前言
在前两篇,详细了解了谷歌gRPC的使用,以及gRPC实际使用中的几种通信模式,本篇通过实际案例了解下 gRPC与springboot的整合过程;
整合过程
案例为了模拟真实的场景,仍然分为Server端,和Client端,这个和前两篇保持一致,分为2个工程模块,服务端发布服务,客户端调服务,整体步骤和之前差不多;

一、服务端:grpc-server
1、导入maven相关依赖
<repositories>
<repository>
<id>alimaven</id>
<name>aliyun maven</name>
<url>http://maven.aliyun.com/nexus/content/groups/public/</url>
</repository>
</repositories>
<pluginRepositories>
<pluginRepository>
<id>alimaven</id>
<name>aliyun maven</name>
<url>http://maven.aliyun.com/nexus/content/groups/public/</url>
</pluginRepository>
</pluginRepositories>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>net.devh</groupId>
<artifactId>grpc-server-spring-boot-starter</artifactId>
<version>2.13.0.RELEASE</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
<build>
<extensions>
<extension>
<groupId>kr.motd.maven</groupId>
<artifactId>os-maven-plugin</artifactId>
<version>1.6.0</version>
</extension>
</extensions>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-maven-plugin</artifactId>
<executions>
<execution>
<goals>
<goal>repackage</goal>
</goals>
</execution>
</executions>
</plugin>
<!--跳过test测试-->
<plugin>
<groupId>org.apache.maven.plugins</groupId>
<artifactId>maven-surefire-plugin</artifactId>
<configuration>
<skip>true</skip>
</configuration>
</plugin>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.xolstice.maven.plugins</groupId>
<artifactId>protobuf-maven-plugin</artifactId>
<version>0.6.1</version>
<configuration>
<protocArtifact>com.google.protobuf:protoc:3.5.1:exe:${os.detected.classifier}</protocArtifact>
