samples_per_gpu=1, ## 单个 GPU 的批量大小
workers_per_gpu=4, ## 为每个 GPU 预取数据的 Worker
1、tools/train.py
CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES=7指定固定的GPU,--work-dir表示configs保存的目录
CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES=7 python tools/train.py configs/seaformer/seaformer_base_512x512_160k_2x8_ade20k.py --work-dir result/seaformer/base16
**tools/dist_train.sh **
该脚本是用于启动单机多卡/多机多卡分布式训练的,里面内容不多,无非是对
python -m torch.distributed.launch ...
的封装,留给用户的接口很简单,只需要指定想要用的 GPU 的个数即可,
bash tools/dist_train.sh configs/seaformer/seaformer_base_512x512_160k_2x8_ade20k.py --work-dir result/seaformer/base16 3
2、tools/test.py
输出可视化结果至目录文件夹
- 可以选择评估方式
--eval,对于 COCO 数据集,可选 bbox 、segm、proposal ;对于 VOC 数据集,可选 map、recall - 也可以选择
--out,指定测试结果的 pkl 输出文件
python tools/test.py ${CONFIG_FILE} ${CHECKPOINT_FILE} [--out ${RESULT_FILE}] [--eval ${EVAL_METRICS}] [--show]
可视化具体实例如下:
#1、验证图像的可视化
python tools/test.py configs/fcn/fcn_r50-d8_512x512_20k_voc12.py work_dir/latest.pth --show-dir="output"
#或者
python tools/test.py configs/fcn/fcn_r50-d8_512x512_20k_voc12.py work_dir/latest.pth --show-dir output
#2、衡量指标显示
python tools/test.py configs/fcn/fcn_r50-d8_512x512_20k_voc12.py work_dir/latest.pth --eval mAp
RESULT_FILE:输出结果的文件名,采用pickle格式。如果未指定,结果将不会保存到文件中。EVAL_METRICS:要根据结果评估的项目。允许的值是:COCO:proposal_fast,proposal,bbox,segmPASCAL VOC:mAP,recall--show:如果指定,检测结果将绘制在图像上并显示在新窗口中。仅适用于单GPU测试,用于调试和可视化。请确保您的环境中可以使用GUI,否则您可能会遇到类似的错误。cannot ``````connect ``````to ``````X ``````server--show-dir: 如果指定,检测结果将绘制在图像上并保存到指定的目录中。仅适用于单GPU测试,用于调试和可视化。使用此选项时,您的环境中不需要可用的GUI。--show-score-thr: 如果指定,则将删除分数低于此阈值的检测。
show-dir 参数来控制是否输出绘制的图像,表示输出图像的路径。
指定输出到 pkl 文件:
python tools/test.py configs/my_coco_config/my_coco_config.py checkpoints/faster_rcnn_r50_fpn_1x_coco_20200130-047c8118.pth --out faster_rcnn_fpn_coco.pkl
3. 分析日志
pip install seaborn
python tools/analyze_logs.py plot_curve [--keys ${KEYS}] [--title ${TITLE}] [--legend ${LEGEND}] [--backend ${BACKEND}] [--style ${STYLE}] [--out ${OUT_FILE}]
绘制分类损失
python tools/analyze_logs.py plot_curve log.json --keys loss_cls --legend loss_cls日志分析:
- 用于分析我们训练过程中得到的日志文件,注意这里传入的日志文件必须是 json 文件,而第一个参数
plot_curve有两个可选项:plot_curve和cal_train_time,同样可以通过--out指定输出图片文件。 - 具体实例如下:
python tools/analysis_tools/analyze_logs.py plot_curve work_dirs/my_coco_config/20220503_165551.log.json --out log_curve.png
