写在前面
前些天发现了一个巨牛的人工智能学习网站,通俗易懂,风趣幽默,忍不住分享一下给大家:人工智能学习网站
Vue
前言
概述:Vue是一款前端渐进式框架,可以提高前端开发效率。
特点:
Vue通过MVVM模式,能够实现视图与模型的双向绑定。
简单来说,就是数据变化的时候, 页面会自动刷新, 页面变化的时候,数据也会自动变化.
Vue.js三种安装方式
此处引荐下大佬的文章 讲的非常详细
Vue.js三种方式安装
一、 Vue导入
概述:Vue是一个类似于Jquery的一个JS框架,所以,如果想使用Vue,则在当前页面导入Vue.js文件即可。
语法:
<!-- 在线导入 --><!-- 开发环境版本,包含了用帮助的命令行警告 --><script src="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/vue/dist/vue.js"></script><!-- 生产环境版本,优化了尺寸和速度 --><script src="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/vue"></script><!-- 本地导入 --><script src="node_modules/vue/dist/vue.js"></script>
案例
<div id="app"><h1>用户名:<input type="text" v-model="name"/></h1><br/><h1>您输入的用户名是:{{name}}</h1></div><script type="text/javascript">//创建一个Vue对象var app =newVue({//指定,该对象代表<div id="app">,也就是说,这个div中的所有内容,都被当前的app对象管理el:"#app",//定义vue中的数据data:{name:""}});</script>
二、Vue基本语法
1.钩子函数
概述:钩子函数, 其实就是Vue提前定义好的事件, 其作用类似于Servlet的init方法和distory方法
语法:
<script type="text/javascript">var app =newVue({el:"#app",//钩子函数created,该方法在页面显示之后,自动执行created(){
console.log("created...");}});</script>
补充:Vue声明周期和钩子函数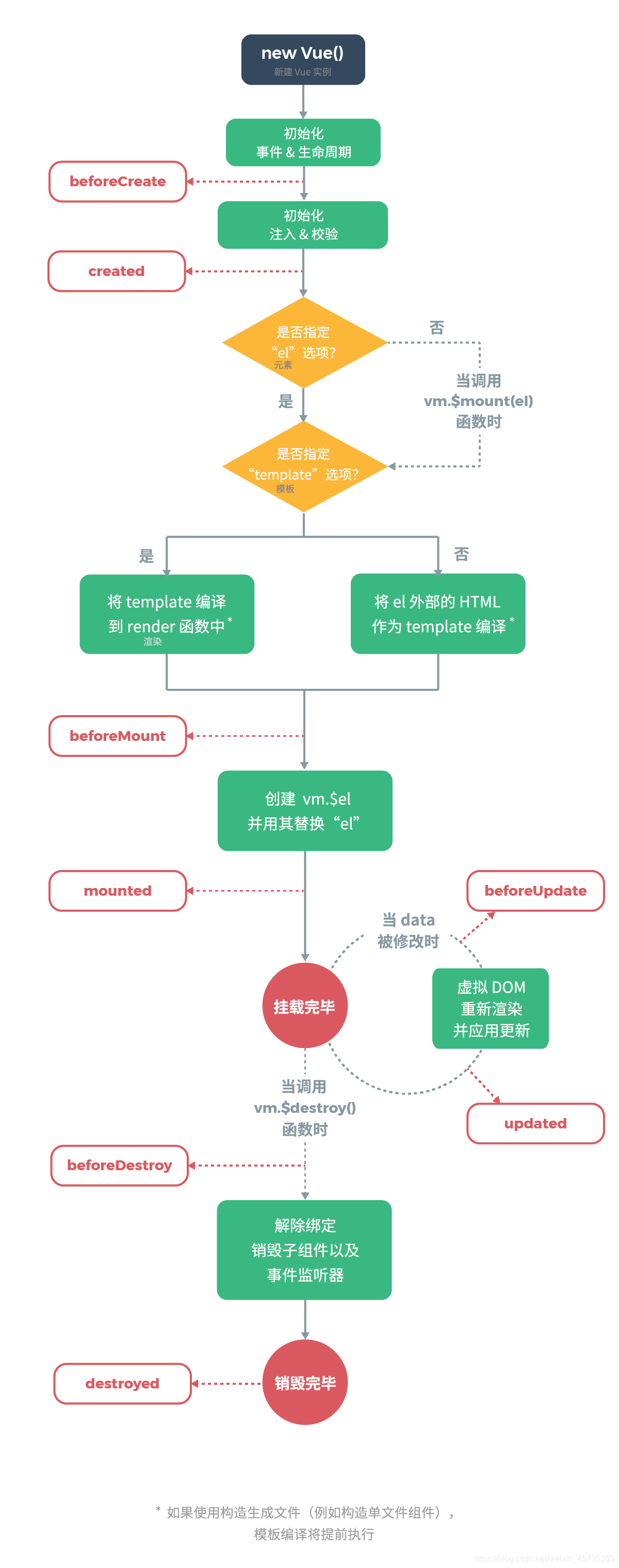
(1)什么是vue生命周期?
