前面我们大致把各个代码块梳理出来了,但是得到的信息非常杂乱,一大堆的代码,不知道怎么来的ui,那个拷贝的datas也没说是什么情况,对于我们没有怎么整过ui的来说阅读非常困难,所以在开始之前我们先需要学习一些关于ui的知识点,然后在通过ui页面的元素去推理整个执行过程,我们首先需要知道ui功能里面有那些组件
qt设计师基础控件
Qt Designer 是一个图形界面设计工具,用于创建 Qt 应用程序的用户界面。它提供了丰富的控件(也称为窗口部件或widgets)来构建各种类型的用户界面
类型窗口部件说明基础控件QLabel显示静态文本或图像基础控件QPushButton用户可以点击的按钮基础控件QLineEdit单行文本输入框基础控件QTextEdit多行文本编辑器基础控件QCheckBox复选框,用户可以选择或取消选择基础控件QRadioButton单选按钮,用于一组互斥的选择项基础控件QComboBox下拉列表框,用户可以从列表中选择一项基础控件QSlider滑块控件,用于数值的选择范围基础控件QSpinBox/QDoubleSpinBox数字输入框,用户可以输入整数或浮点数基础控件QProgressBar进度条,显示任务完成的进度基础控件QToolButton工具按钮,常用于工具栏上,支持弹出菜单基础控件QGraphicsView图形视图,用于显示复杂的图形场景布局管理器QVBoxLayout垂直布局管理器,用于管理控件的