Mac 安装 Python2、Python3 。
零、基础准备
- 官网 - https://www.python.org/
- 下载入口 - https://www.python.org/downloads/- https://www.python.org/downloads/macos/
一、安装包下载及安装
安装包下载的页面路径是:官网>>> Downloads>>> macOS
其他平台根据请自己的实际情况选择
安装包下载的页面路径也可以是:官网>>> Downloads(点击)
进入到版本选择页面
最上面是最新的 Release 版本,分别是2.x的最新版本和3.x的最新版。
可以下载最新的 Release 版本进行安装,也可以通过搜索选择自己想要的版本进行安装。
通过搜索找到「2.7.16」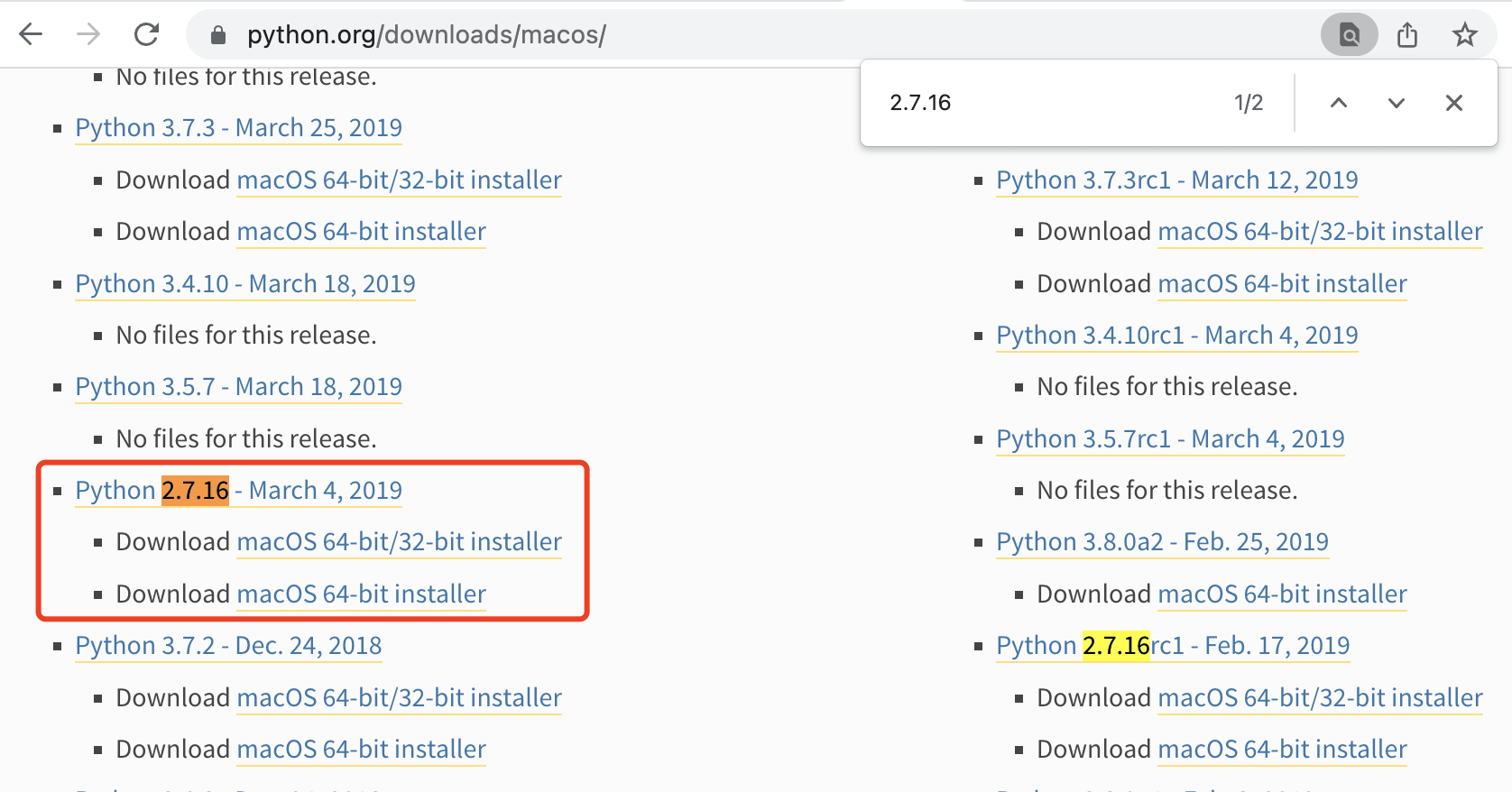
通过搜索找到「3.9.9」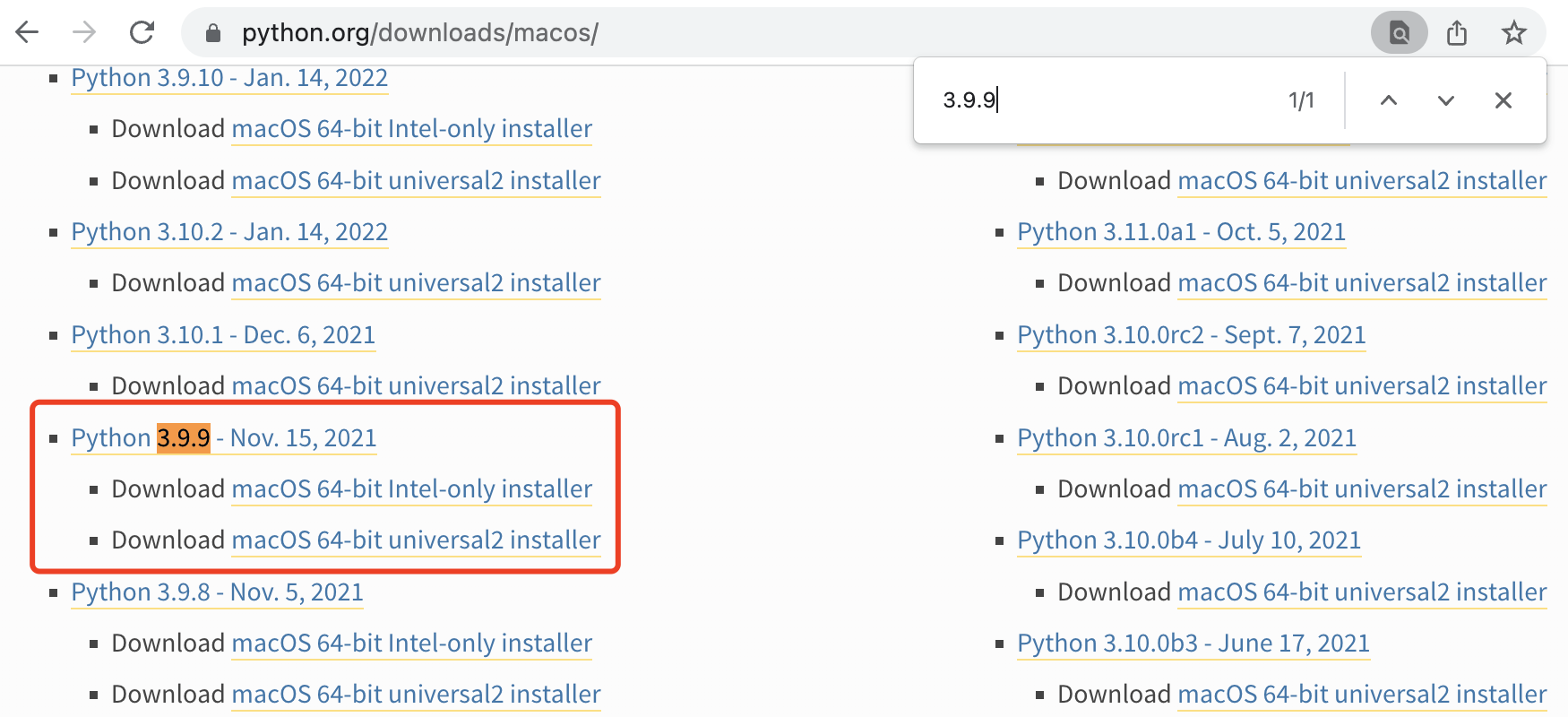
强烈推荐下载最新的 Release 版进行安装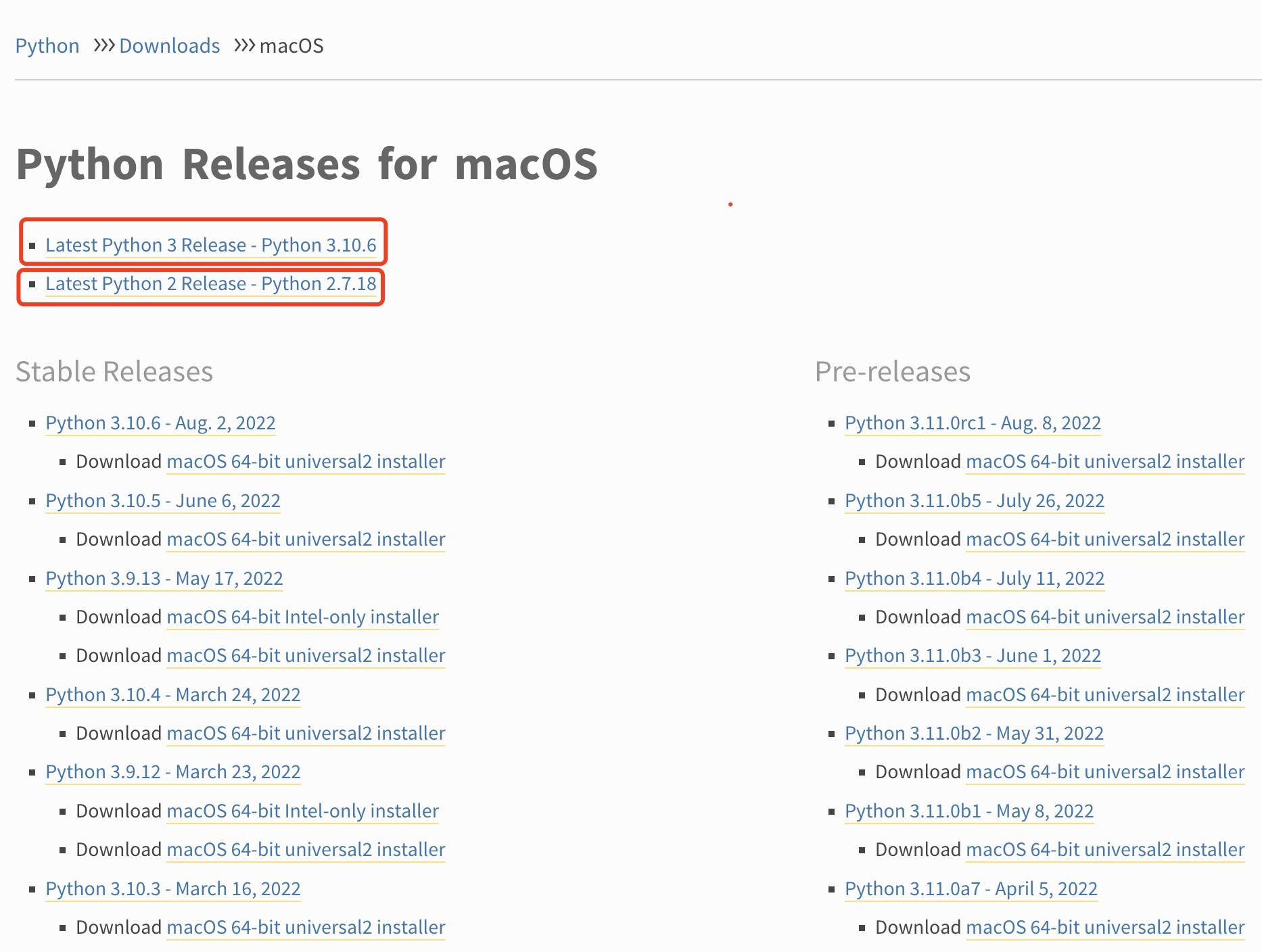
点击对应的链接分别下载即可(下载的过程中注意操作系统的架构和位数)。
👆下载「2.7.18」
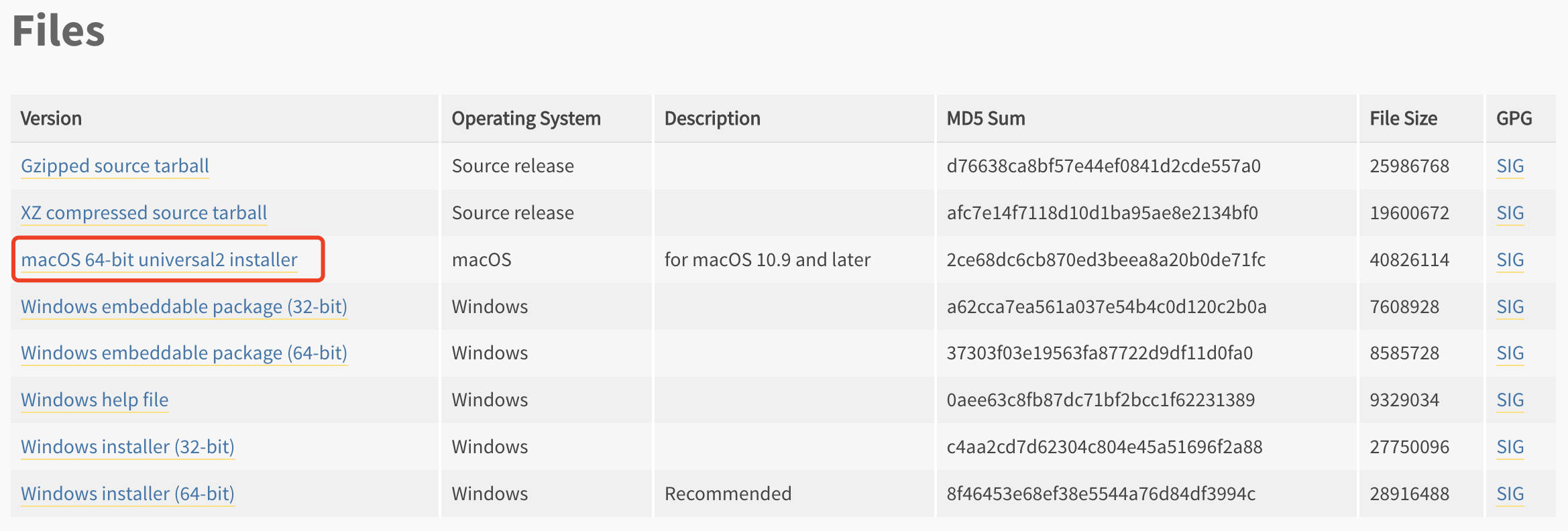