Vue 实例从创建到销毁的过程,就是生命周期。也就是从开始创建、初始化数据、编译模板、挂载Dom→渲染、更新→渲染、卸载等一系列过程,我们称这是 Vue 的生命周期。
(2)vue生命周期的作用是什么?
Vue生命周期中有多个事件钩子,让我们在控制整个Vue实例过程时更容易形成好的逻辑。
(3)vue生命周期总共有几个阶段?
可以总共分为8个阶段:创建前/后, 载入前/后,更新前/后,销毁前/后。
(4)第一次页面加载会触发哪几个钩子?
第一次页面加载时会触发 beforeCreate, created, beforeMount, mounted 这几个钩子
(5)DOM 渲染在 哪个周期中就已经完成?
DOM 渲染在 mounted 中就已经完成了。
(6)简单描述每个周期具体适合哪些场景?
生命周期钩子的一些使用方法:
beforecreate : 可以在此阶段加loading事件,在加载实例时触发;
created : 初始化完成时的事件写在这里,如在这结束loading事件,异步请求也适宜在这里调用;
mounted : 挂载元素,获取到DOM节点;
updated : 如果对数据统一处理,在这里写上相应函数;
beforeDestroy : 可以做一个确认停止事件的确认框;
nextTick : 更新数据后立即操作dom;
2. 插值表达式
概述:插值表达式用户把vue中所定义的数据,显示在页面上. 插值表达式允许用户输入"JS代码片段"
语法:
{{ 变量名/对象.属性名 }}
案例:
<htmllang="en"><head><metacharset="UTF-8"><title>vue插值表达式</title><scriptsrc="node_modules/vue/dist/vue.js"></script></head><body><divid="app"><h1>欢迎来到-->{{ name }}</h1></div><scripttype="text/javascript">//创建vue对象var app =newVue({//让vue接管div标签el:"#app",//定义数据,里边包含一个属性name,值为"白大锅"data:{name:"白大锅"}});</script></body></html>
3.显示数据(v-text和v-html)
概述:
v-text和v-html专门用来展示数据, 其作用和插值表达式类似。v-text和v-html可以避免插值闪烁问题.
当网速比较慢时, 使用{{}}来展示数据, 有可能会产生插值闪烁问题。
插值闪烁: 在数据未加载完成时,页面会显示出原始的{{}}, 过一会才会展示正常数据.
语法:
v-text:<spanv-text="msg"></span><!-- 相当于<span>{{msg}}</span> -->
v-html:<spanv-html="msg"></span><!-- 相当于<span>{{msg}}</span> -->
区别:
v-text:把数据当作纯文本显示.
v-html:遇到html标签,会正常解析
4.数据双向绑定数据(v-model)
概述:
Vue的双向绑定可以实现: 数据变化的时候, 页面会自动刷新, 页面变化的时候,数据也会自动变化.