垂直排列布局管理器QHBoxLayout水平布局管理器,用于管理控件的水平排列布局管理器QGridLayout网格布局管理器,用于将控件放置在网格单元格中布局管理器QFormLayout表单布局管理器,用于创建标签和控件成对出现的布局布局管理器QStackedLayout堆叠布局管理器,用于堆叠多个控件,一次只显示一个容器QWidget最基础的窗口部件,可以包含其他控件容器QFrame带边框的容器,可以设置不同的样式容器QGroupBox带标题的框架,常用于分组控件容器QTabWidget带标签页的容器,允许用户在多个页面之间切换容器QScrollArea滚动区域,当内容超过显示区域时提供滚动条容器QDockWidget码头窗口,通常用于显示附加信息或工具对话框QMessageBox提示信息对话框,用于显示警告、错误等消息对话框QFileDialog文件对话框,用于选择文件或目录对话框QColorDialog颜色选择对话框,用于选取颜色对话框QFontDialog字体选择对话框,用于选取字体其他QMenuBar菜单栏,通常位于窗口顶部其他QToolBar工具栏,通常包含一些快捷按钮其他QStatusBar状态栏,显示临时的消息
我们打开窗口的时候会发现中间有一块显示大屏,如下

我们先看看怎么实现这个大屏显示,打开qt设计师
新建项目目录
我们先不在原本的项目上找,先根据已有的信息参考源代码进行推断
