文章目录
一、如何在 Linux 中配置 sudo 的访问权限
1.1、添加一个Linux普通用户有 sudo 权限
[root@localhost ~]# useradd test // 创建一个普通用户为:test
[root@localhost ~]#
[root@localhost ~]# passwd test // 设置用户test密码为:test
Changing password for user test.
New password: # test
BAD PASSWORD: The password is shorter than 8 characters
Retype new password: # test
passwd: all authentication tokens updated successfully. # 看到successfully 表示设置成功
[root@localhost ~]#
[root@localhost ~]# id test
uid=1000(test) gid=1000(test) groups=1000(test)
[root@localhost ~]#
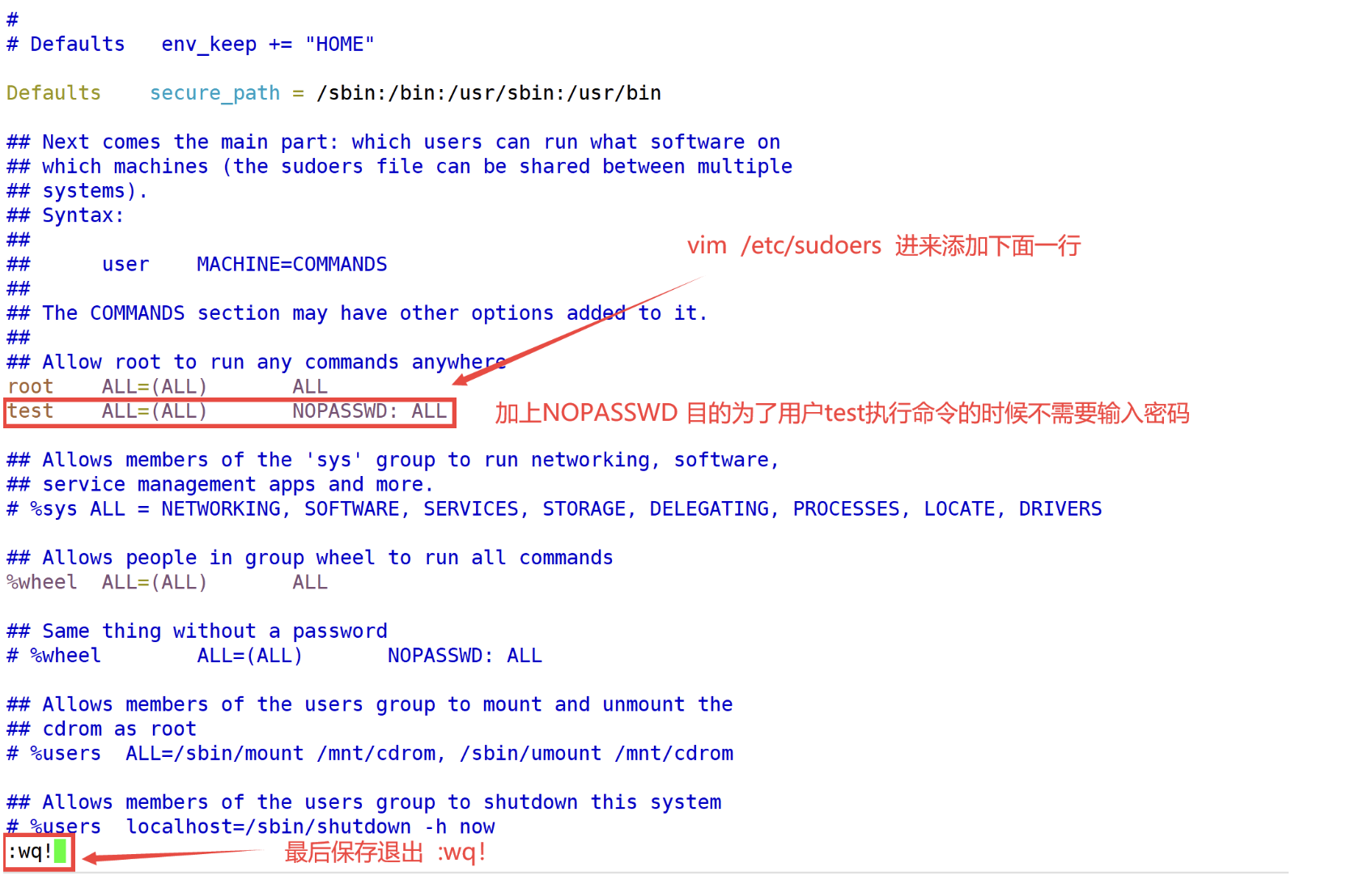
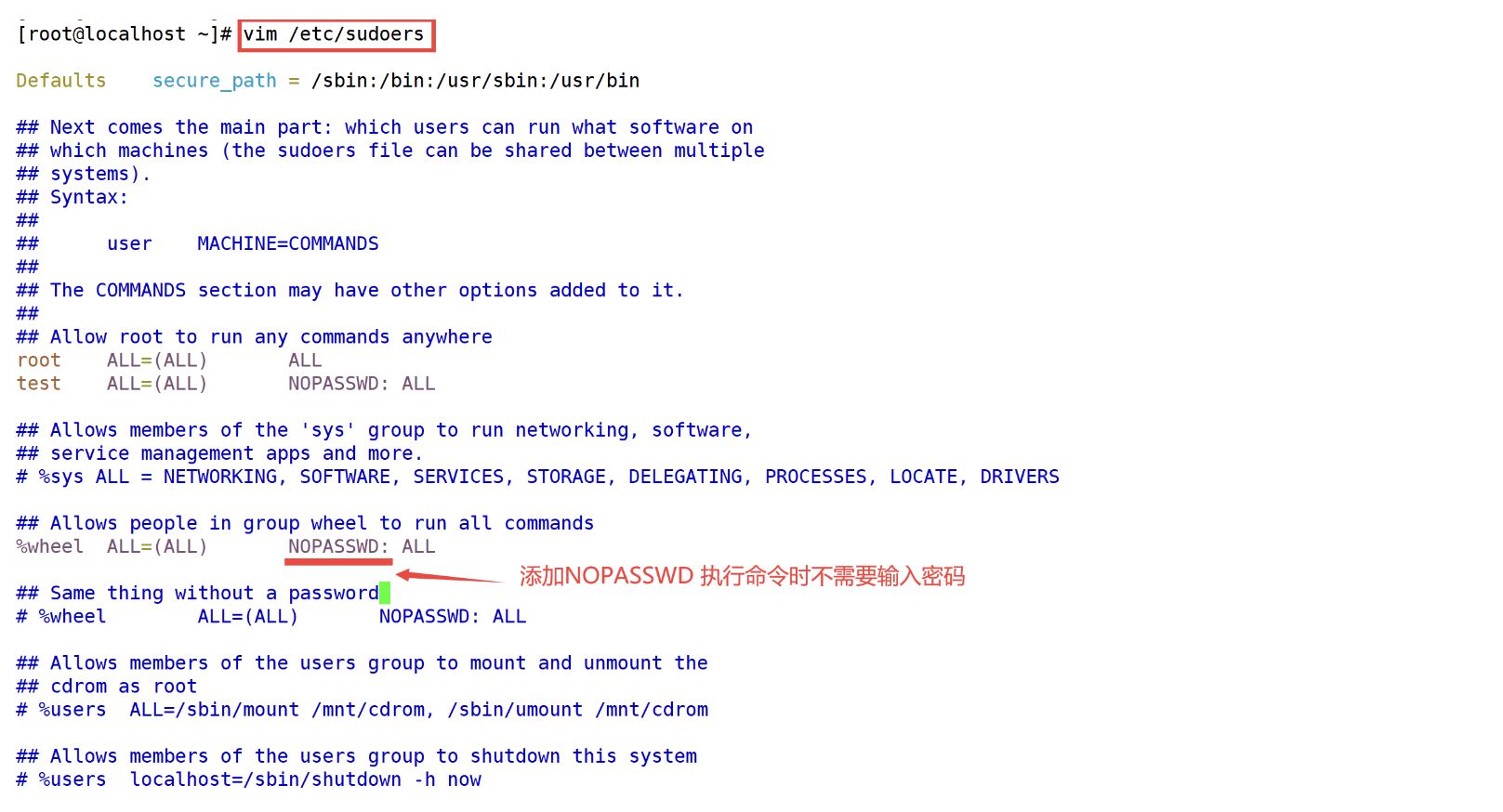
[root@localhost ~]# vim /etc/sudoers
...省略N
root ALL=(ALL) ALL
test ALL=(ALL) NOPASSWD: ALL // 添加这一行
...省略N
1.2、测试普通用户的 sudo 权限
[root@localhost ~]# su - test // 登录用户 test
Last login: Wed Jun 28 16:35:53 CST 2023 from 192.168.192.1 on pts/1
[test@localhost ~]$
[test@localhost ~]$ cd /opt/
[test@localhost opt]$
[test@localhost opt]$ ll
total 0
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 0 Jun 28 16:38 school // 文件school 所有者和所属组为:root
[test@localhost opt]$
[test@localhost opt]$ cp school test.txt // 使用用户test 复制school 文件为 test.txt
cp: cannot create regular file ‘test.txt’: Permission denied # 提示权限不够
[test@localhost opt]$
[test@localhost opt]$ ll
total 0
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 0 Jun 28 16:38 school
[test@localhost opt]$
[test@localhost opt]$ sudo cp school test.txt // 需要加上 sudo
[test@localhost opt]$
[test@localhost opt]$ ll
total 0
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 0 Jun 28 16:38 school
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 0 Jun 28 17:13 test.txt # 复制成功
[test@localhost opt]$
1.3、添加多个Linux普通用户有 sudo 权限
# 创建多个普通用户
[root@localhost ~]# useradd user1 // 创建用户:user1
[root@localhost ~]#
[root@localhost ~]# passwd user1 // 设置密码为:user1
Changing password for user user1.