- 绘制训练时的分类和回归损失,并将该图保存为pdf。
python tools/analyze_logs.py plot_curve log.json --keys loss_cls loss_bbox --out losses.pdf- 在同一个图中绘制两次训练的bbox mAP
python tools/analyze_logs.py plot_curve log1.json log2.json --keys bbox_mAP --legend run1 run2## 4、Flops、Params、fps的实现- 本工具用于统计模型的参数量,可以通过
--shape参数指定输入图片的尺寸 python tools/get_flops.py ${CONFIG_FILE} [--shape ${INPUT_SHAPE}]例如:python tools/get_flops.py configs/danet/danet_r101-d8_512x512_20k_voc12aug.py#如果想在指定GPU上运行则执行以下代码 CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES=2 python tools/get_flops.py configs/danet/danet_r101-d8_512x512_20k_voc12aug.py python tools/analysis_tools/get_flops.py configs/my_coco_config/my_coco_config.py --shape 640 480输出结果为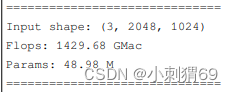 ## fps的实现:
## fps的实现:tools/benchmark.py 此工具是用来测试模型在当前环境下的推理速度的,模型会跑一遍配置文件中指定的测试集,计算单图推理时间(FPS)。
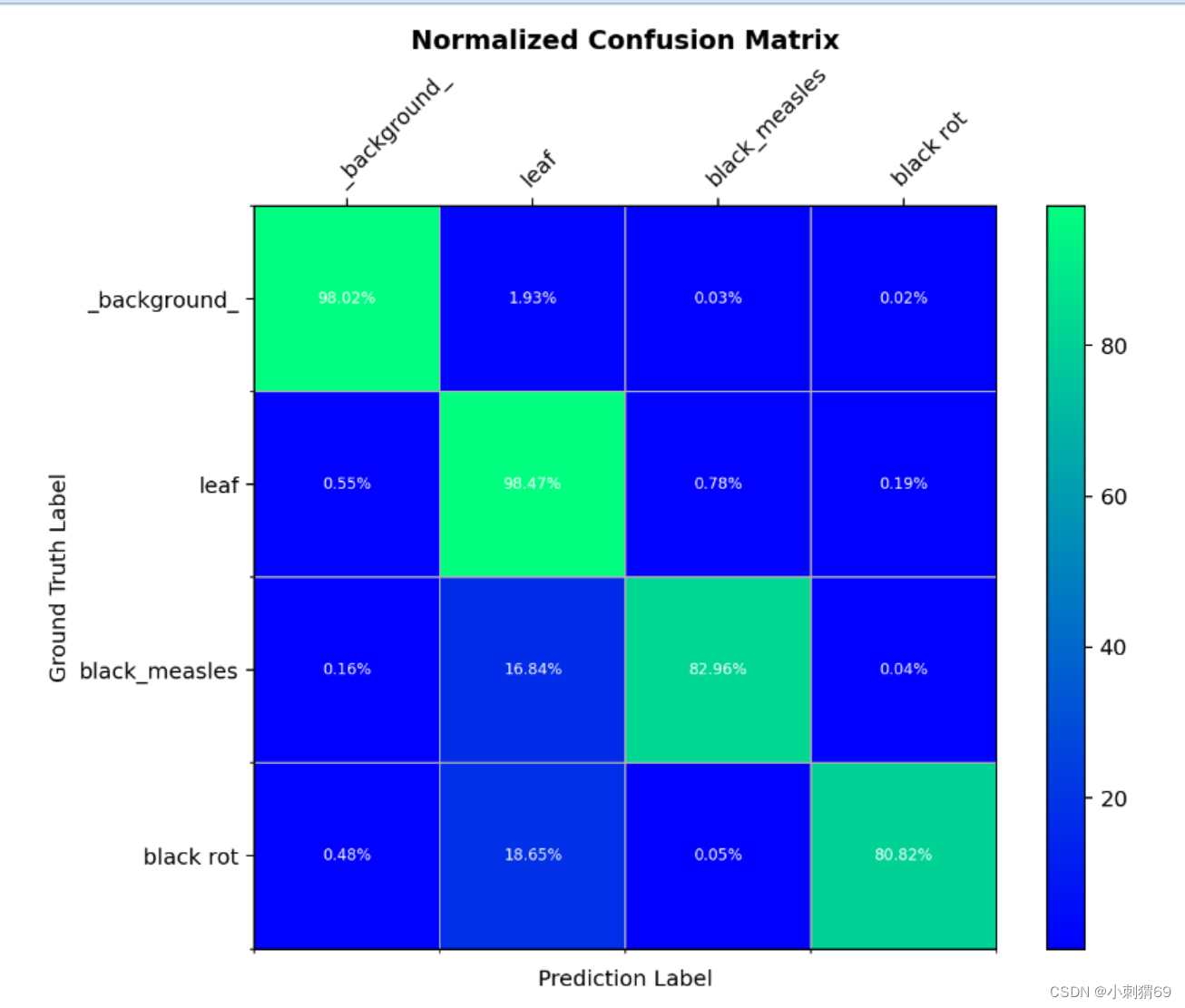
CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES=4 python tools/benchmark.py configs/seaformer/seaformer_large_512x512_160k_2x8_ade20k.py result/seaformer/large16/iter_150000.pth## 5、混淆矩阵- 计算混淆矩阵,需要输入的三个参数是:config文件,pkl结果文件,输出目录
- mkdir coco_confusion_matrix python tools/analysis_tools/confusion_matrix.py configs/my_coco_config/my_coco_config.py faster_rcnn_fpn_coco.pkl coco_confusion_matrix
6、画 PR 曲线 plot_pr_curve.py
import osimport sysimport mmcvimport numpy as npimport argparseimport matplotlib.pyplot as pltfrom pycocotools.coco import COCOfrom pycocotools.cocoeval import COCOevalfrom mmcv import Configfrom mmdet.datasets import build_datasetdef plot_pr_curve(config_file, result_file, out_pic, metric="bbox"): """plot precison-recall curve based on testing results of pkl file. Args: config_file (list[list | tuple]): config file path. result_file (str): pkl file of testing results path. metric (str): Metrics to be evaluated. Options are 'bbox', 'segm'. """ cfg = Config.fromfile(config_file) # turn on test mode of dataset if isinstance(cfg.data.test, dict): cfg.data.test.test_mode = True elif isinstance(cfg.data.test, list): for ds_cfg in cfg.data.test: ds_cfg.test_mode = True # build dataset dataset = build_dataset(cfg.data.test) # load result file in pkl format pkl_results = mmcv.load(result_file) # convert pkl