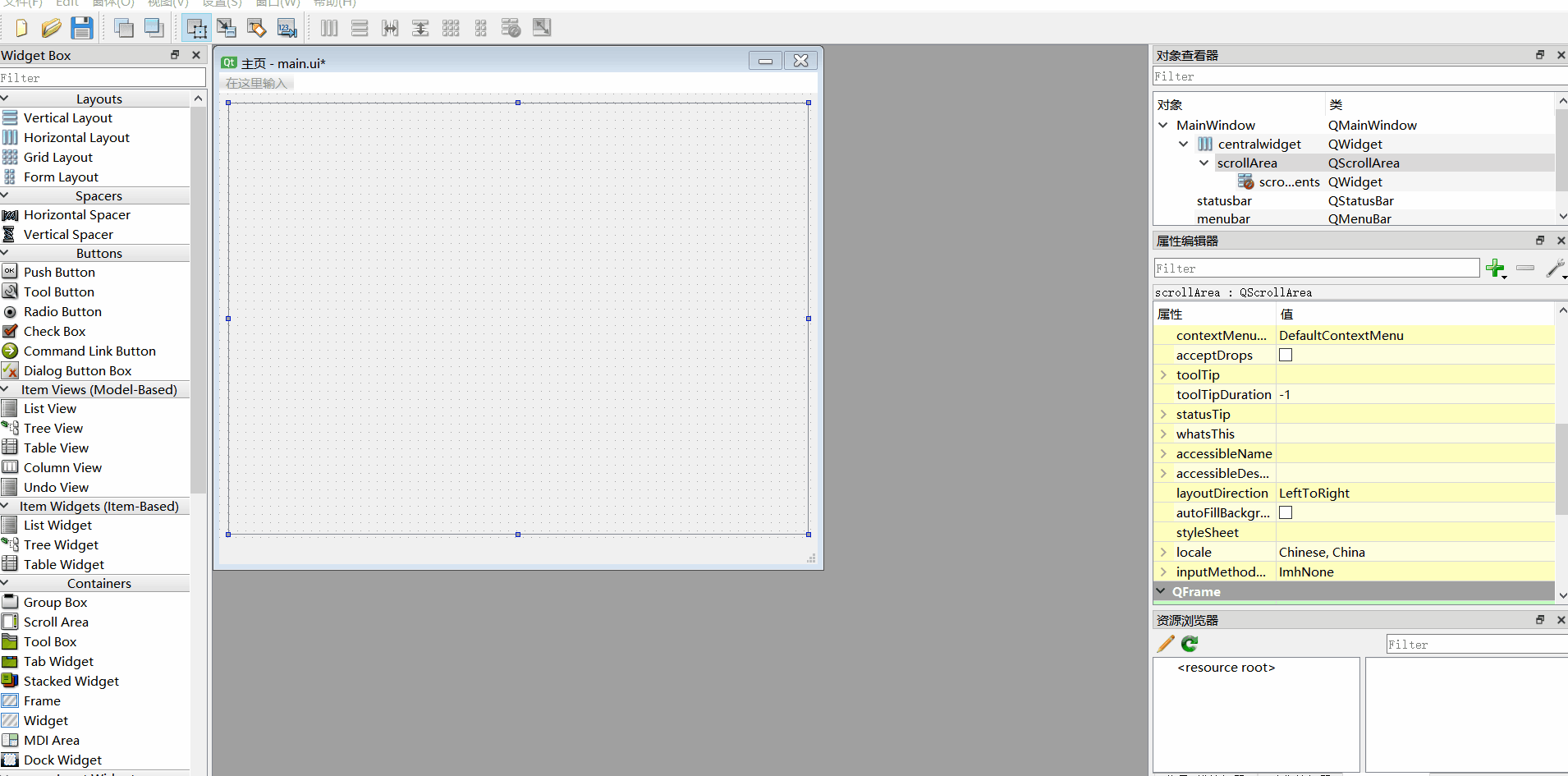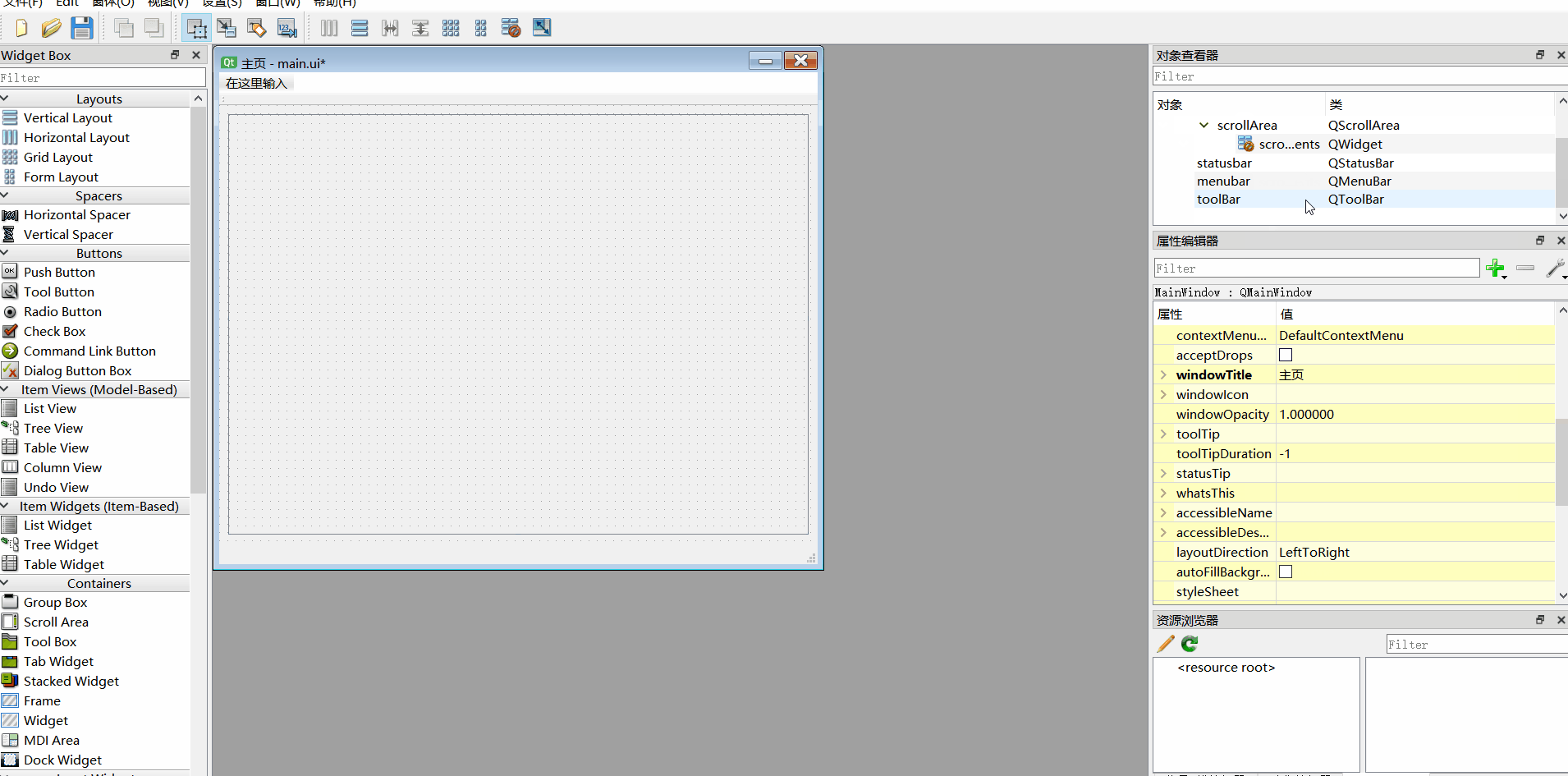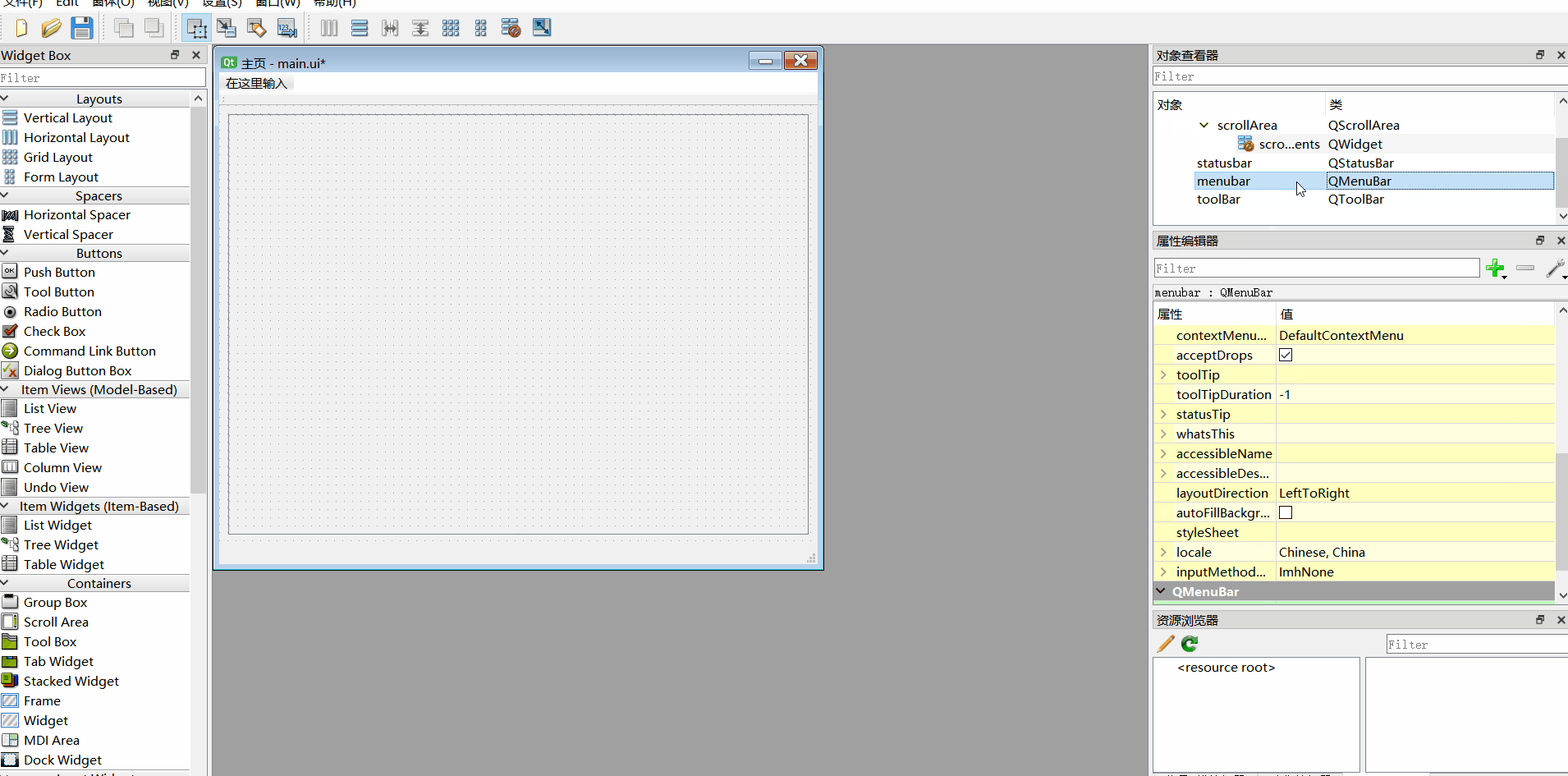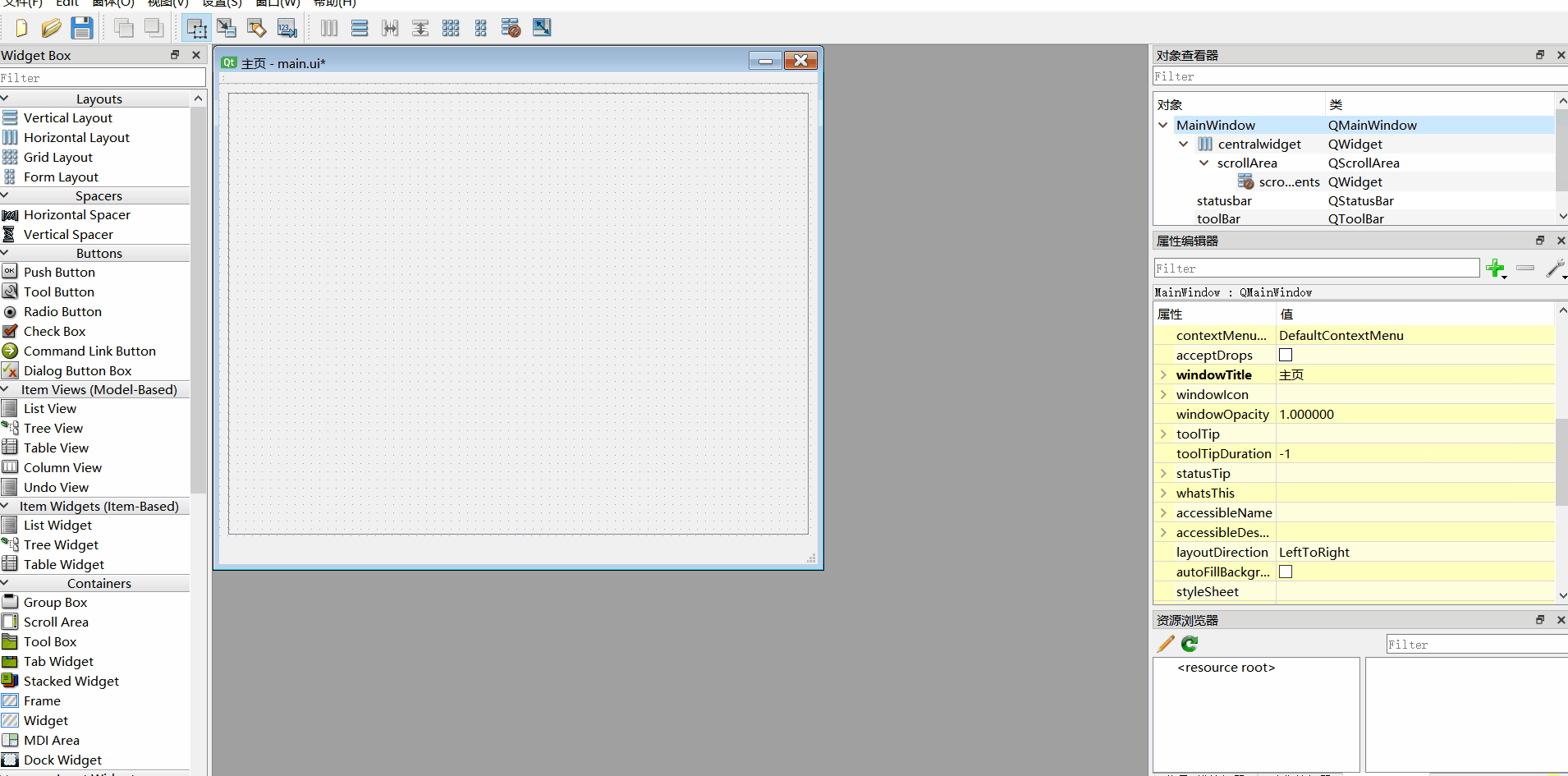
一、添加主窗口
1、主窗口、窗口大小、标题
1、打开Qt Designer。 (命令designer)
2、选择“文件” > “新建”,创建一个新的Qt Designer文档。
3、在“选择类”对话框中,选择QMainWindow作为基础类,并命名为mainWindow。4、添加布局,layouts--Horizontal layouts--- 添加后选择类名右键--布局--水平布局,然后将我们刚才添加的Horizontal layouts删除
5、设置窗口大小(geometry关键字)为800x600像素,并设置窗口标题(windowTitle)为 "主页"6、添加容器空间containers--scroll area 直接拖到窗口会自动根据水平进行布局
(后面才知道步骤4添加布局的时候,其实不是非得用对应的Horizontal layouts才能添加水平布局,我们任意仍个组件上去就可以右键设置主窗口的布局了)
2、添加工具栏、移除菜单栏
3、组件重命名
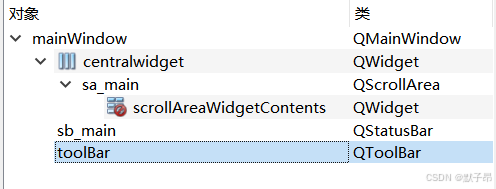
