一,Spring启动流程概述
Spring的IoC容器在实现控制反转和依赖注入的过程中,可以划分为两个阶段:
- 容器启动阶段
- Bean实例化阶段
容器初始化
- 加载配置
- 分析配置信息
- 将Bean信息装配到BeanDefinition
- 将Bean信息注册到相应的BeanDefinitionRegistry
- 其他后续处理
容器实例化
- 根据策略实例化对象
- 装配依赖
- Bean初始化前处理
- 对象初始化
- 对象其他处理
- 注册回调接口
二,Spring启动流程详解
启动流程源码概览
ClassPathXmlApplicationContext
public ClassPathXmlApplicationContext(String[] configLocations, boolean refresh, ApplicationContext parent)
throws BeansException {
super(parent);
setConfigLocations(configLocations);
if (refresh) {
refresh();
}
}
public ClassPathXmlApplicationContext(String[] paths, Class<?> clazz, ApplicationContext parent)
throws BeansException {
super(parent);
Assert.notNull(paths, "Path array must not be null");
Assert.notNull(clazz, "Class argument must not be null");
this.configResources = new Resource[paths.length];
for (int i = 0; i < paths.length; i++) {
this.configResources[i] = new ClassPathResource(paths[i], clazz);
}
refresh();
}
AbstractApplicationContext
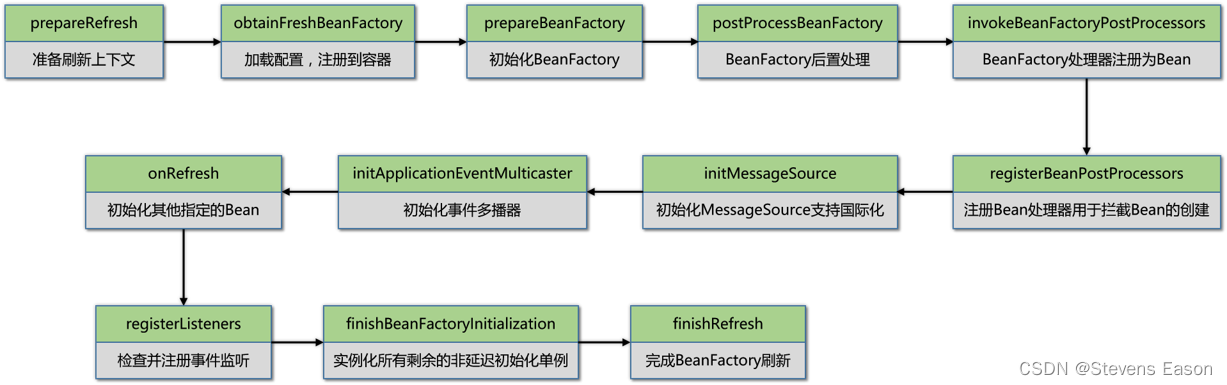
public void refresh() throws BeansException, IllegalStateException {
// 方法加锁避免多线程同时刷新Spring上下文
synchronized (this.startupShutdownMonitor) {
// 准备上下文刷新
prepareRefresh();
// 告诉子类刷新内部的beanFactory返回新的BeanFactory
ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = obtainFreshBeanFactory();
// 在当前上下文中准备要beanFactory
prepareBeanFactory(beanFactory);
try {
// 允许在上下文子类中对beanFactory进行后置处理
postProcessBeanFactory(beanFactory);
// 在上下文中将BeanFactory处理器注册为Bean
invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(beanFactory);
// 注册Bean处理器用于拦截Bean的创建
registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory);
// 在上下文中初始化国际化信息
initMessageSource();
// 在上下文中初始化event multicaster(事件多播器)
initApplicationEventMulticaster();
// 在指定的上下文子类中初始化其他指定的beans
onRefresh();
// 检查并注册事件监听
registerListeners();
// 实例化所有剩余的(非延迟初始化)单例
finishBeanFactoryInitialization(beanFactory);
// 最后一步:发布相应的事件
finishRefresh();
}
catch (BeansException ex) {
if (logger.isWarnEnabled()) {
logger.warn("Exception encountered during context initialization - " +
"cancelling refresh attempt: " + ex);
}
// 如果出现异常则销毁已创建的单例
destroyBeans();
// 重置活动标志。
cancelRefresh(ex);
// 将异常传递给调用者
throw ex;
}
finally {
// Reset common introspection caches in Spring's core, since we
// might not ever need metadata for singleton beans anymore...
resetCommonCaches();
}
}
}
整个refresh()的代码都是同步的,而对应的同步对象是startupShutdownMonitor。startupShutdownMonitor只在refresh()和close()两个方法里被用到,而它是用来同步applicationContext的刷新和销毁。
面试题
Spring的registerShutdownHook和close有什么区别?
当close()被调用时会立即关闭或者停止ApplicationContext;而调用registerShutdownHook()将在稍后JVM关闭时关闭或停止ApplicationContext,该方法主要通过JVM ShutdownHook来实现。
ShutdownHook
Java 语言提供一种 ShutdownHook(钩子)机制,当 JVM 接受到系统的关闭通知之后,调用 ShutdownHook 内的方法,用以完成清理操作,从而实现平滑退出应用。
第一步 刷新准备
protected void prepareRefresh() {
// 设置启动时间。当前毫秒数代表当前applicationContext的创建时间
this.startupDate = System.currentTimeMillis();
// 设置容器关闭标志
this.closed.set(false);
// 设置启动标志
this.active.set(true);
if (logger.isInfoEnabled()) {
logger.info("Refreshing " + this);
}
// 初始化属性资源
initPropertySources();
// 验证所有的属性是否都是可解析的
getEnvironment().validateRequiredProperties();
// ApplicationEvent初始化
this.earlyApplicationEvents = new LinkedHashSet<ApplicationEvent>();
}
第二步 获取BeanFactory
protected ConfigurableListableBeanFactory obtainFreshBeanFactory() {
refreshBeanFactory();
ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = getBeanFactory();
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Bean factory for " + getDisplayName() + ": " + beanFactory);
}
return beanFactory;
}
该方法对BeanFactory进行刷新。如果刷新前已经存在一个BeanFactory则需要先进行关闭操作,而后初始化一个新BeanFactory。
protected final void refreshBeanFactory() throws BeansException {
// 判断是否已经存在一个BeanFactory
if (hasBeanFactory()) {
// 销毁已经存在BeanFactory中的所有Bean
destroyBeans();
// 关闭BeanFactory
closeBeanFactory();
}
try {
// 创建新的BeanFactory对象(DefaultListableBeanFactory)
DefaultListableBeanFactory beanFactory = createBeanFactory();
// 给BeanFactory设置Id
beanFactory.setSerializationId(getId());
// 该方法主要对2个标志进行设置:allowBeanDefinitionOverriding和allowCircularReferences
// allowBeanDefinitionOverriding:是否允许使用相同名称重新注册不同的bean(Spring默认true,SpringBoot默认false)
// allowCircularReferences:是否允许循环依赖
customizeBeanFactory(beanFactory);
// 加载配置文件
loadBeanDefinitions(beanFactory);
synchronized (this.beanFactoryMonitor) {
// 新创建的BeanFactory赋给成员变量beanFactory
this.beanFactory = beanFactory;
}
}
catch (IOException ex) {
throw new ApplicationContextException("I/O error parsing bean definition source for " + getDisplayName(), ex);
}
}
DefaultSingletonBeanRegistry
// 当前这个单例是否正在被销毁
// true:表示单例已经执行了destroy方法,或者出现异常时执行了destroySingleton方法
private boolean singletonsCurrentlyInDestruction = false;
// 缓存两个Bean之间的包含关系。如:一个Bean中包含了一个内部Bean。
private final Map<String, Set<String>> containedBeanMap = new ConcurrentHashMap<String, Set<String>>(16);
// 缓存Bean与其他依赖Bean的关系
private final Map<String, Set<String>> dependentBeanMap = new ConcurrentHashMap<String, Set<String>>(64);
// 缓存被依赖Bean与其他依赖Bean的关系
private final Map<String, Set<String>> dependenciesForBeanMap = new ConcurrentHashMap<String, Set<String>>(64);
// 销毁所有的Bean实例
public void destroySingletons() {
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Destroying singletons in " + this);
}
synchronized (this.singletonObjects) {
// 设置销毁标志
this.singletonsCurrentlyInDestruction = true;
}
// 销毁disposableBeans缓存中所有单例bean
String[] disposableBeanNames;
synchronized (this.disposableBeans) {
disposableBeanNames = StringUtils.toStringArray(this.disposableBeans.keySet());
}
for (int i = disposableBeanNames.length - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
destroySingleton(disposableBeanNames[i]);
}
// 清空包含关系
this.containedBeanMap.clear();
// 清空依赖和被依赖关系
this.dependentBeanMap.clear();
this.dependenciesForBeanMap.clear();
// 清空缓存
clearSingletonCache();
}
加载配置

AbstractXmlApplicationContext
protected void loadBeanDefinitions(XmlBeanDefinitionReader reader) throws BeansException, IOException {
// 以Resource方式加载配置
Resource[] configResources = getConfigResources();
if (configResources != null) {
// 读取配置文件
reader.loadBeanDefinitions(configResources);
}
// 以String方式加载配置
String[] configLocations = getConfigLocations();
if (configLocations != null) {
// 读取配置文件
reader.loadBeanDefinitions(configLocations);
}
}
AbstractBeanDefinitionReader
@Override
// 通过String数组参数locations加载Bean,并返回加载Bean的数量
public int loadBeanDefinitions(String... locations) throws BeanDefinitionStoreException {
Assert.notNull(locations, "Location array must not be null");
int counter = 0;
for (String location : locations) {
// 加载BeanDefinintion
counter += loadBeanDefinitions(location);
}
// 返回加载Bean的数量
return counter;
}
@Override
// 通过Resource数组参数locations加载Bean,并返回加载Bean的数量
public int loadBeanDefinitions(Resource... resources) throws BeanDefinitionStoreException {
Assert.notNull(resources, "Resource array must not be null");
int counter = 0;
for (Resource resource : resources) {
// 加载BeanDefinintion
counter += loadBeanDefinitions(resource);
}
// 返回加载Bean的数量
return counter;
}
XmlBeanDefinitionReader
// 从配置文件中加载Bean
public int loadBeanDefinitions(EncodedResource encodedResource) throws BeanDefinitionStoreException {
Assert.notNull(encodedResource, "EncodedResource must not be null");
if (logger.isInfoEnabled()) {
logger.info("Loading XML bean definitions from " + encodedResource);
}
Set<EncodedResource> currentResources = this.resourcesCurrentlyBeingLoaded.get();
if (currentResources == null) {
currentResources = new HashSet<EncodedResource>(4);
this.resourcesCurrentlyBeingLoaded.set(currentResources);
}
if (!currentResources.add(encodedResource)) {
throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException(
"Detected cyclic loading of " + encodedResource + " - check your import definitions!");
}
try {
// 将Resource资源转化为输入流InputStream
InputStream inputStream = encodedResource.getResource().getInputStream();
try {
InputSource inputSource = new InputSource(inputStream);
if (encodedResource.getEncoding() != null) {
inputSource.setEncoding(encodedResource.getEncoding());
}
// 执行加载Bean的过程
return doLoadBeanDefinitions(inputSource, encodedResource.getResource());
}
finally {
inputStream.close();
}
}
catch (IOException ex) {
throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException(
"IOException parsing XML document from " + encodedResource.getResource(), ex);
}
finally {
currentResources.remove(encodedResource);
if (currentResources.isEmpty()) {
this.resourcesCurrentlyBeingLoaded.remove();
}
}
}
// 加载Bean的函数
protected int doLoadBeanDefinitions(InputSource inputSource, Resource resource)
throws BeanDefinitionStoreException {
try {
// 加载XML文件,构造XML Document对象
Document doc = doLoadDocument(inputSource, resource);
// 注册Bean
return registerBeanDefinitions(doc, resource);
}
// 抛出各种异常
......