注意:
- 双向绑定, 只能绑定“文本框,单选按钮,复选框,文本域,下拉列表”等
- 文本框/单选按钮/textarea, 绑定的数据是字符串类型
- 单个复选框, 绑定的是boolean类型
- 多个复选框, 绑定的是数组
- select单选对应字符串,多选对应也是数组
4.1.绑定文本框
代码:
<div id="app">用户名:<input type="text" v-model="username"/></div><script type="text/javascript">var app =newVue({el:"#app",data:{//该属性值和文本框的value属性值,保持一致username:""}});</script>
效果:
4.2.绑定单个复选框
代码:
<div id="app"><input type="checkbox" v-model="agree">同意<br></div><script type="text/javascript">var app =newVue({el:"#app",data:{agree:true}});</script>
效果:
4.3.绑定多个复选框
代码:
<div id="app"><input type="checkbox" value="Java" v-model="language">Java<br><input type="checkbox" value="Python" v-model="language">Python<br><input type="checkbox" value="Swift" v-model="language">Swift<br></div><script type="text/javascript">var app =newVue({el:"#app",data:{//数组中的值,就是被选中的元素的value属性值language:["Java","Python"]}});</script>
效果: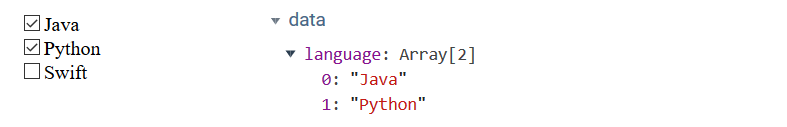
4.4.form表单数据提交
例子:传json格式跟formData格式的两种情况
<template><div class="from_box"><form action=""><input type="text" placeholder="请输入昵称" v-model="formMess.account"><input type="password" placeholder="请输入密码" v-model="formMess.act_pwd"><input type="text" placeholder="请输入手机号" v-model="formMess.phone"></form><span class="but" @click="onSubmit()">提交</span></div></template><script>import axios from'axios';exportdefault{name:"from",data(){return{formMess:{"account":"","act_pwd":"","phone":""}};},methods:{onSubmit(){/* json格式提交: */// let formData = JSON.stringify(this.formMess);/* formData格式提交: */let formData =newFormData();for(var key inthis.formMess){
formData.append(key,this.formMess[key]);}axios({method:"post",url:"xxxxxxx",headers:{"Content-Type":"multipart/form-data"},withCredentials:true,data:formData
}).then((res)=>{
console.log(res);});}}};</script><!-- Add "scoped" attribute to limit CSS to this component only --><style scoped lang="less">.from_box{
form{width:90%;margin: auto;border:.01rem solid gray;display: flex;
flex-wrap: wrap;
input{width:80%;height:.5rem;
margin-bottom:.2rem;border:.01rem solid black;height:.5rem;}}.but{
font-size:.14rem;
margin-left:5%;}}</style>
5.事件处理(v-on)
5.1.事件绑定(v-on)
概述:
Vue中也可以给页面元素绑定事件.
语法:
<!--完整写法--><buttonv-on:事件名="函数名/vue表达式">点我</button><!--简化写法--><button@事件名="函数名/vue表达式">点我</button>
注意:
Vue支持html中所有已知事件. 如: @click, @submit等, 只不过事件的名字不带on
案例:
<html lang="en"><head><meta charset="UTF-8"><title>vue事件处理</title><script src="node_modules/vue/dist/vue.js"></script></head><body><div id="app"><button @click="show">点我</button></div><script type="text/javascript">//创建vue对象var app =newVue({//获取id为app的元素,该元素被vue对象所管理.只有被vue对象管理的标签,其内部才允许书写vue语法el:"#app",//定义vue的方法methods:{//定义show方法,弹出提示框show(){alert("Hello Vue!!!");}}});</script></body></html>
5.2.事件修饰符
概述:事件修饰符主要对事件的发生范围进行限定
语法:
<button @事件名.事件修饰符="函数名/vue表达式">点我</button>
分类:
.stop :阻止事件冒泡, 也就是当前元素发生事件,但当前元素的父元素不发生该事件
.prevent :阻止默认事件发生
.capture :使用事件捕获模式, 主动获取子元素发生事件, 把获取到的事件当自己的事件执行
.self :只有元素自身触发事件才执行。(冒泡或捕获的都不执行)
.once :只执行一次
案例:
<html lang="en"><head><meta charset="UTF-8"><title>vue事件处理</title><script src="node_modules/vue/dist/vue.js"></script></head><body><div id="app"><button @click="show">点我</button></div><script type="text/javascript">//创建vue对象var app =newVue({//获取id为app的元素,该元素被vue对象所管理.只有被vue对象管理的标签,其内部才允许书写vue语法el:"#app",//定义vue的方法methods:{//定义show方法,弹出提示框show(){alert("Hello Vue!!!");}}});</script></body></html>
6.循环遍历(v-for)
6.1.遍历数组
语法:
v-for="item in items"
v-for="(item,index) in items"
items:要迭代的数组
item:存储数组元素的变量名
index:迭代到的当前元素索引,从0开始。
代码:
<div id="app"><ul><li v-for="(user, index) in users">{{index}}--{{user.name}}--{{user.age}}--{{user.gender}}</li></ul></div><script>var app =newVue({el:"#app",//el即element,要渲染的页面元素data:{users:[{"name":"白卓冉","age":8,"gender":"男"},{"name":"白大锅","age":12,"gender":"女"},{"name":"白仙女","age":4,"gender":"男"}]}});</script>
6.2.遍历对象
语法:
v-for="value in object"
v-for="(value,key) in object"
v-for="(value,key,index) in object"
value,对象的值
key, 对象的键
index, 索引,从0开始
代码:
<div id="app"><ul><li v-for="(value,key,index) in person">{{index}}--{{key}}--{{value}}</li></ul></div><script>var app =newVue({el:"#app",//el即element,要渲染的页面元素data:{person:{"name":"白大锅","age":3,"address":"中国"}}});</script>
6.3.key
概述:
:key 一般配合v-for一起使用. 用来在特定情况下, 保证被遍历的数组中的元素的顺序.
案例:
<divid="app"><button@click="add">添加</button><ul><liv-for="name in list"><inputtype="checkbox"> {{name}}
</li></ul></div><script>var app =newVue({el:'#app',data:{list:["孙悟空","猪八戒","沙和尚"]},methods:{add(){//注意这里是unshift,向数组的头部添加一个元素this.list.unshift("唐僧");}}});</script>
效果: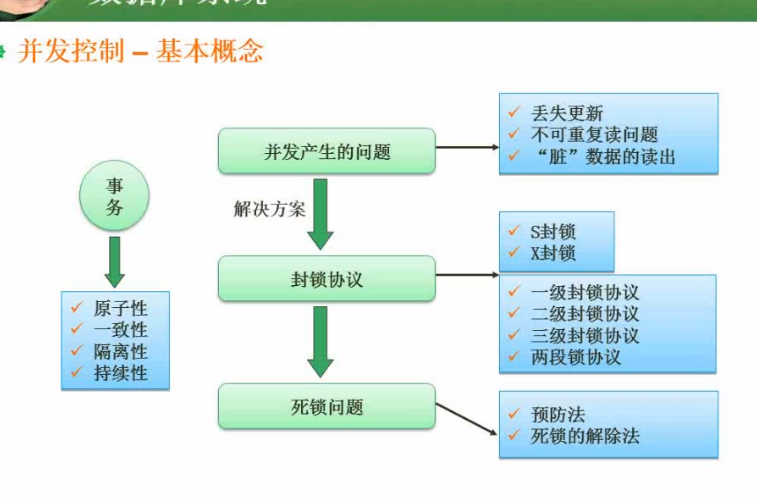
解决方案:
<divid="app"><button@click="add">添加</button><ul><!-- 添加:key即可. 注意,key中的值必须是唯一且不会改变的值--><liv-for="name in list":key="name"><inputtype="checkbox"> {{name}}
</li></ul></div>
7.判断语法(v-if和v-show)
概述:
v-if与v-show可以根据条件的结果,来决定是否显示指定内容.
v-if: 条件不满足时, 元素不会存在.
v-show: 条件不满足时, 元素不会显示(但仍然存在).