mainWindow
centralwidget
sa_main
scrollAreaWidgetContents
sb_main
toolBar
这里我们给布局内的各个元素重命名后,我们在ui转py会转换为各个关键字方便使用
4、布局重命名
我们在上面中,给主窗口添加了一个水平布局,这个布局也是有名称的,如果存在多个布局需要区分开,这里我们要查看下布局是什么名称,如果和下图不一样统一修改
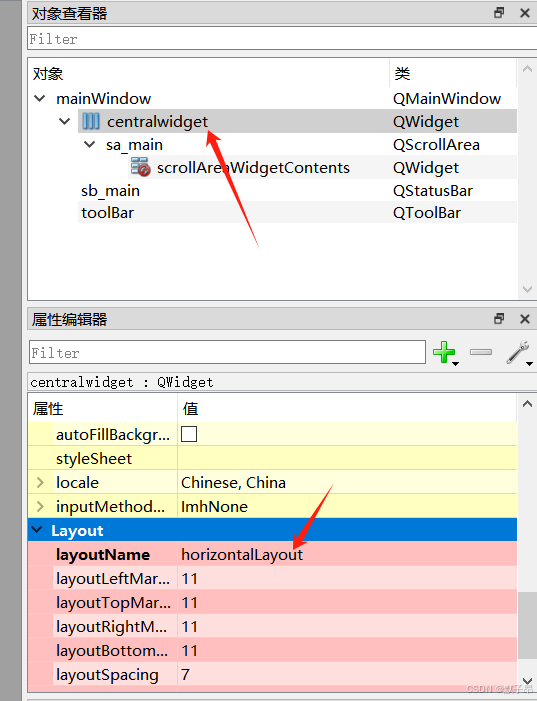
5、工具栏调整到侧边
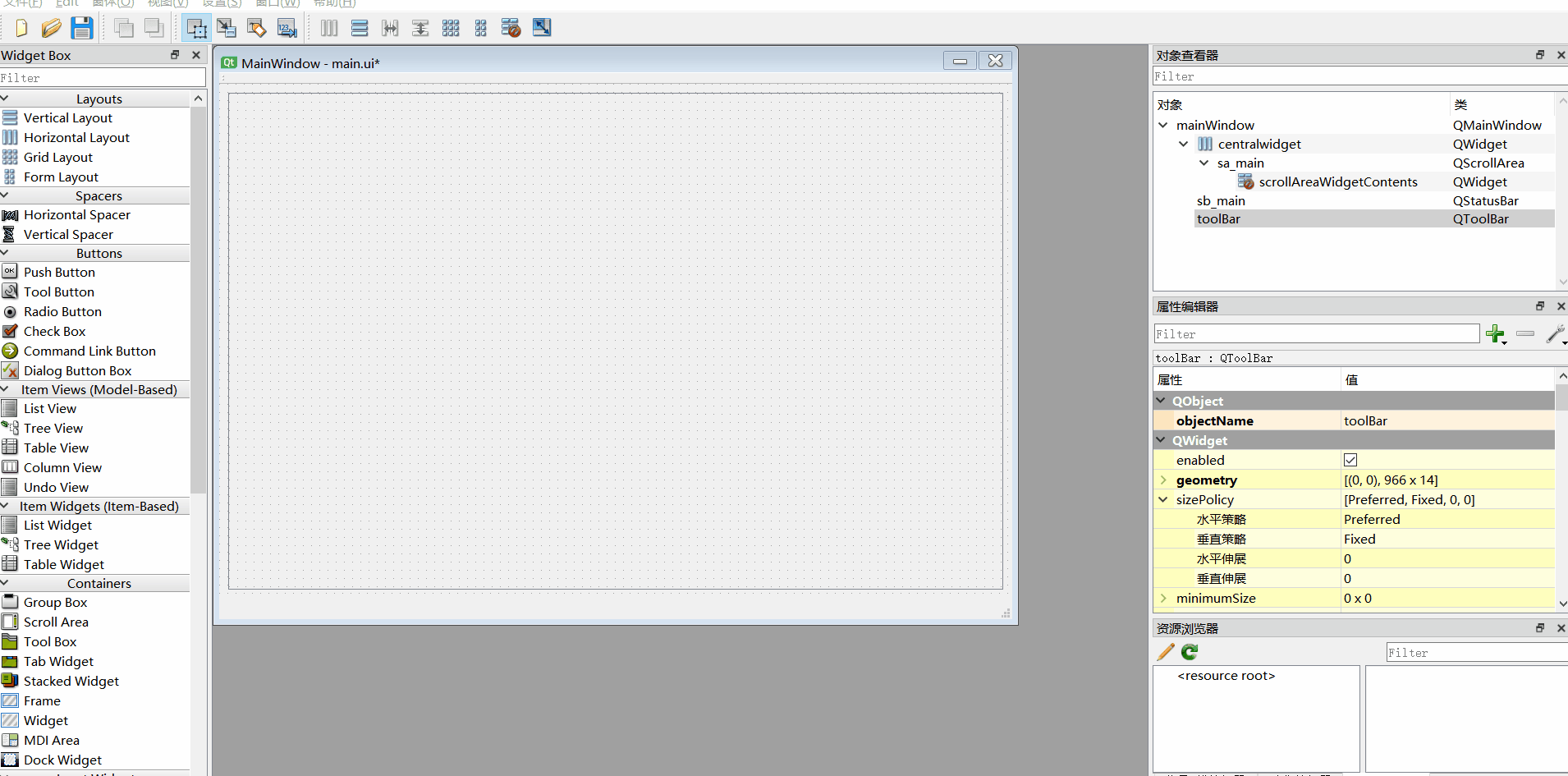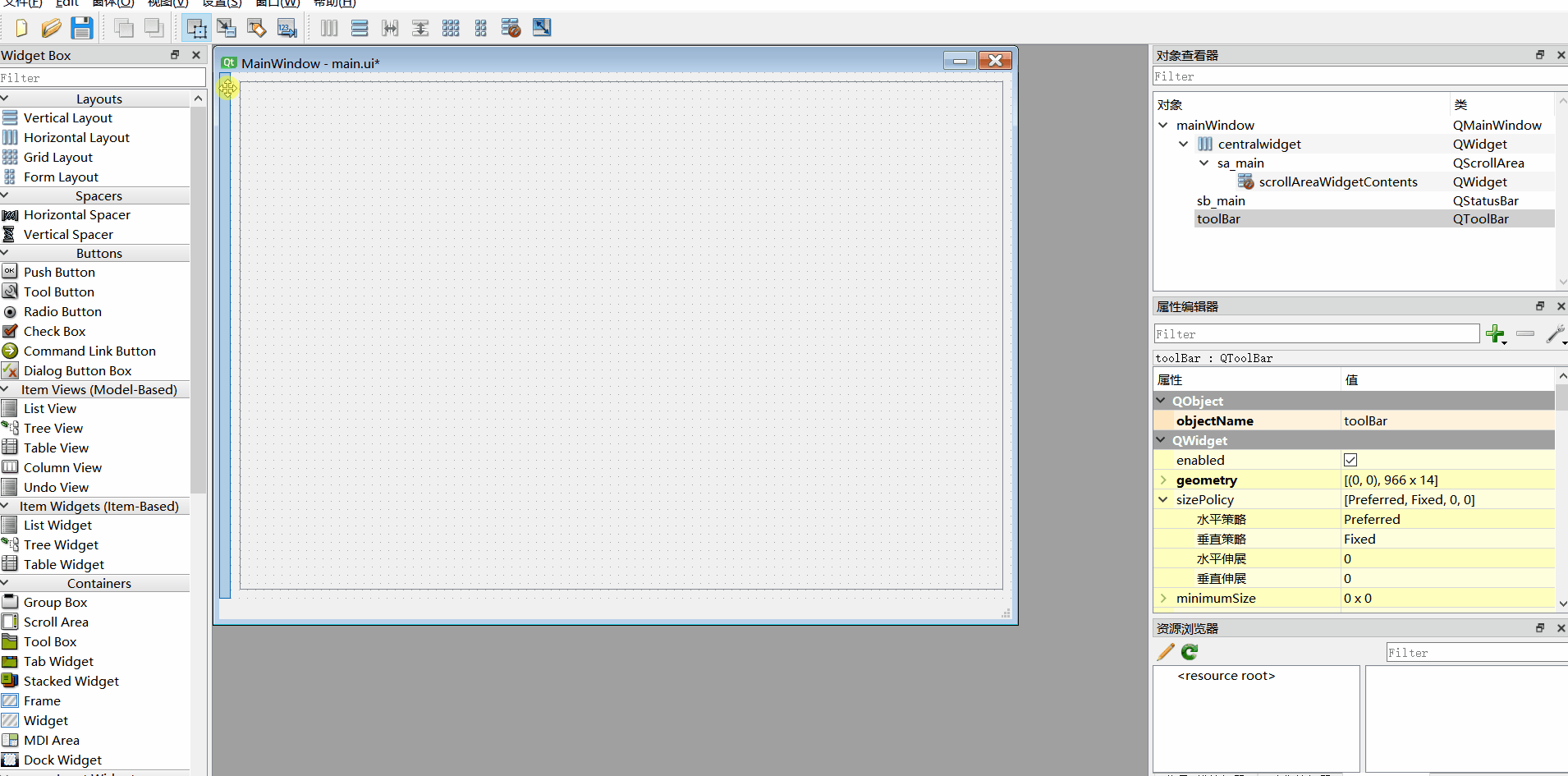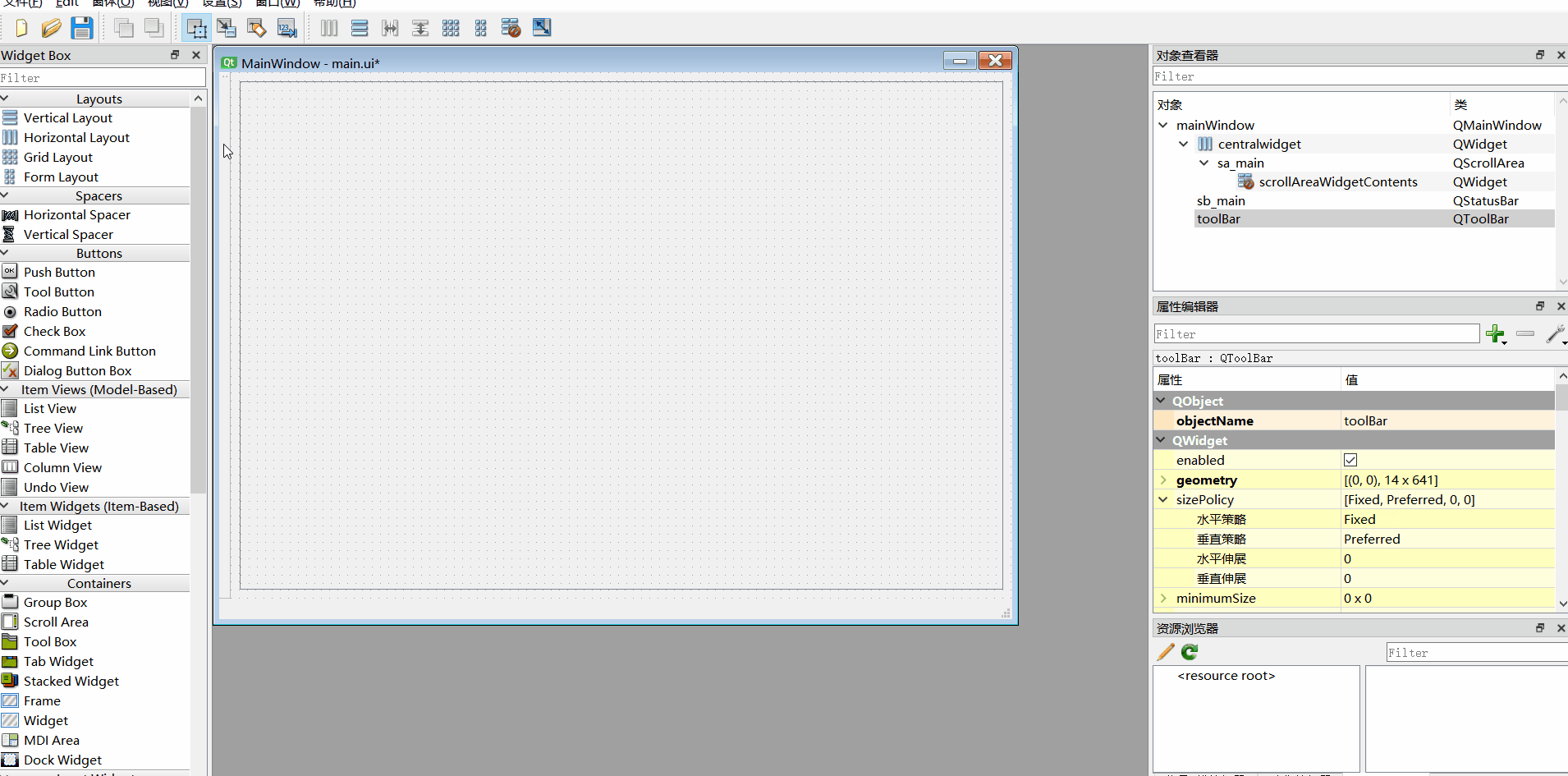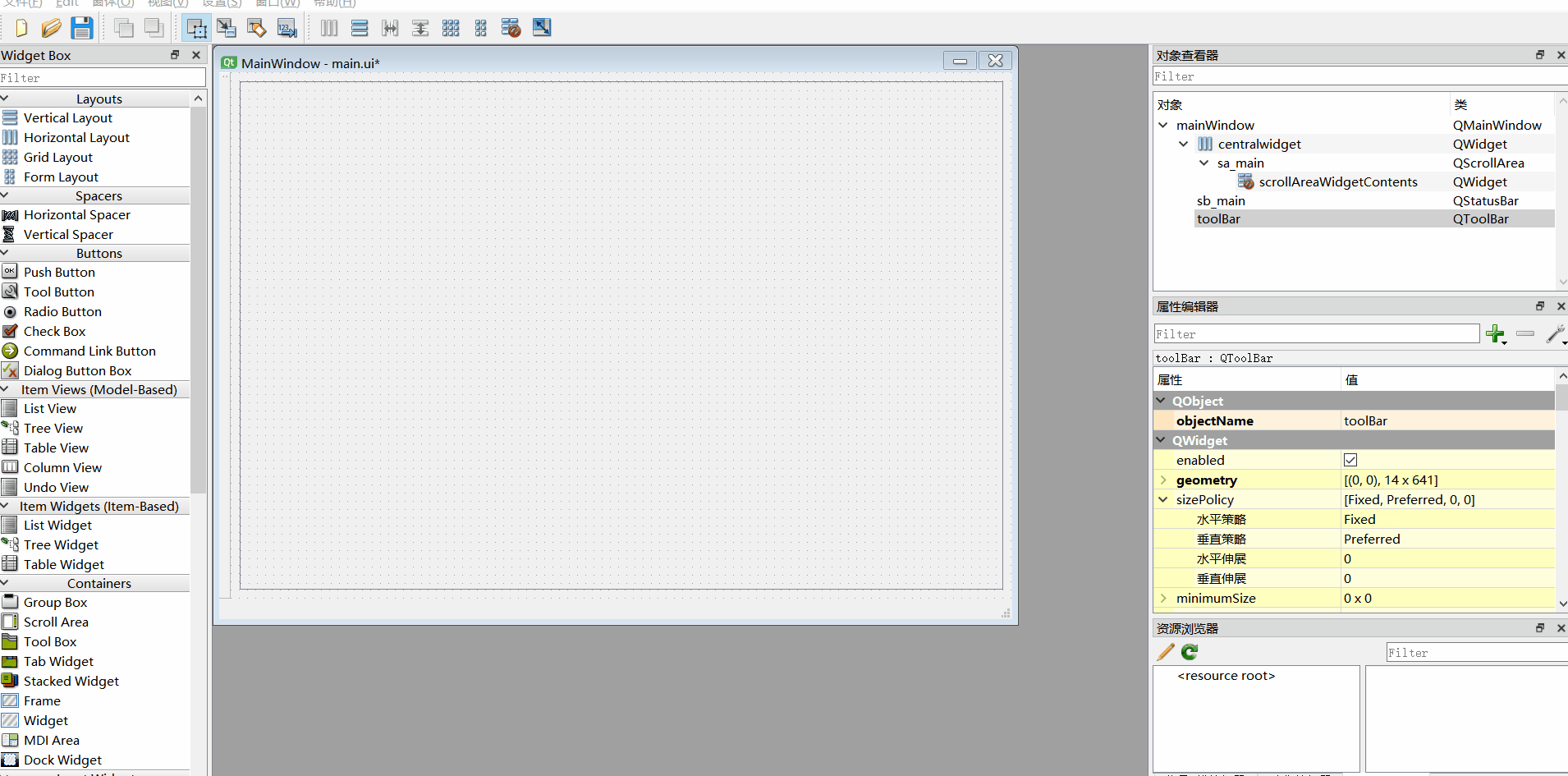
6、添加动作、ui转py
#动作文本名称如下
Save_All
Add_Mode
Add_Script
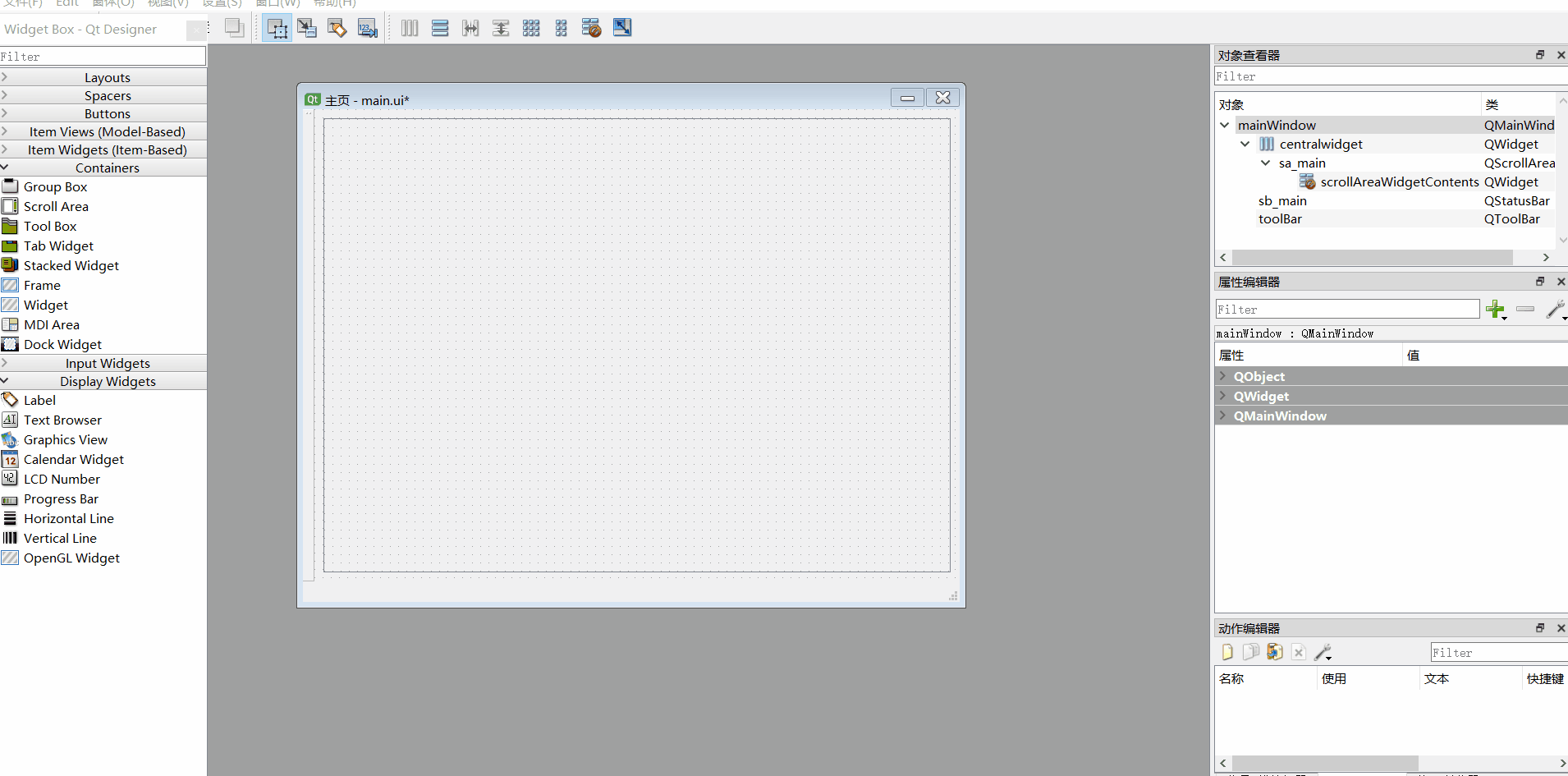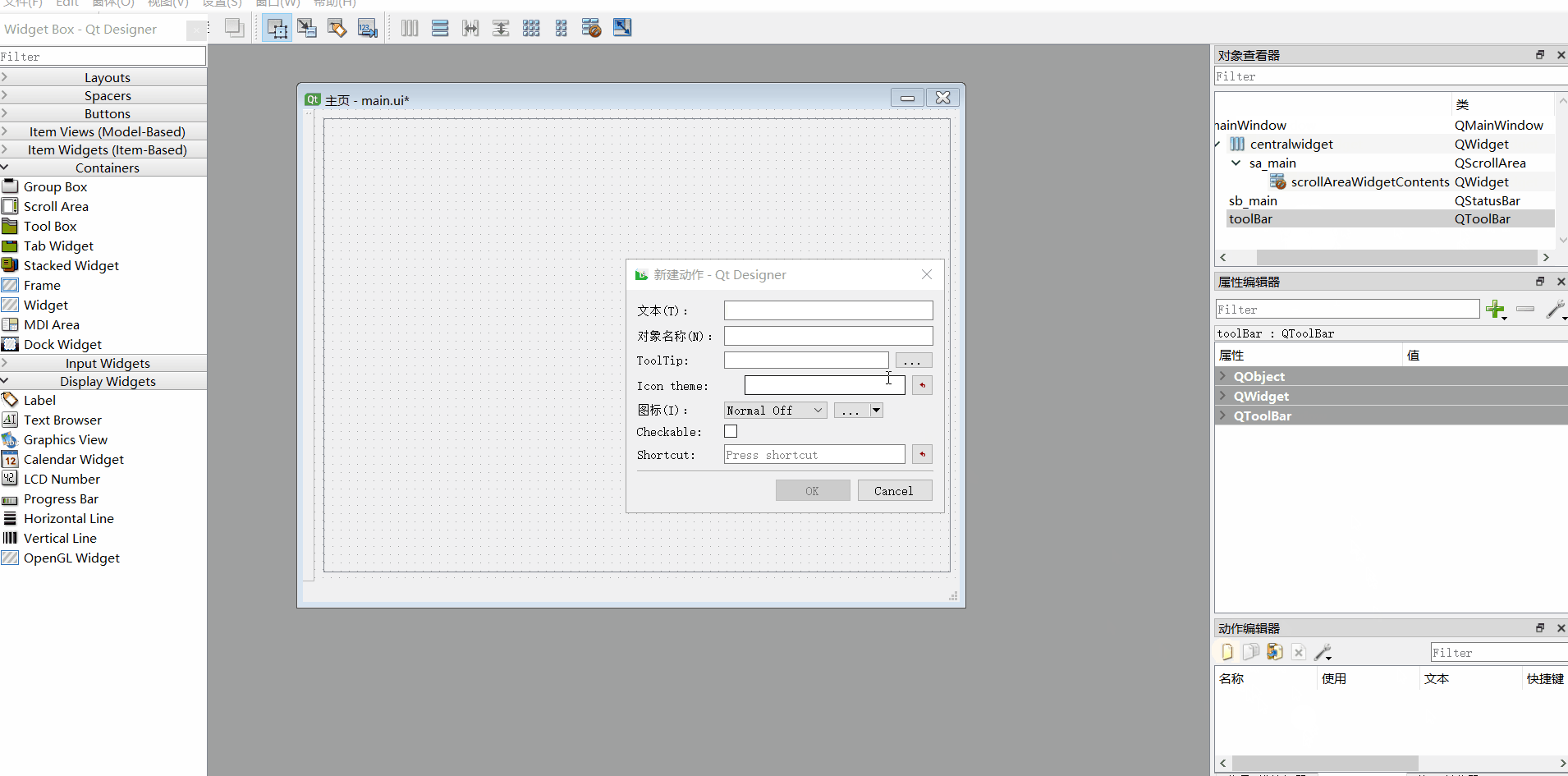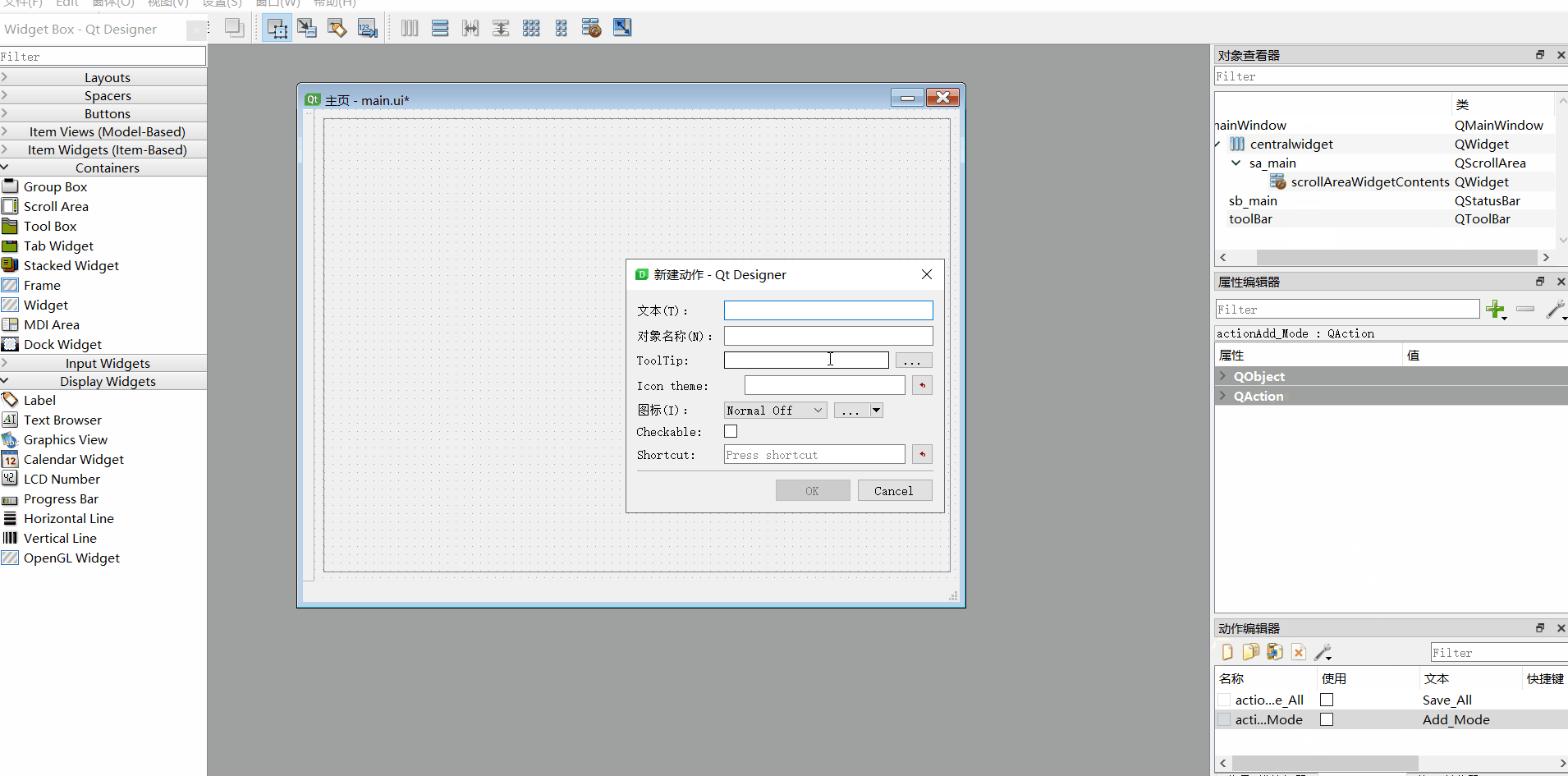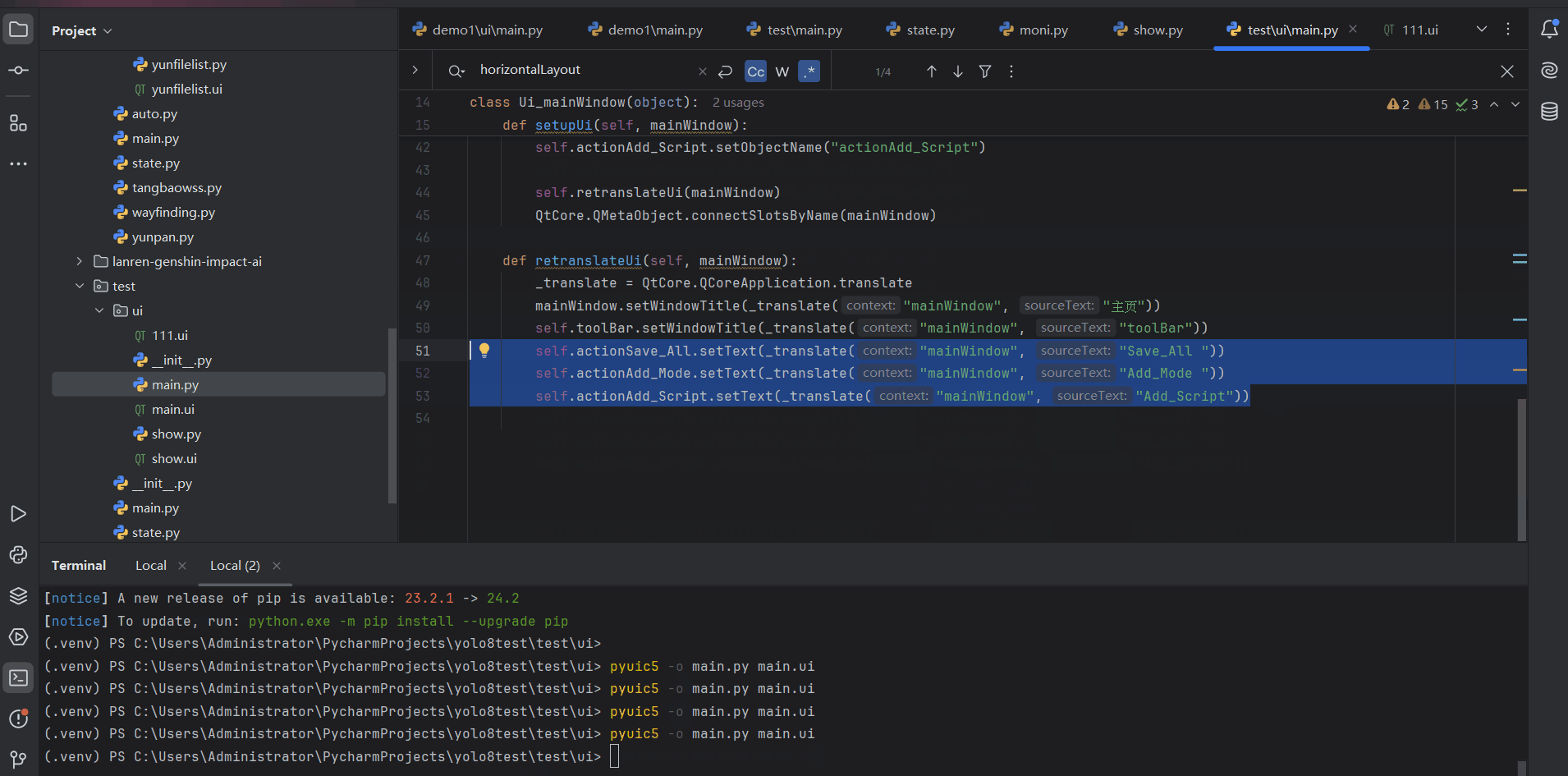