}
Bean的解析与注册
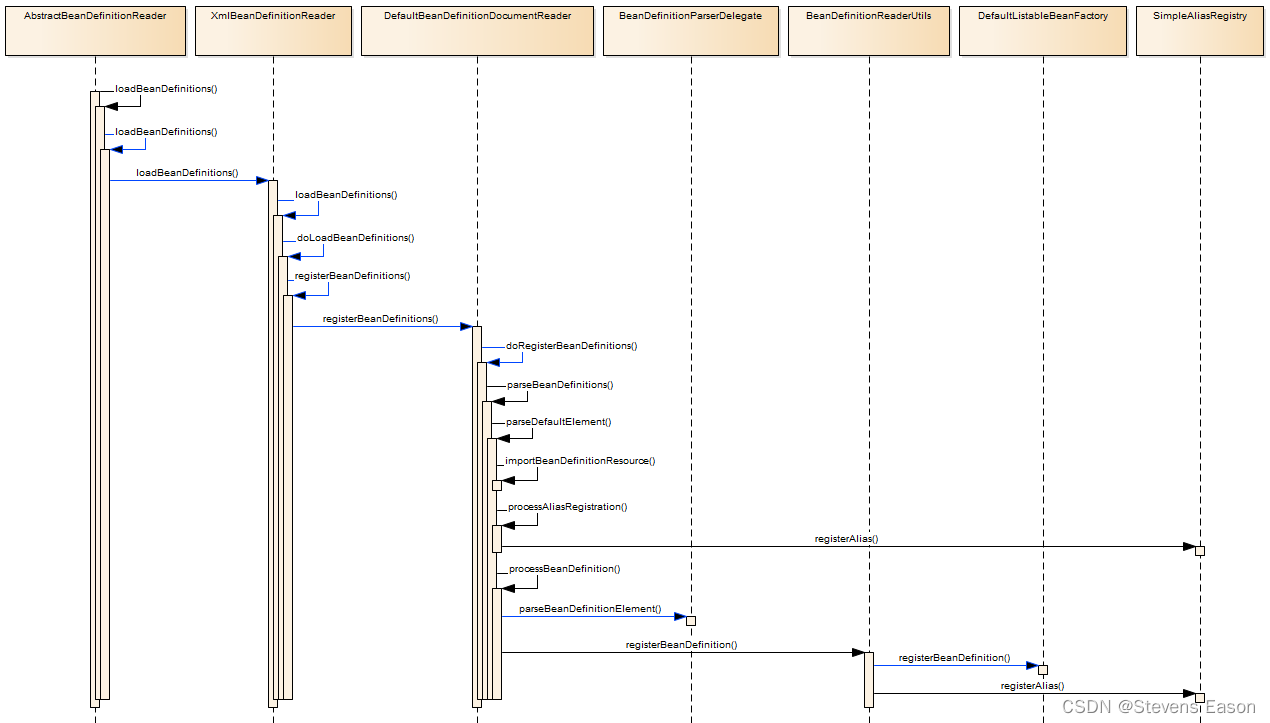
DefaultBeanDefinitionDocumentReader
// XML配置文件中beans元素
public static final String NESTED_BEANS_ELEMENT = "beans";
// XML配置文件中alias别名元素
public static final String ALIAS_ELEMENT = "alias";
// XML配置文件中name属性
public static final String NAME_ATTRIBUTE = "name";
// XML配置文件中alias属性
public static final String ALIAS_ATTRIBUTE = "alias";
// XML配置文件中import元素
public static final String IMPORT_ELEMENT = "import";
// XML配置文件中resource属性
public static final String RESOURCE_ATTRIBUTE = "resource";
// XML配置文件中profile属性
public static final String PROFILE_ATTRIBUTE = "profile";
protected void doRegisterBeanDefinitions(Element root) {
BeanDefinitionParserDelegate parent = this.delegate;
// 创建Bean解析代理工具类
this.delegate = createDelegate(getReaderContext(), root, parent);
if (this.delegate.isDefaultNamespace(root)) {
// 解析profile属性
String profileSpec = root.getAttribute(PROFILE_ATTRIBUTE);
if (StringUtils.hasText(profileSpec)) {
String[] specifiedProfiles = StringUtils.tokenizeToStringArray(
profileSpec, BeanDefinitionParserDelegate.MULTI_VALUE_ATTRIBUTE_DELIMITERS);
if (!getReaderContext().getEnvironment().acceptsProfiles(specifiedProfiles)) {
if (logger.isInfoEnabled()) {
logger.info("Skipped XML bean definition file due to specified profiles [" + profileSpec +
"] not matching: " + getReaderContext().getResource());
}
return;
}
}
}
preProcessXml(root);
// 解析XML并执行Bean注册
parseBeanDefinitions(root, this.delegate);
postProcessXml(root);
this.delegate = parent;
}
protected void parseBeanDefinitions(Element root, BeanDefinitionParserDelegate delegate) {
// root根节点是默认标签
if (delegate.isDefaultNamespace(root)) {
NodeList nl = root.getChildNodes();
// 遍历XML Document的每个节点
for (int i = 0; i < nl.getLength(); i++) {
Node node = nl.item(i);
if (node instanceof Element) {
Element ele = (Element) node;
if (delegate.isDefaultNamespace(ele)) {
// 解析默认标签
parseDefaultElement(ele, delegate);
}
else {
// 解析自定义标签
delegate.parseCustomElement(ele);
}
}
}
}
// root根节点是自定义标签
else {
delegate.parseCustomElement(root);
}
}
// 解析XML配置文件的节点元素
private void parseDefaultElement(Element ele, BeanDefinitionParserDelegate delegate) {
// 如果是Import元素
if (delegate.nodeNameEquals(ele, IMPORT_ELEMENT)) {
importBeanDefinitionResource(ele);
}
// 如果是Alias别名元素
else if (delegate.nodeNameEquals(ele, ALIAS_ELEMENT)) {
processAliasRegistration(ele);
}
// 如果是Bean元素
else if (delegate.nodeNameEquals(ele, BEAN_ELEMENT)) {
processBeanDefinition(ele, delegate);
}
// 如果是嵌套Bean元素(Beans)
else if (delegate.nodeNameEquals(ele, NESTED_BEANS_ELEMENT)) {
// recurse
doRegisterBeanDefinitions(ele);
}
}
Import解析
虽然每个单独的XML配置文件都代表体系结构中的逻辑层或模块,但我们可以从多个XML片段中加载Bean定义。如项目中有多个Resource位置,可以使用一个或多个<import />从另外的XML文件中加载Bean定义。
标签用法示例:
<import resource="applicationDao.xml" />
<import resource="applicationService.xml" />
解析标签的源码:
DefaultBeanDefinitionDocumentReader
protected void importBeanDefinitionResource(Element ele) {
String location = ele.getAttribute(RESOURCE_ATTRIBUTE);
if (!StringUtils.hasText(location)) {
getReaderContext().error("Resource location must not be empty", ele);
return;
}
// 解析路径和占位符
location = getReaderContext().getEnvironment().resolveRequiredPlaceholders(location);
// 解析好的资源要放到Set里面
Set<Resource> actualResources = new LinkedHashSet<Resource>(4);
// 解析location是相对路径还是绝对路径
boolean absoluteLocation = false;
try {
absoluteLocation = ResourcePatternUtils.isUrl(location) || ResourceUtils.toURI(location).isAbsolute();
}
catch (URISyntaxException ex) {
// cannot convert to an URI, considering the location relative
// unless it is the well-known Spring prefix "classpath*:"
}
// 如果是绝对路径
if (absoluteLocation) {
try {
// 直接根据路径加载相应的配置文件
int importCount = getReaderContext().getReader().loadBeanDefinitions(location, actualResources);
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Imported " + importCount + " bean definitions from URL location [" + location + "]");
}
}
catch (BeanDefinitionStoreException ex) {
getReaderContext().error(
"Failed to import bean definitions from URL location [" + location + "]", ele, ex);
}
}
else {
try {
int importCount;
// 如果是相对路径,则先根据路径得到Resource
Resource relativeResource = getReaderContext().getResource().createRelative(location);
// 如果Resource存在
if (relativeResource.exists()) {
importCount = getReaderContext().getReader().loadBeanDefinitions(relativeResource);
actualResources.add(relativeResource);
}
else {
// Resource类解析不成功,在classpath路径中去加载。如果没有则抛出异常
String baseLocation = getReaderContext().getResource().getURL().toString();
importCount = getReaderContext().getReader().loadBeanDefinitions(
StringUtils.applyRelativePath(baseLocation, location), actualResources);
}
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Imported " + importCount + " bean definitions from relative location [" + location + "]");
}
}
catch (IOException ex) {
getReaderContext().error("Failed to resolve current resource location", ele, ex);
}
catch (BeanDefinitionStoreException ex) {
getReaderContext().error("Failed to import bean definitions from relative location [" + location + "]",
ele, ex);
}
}
Resource[] actResArray = actualResources.toArray(new Resource[actualResources.size()]);
getReaderContext().fireImportProcessed(location, actResArray, extractSource(ele));
}
Alias别名注册
每个bean具有一个或多个标识符。这些标识符在承载Bean的容器内必须是唯一的。 Bean通常只有一个标识符,但是如果需要多个标识符,则多余的标识符可以被视为别名。
标签用法示例:
<alias name="dataSource" alias="systemA-dataSource"/>
<alias name="dataSource" alias="systemB-dataSource"/>
在Bean定义中,可以通过使用id属性最多指定的一个名称,同时可以通过name属性中定义任意数量的其他名称来为Bean提供多个名称。但在定义Bean的地方指定所有别名可能并不能满足需求,有时需要在其他地方为Bean定义别名。
解析标签的源码:
SimpleAliasRegistry
// 存放别名的缓存
private final Map<String, String> aliasMap = new ConcurrentHashMap<String, String>
// 根据Bean的别名进行注册
public void registerAlias(String name, String alias) {
Assert.hasText(name, "'name' must not be empty");
Assert.hasText(alias, "'alias' must not be empty");
synchronized (this.aliasMap) {
// 如果别名和名字相同
if (alias.equals(name)) {
this.aliasMap.remove(alias);
}
else {
// 如果别名和名字不相同,根据别名获取Bean名称
String registeredName = this.aliasMap.get(alias);
if (registeredName != null) {
// 如果缓存中已经存在该别名,不需要注册到缓存
if (registeredName.equals(name)) {
// An existing alias - no need to re-register
return;
}
// 如果不允许相同的Bean使用不同的名称则抛出异常
if (!allowAliasOverriding()) {
throw new IllegalStateException("Cannot register alias '" + alias + "' for name '" +
name + "': It is already registered for name '" + registeredName + "'.");
}
}
// 对别名进行循环检查
checkForAliasCircle(name, alias);
// 把别名放入别名缓存
this.aliasMap.put(alias, name);
}
}
}
// 别名循环检查
public boolean hasAlias(String name, String alias) {
for (Map.Entry<String, String> entry : this.aliasMap.entrySet()) {
// 获取Bean注册名
String registeredName = entry.getValue();
// 判断name参数和Bean注册名是否相同
if (registeredName.equals(name)) {
