文章目录
先创建一个springboot项目,并在pom文件中添加web依赖:
<dependency><groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId><artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId></dependency>
创建user对象:
publicclassUser{privateString name;privateInteger age;publicStringgetName(){return name;}publicvoidsetName(String name){this.name = name;}publicIntegergetAge(){return age;}publicvoidsetAge(Integer age){this.age = age;}@OverridepublicStringtoString(){return"User{"+"name='"+ name +'\''+", age="+ age +'}';}}
创建一个controller:
@RestController@RequestMapping("/store")publicclassTestController{}
1、java方法入参里面什么注解都没有
/**
* 第一种:java方法入参里面什么注解都没有
* */@RequestMapping("/noAnnotation")publicStringnoAnnotation(User user){return user.toString();}
结果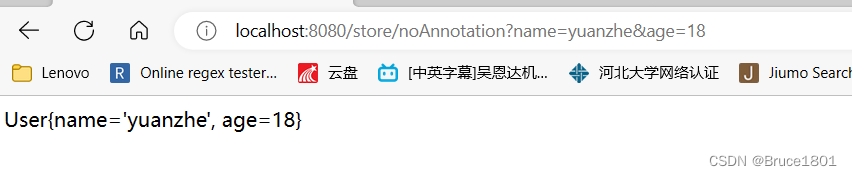
适用于:请求参数比较少
缺点:请求参数比较多的时候,可能会丢参数,因为get请求有长度限制。
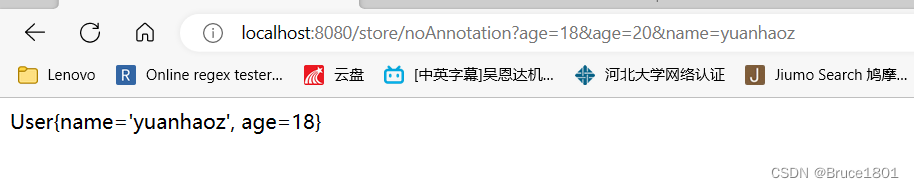
如果参数重复了,比如:http://localhost:8080/store/noAnnotation?age=18&age=20&name=yuanhaoz,参数中age有两个,一个等于18,另一个等于20,如果是int类型的则取最先声明的那个;如果是String类型的,则会叠加
2、@PathVariable这种方式接收URL路径参数作为参数
/**
* 第二种:不使用?&来拼接参数
* */@RequestMapping("/havaPathVariable/{name}/{age}")publicStringhavaPathVariable(@PathVariable(value ="name")String name,@PathVariable(value ="age")int age ){return name+age;}