👆下载「3.10.6」

👆下载好的安装包
使用下载好的安装包一直「下一步」即可安装对应版本的 python。
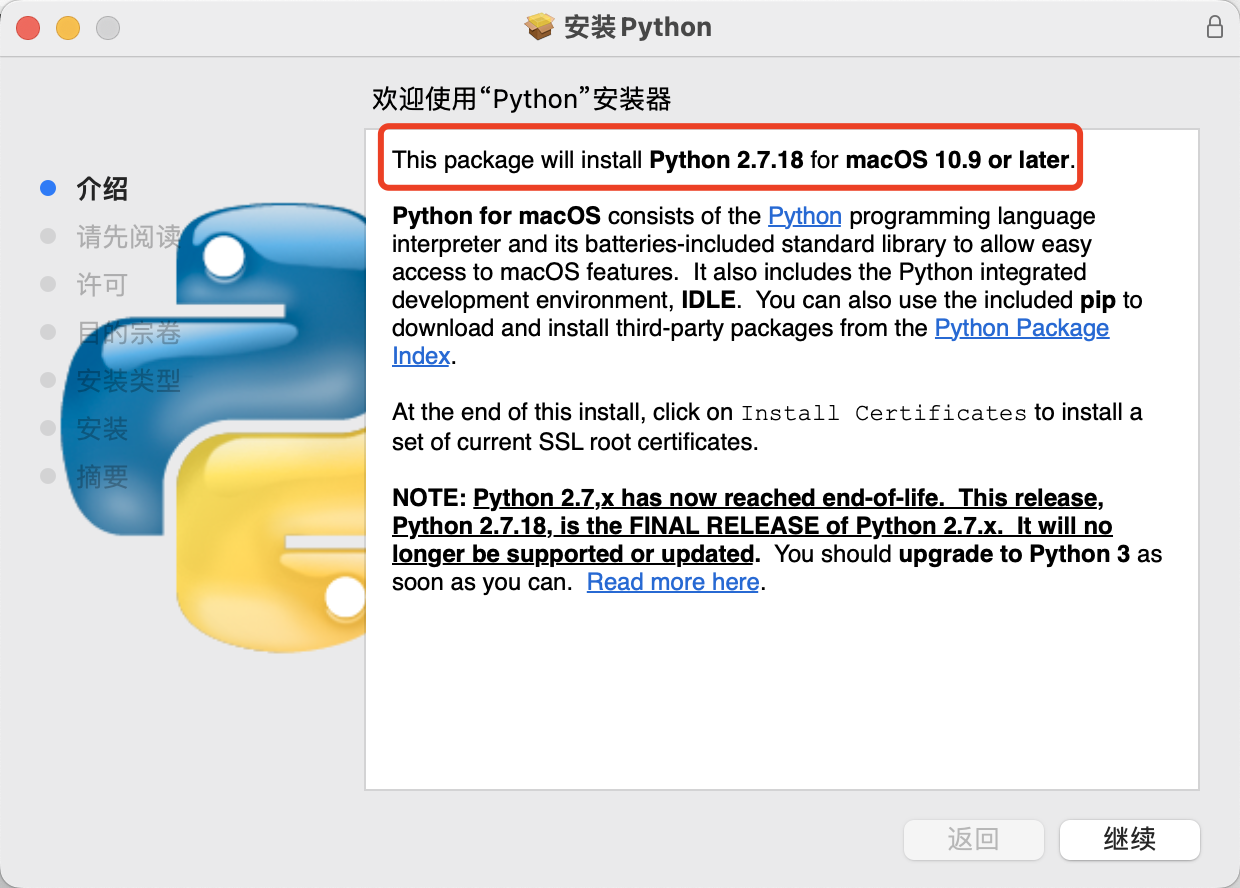

二、安装确认
1、Python2
- 查看版本号
$ python -V
Python 2.7.18
- 帮助命令
$ python -h
usage: /Library/Frameworks/Python.framework/Versions/2.7/Resources/Python.app/Contents/MacOS/Python [option] ... [-c cmd | -m mod | file | -] [arg] ...
Options and arguments (and corresponding environment variables):
-b : issue warnings about comparing bytearray with unicode
(-bb: issue errors)
-B : don't write .py[co] files on import; also PYTHONDONTWRITEBYTECODE=x
-c cmd : program passed in as string (terminates option list)