// 获取别名
String registeredAlias = entry.getKey();
// 判断别名是否相同
// 递归调用hasAlias
if (registeredAlias.equals(alias) || hasAlias(registeredAlias, alias)) {
return true;
}
}
}
return false;
}
别名循环检查:A为名称,B为A的别名,需要注册别名<B, A>
- 检查B是否有别名,如果没有则返回false
- 如果B有别名C,检查C是否与A相同。如果相同返回true,说明有别名循环。如果不相同递归hasAlias(C, B)方法
- 如果C无别名,返回false;如果C有别名D且等于A,返回true。如果不相同继续递归hasAlias(D, B)
Bean注册

Spring会自动检测构造型类,并向容器注册相应的BeanDefinition。
DefaultBeanDefinitionDocumentReader
protected void processBeanDefinition(Element ele, BeanDefinitionParserDelegate delegate) {
// 解析XML中的BeanDefinition元素
BeanDefinitionHolder bdHolder = delegate.parseBeanDefinitionElement(ele);
if (bdHolder != null) {
bdHolder = delegate.decorateBeanDefinitionIfRequired(ele, bdHolder);
try {
// 注册BeanDefinition
BeanDefinitionReaderUtils.registerBeanDefinition(bdHolder, getReaderContext().getRegistry());
}
catch (BeanDefinitionStoreException ex) {
getReaderContext().error("Failed to register bean definition with name '" +
bdHolder.getBeanName() + "'", ele, ex);
}
// 发送注册事件
getReaderContext().fireComponentRegistered(new BeanComponentDefinition(bdHolder));
}
}
BeanDefinitionParserDelegate
基于单一职责的缘故,BeanDefinitionParserDelegate专门负责解析XML元素的工作,而DefaultBeanDefinitionDocumentReader则主要负责读取XML配置文件的职责。
public BeanDefinitionHolder parseBeanDefinitionElement(Element ele, BeanDefinition containingBean) {
// 获取id属性
String id = ele.getAttribute(ID_ATTRIBUTE);
// 获取name属性
String nameAttr = ele.getAttribute(NAME_ATTRIBUTE);
// 定义别名list
List<String> aliases = new ArrayList<String>();
if (StringUtils.hasLength(nameAttr)) {
// 因为可以多个别名用,所以解析成别名数组
String[] nameArr = StringUtils.tokenizeToStringArray(nameAttr, MULTI_VALUE_ATTRIBUTE_DELIMITERS);
aliases.addAll(Arrays.asList(nameArr));
}
// beanName默认为id
String beanName = id;
// 如果没有beanName,那么取出别名数组中的第一个作为beanName
if (!StringUtils.hasText(beanName) && !aliases.isEmpty()) {
beanName = aliases.remove(0);
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("No XML 'id' specified - using '" + beanName +
"' as bean name and " + aliases + " as aliases");
}
}
if (containingBean == null) {
checkNameUniqueness(beanName, aliases, ele);
}
AbstractBeanDefinition beanDefinition = parseBeanDefinitionElement(ele, beanName, containingBean);
if (beanDefinition != null) {
if (!StringUtils.hasText(beanName)) {
try {
if (containingBean != null) {
// 生成Bean名
beanName = BeanDefinitionReaderUtils.generateBeanName(
beanDefinition, this.readerContext.getRegistry(), true);
}
else {
// 生成Bean名
beanName = this.readerContext.generateBeanName(beanDefinition);
String beanClassName = beanDefinition.getBeanClassName();
if (beanClassName != null &&
beanName.startsWith(beanClassName) && beanName.length() > beanClassName.length() &&
!this.readerContext.getRegistry().isBeanNameInUse(beanClassName)) {
aliases.add(beanClassName);
}
}
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Neither XML 'id' nor 'name' specified - " +
"using generated bean name [" + beanName + "]");
}
}
catch (Exception ex) {
error(ex.getMessage(), ele);
return null;
}
}
String[] aliasesArray = StringUtils.toStringArray(aliases);
return new BeanDefinitionHolder(beanDefinition, beanName, aliasesArray);
}
return null;
}
// 解析Bean定义不考虑名称或别名。如果在Bean解析过程中产生异常,则返回null
public AbstractBeanDefinition parseBeanDefinitionElement(
Element ele, String beanName, BeanDefinition containingBean) {
this.parseState.push(new BeanEntry(beanName));
String className = null;
// 解析Bean的class属性
if (ele.hasAttribute(CLASS_ATTRIBUTE)) {
className = ele.getAttribute(CLASS_ATTRIBUTE).trim();
}
try {
String parent = null;
// 解析parent属性
if (ele.hasAttribute(PARENT_ATTRIBUTE)) {
parent = ele.getAttribute(PARENT_ATTRIBUTE);
}
// 为指定的类名和Parent名称创建一个BeanDefinition
AbstractBeanDefinition bd = createBeanDefinition(className, parent);
// 解析Bean元素的属性并应用于Bean
parseBeanDefinitionAttributes(ele, beanName, containingBean, bd);
// 设置Bean的描述信息
bd.setDescription(DomUtils.getChildElementValueByTagName(ele, DESCRIPTION_ELEMENT));
// 解析Bean定义的元数据信息(meta以键值对形式存在)
parseMetaElements(ele, bd);
// 解析lookup-method元素
parseLookupOverrideSubElements(ele, bd.getMethodOverrides());
// 解析replaced-method元素
parseReplacedMethodSubElements(ele, bd.getMethodOverrides());
// 解析构造函数参数
parseConstructorArgElements(ele, bd);
// 解析property元素
parsePropertyElements(ele, bd);
// 解析qualifier元素
parseQualifierElements(ele, bd);
bd.setResource(this.readerContext.getResource());
bd.setSource(extractSource(ele));
return bd;
}
catch (ClassNotFoundException ex) {
error("Bean class [" + className + "] not found", ele, ex);
}
catch (NoClassDefFoundError err) {
error("Class that bean class [" + className + "] depends on not found", ele, err);
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
error("Unexpected failure during bean definition parsing", ele, ex);
}
finally {
this.parseState.pop();
}
return null;
}
BeanDefinitionReaderUtils
该类的主要职责用于生产新的BeanDefiniti实例,给Bean生成一个名称及调用BeanDefinitionRegistry进行Bean的注册。
public static String generateBeanName(
BeanDefinition definition, BeanDefinitionRegistry registry, boolean isInnerBean)
throws BeanDefinitionStoreException {
String generatedBeanName = definition.getBeanClassName();
if (generatedBeanName == null) {
// 如果有父类,名称为:definition.getParentName() + “$child”
if (definition.getParentName() != null) {
generatedBeanName = definition.getParentName() + "$child";
}
// 如果有指定的工厂类,名称为:definition.getFactoryBeanName() + “$created”
else if (definition.getFactoryBeanName() != null) {
generatedBeanName = definition.getFactoryBeanName() + "$created";
}
}
if (!StringUtils.hasText(generatedBeanName)) {
throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException("Unnamed bean definition specifies neither " +
"'class' nor 'parent' nor 'factory-bean' - can't generate bean name");
}
String id = generatedBeanName;
if (isInnerBean) {
// 如果是innerBean,名称为
id = generatedBeanName + GENERATED_BEAN_NAME_SEPARATOR + ObjectUtils.getIdentityHexString(definition);
}
else {
// 如果不是InnerBean则为顶层Bean,使用简单的类名。计数器加1
int counter = -1;
while (counter == -1 || registry.containsBeanDefinition(id)) {
counter++;
id = generatedBeanName + GENERATED_BEAN_NAME_SEPARATOR + counter;
}
}
return id;
}
- parent
Bean定义可以包含许多配置信息,包括容器相关的信息(比如初始化方法,静态工厂方法等等)以及构造函数参数和属性的值。子Bean可以定义从父Bean定义中继承配置数据,而后它可以根据需要覆盖某些值,或添加其他值。使用父子Bean可以节省很多输入工作。
- lookup-method
lookup-method注入是容器重写Bean上的方法的一种能力,它可以在容器中根据一个Bean的名字返回查找结果。lookup-method通常涉及Prototype Bean。Spring框架通过使用CGLIB来覆盖该方法的子类以实现lookup-method的注入。该功能可用于在一些可插拔的功能上解除依赖。
- replace-method
用于在运行时调用使用新的方法替换原有的方法,还能动态的改变原有方法的逻辑。
DefaultListableBeanFactory
// 手动注册的单例名称列表
private volatile Set<String> manualSingletonNames = new LinkedHashSet<String>(16);
public void registerBeanDefinition(String beanName, BeanDefinition beanDefinition)
throws BeanDefinitionStoreException {