ui转换
pyuic5 -o main.py main.ui
ui/main.py
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
# Form implementation generated from reading ui file 'main.ui'
#
# Created by: PyQt5 UI code generator 5.15.11
#
# WARNING: Any manual changes made to this file will be lost when pyuic5 is
# run again. Do not edit this file unless you know what you are doing.
from PyQt5 import QtCore, QtGui, QtWidgets
class Ui_mainWindow(object):
def setupUi(self, mainWindow):
mainWindow.setObjectName("mainWindow")
mainWindow.resize(800, 600)
self.centralwidget = QtWidgets.QWidget(mainWindow)
self.centralwidget.setObjectName("centralwidget")
self.horizontalLayout = QtWidgets.QHBoxLayout(self.centralwidget)
self.horizontalLayout.setObjectName("horizontalLayout")
self.sa_main = QtWidgets.QScrollArea(self.centralwidget)
self.sa_main.setWidgetResizable(True)
self.sa_main.setObjectName("sa_main")
self.scrollAreaWidgetContents = QtWidgets.QWidget()
self.scrollAreaWidgetContents.setGeometry(QtCore.QRect(0, 0, 762, 551))
self.scrollAreaWidgetContents.setObjectName("scrollAreaWidgetContents")
self.sa_main.setWidget(self.scrollAreaWidgetContents)
self.horizontalLayout.addWidget(self.sa_main)
mainWindow.setCentralWidget(self.centralwidget)
self.sb_main = QtWidgets.QStatusBar(mainWindow)
self.sb_main.setObjectName("sb_main")
mainWindow.setStatusBar(self.sb_main)
self.toolBar = QtWidgets.QToolBar(mainWindow)
self.toolBar.setObjectName("toolBar")
mainWindow.addToolBar(QtCore.Qt.LeftToolBarArea, self.toolBar)
self.actionSave_All = QtWidgets.QAction(mainWindow)
self.actionSave_All.setObjectName("actionSave_All")
self.actionAdd_Mode = QtWidgets.QAction(mainWindow)
self.actionAdd_Mode.setObjectName("actionAdd_Mode")
self.actionAdd_Script = QtWidgets.QAction(mainWindow)
self.actionAdd_Script.setObjectName("actionAdd_Script")
self.retranslateUi(mainWindow)
QtCore.QMetaObject.connectSlotsByName(mainWindow)
def retranslateUi(self, mainWindow):
_translate = QtCore.QCoreApplication.translate
mainWindow.setWindowTitle(_translate("mainWindow", "主页"))
self.toolBar.setWindowTitle(_translate("mainWindow", "toolBar"))
self.actionSave_All.setText(_translate("mainWindow", "Save_All "))
self.actionAdd_Mode.setText(_translate("mainWindow", "Add_Mode "))
self.actionAdd_Script.setText(_translate("mainWindow", "Add_Script"))
7、打开主窗口
vi main.py
import ctypes
import sys
#ui有好多方法,挨个导入太麻烦了,这里直接全量导入
#如果下面有找不到在哪里的函数就来这里找
from PyQt5.QtCore import *
from PyQt5.QtGui import *
from PyQt5.QtWidgets import *
#引入主窗口函数
from ui.main import Ui_mainWindow
#添加主窗口类, 他会继承QMainWindow主窗口类 和 Ui_mainWindow ui下所有的方法
class MainWindow(QMainWindow, Ui_mainWindow):
def __init__(self):
super(MainWindow, self).__init__()
self.setupUi(self) # 设置UI布局
self.retranslateUi(self) # 重新翻译UI组件的文字
if __name__ == '__main__':
# 获取屏幕宽度和高度
screen_width = ctypes.windll.user32.GetSystemMetrics(0)
screen_height = ctypes.windll.user32.GetSystemMetrics(1)
# 初始化QT应用
app = QApplication(sys.argv)
ratio = screen_width / 2560 # 分辨率比例
# 设置全局字体大小 计算字体大小
base_font_size = 13
# 基准字体大小,适合1920*1080分辨率
new_font_size = int(base_font_size * ratio)
font = QFont("Arial", new_font_size)
# 子控件的宽度
item_width = 320
item_height = 240
item_height_min = 60
window_main = MainWindow()
window_main.show() # 开启主窗口
sys.exit(app.exec_()) # 监听消息不关闭
8、主窗口样式
class MainWindow(QMainWindow, Ui_mainWindow):
def __init__(self):
super(MainWindow, self).__init__()
self.setupUi(self)
self.retranslateUi(self)
#添加样式
self.set_ui()
# 设置主窗口样式
def set_ui(self):
# 设置主题样式为 Flatwhite
# 创建 QtitanRibbon 实例
from qt_material import apply_stylesheet
apply_stylesheet(app, theme='dark_pink.xml')
self.setStyleSheet("""
QScrollBar::handle:horizontal {
background-color: #A50F2C; /* 设置滑块颜色 */
}
QScrollBar::handle:horizontal:hover{
background-color: #FF1744; /* 设置滑块颜色 */
}
QPushButton:hover{
background-color: #DFC472; /* 设置颜色 */
}
QPlainTextEdit{padding: 0px;margin: 0px;}
QPushButton{padding: 0px;margin: 1px;}
""" + "font-family: {}; font-size: {}pt;".format(font.family(), font.pointSize()))
9、窗口伸缩
class MainWindow(QMainWindow, Ui_mainWindow):
def __init__(self):
super(MainWindow, self).__init__()
self.setupUi(self)
self.retranslateUi(self)
self.set_ui() #添加样式
#sa_main是我们之前定义的QScrollArea 也就是滚动条类型的容器
#我们在滚动条布局sa_main内放了一个普通部件QWidget() ,self.sa_main.setWidget(self.container_widget)
#这样一来,如果普通部件内的数据超出了显示范围,就能通过滚动条查看了
self.g_box = QGridLayout()
#创建了一个普通的窗口部件(QWidget),这个部件将用于包含所有的子控件
#并且可以独立于其父窗口进行尺寸调整,为了可以让g_布局超过窗口大小
self.container_widget = QWidget() # 创建一个中间部件
self.container_widget.setLayout(self.g_box) # 将网格布局设置给中间部件
self.g_box.setAlignment(Qt.AlignTop | Qt.AlignLeft) # 布局 左上对齐
self.g_box.setContentsMargins(0, 0, 0, 0) # 边距
self.g_box.setAlignment(Qt.AlignTop)
self.sa_main.setWidget(self.container_widget) # 将中间部件设置为QScrollArea的子部件
# 获取纵向滚动条控件
vertical_scrollbar = self.findChild(QScrollArea)
self.v_scrollbar = vertical_scrollbar.verticalScrollBar()
self.setWindowFlags(Qt.WindowStaysOnTopHint)
self.row = 0
self.column = -1
self.run_times = 1
self.column_step = 310
# 获取主窗口的状态栏对象
self.statusbar = self.statusBar()
# 设置状态栏文本
self.statusbar.showMessage('欢迎使用')
10、添加窗口标题、大小、起始位置
def __init__(self):
...
# self.setWindowIcon(QIcon("datas/logo.png")) 设置图标
self.setWindowTitle(f" 修改主页标题")
self.resize(640, 900) # 窗口的长宽
self.move(0, 300) # 窗口的起点位置
11、延迟布局更新
当窗口尺寸变化或其他条件满足时(例如计时器触发),重新计算并更新网格布局中的控件位置,使其适应当前窗口的大小
class MainWindow(QMainWindow, Ui_mainWindow):
def __init__(self):
...
# 所有数据
self.datas = []
# 创建一个计时器,用于延迟布局
self.timer = QTimer(self)
self.timer.setSingleShot(True) # 设置为单次触发
self.timer.timeout.connect(self.update_layout)
#计算窗口位置动态调整布局
def update_layout(self):
try:
# 获取主窗口的宽度
width = self.centralWidget().width()
# 计算每行可以容纳的组件数量
num_per_row = (width) // (self.column_step * ratio) # 假设每个组件的宽度为200
if num_per_row < 1:
num_per_row = 1
# 清空当前布局
for i in reversed(range(self.g_box.count())):
self.g_box.itemAt(i).widget().setParent(None)
# 重新添加组件到网格布局
for i, data in enumerate(self.datas):
self.row = int(i // num_per_row)
self.column = int(i % num_per_row)
self.g_box.addWidget(data["f_item"], self.row, self.column)
except:
pass
12、全量py代码
import ctypes
import sys
from PyQt5.QtCore import *
from PyQt5.QtGui import *
from PyQt5.QtWidgets import *
#引入主窗口函数
from ui.main import Ui_mainWindow
#添加主窗口类, 他会继承QMainWindow主窗口类 和 Ui_mainWindow ui下所有的方法
class MainWindow(QMainWindow, Ui_mainWindow):
def __init__(self):
super(MainWindow, self).__init__()
self.setupUi(self) # 设置UI布局
self.retranslateUi(self) # 重新翻译UI组件的文字
#添加样式
self.set_ui()
# self.setWindowIcon(QIcon("datas/logo.png")) 设置图标
self.setWindowTitle(f" 修改主页标题")
self.resize(640, 900) # 窗口的长宽
self.move(0, 300) # 窗口的起点位置
#sa_main是我们之前定义的QScrollArea 也就是滚动条类型的容器
#我们在滚动条布局sa_main内放了一个普通部件QWidget() ,self.sa_main.setWidget(self.container_widget)
#这样一来,如果普通部件内的数据超出了显示范围,就能通过滚动条查看了