-d : debug output from parser; also PYTHONDEBUG=x
-E : ignore PYTHON* environment variables (such as PYTHONPATH)
-h : print this help message and exit (also --help)
-i : inspect interactively after running script; forces a prompt even
if stdin does not appear to be a terminal; also PYTHONINSPECT=x
-m mod : run library module as a script (terminates option list)
-O : optimize generated bytecode slightly; also PYTHONOPTIMIZE=x
-OO : remove doc-strings in addition to the -O optimizations
-R : use a pseudo-random salt to make hash() values of various types be
unpredictable between separate invocations of the interpreter, as
a defense against denial-of-service attacks
-Q arg : division options: -Qold (default), -Qwarn, -Qwarnall, -Qnew
-s : don't add user site directory to sys.path; also PYTHONNOUSERSITE
-S : don't imply 'import site' on initialization
-t : issue warnings about inconsistent tab usage (-tt: issue errors)
-u : unbuffered binary stdout and stderr; also PYTHONUNBUFFERED=x
see man page for details on internal buffering relating to '-u'
-v : verbose (trace import statements); also PYTHONVERBOSE=x
can be supplied multiple times to increase verbosity
-V : print the Python version number and exit (also --version)
-W arg : warning control; arg is action:message:category:module:lineno
also PYTHONWARNINGS=arg
-x : skip first line of source, allowing use of non-Unix forms of #!cmd
-3 : warn about Python 3.x incompatibilities that 2to3 cannot trivially fix
file : program read from script file
- : program read from stdin (default; interactive mode if a tty)
arg ...: arguments passed to program in sys.argv[1:]
Other environment variables:
PYTHONSTARTUP: file executed on interactive startup (no default)
PYTHONPATH : ':'-separated list of directories prefixed to the
default module search path. The result is sys.path.