Assert.hasText(beanName, "Bean name must not be empty");
Assert.notNull(beanDefinition, "BeanDefinition must not be null");
if (beanDefinition instanceof AbstractBeanDefinition) {
try {
// 对于AbstractBeanDefinition属性中的methodOverrides校验
// 校验methodOverrides是否与工厂方法并存或者methodOverrides对应的方法根本不存在
((AbstractBeanDefinition) beanDefinition).validate();
}
catch (BeanDefinitionValidationException ex) {
throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException(beanDefinition.getResourceDescription(), beanName,
"Validation of bean definition failed", ex);
}
}
// 从缓存中根据beanName获取BeanDefinition
BeanDefinition existingDefinition = this.beanDefinitionMap.get(beanName);
if (existingDefinition != null) {
// 如果BeanDefinition存在并且不允许同名覆盖,则抛出异常
if (!isAllowBeanDefinitionOverriding()) {
throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException(beanDefinition.getResourceDescription(), beanName,
"Cannot register bean definition [" + beanDefinition + "] for bean '" + beanName +
"': There is already [" + existingDefinition + "] bound.");
}
// Bean的角色检查
else if (existingDefinition.getRole() < beanDefinition.getRole()) {
// e.g. was ROLE_APPLICATION, now overriding with ROLE_SUPPORT or ROLE_INFRASTRUCTURE
if (logger.isWarnEnabled()) {
logger.warn("Overriding user-defined bean definition for bean '" + beanName +
"' with a framework-generated bean definition: replacing [" +
existingDefinition + "] with [" + beanDefinition + "]");
}
}
// 如果名字相同,但是BeanDefinition不同打印覆盖日志
else if (!beanDefinition.equals(existingDefinition)) {
if (logger.isInfoEnabled()) {
logger.info("Overriding bean definition for bean '" + beanName +
"' with a different definition: replacing [" + existingDefinition +
"] with [" + beanDefinition + "]");
}
}
else {
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Overriding bean definition for bean '" + beanName +
"' with an equivalent definition: replacing [" + existingDefinition +
"] with [" + beanDefinition + "]");
}
}
// 在缓存中注册Bean
this.beanDefinitionMap.put(beanName, beanDefinition);
}
else {
// 检查工厂的Bean创建阶段是否已经开始
if (hasBeanCreationStarted()) {
// 进入创建阶段,此时无法再修改启动时集合元素(为了稳定迭代)
synchronized (this.beanDefinitionMap) {
this.beanDefinitionMap.put(beanName, beanDefinition);
List<String> updatedDefinitions = new ArrayList<String>(this.beanDefinitionNames.size() + 1);
updatedDefinitions.addAll(this.beanDefinitionNames);
updatedDefinitions.add(beanName);
this.beanDefinitionNames = updatedDefinitions;
// beanName在manualSingletonNames中,说明是手动注册
if (this.manualSingletonNames.contains(beanName)) {
Set<String> updatedSingletons = new LinkedHashSet<String>(this.manualSingletonNames);
updatedSingletons.remove(beanName);
this.manualSingletonNames = updatedSingletons;
}
}
}
else {
// 工厂还未到创建阶段,仍然在注册阶段
this.beanDefinitionMap.put(beanName, beanDefinition);
this.beanDefinitionNames.add(beanName);
this.manualSingletonNames.remove(beanName);
}
this.frozenBeanDefinitionNames = null;
}
// 待注册的Bean的已经在beanDefinitionMap缓存中存在,或者已经存在于单例Bean缓存中
if (existingDefinition != null || containsSingleton(beanName)) {
// 重置给定Bean的所有BeanDefinition缓存,包括从其派生的Bean的缓存
resetBeanDefinition(beanName);
}
}
AbstractBeanFactory
// 保存在至少被创建过一次的beanName
// 如果这个集合中存在beanName,那么说明已经进入了Bean创建阶段
private final Set<String> alreadyCreated =
Collections.newSetFromMap(new ConcurrentHashMap<String, Boolean>(256))
第三步 准备BeanFactory
这个阶段主要是当Spring获取了BeanFactory之后,还要做些处理工作(配置工厂的上下文),如:上下文的ClassLoader和BeanPostProcessor。
protected void prepareBeanFactory(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory) {
// 内部BeanFactory使用Context上下文的类加载器
beanFactory.setBeanClassLoader(getClassLoader());
beanFactory.setBeanExpressionResolver(new StandardBeanExpressionResolver(beanFactory.getBeanClassLoader()));
beanFactory.addPropertyEditorRegistrar(new ResourceEditorRegistrar(this, getEnvironment()));
// 配置BeanFactory的Context上下文回调
beanFactory.addBeanPostProcessor(new ApplicationContextAwareProcessor(this));
beanFactory.ignoreDependencyInterface(EnvironmentAware.class);
beanFactory.ignoreDependencyInterface(EmbeddedValueResolverAware.class);
beanFactory.ignoreDependencyInterface(ResourceLoaderAware.class);
beanFactory.ignoreDependencyInterface(ApplicationEventPublisherAware.class);
beanFactory.ignoreDependencyInterface(MessageSourceAware.class);
beanFactory.ignoreDependencyInterface(ApplicationContextAware.class);
// BeanFactory接口不在普通工厂中注册为可解析类型
// MessageSource 注册(找到并自动装配)为一个Bean
beanFactory.registerResolvableDependency(BeanFactory.class, beanFactory);
beanFactory.registerResolvableDependency(ResourceLoader.class, this);
beanFactory.registerResolvableDependency(ApplicationEventPublisher.class, this);
beanFactory.registerResolvableDependency(ApplicationContext.class, this);
// Register early post-processor for detecting inner beans as ApplicationListeners.
// 注册早期的后处理器用来将内部Bean检测为ApplicationListeners。
beanFactory.addBeanPostProcessor(new ApplicationListenerDetector(this));
// 如果发现LoadTimeWeaver,则准备织入
if (beanFactory.containsBean(LOAD_TIME_WEAVER_BEAN_NAME)) {
beanFactory.addBeanPostProcessor(new LoadTimeWeaverAwareProcessor(beanFactory));
// 给类型匹配设置一个临时的ClassLoader
beanFactory.setTempClassLoader(new ContextTypeMatchClassLoader(beanFactory.getBeanClassLoader()));
}
// 注册默认的environment
if (!beanFactory.containsLocalBean(ENVIRONMENT_BEAN_NAME)) {
beanFactory.registerSingleton(ENVIRONMENT_BEAN_NAME, getEnvironment());
}
// 注册systemProperties
if (!beanFactory.containsLocalBean(SYSTEM_PROPERTIES_BEAN_NAME)) {
beanFactory.registerSingleton(SYSTEM_PROPERTIES_BEAN_NAME, getEnvironment().getSystemProperties());
}
// 注册systemEnvironment
if (!beanFactory.containsLocalBean(SYSTEM_ENVIRONMENT_BEAN_NAME)) {
beanFactory.registerSingleton(SYSTEM_ENVIRONMENT_BEAN_NAME, getEnvironment().getSystemEnvironment());
}
}
BeanExpressionResolver
通过将值作为表达式进行评估来解析值。它的唯一实现类是StandardBeanExpressionResolver。
PropertyEditor
Spring使用PropertyEditor的来实现对象和字符串之间的转换。有时用与对象本身不同的方式表示属性可能更为方便。如:“2019-09-13”字符串形式阅读起来更友好,但也可以将任何方便阅读的日期表现形式转换为日期对象。
Spring提供了很多内置的PropertyEditor,它们都位于org.springframework.beans.propertyeditors包中。默认情况下,大多数由BeanWrapperImpl注册。
类
描述
ByteArrayPropertyEditor
字节数组属性编辑器。字符串将地转换为相应的字节形式。默认情况下由BeanWrapperImpl注册。
ClassEditor
将表示类的字符串解析为实际类,反之亦然。当找不到类时,将抛出IllegalArgumentException。默认情况下由BeanWrapperImpl注册。
CustomBooleanEditor
布尔属性编辑器。默认情况下由BeanWrapperImpl注册,但是可以通过将其自定义实例注册为自定义编辑器来覆盖。
CustomCollectionEditor
集合属性编辑器,可将任何源集合转换为给定的目标集合类型。
CustomDateEditor
Date自定义属性编辑器,支持自定义DateFormat。
CustomNumberEditor
Number自定义属性编辑器。可用于任何Number子类,如Integer,Long,Float,Double。默认情况下由BeanWrapperImpl注册,但是可以通过将其自定义实例注册为自定义编辑器来覆盖。
FileEditor
将字符串解析为java.io.File对象。默认情况下由BeanWrapperImpl注册。
InputStreamEditor
单向属性编辑器,根据文本字符串生成(通过中间的ResourceEditor和Resource)InputStream,因此InputStream属性可以直接设置为Strings。默认情况下由BeanWrapperImpl注册。请注意,默认用法不会关闭InputStream!