@PathVariable根据value将url中的参数取出来
结果: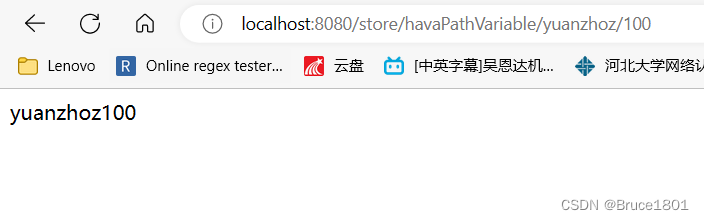
适用于:参数比较少,以及动态接口情况
如何改成参数非必传:
不仅要在@PathVariable()中加required = false,还要设置多个url path,这是因为url要求带参,属于REST参数。
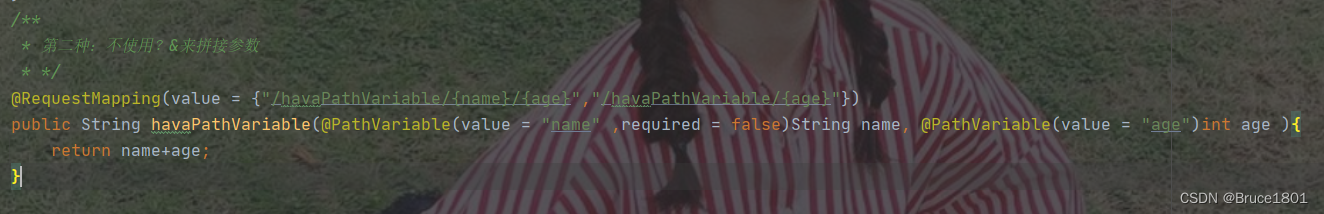
结果: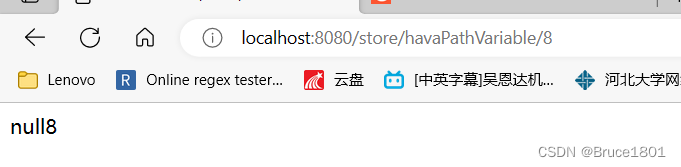
如果只设置required = false话,是无法请求的。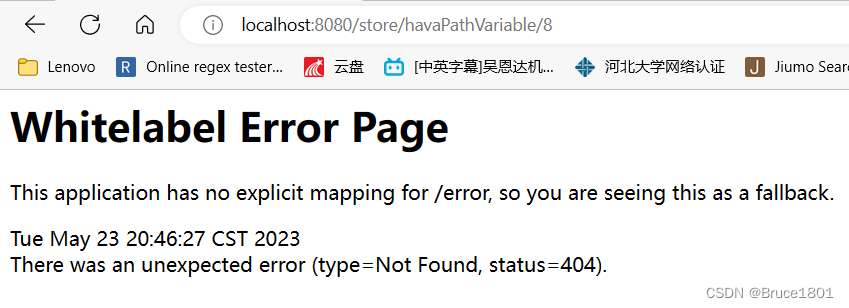
3、@RequestBody这种方式接收前端发送过来的请求体
/**
* 第三种:@RequestBody
* */@RequestMapping("/haveRequestBody")publicStringhaveRequestBody(@RequestBodyUser user){return user.toString();}
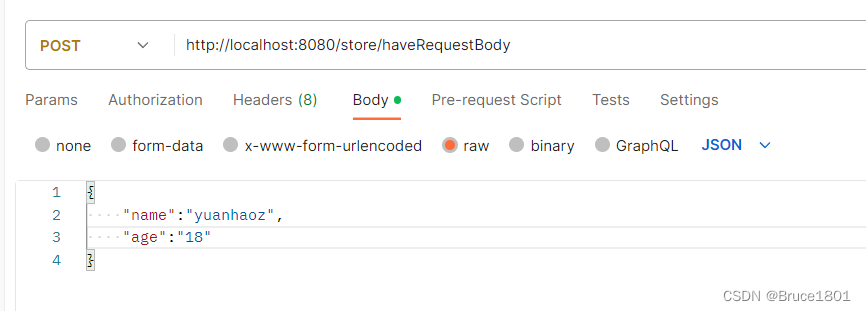
结果: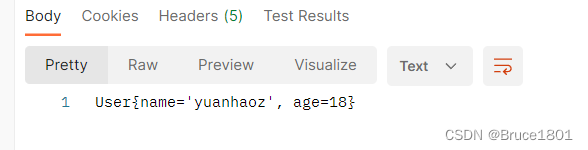
这个注解会从http请求的body当中拿到json,并且反序列化成java对象
适用于:请求参数非常多(因为body没有长度限制)
如果参数重复了,无论什么类型取声明的最后一个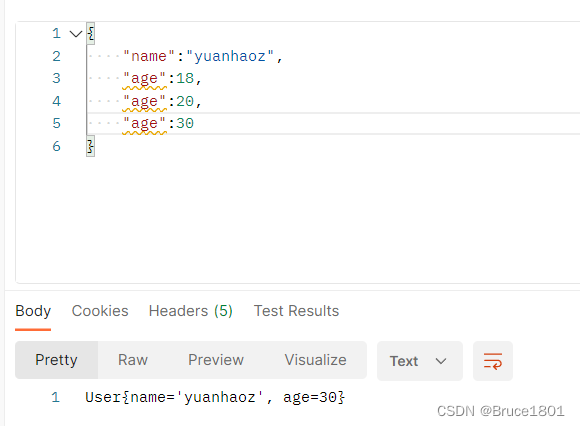
解析list怎么写
body: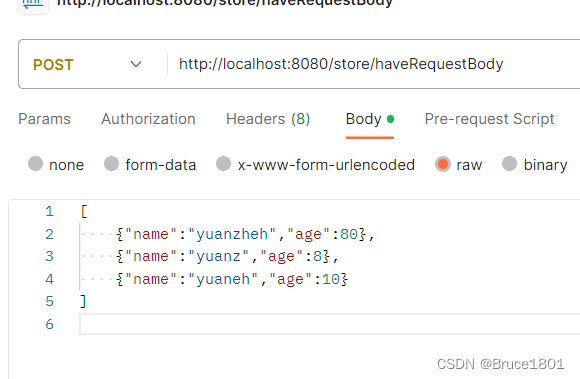
controller: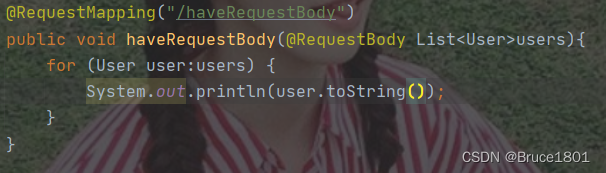
解析嵌套对象怎么写
body:
在json中的每个对象里添加一个phone对象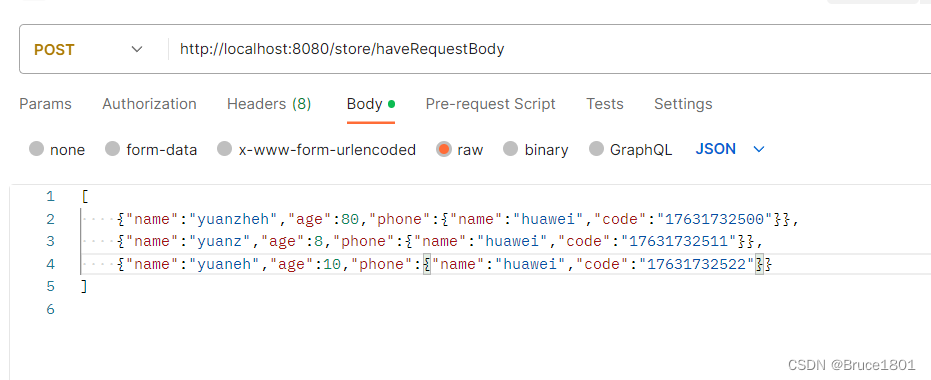
创建phone对象(可以根据json中的phone对象创建所有字段,也可设置部分字段)
publicclassPhone{privateString name;privateString code;publicStringgetName(){return name;}publicvoidsetName(String name){this.name = name;}publicStringgetCode(){return code;}publicvoidsetCode(String code){this.code = code;}@OverridepublicStringtoString(){return"Phone{"+"name='"+ name +'\''+", code='"+ code +'\''+'}';}}