案例:
<divid="app"><button@click="show = !show">点我</button><h1v-if="show">Hello v-if.</h1><h1v-show="show">Hello v-show.</h1></div><script>var app =newVue({el:"#app",data:{show:true}});</script>
8.显示数据(v-bind)
概述:
v-bind的作用和插值表达式差不多, 只不过, v-bind主要用于动态设置标签的属性值
语法:
<!--完整写法--><标签名v-bind:标签属性名="vue实例中的数据属性名"/><!--简化写法--><标签名:标签属性名="vue实例中的数据属性名"/>
案例:
<divid="app"><inputtype="button":value="msg"/></div><scripttype="text/javascript">var app =newVue({el:"#app",data:{msg:"我是按钮"}});</script>
9.Vue页面跳转(两种方法)
9.1.方法一(标签实现)
<router-link:to="{name: 'bookshelf', params: { entityId: this.entityId } }":class="{'flex-item-1':'flex-item-1',cur:tabs[0].isShow}"href="javascript:"><spanclass="tabNav-ico tabNav-book"></span><spanclass="tabNav-txt">书 架</span></router-link>
9.1.方法二(this.$router.push()实现)
当this.$router.push()只有一个参数时 默认为跳转地址 最多可传两个参数 第二个参数为地址参数
<a @click="toIndex":class="{'flex-item-1':'flex-item-1',cur:tabs[2].isShow}" href="javascript:"><span class="tabNav-ico tabNav-home"></span><span class="tabNav-txt">首 页</span></a>toIndex:function(){this.$router.push("/?entityId="+ localStorage.getItem("entityId"));}
三、Vue其他语法
3.1.计算属性
概述:计算属性就是一个提前定义好的方法, 该方法可以看作是一个特殊的值, 可以在插值表达式中使用.
语法:
var app =newVue({el:"#app",//计算属性必须放在Vue的computed中computed:{//定义计算属性属性名(){return"返回值";}}});
案例:
<div id="app"><h1>{{birth}}</h1><h1 v-text="birth"></h1><h1 v-html="birth"></h1></div><script type="text/javascript">var app =newVue({el:"#app",computed:{//定义一个birth方法,该方法就是一个计算属性,可以在插值表达式中使用birth(){let date =newDate();let year = date.getFullYear();let month = date.getMonth()+1;let day = date.getDay();return year +"-"+ month +"-"+ day;}}});</script>
3.2.watch监控
概述:
watch可以监听简单属性值及其对象中属性值的变化.
watch类似于onchange事件,可以在属性值修改的时候,执行某些操作.
语法:
var app =newVue({el:"#app",data:{message:"白大锅",person:{"name":"heima","age":13}},//watch监听watch:{//监听message属性值,newValue代表新值,oldValue代表旧值message(newValue, oldValue){
console.log("新值:"+ newValue +";旧值:"+ oldValue);},//监控person对象的值,对象的监控只能获取新值person:{//开启深度监控;监控对象中的属性值变化deep:true,//获取到对象的最新属性数据(obj代表新对象)handler(obj){
console.log("name = "+ obj.name +"; age="+ obj.age);}}}});
四、Vue组件
4.1.基本使用
概述:
组件, 类似于模版, 模块. 在项目需要重用某个模块(头部、尾部、新闻。。。)的时候,可以将模块抽取成组件,其它页面中注册组件并引用。
案例:
<divid="app"><!--使用组件(组件名称),如果组件名称中有大写字母,如"myList",则这里需要书写<my-list>--><counter></counter><counter></counter></div><scripttype="text/javascript">//定义组件const counterTemp ={//定义组件的模版template:`<button @click='num++'>你点击了{{num}}次</button>`,//定义组件中使用到的数据属性data(){return{num:0}}};//全局注册组件:在所有的vue实例中都可以使用组件//参数1:组件名称,参数2:具体的组件//Vue.component("counter", counterTemp);var app =newVue({el:"#app",//局部注册组件: 只能在当前Vue实例中使用components:{//组件名称:具体组件counter: counterTemp
}});</script>
注意:
- 组件的模版中, 只能书写一个跟标签
- 组件的定义必须放在Vue创建对象之前, 否则报错
4.2.父组件向子组件通信
概述:
子组件无法直接使用父组件中的数据, 如果需要使用, 则必须由父组件把数据传递给子组件才可以.
本质: 让子组件中的属性与父组件中的属性进行关联绑定, 然后子组件使用该属性, 这样才能做到数据传递
意义:
可以把父组件中的数据, 更新传递到子组件
示例:
<divid="app"><!-- 把父组件中的count传递给子组件的number属性,把父arr传递给子ids,把父p传递给子person --><aaa:number="count":ids="arr":person="p"></aaa></div><script>var aaa ={//定义组件的模版template:`<h2>{{num}}---{{number}}--{{ids}}--{{person}}</h2>`,//定义组件中使用到的数据属性data(){return{num:0}},//给组件添加属性props:{//普通属性numbernumber:"",//数组属性idsids:[],//对象属性personperson:{}/*
* //以上属性还可以书写为以下格式
* items:{
* //数据类型,如果是数组则是Array,如果是对象则是Object
* type:Array,
* //默认值
* default:[]
* }
*/}};//注册:全局注册
Vue.component("aaa", aaa);var app =newVue({el:"#app",data:{count:5,arr:[1,2,3],p:{username:"zhangsan",age:23}}});</script>
4.3.子组件向父组件通信
概述:
子组件无法直接给父组件传递数据. 也无法操作父组件中的数据, 更无法调用父组件中的方法.