LocaleEditor
将字符串解析为Locale对象,反之亦然(String格式为[country] [variant],与Locale的toString()方法提供的功能相同)。默认情况下由BeanWrapperImpl注册。
PatternEditor
将字符串解析为java.util.regex.Pattern对象,反之亦然。
PropertiesEditor
将字符串转换为Properties对象。默认情况下由BeanWrapperImpl注册。
StringTrimmerEditor
修剪字符串的属性编辑器。 允许将空字符串转换为Null值。
URLEditor
将URL的字符串表示形式解析为实际的URL对象。默认情况下由BeanWrapperImpl注册。
ResourceEditor
资源描述符属性编辑器,可将字符串转换为Resource属性。如:将file:C:/myfile.txt或classpath:myfile.txt转换为Resource属性。 该路径可能包含$ {...}占位符,将被解析为Environment属性,如$ {user.dir}。默认情况下,无法解析的占位符将被忽略。
Aware感知
如果在某个Bean里面想要使用Spring框架提供的功能,可以通过Aware接口来实现。通过实现 Aware 接口,Spring 可以在启动时,调用接口定义的方法,并将 Spring 底层的一些组件注入到自定义的 Bean 中。
类
描述
ApplicationContextAware
当ApplicationContext创建实现ApplicationContextAware接口的Bean实例时,将为该Bean实例提供对该ApplicationContext的引用。
ApplicationEventPublisherAware
为Bean实例提供对ApplicationEventPublisherAware的引用。
BeanFactoryAware
为Bean实例提供对BeanFactory的引用
BeanNameAware
获取Bean在BeanFactory中配置的名字
MessageSourceAware
为Bean实例提供对MessageSource的引用
EnvironmentAware
获得Environment支持,这样可以获取环境变量
ResourceLoaderAware
获得资源加载器以获得外部资源文件
代码示例
public class AwareBean implements ApplicationContextAware, BeanNameAware {
@Override
public void setBeanName(String name) {
System.out.println("=====>" + name);
}
@Override
public void setApplicationContext(ApplicationContext ctx)
throws BeansException {
System.out.println("=====>" + ctx.getBean("awareBean"));
}
}
Xml配置文件
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<bean id="awareBean" class="xxx.xxx.aware.AwareBean"/>
</beans>
忽略自动装配
Spring在ConfigurableListableBeanFactory接口中提供了2个可以忽略自动装配的方法:
// 自动装配时忽略指定接口或类的依赖注入
void ignoreDependencyType(Class<?> type);
// 忽略接口实现类中存在依赖外部的Bean注入
void ignoreDependencyInterface(Class<?> ifc);
忽略自动装配的做法使得一些基础组件(如:ApplicationContext或BeanFactory)依赖在自动装配时被忽略,而由框架统一设置依赖。如ApplicationContextAware接口的设置会在ApplicationContextAwareProcessor类中完成。
示例公用xml文件
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<bean class="ai.yunxi.TestBean" name="testB1;testB2"/>
<bean id="human" class="ai.yunxi.autowired.Human"/>
<bean id="humanService" class="xxx.xxx.autowired.HumanService" autowire="byName"/>
<!-- 去掉下面的注释,则ignoreDependencyType生效 -->
<!--<bean class="ai.yunxi.autowired.HumanAutowiringProcessor"/>-->
<bean id="list" class="java.util.ArrayList">
<constructor-arg>
<list>
<value>foo</value>
<value>bar</value>
</list>
</constructor-arg>
</bean>
<bean id="ignoreImpl" class="xxx.xxx.autowired.IgnoreImpl" autowire="byName" />
<!-- 去掉下面的注释,则ignoreDependencyInterface生效 -->
<!--<bean class="xxx.xxx.autowired.InterfaceIgnoreProcessor"/>-->
</beans>
ignoreDependencyType
public class Human {
private String name;
public Human( String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
}
实现了BeanFactoryPostProcessor的忽略自动装配处理器,这里是忽略的类。
public class HumanAutowiringProcessor implements BeanFactoryPostProcessor {
@Override
public void postProcessBeanFactory(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory)
throws BeansException {
beanFactory.ignoreDependencyType(Human.class);
}
}
ignoreDependencyInterface
接口类
public interface IgnoreInterface {
void setList(List<String> list);
}
实现类
public class IgnoreImpl implements IgnoreInterface {
private List<String> list;
@Override
public void setList(List<String> list) {
this.list = list;
System.out.println("ok.......");
}
public List<String> getList() {
return list;
}
}
实现了BeanFactoryPostProcessor的忽略自动装配处理器,这里忽略的是接口。
public class InterfaceIgnoreProcessor implements BeanFactoryPostProcessor {
@Override
public void postProcessBeanFactory(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory)
throws BeansException {
beanFactory.ignoreDependencyInterface(IgnoreInterface.class);
}
}
BeanPostProcessor
如果想在Spring容器中完成Bean实例化、配置以及其他初始化方法前后要添加一些自己逻辑处理,就需要定义一个或多个BeanPostProcessor接口实现类,然后注册到Spring IoC容器中。
第四步 BeanFactory后处理
protected void postProcessBeanFactory(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory) {
// ServletContextAwareProcessor中拿到应用上下文持有的servletContext引用和servletConfig引用
// 添加ServletContextAwareProcessor后处理器
beanFactory.addBeanPostProcessor(new ServletContextAwareProcessor(this.servletContext, this.servletConfig));
// 在自动注入时忽略指定的依赖接口
beanFactory.ignoreDependencyInterface(ServletContextAware.class);
beanFactory.ignoreDependencyInterface(ServletConfigAware.class);
// 向WebApplicationContext使用的BeanFactory注册Web相关作用域对象
WebApplicationContextUtils.registerWebApplicationScopes(beanFactory, this.servletContext);
// 注册和Environment有关的beans
WebApplicationContextUtils.registerEnvironmentBeans(beanFactory, this.servletContext, this.servletConfig);
}
WebApplicationContextUtils
该类位于包org.springframework.web.context.support是一个使检索指定ServletContext的根WebApplicationContext的便捷工具类。它如下工具方法:
- 在Web容器启动过程中注册Web相关作用域Bean(request/session/globalSession/application)
- 在Web容器启动过程中注册相应类型的工厂Bean ,依赖注入的Bean时能访问到正确的对象(ServletRequest/ServletResponse/HttpSession/WebRequest)
- 在Web容器启动过程中注册Web相关环境Bean
- 在Web容器启动过程中初始化Servlet propertySources
- 在客户化Web视图或者MVC action中,使用该工具类可以很方便地在程序中访问Spring应用上下文(application context)。
自定义作用域
Scope也称作用域,在Soring Ioc容器指其创建的Bean对象对其他Bean对象的请求可见范围,是用来声明IoC容器中的对象应该处的限定场景或者说该对象的存活空间,即在IOC容器在对象进入相应的Scope之前,生成并装配这些对象,在该对象不再处于这些scope的限定之后,容器通常会销毁这些对象。
诸如WebApplicationContext之类的ApplicationContext可以注册相对于标准作用域(Singleton/Prototype)的特定环境Scope作用域,例如:“request”和“session”作用域。
Bean的Scope作用域范围同样是可扩展的:即可以定义自己的范围,甚至重新定义现有范围,但不能覆盖内置的Singleton和Prototype范围。
// 从scope中根据名字返回对象
Object get(String name, ObjectFactory objectFactory);
// 从Scope中删除该对象
Object remove(String name);
// 注册的Scope被销毁或Scope中的指定对象被销毁时执行回调
void registerDestructionCallback(String name, Runnable destructionCallback);
// 获取Scope的会话标识符
String getConversationId();
ConfigurableBeanFactory接口中允许使用自定义的作用域范围扩展BeanFactory的标准作用域“ Singleton”和“ Prototype”,并为新的作用域范围进行注册。在编写好自定义Scope之后,需要让Spring容器识别新的Scope作用域。
代码方式注册
以下方法是在Spring容器中注册新Scope的主要方法,该方法在ConfigurableBeanFactory接口中定义:
// 第一个参数是与该Scope的全局唯一名称。在Spring容器中,此名称是Singleton和Prototype
// 第二个参数是希望注册和使用的自定义Scope实例
void registerScope(String scopeName, Scope scope);
如果已经写好了自己的自定义Scope实现,并且已经将其进行了注册:
Scope threadScope = new SimpleThreadScope();
beanFactory.registerScope("thread", threadScope);
然后就可以在配置文件中创建与自定义Scope规则对应的Bean定义:
<bean id="..." class="..." scope="thread"/>
配置方式注册
对于ApplicationContext来说,因为它可以自动识别并加载BeanFactoryPostProcessor,所以我们就可以直接在配置文件中,通过这个CustomScopeConfigurer注册来使新的Scope作用域范围生效
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop https://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop.xsd">
<bean class="org.springframework.beans.factory.config.CustomScopeConfigurer">
<property name="scopes">
<map>
<entry key="customerScope" value="xxx.xxx.scope.CustomerScope"/>
</map>
</property>
</bean>-->
<bean id="human" class="xxx.xxx.autowired.Human" scope="customerScope">
<!-- 让Bean符合自定义的作用域 -->
<!--<aop:scoped-proxy/>-->
</bean>
</beans>
测试类
public class TestScope {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ClassPathXmlApplicationContext ctx =
new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("scope.xml");
// 代码方式注册新的Scope作用域
// ctx.getBeanFactory().registerScope("customerScope", new CustomerScope());
System.out.println(ctx.getBeanFactory().getBeanDefinition("human").getScope());