<pluginId>grpc-java</pluginId>
<pluginArtifact>io.grpc:protoc-gen-grpc-java:1.11.0:exe:${os.detected.classifier}</pluginArtifact>
<!--默认值-->
<protoSourceRoot>${project.basedir}/src/main/proto</protoSourceRoot>
<!--默认值-->
<!--<outputDirectory>${project.build.directory}/generated-sources/protobuf/java</outputDirectory>-->
<outputDirectory>${project.basedir}/src/main/java</outputDirectory>
<!--设置是否在生成java文件之前清空outputDirectory的文件,默认值为true,设置为false时也会覆盖同名文件-->
<clearOutputDirectory>false</clearOutputDirectory>
</configuration>
<executions>
<execution>
<!--在执行mvn compile的时候会执行以下操作-->
<phase>compile</phase>
<goals>
<!--生成OuterClass类-->
<goal>compile</goal>
<!--生成Grpc类-->
<goal>compile-custom</goal>
</goals>
</execution>
</executions>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>
2、创建proto目录并定义proto服务文件
通过前两篇的学习,相信大家对这个服务文件的定义应该非常熟悉了,服务端提供一个 hello的服务接口,入参和出参均为字符串;
syntax = "proto3";
option java_multiple_files = false;
option java_package = "com.congge.news.proto";
option java_outer_classname = "NewsProto";
package news;
service NewsService {
rpc hello(StringRequest) returns (StringResponse){}
}
message StringRequest{
string name = 1;
}
message StringResponse{
string result = 1;
}
3、编译并生成服务端相关的服务目录和类文件
依次点击下面两个按钮,生成服务相关的文件
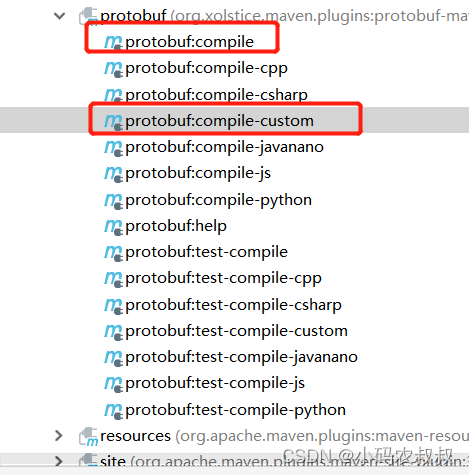
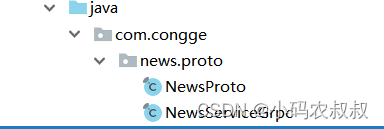
4、重写服务接口的方法
在该方法中,就是具体编写服务接口方法实现的逻辑,实际开发中,就是实际要关注业务逻辑的位置;
import com.congge.news.proto.NewsProto;
import com.congge.news.proto.NewsServiceGrpc;
import io.grpc.stub.StreamObserver;