User中要添加与json中对应的对象,才会将json中的嵌套对象解析出来。
在user对象中添加phone,并修改tostring方法;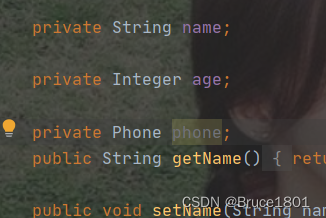
controller: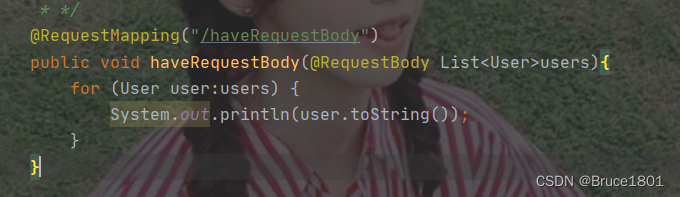
结果: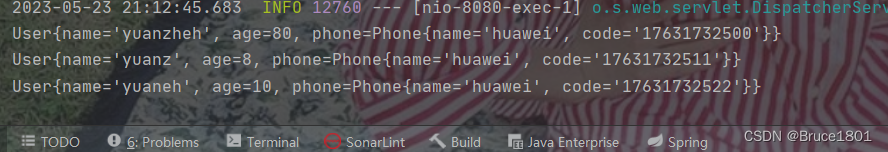
4、RestFul风格
概念
Restful就是一个资源定位及资源操作的风格。不是标准也不是协议,只是一种风格。基于这个风格设计的软件可以更简洁,更有层次,更易于实现缓存等机制。
功能
资源:互联网所有的事物都可以被抽象为资源
资源操作:使用POST、DELETE、PUT、GET,使用不同方法对资源进行操作。
分别对应 添加、 删除、修改、查询。
传统方式操作资源:通过不同的参数来实现不同的效果!方法单一,post 和 get
http://127.0.0.1/item/queryItem.action?id=1 查询,GET
http://127.0.0.1/item/saveItem.action 新增,POST
http://127.0.0.1/item/updateItem.action 更新,POST
http://127.0.0.1/item/deleteItem.action?id=1 删除,GET或POST
使用RestFul操作资源:可以通过不同的请求方式来实现不同的效果!如下:请求地址一样,但是功能可以不同!
http://127.0.0.1/item/1 查询,GET
http://127.0.0.1/item 新增,POST
http://127.0.0.1/item 更新,PUT
http://127.0.0.1/item/1 删除,DELETE
相比于传统方式使用链接来访问请求,Resful可以通过使用通过不同的请求方式来达到不同的效果
基本使用
@RequestMapping("/noAnnotation",method ={RequestMethod.GET})publicStringnoAnnotation(User user){return user.toString();}
也可通过将RequestMapping替换为:
@GetMapping@PostMapping@PutMapping@DeleteMapping@PatchMapping
例如:
@GetMapping("/noAnnotation")publicStringnoAnnotation(User user){return user.toString();}
注:所有的地址栏请求默认都会是 HTTP GET 类型的。
版权归原作者 Bruce1801 所有, 如有侵权,请联系我们删除。