所以, 所谓的子组件向父组件通讯, 其实就是想办法让子组件调用父组件的方法. 进而响应到父组件中的数据.
意义:
子组件可以调用父组件中的方法
示例:
<divid="app"><h1>父组件中:app_num={{app_num}}</h1><!-- 把父组件的add方法,绑定给子组件的aaa属性,绑定方法使用@属性名="方法名" --><!-- 把父组件的rem方法,绑定给子组件的bbb属性,绑定方法使用@属性名="方法名 --><!-- 把父组件的app_num变量,绑定给子组件的counter_num属性,绑定变量使用:属性名="方法名 --><counter@aaa="add"@bbb="rem":counter_num="app_num"></counter></div><script>//定义一个组件(模版)let counter ={template:`
<div>
<h1>子组件中:counter_num={{counter_num}}</h1>
<input type="button" @click="fun1" value="+"/>
<input type="button" @click="fun2" value="-"/>
</div>
`,props:{//定义属性counter_num,用来接收父组件传递的数据counter_num:null,//定义aaa属性,用来绑定父组件的方法,当然,该定义也可以省略aaa:function(){},//定义bbb属性,用来绑定父组件的方法,当然,该定义也可以省略bbb:function(){},},methods:{fun1(){//找到aaa属性所绑定的那个方法,执行那个方法returnthis.$emit("aaa");},fun2(){//找到bbb属性所绑定的那个方法,执行那个方法returnthis.$emit("bbb");}}}var app =newVue({el:'#app',data:{app_num:0},components:{
counter
},methods:{add(){this.app_num++;},rem(){this.app_num--;}}});</script>
五、axios异步请求
5.1 axios概述
概述:
axios是一个基于 promise 的 HTTP 库, 主要用于:发送异步请求获取数据。
常见的方法:
axios(config)
axios.get(url, [config])
axios.post(url, [data])
发送数据config常用参数:
{url:'请求的服务器',method:'请求方式',// 默认是 get// GET请求参数params:{参数名: 参数值
},// POST请求参数, 如果使用axios.post,则参数在url之后直接书写,不需要该位置传递参数data:{参数名: 参数值
},// 响应数据格式,默认jsonresponseType:'json'}
响应数据常用参数:
{data:{},//真正的响应数据(响应体)status:200,//响应状态码statusText:'OK',//响应状态描述headers:{},//响应头config:{}//其他配置信息}
5.2.Get请求
var app =newVue({el:"#app",data:{user:{}},//当页面加载完毕后created(){//发送GET请求axios.get("请求路径",{ config });
axios.get("请求路径",{//get请求参数params:{name:"zhangsan",age:23},//响应数据格式为"json"responseType:'json'}).then(res=>{//打印响应数据
console.log(res);//把响应数据赋值给Vue中的user属性
app.user = res.data;}).catch(err=>{//打印响应数据(错误信息)
console.log(err);});}});
5.3.Post请求
var app =newVue({el:"#app",data:{user:{}},//当页面加载完毕后created(){//发送POST请求axios.post("请求路径",{ 参数 });
axios.post("请求路径",{name:"zhangsan",age:23}).then(res=>{
console.log(res);
app.user = res.data;}).catch(err=>{
console.log(err);});}});
5.4.跨域请求
跨域请求:在前端js中如果发送异步请求的话,请求的地址与当前服务器的ip或者端口号不同都是跨域请求.