import net.devh.boot.grpc.server.service.GrpcService;
@GrpcService
public class NewsService extends NewsServiceGrpc.NewsServiceImplBase {
@Override
public void hello(NewsProto.StringRequest request, StreamObserver<NewsProto.StringResponse> responseObserver) {
String name = request.getName();
NewsProto.StringResponse response = NewsProto.StringResponse.newBuilder().setResult("hello :" + name).build();
responseObserver.onNext(response);
responseObserver.onCompleted();
}
}
5、配置文件
spring:
application:
name: rpc-server
grpc:
server:
port: 9988
server:
port: 8088
6、提供一个启动类并启动服务
通过启动日志可以发现,服务端自身的web端口以及grpc服务监听的端口都已经生效;
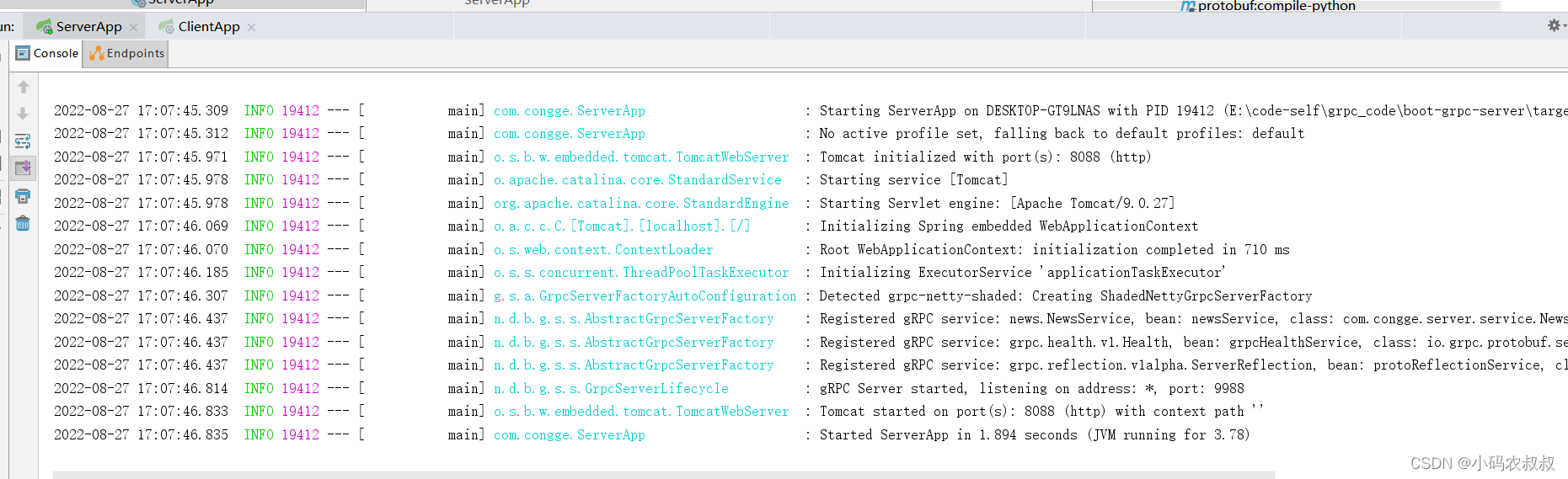
到这里,服务端的整合过程就基本完成了,接下来看客户端的整合步骤吧;
二、服务端:grpc-client
1、导入依赖
同上
2、创建proto目录并定义proto服务文件
同上
3、编译并生成服务端相关的服务目录和类文件
同上
4、配置文件
spring:
application:
name: rpc-client
grpc:
client:
grpc-server:
address: 'static://127.0.0.1:9988'
negotiationType: plaintext
server:
port: 8087
5、提供一个web接口
为了模拟外部的接口调用,这里提供一个用于测试的web接口,在接口中远程调用服务端的服务接口;
@RestController
public class NewsController {
@GrpcClient("grpc-server")
private NewsServiceGrpc.NewsServiceBlockingStub newsServiceBlockingStub;
@GetMapping("/hello")
public String hello(String name) {
NewsProto.StringResponse response = newsServiceBlockingStub.hello(NewsProto.StringRequest.newBuilder().setName(name).build());
return response.getResult();
}
}
6、提供一个启动类并启动服务
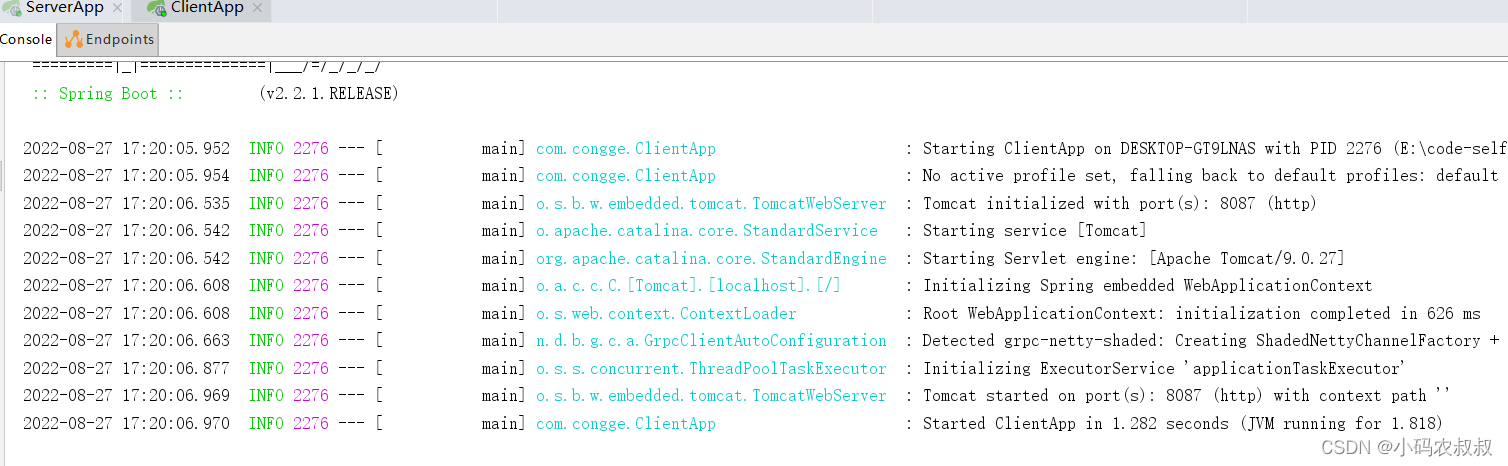
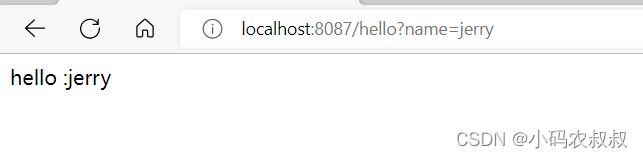
浏览器调用下上面的客户端提供的接口进行测试,效果如下:
版权归原作者 小码农叔叔 所有, 如有侵权,请联系我们删除。