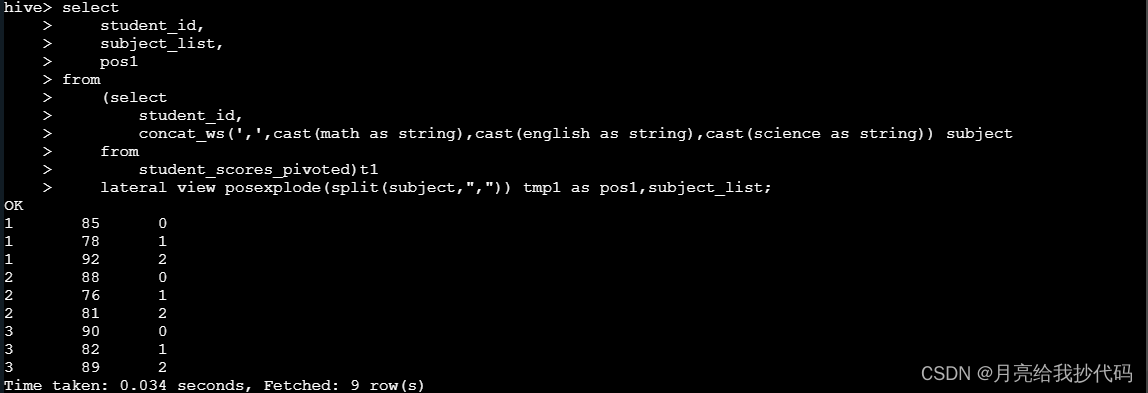
在只使用一个扩展函数时,并不会产生笛卡尔积,如下所示:
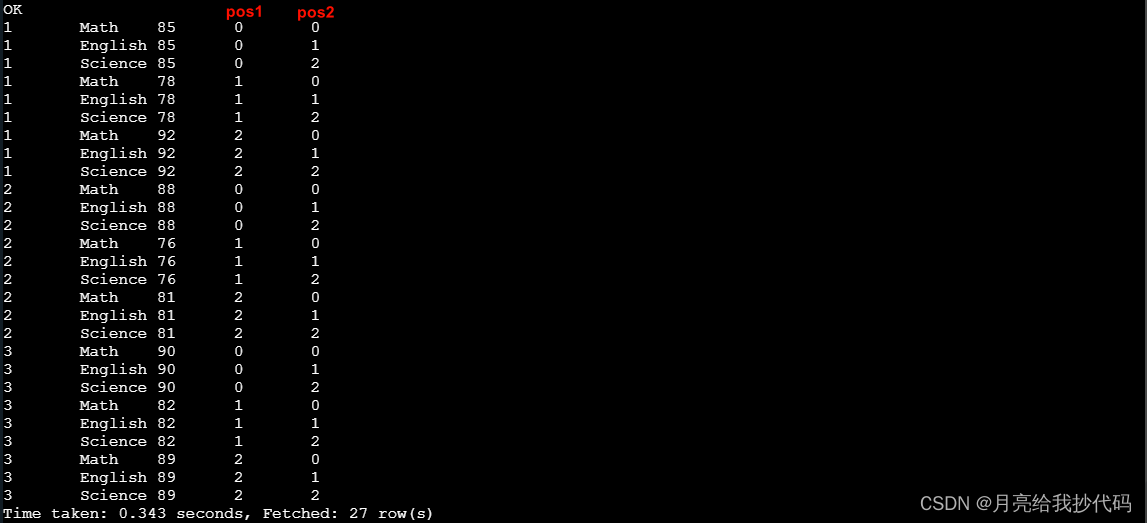
如果同时使用两个扩展函数,那么就会产生笛卡尔积,会随着后续每行的数据量成倍数增长,如下所示:
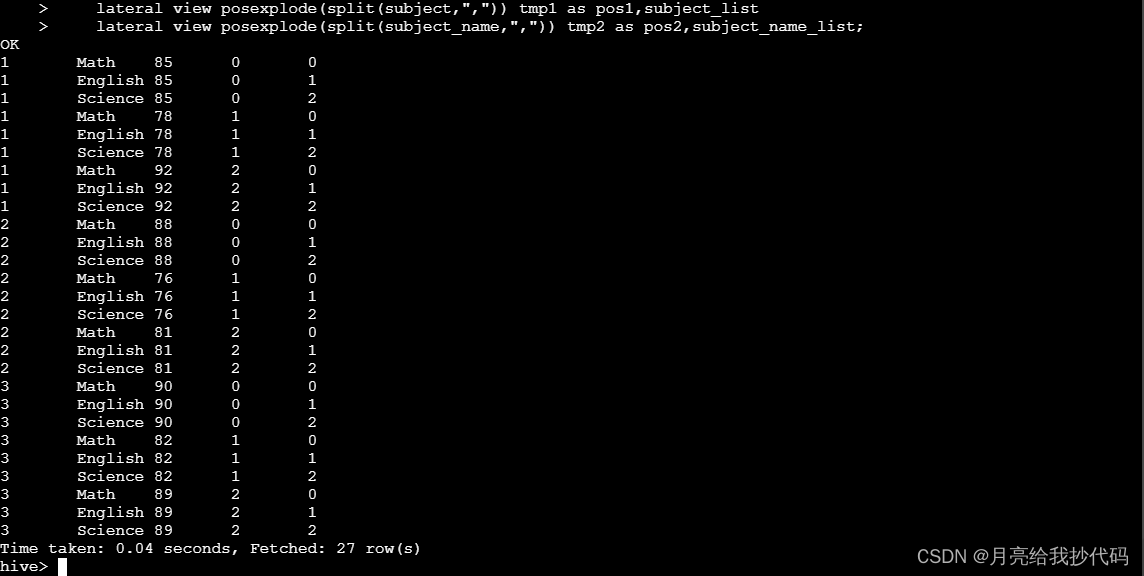
在使用
posexplode
函数形成笛卡尔积后,我们可以通过设置
where
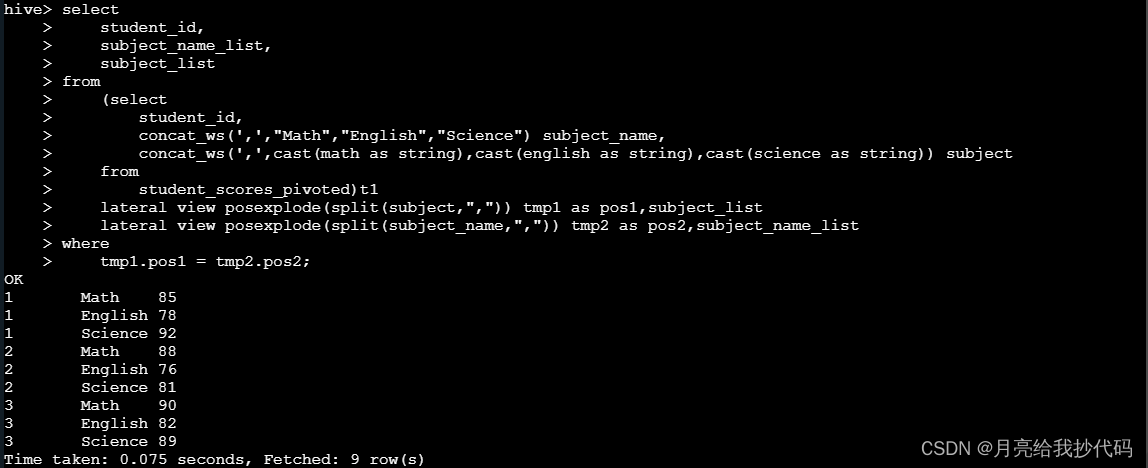
条件来进行过滤,取到对应的数据。
通过观察可以发现,只有当两个索引列的值相同时,其扩展的数据行才是正确的,我们可以通过这一特性来对数据进行过滤,获取最终的结果:
其实,列转行还有其它的写法,这里提供另一种更容易理解的思路:
- 先通过子查询获取单科的成绩;
- 然后再进行合并。
如下所示:
select
student_id,"math" subject_name,
math score
from
student_scores_pivoted
unionallselect
student_id,"english" subject_name,
english score
from
student_scores_pivoted
unionallselect
student_id,"science" subject_name,
science score
from
student_scores_pivoted;
输出结果如下:

解决问题的方式有许多种,但往往我们需要去注重学习解决问题的思路,希望本文对你有所帮助。
版权归原作者 月亮给我抄代码 所有, 如有侵权,请联系我们删除。