跨域请求需要在服务提供方, 开启允许跨域请求
六、VueJs Ajax
6.1.vue-resource
vue-resource是Vue.js的插件提供了使用XMLHttpRequest或JSONP进行Web请求和处理响应的服务。 当vue更新
到2.0之后,作者就宣告不再对vue-resource更新,而是推荐的axios,在这里大家了解一下vue-resource就可以。
vue-resource的github: https://github.com/pagekit/vue-resource
6.2.axios
Axios 是一个基于 promise 的 HTTP 库,可以用在浏览器和 node.js 中
axios的github:https://github.com/axios/axios
6.2.1.引入axios
首先就是引入axios,如果你使用es6,只需要安装axios模块之后
import axios from ‘axios’;
//安装方法
npm install axios
//或
bower install axios
当然也可以用script引入
<script src="https://unpkg.com/axios/dist/axios.min.js"></script>
6.2.2.get请求
//通过给定的ID来发送请求
axios.get('/user?ID=12345').then(function(response){
console.log(response);}).catch(function(err){
console.log(err);});//以上请求也可以通过这种方式来发送
axios.get('/user',{params:{ID:12345}}).then(function(response){
console.log(response);}).catch(function(err){
console.log(err);});
6.2.3.post请求
axios.post('/user',{firstName:'Fred',lastName:'Flintstone'}).then(function(res){
console.log(res);}).catch(function(err){
console.log(err);});
为方便起见,为所有支持的请求方法提供了别名
axios.request(config)
axios.get(url[, config])
axios.delete(url[, config])
axios.head(url[, config])
axios.post(url[, data[, config]])
axios.put(url[, data[, config]])
axios.patch(url[, data[, config]])
七、综合案例
7.1.需求
完成用户的查询与修改操作
7.2. 数据库设计与表结构
CREATEDATABASE vuejsdemo;USE vuejsdemo;CREATETABLEUSER(
id INTPRIMARYKEYAUTO_INCREMENT,
age INT,
username VARCHAR(20),
PASSWORD VARCHAR(50),
email VARCHAR(50),
sex VARCHAR(20))
User类
publicclassUser{privateInteger id;privateString username;privateString password;privateString sex;privateint age;privateString email;
省略getter/setter
}
7.3.服务器端
7.3.1.配置文件
web.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?><web-appxmlns="http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/javaee"xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"xsi:schemaLocation="http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/javaee
http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/javaee/web-app_3_1.xsd"version="3.1"metadata-complete="true"><!-- 手动指定 spring 配置文件位置 --><context-param><param-name>contextConfigLocation</param-name><param-value>classpath:applicationContext.xml</param-value></context-param><!-- 配置 spring 提供的监听器,用于启动服务时加载容器 。
该间监听器只能加载 WEB-INF 目录中名称为 applicationContext.xml 的配置文件 --><listener><listener-class>
org.springframework.web.context.ContextLoaderListener
</listener-class></listener><!-- 配置 spring mvc 的核心控制器 --><servlet><servlet-name>springmvcDispatcherServlet</servlet-name><servlet-class>org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet</servlet-class><!-- 配置初始化参数,用于读取 springmvc 的配置文件 --><init-param><param-name>contextConfigLocation</param-name><param-value>classpath:springmvc.xml</param-value></init-param><!-- 配置 servlet 的对象的创建时间点:应用加载时创建。取值只能是非 0 正整数,表示启动顺
序 --><load-on-startup>1</load-on-startup></servlet><servlet-mapping><servlet-name>springmvcDispatcherServlet</servlet-name><url-pattern>*.do</url-pattern></servlet-mapping><!-- 配置 springMVC 编码过滤器 --><filter><filter-name>CharacterEncodingFilter</filter-name><filter-class>org.springframework.web.filter.CharacterEncodingFilter</filter-class><!-- 设置过滤器中的属性值 --><init-param><param-name>encoding</param-name><param-value>UTF-8</param-value></init-param><!-- 启动过滤器 --><init-param><param-name>forceEncoding</param-name><param-value>true</param-value></init-param></filter><!-- 过滤所有请求 --><filter-mapping><filter-name>CharacterEncodingFilter</filter-name><url-pattern>/*</url-pattern></filter-mapping><welcome-file-list><welcome-file>index.html</welcome-file><welcome-file>index.htm</welcome-file><welcome-file>index.jsp</welcome-file><welcome-file>default.html</welcome-file><welcome-file>default.htm</welcome-file><welcome-file>default.jsp</welcome-file></welcome-file-list></web-app>
springmvc.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?><beansxmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"xmlns:mvc="http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc"xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc
http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc/spring-mvc.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd"><!-- 配置创建 spring 容器要扫描的包 --><context:component-scanbase-package="com.itheima"><!-- 制定扫包规则 ,只扫描使用@Controller 注解的 JAVA 类 --><context:include-filtertype="annotation"expression="org.springframework.stereotype.Controller"/></context:component-scan><mvc:annotation-driven></mvc:annotation-driven></beans>
applicationContext.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?><beansxmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop"xmlns:tx="http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx"xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx
http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx/spring-tx.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd"><!-- 配置 spring 创建容器时要扫描的包 --><context:component-scanbase-package="com.itheima"><!--制定扫包规则,不扫描@Controller 注解的 JAVA 类,其他的还是要扫描 --><context:exclude-filtertype="annotation"expression="org.springframework.stereotype.Controller"/></context:component-scan><!-- 加载配置文件 --><context:property-placeholderlocation="classpath:db.properties"/><!-- 配置 MyBatis 的 Session 工厂 --><beanid="sqlSessionFactory"class="org.mybatis.spring.SqlSessionFactoryBean"><!-- 数据库连接池 --><propertyname="dataSource"ref="dataSource"/><!-- 加载 mybatis 的全局配置文件 --><propertyname="configLocation"value="classpath:SqlMapConfig.xml"/></bean><!-- 配置数据源 --><beanid="dataSource"class="com.mchange.v2.c3p0.ComboPooledDataSource"><propertyname="driverClass"value="${jdbc.driver}"></property><propertyname="jdbcUrl"value="${jdbc.url}"></property><propertyname="user"value="${jdbc.username}"></property><propertyname="password"value="${jdbc.password}"></property></bean><!-- 配置 Mapper 扫描器 --><beanclass="org.mybatis.spring.mapper.MapperScannerConfigurer"><propertyname="basePackage"value="com.itheima.dao"/></bean><tx:annotation-driven/><!-- (事务管理)transaction manager, use JtaTransactionManager for global tx --><beanid="transactionManager"class="org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DataSourceTransactionManager"><propertyname="dataSource"ref="dataSource"/></bean></beans>
db.properties
jdbc.driver=com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
jdbc.url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/vuejsDemo
jdbc.username=root
jdbc.password=root
7.3.2.Controller
@RequestMapping("/user")@Controller@ResponseBodypublicclassUserController{@AutowiredprivateIUserService userService;@RequestMapping(value="/findAll.do")publicList<User>findAll(){return userService.findAll();}@RequestMapping(value="/findById.do")publicUserfindById(Integer id){return userService.findById(id);}@RequestMapping(value="/update.do")publicUserupdate(@RequestBodyUser user){return userService.update(user);}}
7.3.3.Dao
publicinterfaceIUserDao{@Select("select * from user")publicList<User>findAll();@Select("select * from user where id=#{id}")UserfindById(Integer id);@Update("update user set username=#{username},password=#{password},sex=#{sex},age=#
{age},email=#{email} where id=#{id}")voidupdate(User user);}
7.4.客户端
7.4.1.user.html页面
原因种种 页面代码暂时提供不了 思路大概就是这些 嘻嘻~
7.4.2.user.js
var vue =newVue({el:"#app",data:{user:{id:"",username:"aaa",password:"",age:"",sex:"",email:""},userList:[]},methods:{findAll:function(){var _this =this;
axios.get("/vuejsDemo/user/findAll.do").then(function(response){
_this.userList = response.data;
console.log(_this.userList);}).catch(function(err){
console.log(err);});},findById:function(userid){var _this =this;
axios.get("/vuejsDemo/user/findById.do",{params:{id: userid
}}).then(function(response){
_this.user = response.data;$('#myModal').modal("show");}).catch(function(err){});},update:function(user){var _this =this;
axios.post("/vuejsDemo/user/update.do",_this.user).then(function(response){
_this.findAll();}).catch(function(err){});}},created(){this.findAll();}});
书山有路勤为径 学海无涯苦作舟 学无止境冲冲冲~
本文算是Vue入门到逐渐深入再到与Java结合综合案例使用讲了一遍
学到关注收藏哦(学不到扣眼珠子 嘎嘎~)
版权归原作者 白大锅 所有, 如有侵权,请联系我们删除。