self.g_box = QGridLayout()
#创建了一个普通的窗口部件(QWidget),这个部件将用于包含所有的子控件,并且可以独立于其父窗口进行尺寸调整,为了可以让g_布局超过窗口大小
self.container_widget = QWidget() # 创建一个中间部件
self.container_widget.setLayout(self.g_box) # 将网格布局设置给中间部件
self.g_box.setAlignment(Qt.AlignTop | Qt.AlignLeft) # 布局 左上对齐
self.g_box.setContentsMargins(0, 0, 0, 0) # 边距
self.g_box.setAlignment(Qt.AlignTop)
self.sa_main.setWidget(self.container_widget) # 将中间部件设置为QScrollArea的子部件
# 获取纵向滚动条控件
vertical_scrollbar = self.findChild(QScrollArea)
self.v_scrollbar = vertical_scrollbar.verticalScrollBar()
self.setWindowFlags(Qt.WindowStaysOnTopHint)
self.row = 0
self.column = -1
self.run_times = 1
self.column_step = 310
# 获取主窗口的状态栏对象
self.statusbar = self.statusBar()
# 设置状态栏文本
self.statusbar.showMessage('欢迎使用')
# 所有数据
self.datas = []
# 创建一个计时器,用于延迟布局
self.timer = QTimer(self)
self.timer.setSingleShot(True) # 设置为单次触发
self.timer.timeout.connect(self.update_layout)
def update_layout(self):
try:
# 获取主窗口的宽度
width = self.centralWidget().width()
# 计算每行可以容纳的组件数量
num_per_row = (width) // (self.column_step * ratio) # 假设每个组件的宽度为200
if num_per_row < 1:
num_per_row = 1
# 清空当前布局
for i in reversed(range(self.g_box.count())):
self.g_box.itemAt(i).widget().setParent(None)
# 重新添加组件到网格布局
for i, data in enumerate(self.datas):
self.row = int(i // num_per_row)
self.column = int(i % num_per_row)
self.g_box.addWidget(data["f_item"], self.row, self.column)
except:
pass
# 设置主窗口样式
def set_ui(self):
# 设置主题样式为 Flatwhite
# 创建 QtitanRibbon 实例
from qt_material import apply_stylesheet
apply_stylesheet(app, theme='dark_pink.xml')
self.setStyleSheet("""
QScrollBar::handle:horizontal {
background-color: #A50F2C; /* 设置滑块颜色 */
}
QScrollBar::handle:horizontal:hover{
background-color: #FF1744; /* 设置滑块颜色 */
}
QPushButton:hover{
background-color: #DFC472; /* 设置颜色 */
}
QPlainTextEdit{padding: 0px;margin: 0px;}
QPushButton{padding: 0px;margin: 1px;}
""" + "font-family: {}; font-size: {}pt;".format(font.family(), font.pointSize()))
if __name__ == '__main__':
# 获取屏幕宽度和高度
screen_width = ctypes.windll.user32.GetSystemMetrics(0)
screen_height = ctypes.windll.user32.GetSystemMetrics(1)
# 初始化QT应用
app = QApplication(sys.argv)
ratio = screen_width / 2560 # 分辨率比例
# 设置全局字体大小 计算字体大小
base_font_size = 13
# 基准字体大小,适合1920*1080分辨率
new_font_size = int(base_font_size * ratio)
font = QFont("Arial", new_font_size)
# 子控件的宽度
item_width = 320
item_height = 240
item_height_min = 60
window_main = MainWindow()
window_main.show() # 开启主窗口
sys.exit(app.exec_()) # 监听消息不关闭
13、全量ui代码
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<ui version="4.0">
<class>mainWindow</class>
<widget class="QMainWindow" name="mainWindow">
<property name="geometry">
<rect>
<x>0</x>
<y>0</y>
<width>800</width>
<height>600</height>
</rect>
</property>
<property name="windowTitle">
<string>主页</string>
</property>
<widget class="QWidget" name="centralwidget">
<layout class="QHBoxLayout" name="horizontalLayout">
<item>
<widget class="QScrollArea" name="sa_main">
<property name="widgetResizable">
<bool>true</bool>
</property>
<widget class="QWidget" name="scrollAreaWidgetContents">
<property name="geometry">
<rect>
<x>0</x>
<y>0</y>
<width>762</width>
<height>551</height>
</rect>
</property>
</widget>
</widget>
</item>
</layout>
</widget>
<widget class="QStatusBar" name="sb_main"/>
<widget class="QToolBar" name="toolBar">
<property name="windowTitle">
<string>toolBar</string>
</property>
<attribute name="toolBarArea">
<enum>LeftToolBarArea</enum>
</attribute>
<attribute name="toolBarBreak">
<bool>false</bool>
</attribute>
</widget>
<action name="actionSave_All">
<property name="text">
<string>Save_All</string>
</property>
</action>
<action name="actionAdd_Mode">
<property name="text">
<string>Add_Mode </string>
</property>
</action>
<action name="actionAdd_Script">
<property name="text">
<string>Add_Script</string>
</property>
</action>
</widget>
<resources/>
<connections/>
</ui>
二、添加UI预览窗口
QDockWidget 码头窗口,通常用于显示附加信息或工具
1、预览窗口定义
1、新建项目-窗口部件--QDockWidget (483X565)
2、添加两个label 大小480 X 270 ,设置样式表
3、添加按钮 修改按钮文本 + -
#寻路标签背景颜色为黑色
background-color: rgb(0, 0, 0);
#标签背景颜色为灰色
background-color: rgb(20, 20, 20);
** 这里图里搞错了,yolo那个label应该设置为**background-color: rgb(20, 20, 20);
2、组件名称修改
DockWidget
dockWidgetContents
bt_jia
bt_jian
lb_xunlu
lb_yolov
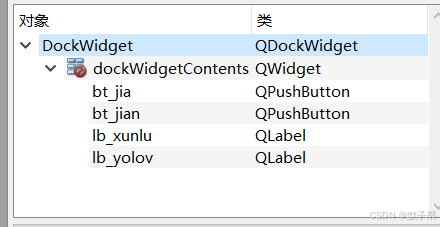
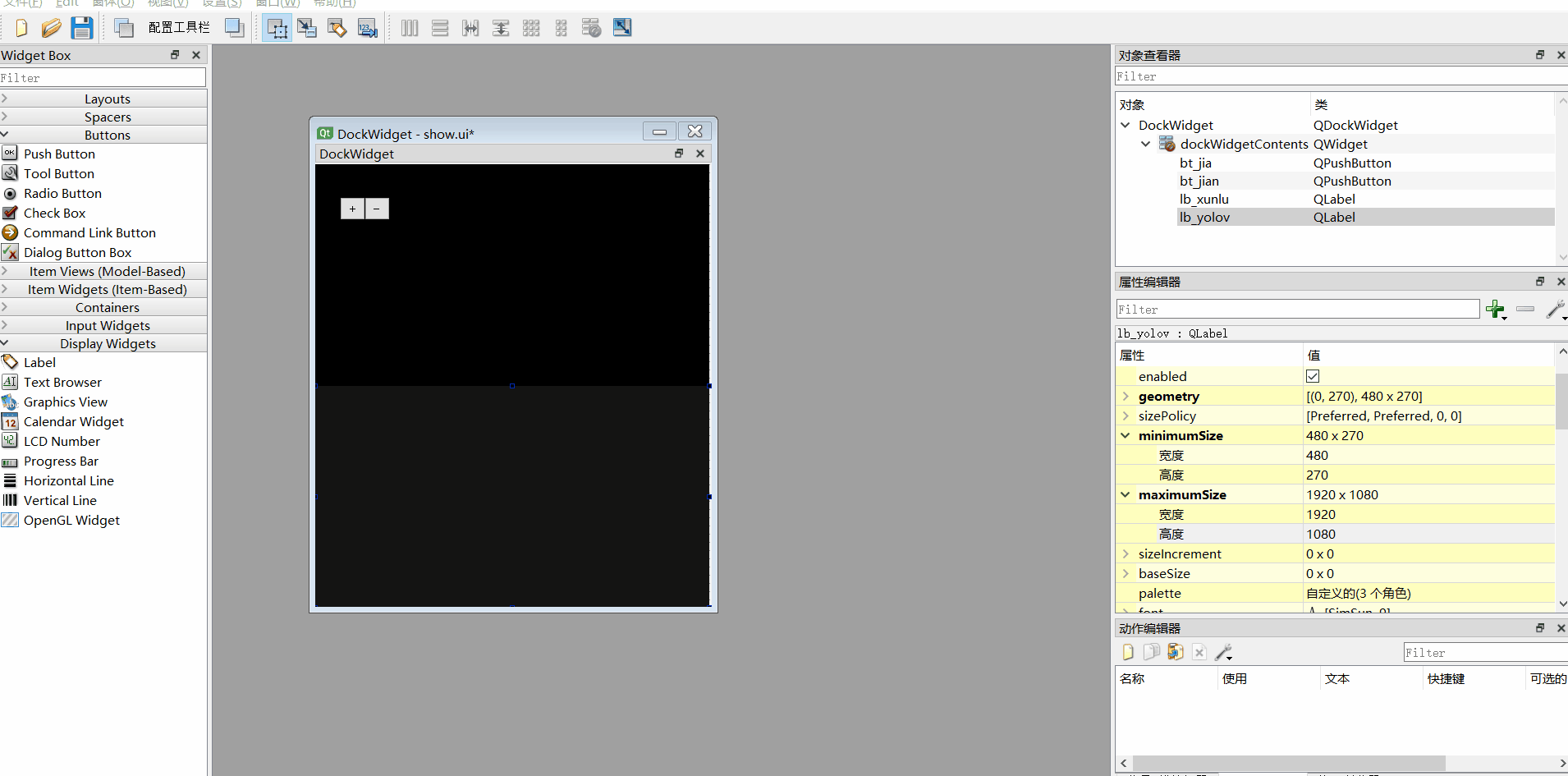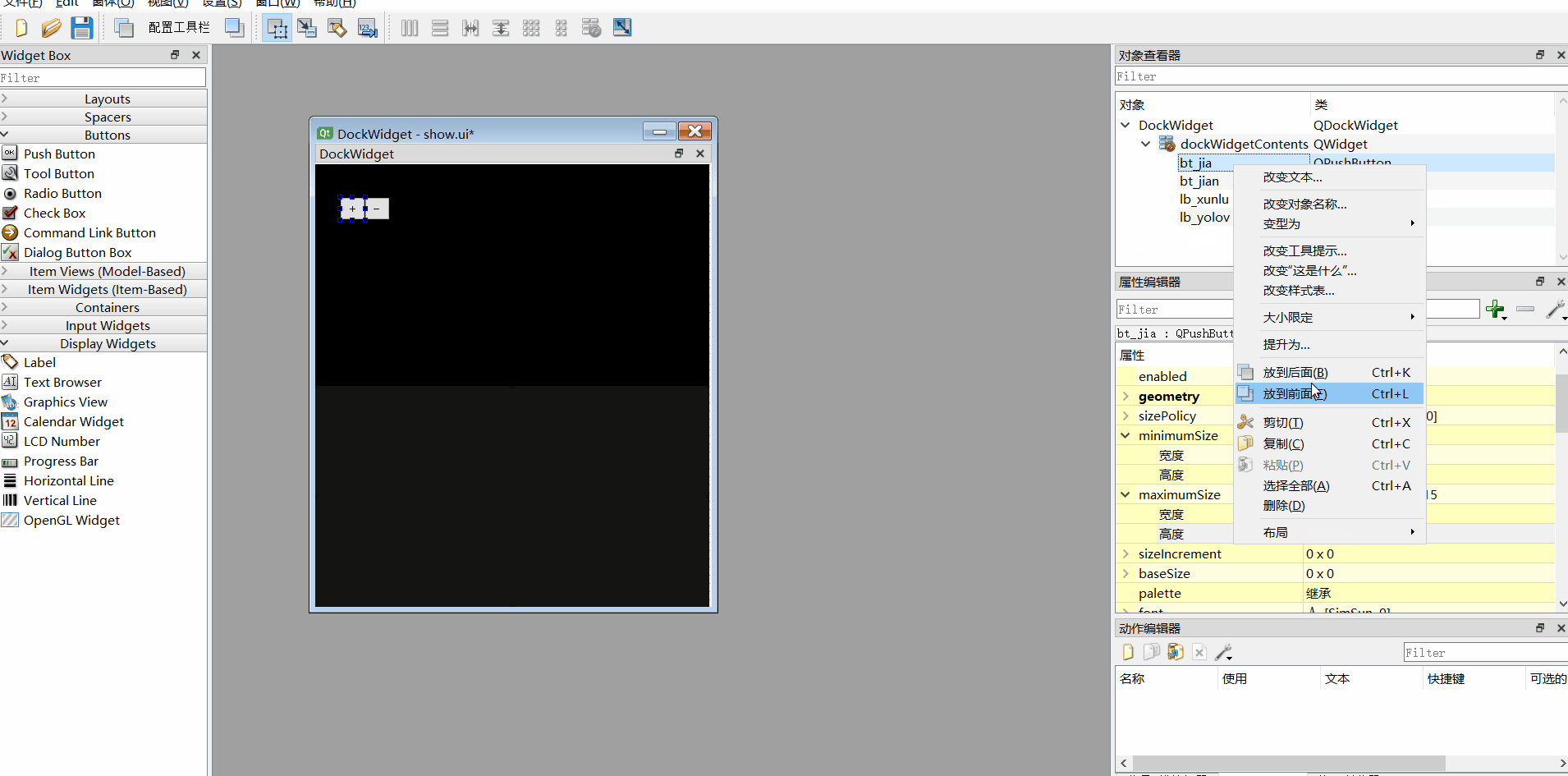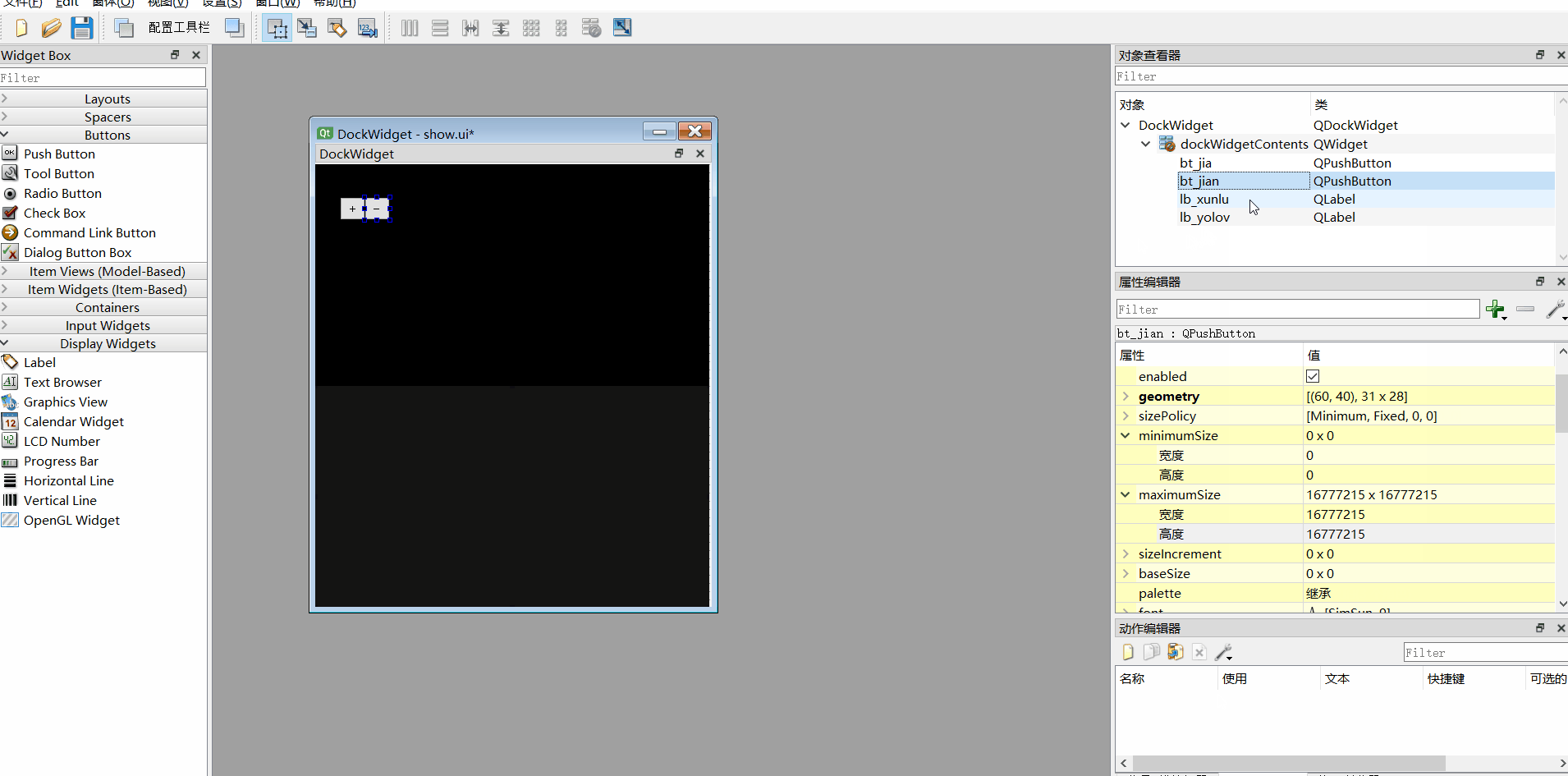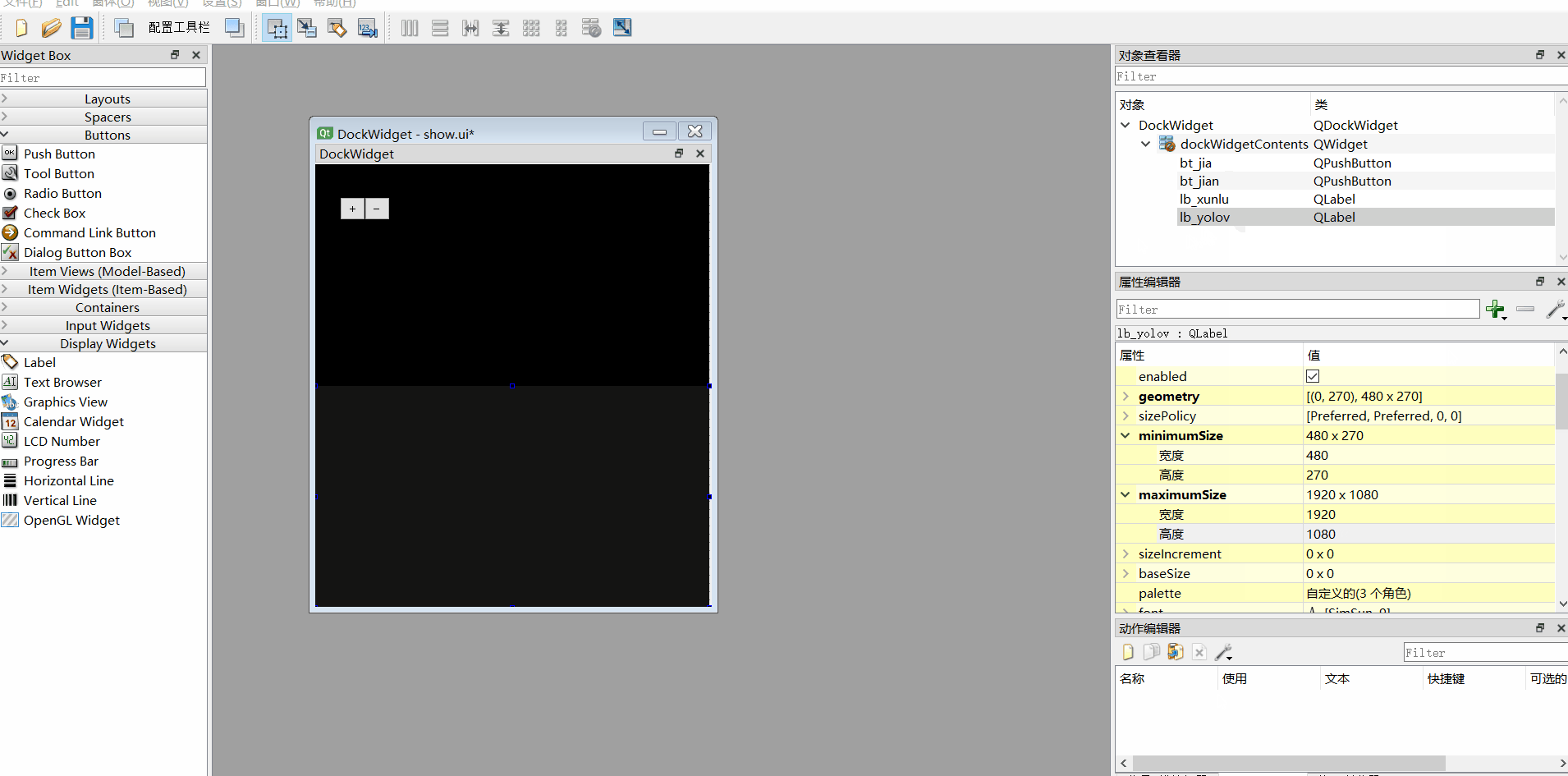
3、label最大尺寸修改
寻路
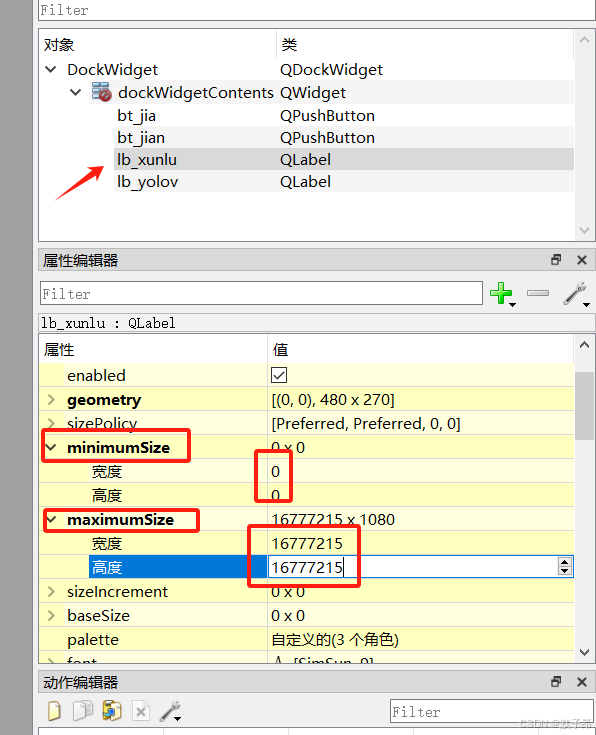
yolo

4、调整各个组件前后台
jia 和jian调整为前台
**xunlu和yolo调整到后台 **
(直接右键组件--放到前面/放到后面)
5、ui转py
pyuic5 -o show.py show.ui
ui全量
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<ui version="4.0">
<class>DockWidget</class>
<widget class="QDockWidget" name="DockWidget">
<property name="geometry">
<rect>
<x>0</x>
<y>0</y>
<width>483</width>
<height>565</height>
</rect>
</property>
<property name="windowTitle">
<string>DockWidget</string>
</property>
<widget class="QWidget" name="dockWidgetContents">
<widget class="QLabel" name="lb_xunlu">
<property name="geometry">
<rect>
<x>0</x>
<y>0</y>
<width>480</width>
<height>270</height>
</rect>
</property>
<property name="minimumSize">
<size>
<width>0</width>
<height>0</height>
</size>
</property>
<property name="maximumSize">
<size>
<width>16777215</width>
<height>16777215</height>
</size>
</property>
<property name="styleSheet">
<string notr="true">background-color: rgb(0, 0, 0);</string>
</property>
<property name="text">
<string/>
</property>
</widget>
<widget class="QLabel" name="lb_yolov">
<property name="geometry">
<rect>
<x>0</x>
<y>270</y>
<width>480</width>
<height>270</height>
</rect>
</property>
<property name="minimumSize">
<size>
<width>480</width>
<height>270</height>
</size>
</property>
<property name="maximumSize">
<size>
<width>1920</width>
<height>1080</height>
</size>
</property>
<property name="styleSheet">
<string notr="true">background-color: rgb(20, 20, 20);</string>
</property>
<property name="text">
<string/>
</property>
</widget>
<widget class="QPushButton" name="bt_jia">
<property name="geometry">
<rect>
<x>30</x>
<y>40</y>
<width>31</width>
<height>28</height>
</rect>
</property>
<property name="text">
<string>+</string>
</property>
</widget>
<widget class="QPushButton" name="bt_jian">
<property name="geometry">
<rect>
<x>60</x>
<y>40</y>
<width>31</width>
<height>28</height>
</rect>
</property>
<property name="text">
<string>-</string>
</property>
</widget>
<zorder>lb_yolov</zorder>
<zorder>lb_xunlu</zorder>
<zorder>bt_jia</zorder>
<zorder>bt_jian</zorder>
</widget>
</widget>
<resources/>
<connections/>
</ui>
py代码
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