String scopes[] = ctx.getBeanFactory().getRegisteredScopeNames();
for (String scope : scopes) {
System.out.println(scope);
}
}
}
第五步 调用后处理器
protected void invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory) {
PostProcessorRegistrationDelegate.invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(beanFactory, getBeanFactoryPostProcessors());
// Detect a LoadTimeWeaver and prepare for weaving, if found in the meantime
// (e.g. through an @Bean method registered by ConfigurationClassPostProcessor)
if (beanFactory.getTempClassLoader() == null && beanFactory.containsBean(LOAD_TIME_WEAVER_BEAN_NAME)) {
beanFactory.addBeanPostProcessor(new LoadTimeWeaverAwareProcessor(beanFactory));
beanFactory.setTempClassLoader(new ContextTypeMatchClassLoader(beanFactory.getBeanClassLoader()));
}
}
BeanFactoryPostProcessor
BeanFactoryPostProcessor接口与BeanPostProcessor相似,但有一个主要区别:BeanFactoryPostProcessor用来操作Bean的配置元数据。也就是说,Spring IoC容器允许BeanFactoryPostProcessor读取配置元数据,并能在容器实例化任何Bean之前更改这些元数据。换句话说 :就是可以让我们随心所欲地修改BeanFactory内所有BeanDefinition定义数据。
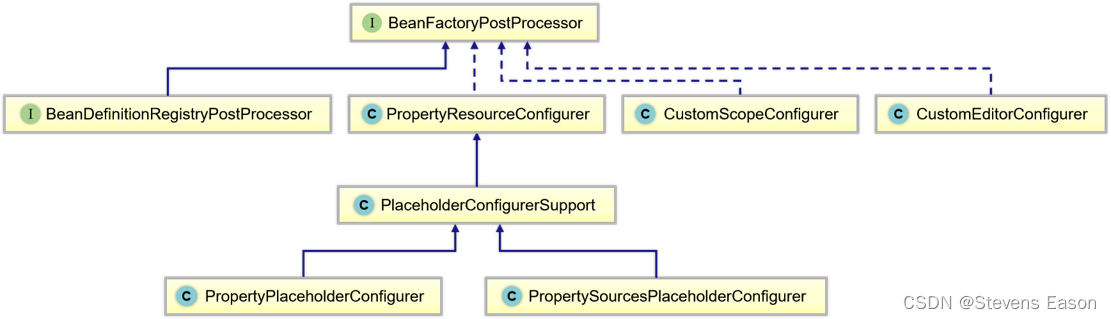
**BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor **是对标准BeanFactoryPostProcessor的扩展,允许在进行常规BeanFactoryPostProcessor检测之前注册其他Bean定义。特别是,BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor注册的Bean定义又定义了BeanFactoryPostProcessor实例。
使用示例
Xml配置文件
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<bean id="car" class="xxx.xxx.processor.Car">
<property name="name" value="benz"/>
</bean>
<bean id="carBeanFactoryPostProcessor1"
class="xxx.xxx.processor.CarBeanFactoryPostProcessor1">
<property name="order" value="0" />
</bean>
<bean id="carBeanFactoryPostProcessor2"
class="xxx.xxx.processor.CarBeanFactoryPostProcessor2">
<property name="order" value="1" />
</bean>
</beans>
自定义BeanFactoryPostProcessor
// 1号后置处理器
public class CarBeanFactoryPostProcessor1 implements BeanFactoryPostProcessor, Ordered {
int order;
@Override
public void postProcessBeanFactory(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory)
throws BeansException {
System.out.println("=======> 执行CarBeanFactoryPostProcessor1");
BeanDefinition bd = beanFactory.getBeanDefinition("car");
bd.getPropertyValues().addPropertyValue("name", "bmw");
}
public void setOrder(int order) {
this.order = order;
}
@Override
public int getOrder() {
return order;
}
}
// 2号后置处理器
public class CarBeanFactoryPostProcessor2 implements BeanFactoryPostProcessor, Ordered {
int order;
@Override
public void postProcessBeanFactory(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory)
throws BeansException {
System.out.println("=======> 执行CarBeanFactoryPostProcessor2");
BeanDefinition bd = beanFactory.getBeanDefinition("car");
bd.getPropertyValues().addPropertyValue("color", "red");
}
public void setOrder(int order) {
this.order = order;
}
@Override
public int getOrder() {
return order;
}
}
// 实现BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor接口的后处理器类
public class MobileBeanFactoryPostProcessor implements BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor {
@Override
public void postProcessBeanDefinitionRegistry(BeanDefinitionRegistry registry) throws BeansException {
System.out.println("=======> 执行MobileBeanFactoryPostProcessor_1");
BeanDefinitionBuilder beanDefinitionBuilder = BeanDefinitionBuilder.genericBeanDefinition(Mobile.class);
registry.registerBeanDefinition("mobile", beanDefinitionBuilder.getBeanDefinition());
}
@Override
public void postProcessBeanFactory(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory) throws BeansException {
System.out.println("=======> 执行MobileBeanFactoryPostProcessor_2");
BeanDefinition bd = beanFactory.getBeanDefinition("mobile");
bd.getPropertyValues().addPropertyValue("number", "123");
}
}
可以在项目中配置多个BeanFactoryPostProcessor,同时通过设置Order属性来控制这些BeanFactoryPostProcessor的执行顺序,当然仅当BeanFactoryPostProcessor实现Ordered接口时,才可以设置此属性。
Spring排序接口
Spring框架中有很多实现了相同接口的类,那么这些实现类之间必定会有优先级的问题。Spring提供了Ordered接口来处理相同接口实现类的优先级问题。Ordered接口,顾名思义,就是用来排序的。
流程源码分析
源码流程
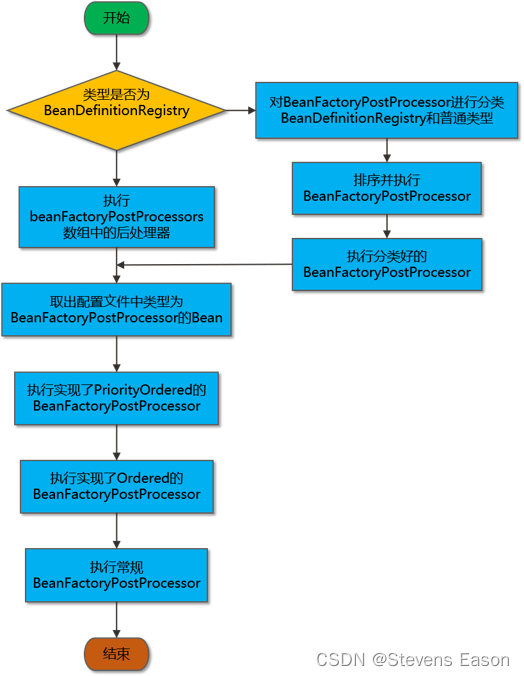
源码解析
public static void invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(
ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory, List<BeanFactoryPostProcessor> beanFactoryPostProcessors) {
// 临时缓存,用来记录已经调用过的BeanFactoryPostProcessor
Set<String> processedBeans = new HashSet<String>();
// 如果BeanFactory实现了BeanDefinitionRegistry接口
// 从类图上可以看到其实是指DefaultListableBeanFactory或者GenericApplicationContext
if (beanFactory instanceof BeanDefinitionRegistry) {
BeanDefinitionRegistry registry = (BeanDefinitionRegistry) beanFactory;
// 存放普通BeanFactoryPostProcessor
List<BeanFactoryPostProcessor> regularPostProcessors = new LinkedList<BeanFactoryPostProcessor>();
// 存放BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor
List<BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor> registryProcessors = new LinkedList<BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor>();
// 循环applicationContext中已经注册的BeanFactoryPostProcessor
for (BeanFactoryPostProcessor postProcessor : beanFactoryPostProcessors) {
// 如果是实现了BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor的后处理器
if (postProcessor instanceof BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor) {
BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor registryProcessor =
(BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor) postProcessor;
// 执行postProcessBeanDefinitionRegistry回调
registryProcessor.postProcessBeanDefinitionRegistry(registry);
// 把该后处理器加入到registryProcessors
registryProcessors.add(registryProcessor);
}
else {
// 否则就是普通的后处理器
regularPostProcessors.add(postProcessor);
}
}
// 在这里先不初始化FactoryBeans,因为需要保留这些Beans让BeanFactoryPostProcessor进行处理
// BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor将按照PriorityOrdered,Ordered进行分类
// 临时缓存,用来记录待执行回调方法的BeanFactoryPostProcessor
List<BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor> currentRegistryProcessors = new ArrayList<BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor>();
// 首先,处理实现了PriorityOrdered接口的BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor
String[] postProcessorNames =
beanFactory.getBeanNamesForType(BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor.class, true, false);
for (String ppName : postProcessorNames) {
if (beanFactory.isTypeMatch(ppName, PriorityOrdered.class)) {
// 保存到待执行BeanFactoryPostProcess回调的缓存
currentRegistryProcessors.add(beanFactory.getBean(ppName, BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor.class));
// 保存到已经执行过BeanFactoryPostProcess回调的缓存
processedBeans.add(ppName);
}
}
// 对待执行缓存进行排序
sortPostProcessors(currentRegistryProcessors, beanFactory);
registryProcessors.addAll(currentRegistryProcessors);
// 执行BeanFactoryPostProcess的回调函数
invokeBeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessors(currentRegistryProcessors, registry);
// 清空待执行BeanFactoryPostProcess回调的缓存
currentRegistryProcessors.clear();
// 其次,再处理实现了Ordered接口的BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor
Next, invoke the BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessors that implement Ordered.