PYTHONHOME : alternate <prefix> directory (or <prefix>:<exec_prefix>).
The default module search path uses <prefix>/pythonX.X.
PYTHONCASEOK : ignore case in 'import' statements (Windows).
PYTHONIOENCODING: Encoding[:errors] used for stdin/stdout/stderr.
PYTHONHASHSEED: if this variable is set to 'random', the effect is the same
as specifying the -R option: a random value is used to seed the hashes of
str, bytes and datetime objects. It can also be set to an integer
in the range [0,4294967295] to get hash values with a predictable seed.
2、Python3
- 查看版本号
$ python3 -V
Python 3.10.6
- 帮助命令
$ python3 -h
usage: /Library/Frameworks/Python.framework/Versions/3.10/bin/python3 [option] ... [-c cmd | -m mod | file | -] [arg] ...
Options and arguments (and corresponding environment variables):
-b : issue warnings about str(bytes_instance), str(bytearray_instance)
and comparing bytes/bytearray with str. (-bb: issue errors)
-B : don't write .pyc files on import; also PYTHONDONTWRITEBYTECODE=x
-c cmd : program passed in as string (terminates option list)
-d : turn on parser debugging output (for experts only, only works on
debug builds); also PYTHONDEBUG=x
-E : ignore PYTHON* environment variables (such as PYTHONPATH)
-h : print this help message and exit (also -? or --help)
-i : inspect interactively after running script; forces a prompt even
if stdin does not appear to be a terminal; also PYTHONINSPECT=x
-I : isolate Python from the user's environment (implies -E and -s)
-m mod : run library module as a script (terminates option list)
-O : remove assert and __debug__-dependent statements; add .opt-1 before
.pyc extension; also PYTHONOPTIMIZE=x
-OO : do -O changes and also discard docstrings; add .opt-2 before
.pyc extension
-q : don't print version and copyright messages on interactive startup
-s : don't add user site directory to sys.path; also PYTHONNOUSERSITE
-S : don't imply 'import site' on initialization
-u : force the stdout and stderr streams to be unbuffered;
this option has no effect on stdin; also PYTHONUNBUFFERED=x
-v : verbose (trace import statements); also PYTHONVERBOSE=x
can be supplied multiple times to increase verbosity
-V : print the Python version number and exit (also --version)
when given twice, print more information about the build
-W arg : warning control; arg is action:message:category:module:lineno
also PYTHONWARNINGS=arg
-x : skip first line of source, allowing use of non-Unix forms of #!cmd
-X opt : set implementation-specific option. The following options are available:
-X faulthandler: enable faulthandler
-X showrefcount: output the total reference count and number of used
memory blocks when the program finishes or after each statement in the
interactive interpreter. This only works on debug builds
-X tracemalloc: start tracing Python memory allocations using the
tracemalloc module. By default, only the most recent frame is stored in a
traceback of a trace. Use -X tracemalloc=NFRAME to start tracing with a
traceback limit of NFRAME frames
-X importtime: show how long each import takes. It shows module name,
cumulative time (including nested imports) and self time (excluding
nested imports). Note that its output may be broken in multi-threaded
application. Typical usage is python3 -X importtime -c 'import asyncio'
-X dev: enable CPython's "development mode", introducing additional runtime
checks which are too expensive to be enabled by default. Effect of the
developer mode:
* Add default warning filter, as -W default
* Install debug hooks on memory allocators: see the PyMem_SetupDebugHooks()
C function
* Enable the faulthandler module to dump the Python traceback on a crash
* Enable asyncio debug mode
* Set the dev_mode attribute of sys.flags to True
* io.IOBase destructor logs close() exceptions
-X utf8: enable UTF-8 mode for operating system interfaces, overriding the default
locale-aware mode. -X utf8=0 explicitly disables UTF-8 mode (even when it would
otherwise activate automatically)
-X pycache_prefix=PATH: enable writing .pyc files to a parallel tree rooted at the
given directory instead of to the code tree
-X warn_default_encoding: enable opt-in EncodingWarning for 'encoding=None'
--check-hash-based-pycs always|default|never:
control how Python invalidates hash-based .pyc files
file : program read from script file
- : program read from stdin (default; interactive mode if a tty)
arg ...: arguments passed to program in sys.argv[1:]
Other environment variables:
PYTHONSTARTUP: file executed on interactive startup (no default)
PYTHONPATH : ':'-separated list of directories prefixed to the
default module search path. The result is sys.path.