file (list[list | tuple | ndarray]) to json json_results, _ = dataset.format_results(pkl_results) # initialize COCO instance coco = COCO(annotation_file=cfg.data.test.ann_file) coco_gt = coco coco_dt = coco_gt.loadRes(json_results[metric]) # initialize COCOeval instance coco_eval = COCOeval(coco_gt, coco_dt, metric) coco_eval.evaluate() coco_eval.accumulate() coco_eval.summarize() # extract eval data precisions = coco_eval.eval["precision"] ''' precisions[T, R, K, A, M] T: iou thresholds [0.5 : 0.05 : 0.95], idx from 0 to 9 R: recall thresholds [0 : 0.01 : 1], idx from 0 to 100 K: category, idx from 0 to ... A: area range, (all, small, medium, large), idx from 0 to 3 M: max dets, (1, 10, 100), idx from 0 to 2 ''' pr_array1 = precisions[0, :, 0, 0, 2] pr_array2 = precisions[1, :, 0, 0, 2] pr_array3 = precisions[2, :, 0, 0, 2] pr_array4 = precisions[3, :, 0, 0, 2] pr_array5 = precisions[4, :, 0, 0, 2] pr_array6 = precisions[5, :, 0, 0, 2] pr_array7 = precisions[6, :, 0, 0, 2] pr_array8 = precisions[7, :, 0, 0, 2] pr_array9 = precisions[8, :, 0, 0, 2] pr_array10 = precisions[9, :, 0, 0, 2] x = np.arange(0.0, 1.01, 0.01) # plot PR curve plt.plot(x, pr_array1, label="iou=0.5") plt.plot(x, pr_array2, label="iou=0.55") plt.plot(x, pr_array3, label="iou=0.6") plt.plot(x, pr_array4, label="iou=0.65") plt.plot(x, pr_array5, label="iou=0.7") plt.plot(x, pr_array6, label="iou=0.75") plt.plot(x, pr_array7, label="iou=0.8") plt.plot(x, pr_array8, label="iou=0.85") plt.plot(x, pr_array9, label="iou=0.9") plt.plot(x, pr_array10, label="iou=0.95") plt.xlabel("recall") plt.ylabel("precison") plt.xlim(0, 1.0) plt.ylim(0, 1.01) plt.grid(True) plt.legend(loc="lower left") plt.savefig(out_pic)if __name__ == "__main__": parser = argparse.ArgumentParser() parser.add_argument('config', help='config file path') parser.add_argument('pkl_result_file', help='pkl result file path') parser.add_argument('--out', default='pr_curve.png') parser.add_argument('--eval', default='bbox') cfg = parser.parse_args() plot_pr_curve(config_file=cfg.config, result_file=cfg.pkl_result_file, out_pic=cfg.out, metric=cfg.eval)``````python plot_pr_curve.py configs/my_coco_config/my_coco_config.py faster_rcnn_fpn_coco.pkl这里用到的 pkl 结果文件,即是上面运行tools/test.py指定--out的输出文件。
版权归原作者 小刺猬69 所有, 如有侵权,请联系我们删除。