postProcessorNames = beanFactory.getBeanNamesForType(BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor.class, true, false);
for (String ppName : postProcessorNames) {
if (!processedBeans.contains(ppName) && beanFactory.isTypeMatch(ppName, Ordered.class)) {
// 保存到待执行BeanFactoryPostProcess回调的缓存
currentRegistryProcessors.add(beanFactory.getBean(ppName, BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor.class));
// 保存到已经执行过BeanFactoryPostProcess回调的缓存
processedBeans.add(ppName);
}
}
// 对待执行缓存进行排序
sortPostProcessors(currentRegistryProcessors, beanFactory);
registryProcessors.addAll(currentRegistryProcessors);
// 执行BeanFactoryPostProcess的回调函数
invokeBeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessors(currentRegistryProcessors, registry);
// 清空待执行BeanFactoryPostProcess回调的缓存
currentRegistryProcessors.clear();
// 最后,处理所有其他BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor
boolean reiterate = true;
// 循环处理其他BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor
while (reiterate) {
reiterate = false;
// 把所有实现BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor的类名取出来
postProcessorNames = beanFactory.getBeanNamesForType(BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor.class, true, false);
// 遍历postProcessorNames
for (String ppName : postProcessorNames) {
// 已经处理过的缓存不包含该类名
if (!processedBeans.contains(ppName)) {
// 保存到待执行BeanFactoryPostProcess回调的缓存
currentRegistryProcessors.add(beanFactory.getBean(ppName, BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor.class));
// 保存到已经执行过BeanFactoryPostProcess回调的缓存
processedBeans.add(ppName);
reiterate = true;
}
}
// 对待执行缓存进行排序
sortPostProcessors(currentRegistryProcessors, beanFactory);
registryProcessors.addAll(currentRegistryProcessors);
// 执行BeanFactoryPostProcess的回调函数
invokeBeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessors(currentRegistryProcessors, registry);
// 清空待执行BeanFactoryPostProcess回调的缓存
currentRegistryProcessors.clear();
}
// 处理所有处理器,并执行postProcessBeanFactory回调
invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(registryProcessors, beanFactory);
invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(regularPostProcessors, beanFactory);
}
else {
// 调用在上下文中注册的工厂处理器
invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(beanFactoryPostProcessors, beanFactory);
}
// 在这里不初始化FactoryBeans,因为需要让BeanFactoryPostProcessor来进行处理
// 获取所有实现了BeanFactoryPostProcessor接口的类名称
String[] postProcessorNames =
beanFactory.getBeanNamesForType(BeanFactoryPostProcessor.class, true, false);
// 实现了PriorityOrdered接口的PostProcessor缓存
List<BeanFactoryPostProcessor> priorityOrderedPostProcessors = new ArrayList<BeanFactoryPostProcessor>();
// 实现了Ordered接口的PostProcessor缓存
List<String> orderedPostProcessorNames = new ArrayList<String>();
// 没有实现任何Order接口的PostProcessor缓存
List<String> nonOrderedPostProcessorNames = new ArrayList<String>();
// 遍历postProcessorNames开始处理BeanFactoryPostProcessor
for (String ppName : postProcessorNames) {
if (processedBeans.contains(ppName)) {
// 如果包含,代表在上面的代码已经处理过则跳过
}
// 首先,处理实现了PriorityOrdered接口的BeanFactoryPostProcessor
else if (beanFactory.isTypeMatch(ppName, PriorityOrdered.class)) {
priorityOrderedPostProcessors.add(beanFactory.getBean(ppName, BeanFactoryPostProcessor.class));
}
// 其次,处理实现了Ordered接口的BeanFactoryPostProcessor
else if (beanFactory.isTypeMatch(ppName, Ordered.class)) {
orderedPostProcessorNames.add(ppName);
}
// 最后,处理没有实现任何Order接口接口的BeanFactoryPostProcessor
else {
nonOrderedPostProcessorNames.add(ppName);
}
}
// 首先,处理实现了PriorityOrdered接口的BeanFactoryPostProcessor
sortPostProcessors(priorityOrderedPostProcessors, beanFactory);
invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(priorityOrderedPostProcessors, beanFactory);
// // 其次,再处理实现了Ordered接口的BeanFactoryPostProcessor
List<BeanFactoryPostProcessor> orderedPostProcessors = new ArrayList<BeanFactoryPostProcessor>();
for (String postProcessorName : orderedPostProcessorNames) {
orderedPostProcessors.add(beanFactory.getBean(postProcessorName, BeanFactoryPostProcessor.class));
}
sortPostProcessors(orderedPostProcessors, beanFactory);
invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(orderedPostProcessors, beanFactory);
// // 最后,处理所有其他BeanFactoryPostProcessor
List<BeanFactoryPostProcessor> nonOrderedPostProcessors = new ArrayList<BeanFactoryPostProcessor>();
for (String postProcessorName : nonOrderedPostProcessorNames) {
nonOrderedPostProcessors.add(beanFactory.getBean(postProcessorName, BeanFactoryPostProcessor.class));
}
invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(nonOrderedPostProcessors, beanFactory);
// 清除被缓存的BeanDefinition,因为后处理器可能已经修改了原始元数据,例如:替换占位符
beanFactory.clearMetadataCache();
}
第六步 注册后处理器
// 实例化并且注册所有BeanPostProcessors
protected void registerBeanPostProcessors(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory) {
PostProcessorRegistrationDelegate.registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory, this);
}
BeanPostProcessor
BeanPostProcessor是Spring的Bean工厂中一个非常重要的接口,允许Spring框架在新创建Bean实例时对其进行定制化修改。比如我们对Bean内容进行修改、创建代理对象等等。也就是说,Spring IoC容器实例化了一个Bean,而后BeanPostProcessor开始完成它们的工作。
BeanPostProcessor接口定义了回调方法,可以实现这些方法,以提供自己的实例化逻辑(或覆盖容器的默认值),依赖关系解析逻辑等。如果您想在Spring容器完成Bean的实例化、配置和初始化之后实现一些自定义逻辑,则可以插入一个或多个自定义BeanPostProcessor实现。
public interface BeanPostProcessor {
// Bean初始化之前调用
Object postProcessBeforeInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException;
// Bean初始化之后调用
Object postProcessAfterInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException;
}
在实际使用中可以配置多个BeanPostProcessor实例,并且可以通过设置Order属性来控制这些BeanPostProcessor的执行顺序。只有当BeanPostProcessor实现Ordered接口时,才可以设置此属性。
InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor
InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor实际上继承了BeanPostProcessor接口,主要作用于实例化阶段的前后。
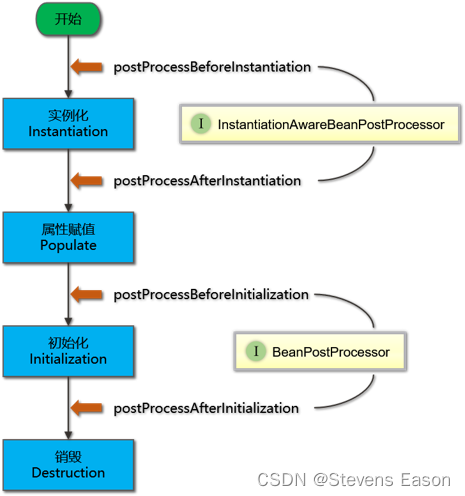
使用方式
public class CarBeanPostProcessor implements BeanPostProcessor {
@Override
public Object postProcessBeforeInitialization(Object bean, String beanName)
throws BeansException {
System.out.println("===> 1.调用postProcessBeforeInitialization()");
return bean;
}
@Override
public Object postProcessAfterInitialization(Object bean, String beanName)
throws BeansException {
System.out.println("===> 1.调用postProcessAfterInitialization()");
return bean;
}
}
public class CarInstantiationBeanPostProcessor implements InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor {
@Override
public Object postProcessBeforeInstantiation(Class<?> beanClass, String beanName)
throws BeansException {
System.out.println("===> 2.调用postProcessBeforeInstantiation()");
return null;
}
@Override
public boolean postProcessAfterInstantiation(Object bean, String beanName)
throws BeansException {
System.out.println("===> 2.调用postProcessAfterInstantiation()");
return false;
}
@Override
public PropertyValues postProcessPropertyValues(PropertyValues pvs, PropertyDescriptor[] pds, Object bean, String beanName)
throws BeansException {
System.out.println("===> 2.调用postProcessPropertyValues()");
return pvs;
}
@Override
public Object postProcessBeforeInitialization(Object bean, String beanName)
throws BeansException {
System.out.println("===> 2.调用postProcessBeforeInitialization()");
return bean;
}
@Override
public Object postProcessAfterInitialization(Object bean, String beanName)
throws BeansException {
System.out.println("===> 2.调用postProcessAfterInitialization()");
return bean;
}
}
Xml配置文件
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<bean id="car" class="xxx.xxx.processor.Car">
<property name="name" value="benz"/>
</bean>
<bean id="testPostProcessor"
class="xxx.xxx.processor.CarBeanPostProcessor"/>
<bean id="testInstantiationBeanPostProcessor"
class="xxx.xxx.processor.CarInstantiationBeanPostProcessor"/>
</beans>
源码解读
public static void registerBeanPostProcessors(
ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory, AbstractApplicationContext applicationContext) {
// 从BeanFactory中获取所有BeanPostProcessor的名字
String[] postProcessorNames = beanFactory.getBeanNamesForType(BeanPostProcessor.class, true, false);
// 注册BeanPostProcessorChecker,以便在BeanPostProcessor实例化期间创建一个Bean时记录一条info消息
int beanProcessorTargetCount = beanFactory.getBeanPostProcessorCount() + 1 + postProcessorNames.length;
beanFactory.addBeanPostProcessor(new BeanPostProcessorChecker(beanFactory, beanProcessorTargetCount));
// 对BeanPostProcessor按照实现的接口PriorityOrdered,Ordered进行分类并存储
// 保存实现PriorityOrdered接口的BeanPostProcessor
List<BeanPostProcessor> priorityOrderedPostProcessors = new ArrayList<BeanPostProcessor>();
List<BeanPostProcessor> internalPostProcessors = new ArrayList<BeanPostProcessor>();
// 保存实现Ordered接口的BeanPostProcessor
List<String> orderedPostProcessorNames = new ArrayList<String>();
// 保存没有实现PriorityOrdered和Ordered接口的BeanPostProcessor
List<String> nonOrderedPostProcessorNames = new ArrayList<String>();
// 遍历postProcessorNames所有的BeanPostProcessor
for (String ppName : postProcessorNames) {
// 如果调用适配函数,发现该类实现了PriorityOrdered接口
if (beanFactory.isTypeMatch(ppName, PriorityOrdered.class)) {
// 从容器中取出BeanPostProcessor
BeanPostProcessor pp = beanFactory.getBean(ppName, BeanPostProcessor.class);
// 保存到List集合中
priorityOrderedPostProcessors.add(pp);
// 如果这个类实现了MergedBeanDefinitionPostProcessor接口
if (pp instanceof MergedBeanDefinitionPostProcessor接口) {
internalPostProcessors.add(pp);
}
}
// 如果调用适配函数,发现该类实现了Ordered接口
else if (beanFactory.isTypeMatch(ppName, Ordered.class)) {
orderedPostProcessorNames.add(ppName);
}
// 既没有实现PriorityOrdered接口也没有实现Ordered接口
else {
nonOrderedPostProcessorNames.add(ppName);
}
}
// 首先,处理实现PriorityOrdered接口的BeanPostProcessor
// 对BeanPostProcessor进行排序
sortPostProcessors(priorityOrderedPostProcessors, beanFactory);
// 注册BeanPostProcessor
registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory, priorityOrderedPostProcessors);
// 其次,处理实现Ordered接口的BeanPostProcessor
List<BeanPostProcessor> orderedPostProcessors = new ArrayList<BeanPostProcessor>();
for (String ppName : orderedPostProcessorNames) {
BeanPostProcessor pp = beanFactory.getBean(ppName, BeanPostProcessor.class);
orderedPostProcessors.add(pp);
if (pp instanceof MergedBeanDefinitionPostProcessor) {
internalPostProcessors.add(pp);
}
}
// 对BeanPostProcessor进行排序
sortPostProcessors(orderedPostProcessors, beanFactory);
// 注册BeanPostProcessor
registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory, orderedPostProcessors);
// 处理其他普通的BeanPostProcessor
List<BeanPostProcessor> nonOrderedPostProcessors = new ArrayList<BeanPostProcessor>();
for (String ppName : nonOrderedPostProcessorNames) {
BeanPostProcessor pp = beanFactory.getBean(ppName, BeanPostProcessor.class);
nonOrderedPostProcessors.add(pp);
if (pp instanceof MergedBeanDefinitionPostProcessor) {
internalPostProcessors.add(pp);
}
}
registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory, nonOrderedPostProcessors);
// 对BeanPostProcessor进行排序.