# Form implementation generated from reading ui file 'show.ui'
#
# Created by: PyQt5 UI code generator 5.15.11
#
# WARNING: Any manual changes made to this file will be lost when pyuic5 is
# run again. Do not edit this file unless you know what you are doing.
from PyQt5 import QtCore, QtGui, QtWidgets
class Ui_DockWidget(object):
def setupUi(self, DockWidget):
DockWidget.setObjectName("DockWidget")
DockWidget.resize(483, 565)
self.dockWidgetContents = QtWidgets.QWidget()
self.dockWidgetContents.setObjectName("dockWidgetContents")
self.lb_xunlu = QtWidgets.QLabel(self.dockWidgetContents)
self.lb_xunlu.setGeometry(QtCore.QRect(0, 0, 480, 270))
self.lb_xunlu.setMinimumSize(QtCore.QSize(0, 0))
self.lb_xunlu.setMaximumSize(QtCore.QSize(16777215, 16777215))
self.lb_xunlu.setStyleSheet("background-color: rgb(0, 0, 0);")
self.lb_xunlu.setText("")
self.lb_xunlu.setObjectName("lb_xunlu")
self.lb_yolov = QtWidgets.QLabel(self.dockWidgetContents)
self.lb_yolov.setGeometry(QtCore.QRect(0, 270, 480, 270))
self.lb_yolov.setMinimumSize(QtCore.QSize(480, 270))
self.lb_yolov.setMaximumSize(QtCore.QSize(1920, 1080))
self.lb_yolov.setStyleSheet("background-color: rgb(20, 20, 20);")
self.lb_yolov.setText("")
self.lb_yolov.setObjectName("lb_yolov")
self.bt_jia = QtWidgets.QPushButton(self.dockWidgetContents)
self.bt_jia.setGeometry(QtCore.QRect(30, 40, 31, 28))
self.bt_jia.setObjectName("bt_jia")
self.bt_jian = QtWidgets.QPushButton(self.dockWidgetContents)
self.bt_jian.setGeometry(QtCore.QRect(60, 40, 31, 28))
self.bt_jian.setObjectName("bt_jian")
self.lb_yolov.raise_()
self.lb_xunlu.raise_()
self.bt_jia.raise_()
self.bt_jian.raise_()
DockWidget.setWidget(self.dockWidgetContents)
self.retranslateUi(DockWidget)
QtCore.QMetaObject.connectSlotsByName(DockWidget)
def retranslateUi(self, DockWidget):
_translate = QtCore.QCoreApplication.translate
DockWidget.setWindowTitle(_translate("DockWidget", "DockWidget"))
self.bt_jia.setText(_translate("DockWidget", "+"))
self.bt_jian.setText(_translate("DockWidget", "-"))
三、主窗口添加子窗口
1、添加预览窗口显示类
#添加预览窗口
from ui.show import Ui_DockWidget
class FormShow(QDockWidget, Ui_DockWidget):
def __init__(self, parent=None):
super(QDockWidget, self).__init__(parent)
self.parent = parent
self.setParent(parent)
self.setupUi(self)
self.set_ui()
# self.timer = QTimer()
self.setWindowTitle("检测预览")
self.lb_yolov.setScaledContents(True)
self.lb_yolov.setAlignment(Qt.AlignCenter)
self.lb_xunlu.setAlignment(Qt.AlignCenter)
self.move(0, 0)
self.setWindowFlags(Qt.WindowStaysOnTopHint)
self.window_height = int(270 * ratio)
self.window_width = int(480 * ratio)
self.setMinimumSize(self.window_width, self.window_height * 2)
self.bt_jia.clicked.connect(self.clicked_jia)
self.bt_jian.clicked.connect(self.clicked_jian)
def set_ui(self):
pass
def clicked_jia(self):
if self.window_height + 108 * ratio > 1080 * ratio:
return
self.window_height += int(108 * ratio)
self.window_width += int(190 * ratio)
self.lb_xunlu.setFixedHeight(self.window_height)
if self.width() >= self.lb_yolov.width() + self.lb_xunlu.width():
self.lb_yolov.move(self.lb_xunlu.width(), 0)
else:
self.lb_yolov.move(0, self.lb_xunlu.height())
self.lb_yolov.setFixedHeight(self.window_height)
self.lb_yolov.setFixedWidth(self.window_width)
def clicked_jian(self):
if self.window_height - 108 * ratio < 270 * ratio:
return
self.window_height -= int(108 * ratio)
self.window_width -= int(190 * ratio)
self.lb_xunlu.setFixedHeight(self.window_height)
if self.width() >= self.lb_yolov.width() + self.lb_xunlu.width():
self.lb_yolov.move(self.lb_xunlu.width(), 0)
else:
self.lb_yolov.move(0, self.lb_xunlu.height())
self.lb_yolov.setFixedHeight(self.window_height)
self.lb_yolov.setFixedWidth(self.window_width)
def closeEvent(self, event):
self.parent.action_isShow.setChecked(False)
def resizeEvent(self, event):
if self.width() >= self.lb_yolov.width() + self.lb_xunlu.width():
self.lb_yolov.move(self.lb_xunlu.width(), 0)
else:
self.lb_yolov.move(0, self.lb_xunlu.height())
2、主窗口添加顶级菜单
class MainWindow(QMainWindow, Ui_mainWindow):
...
#添加菜单控制栏
def connect_set(self):
# 创建一个顶级菜单
self.menu = self.menuBar() #创建菜单栏
self.menu_view = self.menu.addMenu("视图") #定义菜单栏名称
# 创建一个动作
self.action_isShow = QAction("显示检测结果窗口", self) #菜单栏选项, 关联为当前qt窗口self
self.action_isShow.setShortcut(QKeySequence(Qt.CTRL + Qt.Key_F11)) #设置快捷键ctrl + F11
self.action_isShow.triggered.connect(self.hotkey_isShow) #当按钮被按下或者 快捷键时触发函数
self.action_isShow.setCheckable(True) #添加复选框
self.action_isShow.setChecked(True) #默认被选中
# 添加动作到试图窗口
self.menu_view.addAction(self.action_isShow)
# 初始化的时候立刻调用显示qt窗口
self.hotkey_isShow()
3、预测窗口显示
我们在定义菜单栏的时候通过self.action_isShow.triggered.connect 绑定了当被选中时触发的函数,我们下面就定义当按钮被按下的时候会将我们的预览窗口
class MainWindow(QMainWindow, Ui_mainWindow):
...
def hotkey_isShow(self):
if not hasattr(self, "fromshow"):
self.fromshow = FormShow(self) #打开预览ui页面
#self 是当前主窗口的对象,传递给 FormShow 类作为父对象
#这样 FormShow 实例就可以访问主窗口的一些属性和方法
#添加预览窗口到主窗口
self.addDockWidget(Qt.TopDockWidgetArea, self.fromshow)
#设置动作被选中
self.action_isShow.setChecked(True)
else:
if self.fromshow.isVisible(): #isVisible 检查窗口是否可见
self.fromshow.hide() #如果可见则隐藏
self.action_isShow.setChecked(False) #设置为False 清空选中
else:
self.fromshow.show() #如果不可见,设置为可见
self.action_isShow.setChecked(True) #改为True 选中
四、信号槽
上面初步的给主窗口添加了我们做好的预览页面,但是预览页面什么东西都没有,只有俩label的无文本贴图,这里我们让他显示点东西处理
1、添加自定义信号
class MySignal(QObject):
#我们这里给 xunlu和yolo单独定义俩信号
mysig_show_xunlu = pyqtSignal()
mysig_show_yolov = pyqtSignal()
2、添加信号槽
# 绑定信号槽
def connect_set(self):
...
#添加信号
self.sg = MySignal()
#绑定信号槽
#其实和上面绑定按钮差不多,这里是将信号绑定到指定函数
#如果要发送信号则是下面两种方法,进行触发
#方法1 通过父对象访问sg
#self.parent.sg.mysig_show_yolov.emit()
#方法2 通过当前对象的sg,我们sg是定义在主窗口的,所以如果要用的话就是这个
#self.sg.mysig_show_yolov.emit()
self.sg.mysig_show_xunlu.connect(self.show_xunlu) #寻路
self.sg.mysig_show_yolov.connect(self.show_yolov) #推理
3、添加触发函数
这里先偷个懒,直接使用本地图片显示上去,后续整完之后在加具体功能
我们在test目录下创建个/datas/目录 放一张图片,我这里是111.png

def show_xunlu(self, image_path="./datas/111.png"):
# 加载本地图片
pixmap = QPixmap(image_path)
# 设置图片到 lb_xunlu 控件
self.fromshow.lb_xunlu.setPixmap(pixmap)
# 设置宽度固定,高度自适应
self.fromshow.window_width = int(self.fromshow.window_height * pixmap.width() / pixmap.height())
self.fromshow.lb_xunlu.setFixedHeight(self.fromshow.window_height)
self.fromshow.lb_xunlu.setFixedWidth(self.fromshow.window_width)
self.fromshow.lb_xunlu.setScaledContents(True)
def show_yolov(self, image_path="./datas/111.png"):
# 加载本地图片
pixmap1 = QPixmap(image_path)
# 设置图片到 lb_yolov 控件
self.fromshow.lb_yolov.setPixmap(pixmap1)
# 根据窗口宽度调整 lb_yolov 的位置
if self.fromshow.width() >= self.fromshow.lb_yolov.width() + self.fromshow.lb_xunlu.width():
self.fromshow.lb_yolov.move(self.fromshow.lb_xunlu.width(), 0)
else:
self.fromshow.lb_yolov.move(0, self.fromshow.lb_xunlu.height())
4、发送信号
关于怎么去显示,我们在主窗口初始化函数中定义一个定时器,让他每5s发送一次mysig_show_xunlu和mysig_show_yolov信号,信号槽接收到后,触发show_xunlu 和show_yolov 函数,去显示图片
def __init__(self):
...