New password:
BAD PASSWORD: The password is shorter than 7 characters
Retype new password:
passwd: all authentication tokens updated successfully.
[root@localhost ~]#
[root@localhost ~]# id user1
uid=1001(user1) gid=1001(user1) groups=1001(user1)
[root@localhost ~]#
[root@localhost ~]# useradd user2 // 创建用户:user2
[root@localhost ~]#
[root@localhost ~]# passwd user2 // 设置密码为:user2
Changing password for user user2.
New password:
BAD PASSWORD: The password is shorter than 7 characters
Retype new password:
passwd: all authentication tokens updated successfully.
[root@localhost ~]#
[root@localhost ~]# id user2
uid=1001(user2) gid=1001(user2) groups=1001(user2)
[root@localhost ~]#

1.4、验证sudo 权限
# 把 user1 和 user2 添加到拥有超级管理员权限的组(wheel) 里
[root@localhost ~]# getent group wheel
wheel:x:10:
[root@localhost ~]#
[root@localhost ~]# usermod -aG wheel user1 // 添加 user1 用户到 wheel 组了
[root@localhost ~]#
[root@localhost ~]# getent group wheel
wheel:x:10:user1 // 查看已经添加进去
[root@localhost ~]#
[root@localhost ~]# usermod -aG wheel user2 // 添加 user2 用户到 wheel 组了
[root@localhost ~]#
[root@localhost ~]# getent group wheel
wheel:x:10:user1,user2 // 查看已经添加进去
[root@localhost ~]#
[root@localhost ~]# su - user1 // 登录到 user1
[user1@localhost ~]$
[user1@localhost ~]$ cd /opt/
[user1@localhost opt]$
[user1@localhost opt]$ ll
total 0
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 0 Jun 28 16:38 school
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 0 Jun 28 17:13 test.txt
[user1@localhost opt]$
[user1@localhost opt]$ cp school user1.txt // 复制一份会报错权限不够
cp: cannot create regular file ‘user1.txt’: Permission denied
[user1@localhost opt]$
[user1@localhost opt]$ sudo cp school user1.txt // 使用sudo 复制
We trust you have received the usual lecture from the local System
Administrator. It usually boils down to these three things:
#1) Respect the privacy of others.
#2) Think before you type.
#3) With great power comes great responsibility.
[sudo] password for user1: # 提示输入密码。因为,没有在文件/etc/sudoers里的wheel组加上NOPASSWD
[user1@localhost opt]$
[user1@localhost opt]$ ll
total 0
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 0 Jun 28 16:38 school
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 0 Jun 28 17:13 test.txt
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 0 Jun 28 17:55 user1.txt # 创建成功
[user1@localhost opt]$
[root@localhost ~]# su - user2 // 登录 user2
[user2@localhost ~]$
[user2@localhost ~]$ cd /opt/
[user2@localhost opt]$ ll
total 0
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 0 Jun 28 16:38 school
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 0 Jun 28 17:13 test.txt
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 0 Jun 28 17:55 user1.txt
[user2@localhost opt]$
[user2@localhost opt]$ cp school user2 # 复制school文件为 user2
cp: cannot create regular file ‘user2’: Permission denied # 报错权限不够
[user2@localhost opt]$
[user2@localhost opt]$ sudo cp school user2 # 添加sudo。不需要添加密码
[user2@localhost opt]$
[user2@localhost opt]$ ll
total 0
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 0 Jun 28 16:38 school
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 0 Jun 28 17:13 test.txt
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 0 Jun 28 17:55 user1.txt
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 0 Jun 28 18:19 user2
[user2@localhost opt]$
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 0 Jun 28 17:13 test.txt
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 0 Jun 28 17:55 user1.txt
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 0 Jun 28 18:19 user2
[user2@localhost opt]$
本文转载自: https://blog.csdn.net/m0_58805648/article/details/131448563
版权归原作者 阿干tkl 所有, 如有侵权,请联系我们删除。
版权归原作者 阿干tkl 所有, 如有侵权,请联系我们删除。