PYTHONHOME : alternate <prefix> directory (or <prefix>:<exec_prefix>).
The default module search path uses <prefix>/lib/pythonX.X.
PYTHONPLATLIBDIR : override sys.platlibdir.
PYTHONCASEOK : ignore case in 'import' statements (Windows).
PYTHONUTF8: if set to 1, enable the UTF-8 mode.
PYTHONIOENCODING: Encoding[:errors] used for stdin/stdout/stderr.
PYTHONFAULTHANDLER: dump the Python traceback on fatal errors.
PYTHONHASHSEED: if this variable is set to 'random', a random value is used
to seed the hashes of str and bytes objects. It can also be set to an
integer in the range [0,4294967295] to get hash values with a
predictable seed.
PYTHONMALLOC: set the Python memory allocators and/or install debug hooks
on Python memory allocators. Use PYTHONMALLOC=debug to install debug
hooks.
PYTHONCOERCECLOCALE: if this variable is set to 0, it disables the locale
coercion behavior. Use PYTHONCOERCECLOCALE=warn to request display of
locale coercion and locale compatibility warnings on stderr.
PYTHONBREAKPOINT: if this variable is set to 0, it disables the default
debugger. It can be set to the callable of your debugger of choice.
PYTHONDEVMODE: enable the development mode.
PYTHONPYCACHEPREFIX: root directory for bytecode cache (pyc) files.
PYTHONWARNDEFAULTENCODING: enable opt-in EncodingWarning for 'encoding=None'.
三、其他
除了使用
python
、
python3
命令来调用对应版本的 python 外,还可以使用如下的命令来调用对应版本的 python。
$ python2 -V
Python 2.7.18
$ python2.7 -V
Python 2.7.18
$ python3.10 -V
Python 3.10.6
这些都可以可以在
/usr/local/bin
这个目录下看到相关命令对应的「软连接」。
$ pwd
/usr/local/bin
$ ls -l | grep python
python -> ../../../Library/Frameworks/Python.framework/Versions/2.7/bin/python
python-config -> ../../../Library/Frameworks/Python.framework/Versions/2.7/bin/python-config
python2 -> ../../../Library/Frameworks/Python.framework/Versions/2.7/bin/python2
python2-config -> ../../../Library/Frameworks/Python.framework/Versions/2.7/bin/python2-config
python2.7 -> ../../../Library/Frameworks/Python.framework/Versions/2.7/bin/python2.7
python2.7-config -> ../../../Library/Frameworks/Python.framework/Versions/2.7/bin/python2.7-config
python3 -> ../../../Library/Frameworks/Python.framework/Versions/3.10/bin/python3
python3-config -> ../../../Library/Frameworks/Python.framework/Versions/3.10/bin/python3-config
python3-intel64 -> ../../../Library/Frameworks/Python.framework/Versions/3.10/bin/python3-intel64
python3.10 -> ../../../Library/Frameworks/Python.framework/Versions/3.10/bin/python3.10
python3.10-config -> ../../../Library/Frameworks/Python.framework/Versions/3.10/bin/python3.10-config
python3.10-intel64 -> ../../../Library/Frameworks/Python.framework/Versions/3.10/bin/python3.10-intel64
pythonw -> ../../../Library/Frameworks/Python.framework/Versions/2.7/bin/pythonw
pythonw2 -> ../../../Library/Frameworks/Python.framework/Versions/2.7/bin/pythonw2
pythonw2.7 -> ../../../Library/Frameworks/Python.framework/Versions/2.7/bin/pythonw2.7
**PS:
python2
和
python3
的兼容性一直被广大开发者诟病。**
版权归原作者 DevOps前进四 所有, 如有侵权,请联系我们删除。