# 创建定时器 用于周期显示图片
self.timer = QTimer(self)
self.timer.timeout.connect(self.on_timer_timeout)
self.timer.start(5000) # 每5秒触发一次
#发送信号
def on_timer_timeout(self):
# 每隔一段时间自动显示图片
# emit() 方法用于发送信号
self.sg.mysig_show_xunlu.emit()
self.sg.mysig_show_yolov.emit()
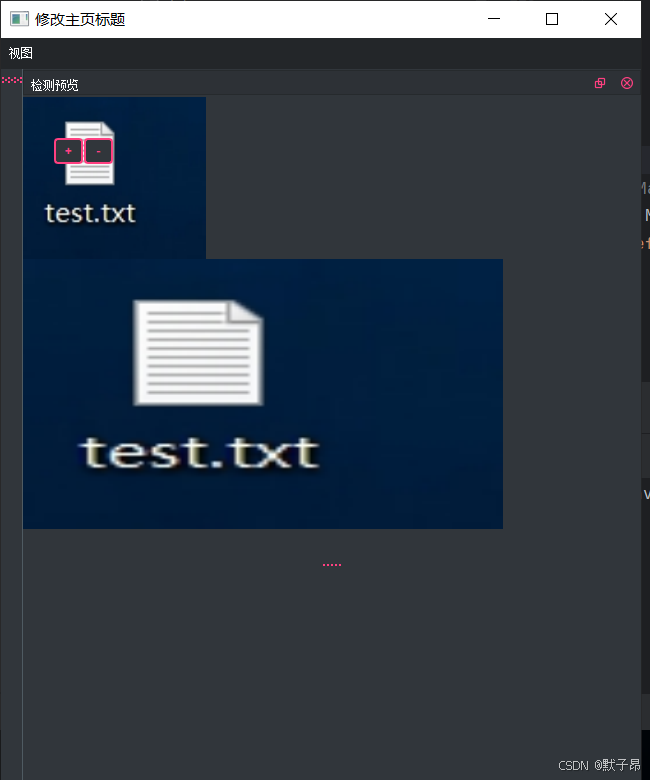
后面使用的时候不会这么草率的显示俩图片,而是通过循环截取地图,将yolo识别的到的视频流和地图位置作为显示查询
5、全量代码
import ctypes
import sys
from PyQt5.QtCore import *
from PyQt5.QtGui import *
from PyQt5.QtWidgets import *
from websockets import connect
#引入主窗口函数
from ui.main import Ui_mainWindow
#添加预览窗口
from ui.show import Ui_DockWidget
class FormShow(QDockWidget, Ui_DockWidget):
def __init__(self, parent=None):
super(QDockWidget, self).__init__(parent)
self.parent = parent
self.setParent(parent)
self.setupUi(self)
self.set_ui()
# self.timer = QTimer()
self.setWindowTitle("检测预览")
self.lb_yolov.setScaledContents(True)
self.lb_yolov.setAlignment(Qt.AlignCenter)
self.lb_xunlu.setAlignment(Qt.AlignCenter)
self.move(0, 0)
self.setWindowFlags(Qt.WindowStaysOnTopHint)
self.window_height = int(270 * ratio)
self.window_width = int(480 * ratio)
self.setMinimumSize(self.window_width, self.window_height * 2)
self.bt_jia.clicked.connect(self.clicked_jia)
self.bt_jian.clicked.connect(self.clicked_jian)
def set_ui(self):
pass
def clicked_jia(self):
if self.window_height + 108 * ratio > 1080 * ratio:
return
self.window_height += int(108 * ratio)
self.window_width += int(190 * ratio)
self.lb_xunlu.setFixedHeight(self.window_height)
if self.width() >= self.lb_yolov.width() + self.lb_xunlu.width():
self.lb_yolov.move(self.lb_xunlu.width(), 0)
else:
self.lb_yolov.move(0, self.lb_xunlu.height())
self.lb_yolov.setFixedHeight(self.window_height)
self.lb_yolov.setFixedWidth(self.window_width)
def clicked_jian(self):
if self.window_height - 108 * ratio < 270 * ratio:
return
self.window_height -= int(108 * ratio)
self.window_width -= int(190 * ratio)
self.lb_xunlu.setFixedHeight(self.window_height)
if self.width() >= self.lb_yolov.width() + self.lb_xunlu.width():
self.lb_yolov.move(self.lb_xunlu.width(), 0)
else:
self.lb_yolov.move(0, self.lb_xunlu.height())
self.lb_yolov.setFixedHeight(self.window_height)
self.lb_yolov.setFixedWidth(self.window_width)
def closeEvent(self, event):
self.parent.action_isShow.setChecked(False)
def resizeEvent(self, event):
if self.width() >= self.lb_yolov.width() + self.lb_xunlu.width():
self.lb_yolov.move(self.lb_xunlu.width(), 0)
else:
self.lb_yolov.move(0, self.lb_xunlu.height())
class MySignal(QObject):
#我们这里给 xunlu和yolo单独定义俩信号
mysig_show_xunlu = pyqtSignal()
mysig_show_yolov = pyqtSignal()
#添加主窗口类, 他会继承QMainWindow主窗口类 和 Ui_mainWindow ui下所有的方法
class MainWindow(QMainWindow, Ui_mainWindow):
def __init__(self):
super(MainWindow, self).__init__()
self.setupUi(self) # 设置UI布局
self.retranslateUi(self) # 重新翻译UI组件的文字
#添加样式
self.set_ui()
# self.setWindowIcon(QIcon("datas/logo.png")) 设置图标
self.setWindowTitle(f" 修改主页标题")
self.resize(640, 900) # 窗口的长宽
self.move(0, 300) # 窗口的起点位置
#sa_main是我们之前定义的QScrollArea 也就是滚动条类型的容器
#我们在滚动条布局sa_main内放了一个普通部件QWidget() ,self.sa_main.setWidget(self.container_widget)
#这样一来,如果普通部件内的数据超出了显示范围,就能通过滚动条查看了
self.g_box = QGridLayout()
#创建了一个普通的窗口部件(QWidget),这个部件将用于包含所有的子控件,并且可以独立于其父窗口进行尺寸调整,为了可以让g_布局超过窗口大小
self.container_widget = QWidget() # 创建一个中间部件
self.container_widget.setLayout(self.g_box) # 将网格布局设置给中间部件
self.g_box.setAlignment(Qt.AlignTop | Qt.AlignLeft) # 布局 左上对齐
self.g_box.setContentsMargins(0, 0, 0, 0) # 边距
self.g_box.setAlignment(Qt.AlignTop)
self.sa_main.setWidget(self.container_widget) # 将中间部件设置为QScrollArea的子部件
# 获取纵向滚动条控件
vertical_scrollbar = self.findChild(QScrollArea)
self.v_scrollbar = vertical_scrollbar.verticalScrollBar()
self.setWindowFlags(Qt.WindowStaysOnTopHint)
self.row = 0
self.column = -1
self.run_times = 1
self.column_step = 310
# 获取主窗口的状态栏对象
self.statusbar = self.statusBar()
# 设置状态栏文本
self.statusbar.showMessage('欢迎使用')
# 所有数据
self.datas = []
# 创建一个计时器,用于延迟布局
self.timer = QTimer(self)
self.timer.setSingleShot(True) # 设置为单次触发
self.timer.timeout.connect(self.update_layout)
#调用菜单栏
self.connect_set()
# 创建定时器 用于周期显示图片
self.timer = QTimer(self)
self.timer.timeout.connect(self.on_timer_timeout)
self.timer.start(5000) # 每5秒触发一次
def on_timer_timeout(self):
# 每隔一段时间自动显示图片
#emit() 方法用于发送信号
self.sg.mysig_show_xunlu.emit()
self.sg.mysig_show_yolov.emit()
def connect_set(self):
#添加信号
self.sg = MySignal()
#绑定信号槽
#这里是给我们上面定义的自定义信号,mysig_show_xunlu 这种绑定给特定的元素
#因为我们上面hotkey_isShow函数中做了FormShow(self)
self.sg.mysig_show_xunlu.connect(self.show_xunlu) #寻路 show_xunlu是下面我们
self.sg.mysig_show_yolov.connect(self.show_yolov) #推理
#如果要发送信号则是
#self.parent.sg.mysig_show_yolov.emit()
#当检查到发送信号的时候会触发函数
# 创建一个顶级菜单
self.menu = self.menuBar() #创建菜单栏
self.menu_view = self.menu.addMenu("视图") #定义菜单栏名称
# 创建一个动作
self.action_isShow = QAction("显示检测结果窗口", self) #菜单栏选项, 关联为当前qt窗口self
self.action_isShow.setShortcut(QKeySequence(Qt.CTRL + Qt.Key_F11)) #设置快捷键ctrl + F11
self.action_isShow.triggered.connect(self.hotkey_isShow) #当按钮被按下或者 快捷键时触发函数
self.action_isShow.setCheckable(True) #添加复选框
self.action_isShow.setChecked(True) #默认被选中
# 添加动作到试图窗口
self.menu_view.addAction(self.action_isShow)
# 初始化的时候立刻调用显示qt窗口
self.hotkey_isShow()
def show_xunlu(self, image_path="./datas/111.png"):
# 加载本地图片
pixmap = QPixmap(image_path)
# 设置图片到 lb_xunlu 控件
self.fromshow.lb_xunlu.setPixmap(pixmap)
# 设置宽度固定,高度自适应
self.fromshow.window_width = int(self.fromshow.window_height * pixmap.width() / pixmap.height())
self.fromshow.lb_xunlu.setFixedHeight(self.fromshow.window_height)
self.fromshow.lb_xunlu.setFixedWidth(self.fromshow.window_width)
self.fromshow.lb_xunlu.setScaledContents(True)
def show_yolov(self, image_path="./datas/111.png"):
# 加载本地图片
pixmap1 = QPixmap(image_path)
# 设置图片到 lb_yolov 控件
self.fromshow.lb_yolov.setPixmap(pixmap1)
# 根据窗口宽度调整 lb_yolov 的位置
if self.fromshow.width() >= self.fromshow.lb_yolov.width() + self.fromshow.lb_xunlu.width():
self.fromshow.lb_yolov.move(self.fromshow.lb_xunlu.width(), 0)
else:
self.fromshow.lb_yolov.move(0, self.fromshow.lb_xunlu.height())
def hotkey_isShow(self):
if not hasattr(self, "fromshow"):
self.fromshow = FormShow(self)
self.addDockWidget(Qt.TopDockWidgetArea, self.fromshow)
self.action_isShow.setChecked(True)
else:
if self.fromshow.isVisible():
self.fromshow.hide()
self.action_isShow.setChecked(False)
else:
self.fromshow.show()
self.action_isShow.setChecked(True)
def update_layout(self):
try:
# 获取主窗口的宽度
width = self.centralWidget().width()
# 计算每行可以容纳的组件数量
num_per_row = (width) // (self.column_step * ratio) # 假设每个组件的宽度为200
if num_per_row < 1:
num_per_row = 1
# 清空当前布局
for i in reversed(range(self.g_box.count())):
self.g_box.itemAt(i).widget().setParent(None)
# 重新添加组件到网格布局
for i, data in enumerate(self.datas):
self.row = int(i // num_per_row)
self.column = int(i % num_per_row)
self.g_box.addWidget(data["f_item"], self.row, self.column)
except:
pass
# 设置主窗口样式
def set_ui(self):
# 设置主题样式为 Flatwhite
# 创建 QtitanRibbon 实例
from qt_material import apply_stylesheet
apply_stylesheet(app, theme='dark_pink.xml')
self.setStyleSheet("""
QScrollBar::handle:horizontal {
background-color: #A50F2C; /* 设置滑块颜色 */
}
QScrollBar::handle:horizontal:hover{
background-color: #FF1744; /* 设置滑块颜色 */
}
QPushButton:hover{
background-color: #DFC472; /* 设置颜色 */
}
QPlainTextEdit{padding: 0px;margin: 0px;}
QPushButton{padding: 0px;margin: 1px;}
""" + "font-family: {}; font-size: {}pt;".format(font.family(), font.pointSize()))
if __name__ == '__main__':
# 获取屏幕宽度和高度
screen_width = ctypes.windll.user32.GetSystemMetrics(0)
screen_height = ctypes.windll.user32.GetSystemMetrics(1)
# 初始化QT应用
app = QApplication(sys.argv)
ratio = screen_width / 2560 # 分辨率比例
# 设置全局字体大小 计算字体大小
base_font_size = 13
# 基准字体大小,适合1920*1080分辨率
new_font_size = int(base_font_size * ratio)
font = QFont("Arial", new_font_size)
# 子控件的宽度
item_width = 320
item_height = 240
item_height_min = 60
window_main = MainWindow()
window_main.show() # 开启主窗口
sys.exit(app.exec_()) # 监听消息不关闭
版权归原作者 默子昂 所有, 如有侵权,请联系我们删除。