sortPostProcessors(internalPostProcessors, beanFactory);
// 注册BeanPostProcessor
registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory, internalPostProcessors);
// 重新注册后BeanPostProcessor,用于内部Bean检测为ApplicationListener,//将其移至处理器链的末尾(用于拾取代理等)
// Re-register post-processor for detecting inner beans as ApplicationListeners,
// moving it to the end of the processor chain (for picking up proxies etc).
beanFactory.addBeanPostProcessor(new ApplicationListenerDetector(applicationContext));
}
Bean的类型
Spring中有两种类型的Bean:
普通Bean
工厂Bean(即:FactoryBean)
FactoryBean
普通Bean可以直接使用Xml进行配置,但如果你的Bean拥有复杂的初始化代码(如涉及到很多其他的Bean),使用XML配置方式比较困难,这时就可以使用FactoryBean,并在该类中编写复杂的初始化,然后将自定义FactoryBean插入容器。
FactoryBean接口提供了三种方法:
T getObject() throws Exception; // 返回此工厂创建的对象实例
Class<?> getObjectType(); // 返回的对象类型,如果对象类型未知则返回null
boolean isSingleton(); // 如果FactoryBean返回单例返回true,否则返回false。
这个接口使你可以提供一个复杂的逻辑来生成Bean。它本质是一个Bean,但这个Bean不是用来注入到其它地方像Service、Dao一样使用的,它是用来生成其它Bean使用的。
Spring框架中的许多地方都使用了FactoryBean概念和接口,Spring附带了50多个FactoryBean接口实现。很多开源项目在集成Spring 时也都使用到FactoryBean,比如 MyBatis3 提供 mybatis-spring项目中的 org.mybatis.spring.SqlSessionFactoryBean。
FactoryBean使用示例:
PersonFactoryBean
public class PersonFactoryBean implements FactoryBean<Person> {
private String jsonInfo;
@Override
public Person getObject() throws Exception {
ObjectMapper om = new ObjectMapper();
return om.readValue(jsonInfo, Person.class);
}
@Override
public Class<?> getObjectType() {
return Person.class;
}
@Override
public boolean isSingleton() {
return false;
}
public String getJsonInfo() {
return jsonInfo;
}
public void setJsonInfo(String jsonInfo) {
this.jsonInfo = jsonInfo;
}
}
beans.xml
<bean id="person" class="xxx.xxx.PersonFactoryBean">
<property name="jsonInfo"
value="{ "id": 1,"name": "abc",
"age": 27, "salary": 5555.0,
"address": "beijing"}"/>
</bean>
Bean生命周期
Spring Bean的生命周期只有四个阶段:
- 实例化(Instantiation):调用构造函数
- 属性赋值(Populate):设置依赖注入
- 初始化(Initialization):调用init方法
- 销毁(Destruction):调用destory方法
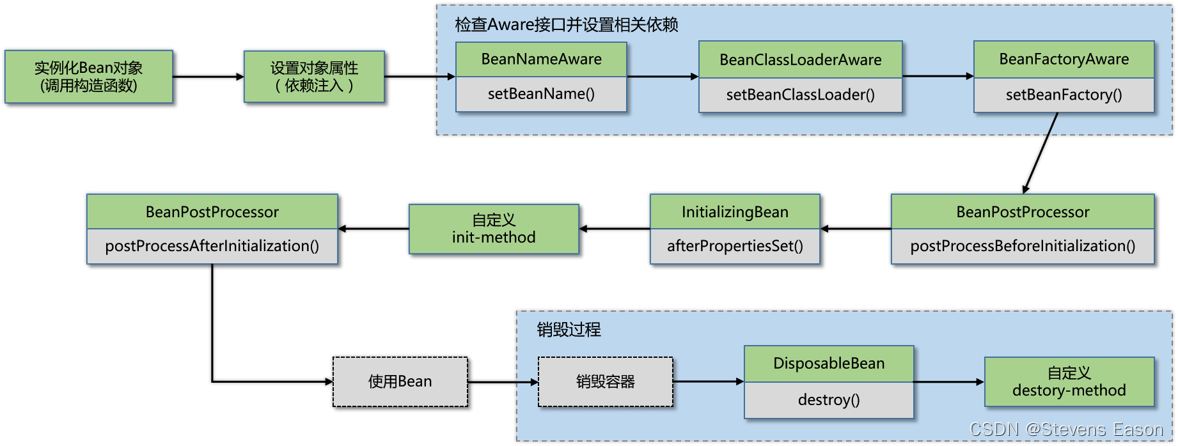
生命周期也可以理解为四个等级。每个等级中都用有相应的接口,实现其中某个接口或者将实现类注入到Spring容器,容器就会在相应的时机调用其方法。
- 工厂级处理器接口
- 容器级生命周期接口
- Bean级生命周期接口
- Bean本身方法
接口
**分类 **
描述
BeanFactoryPostProcessor
工厂后处理器接口
容器创建完毕,装配Bean源后立即调用
InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor
容器后处理器接口
分别在调用构造之前,注入属性之前,实例化完成时调用
BeanPostProcessor
容器后处理器接口
分别在Bean的初始化方法调用前后执行
BeanNameAware
Bean级后置处理器接口
注入属性后调用
BeanFactoryAware
Bean级后置处理器接口
注入属性后调用
InitializingBean
Bean级后置处理器接口
在类本身的初始化方法之前调用其方法(本身也是初始化方法)
DisposableBean
Bean级后置处理器接口
在类本身的销毁方法执行之前调用其方法(本身也是销毁方法)
init方法
Bean本身方法
在注入属性之后调用初始化方法
destroy方法
Bean本身方法
在关闭容器的时候进行销毁
Spring中Bean初始化/销毁的三种方法
- 通过实现 InitializingBean/DisposableBean 接口来定制初始化之后/销毁之前的操作方法;
- 在<bean> 元素上添加 init-method/destroy-method来指定初始化之后 /销毁之前调用的操作方法;
- 在方法上加上@PostConstruct 或@PreDestroy注解来指定该方法是在初始化之后还是销毁之前调用。
public class Person implements InitializingBean {
private int id;
private String name;
private int age;
private BigDecimal salary;
private String address;
public Person() {
System.out.println("Person构造函数");
}
public int getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(int id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
public BigDecimal getSalary() {
return salary;
}
public void setSalary(BigDecimal salary) {
this.salary = salary;
}
public String getAddress() {
return address;
}
public void setAddress(String address) {
this.address = address;
}
@PostConstruct
public void postConstruct(){
System.out.println("调用PostConstruct");
}
public void initMethod(){
System.out.println("调用initMethod");
}
@Override
public void afterPropertiesSet() throws Exception {
System.out.println("调用afterPropertiesSet()");
}
}
Spring Bean的生命周期:
- Spring对Bean进行实例化,调用Bean的构造参数
- 设置对象属性,调用Bean的set方法,将属性注入到bean的属性中
- 检查Bean是否实现BeanNameAware、BeanFactoryAware、ApplicationContextAware接口,如果实现了这几个接口Spring会分别调用其中实现的方法。
- 如果Bean是否实现BeanPostProcessor接口,Spring会在初始化方法的前后分别调用postProcessBeforeInitialization和postProcessAfterInitialization方法
- 如果Bean是否实现InitalizingBean接口,将调用afterPropertiesSet()方法
- 如果Bean声明初始化方法,也会被调用
- 使用Bean。Bean将会一直保留在应用的上下文中,直到该应用上下文被销毁。
- 检查Bean是否实现DisposableBean接口,Spring会调用它们的destory方法
- 如果Bean声明销毁方法,该方法也会被调用
Bean获取
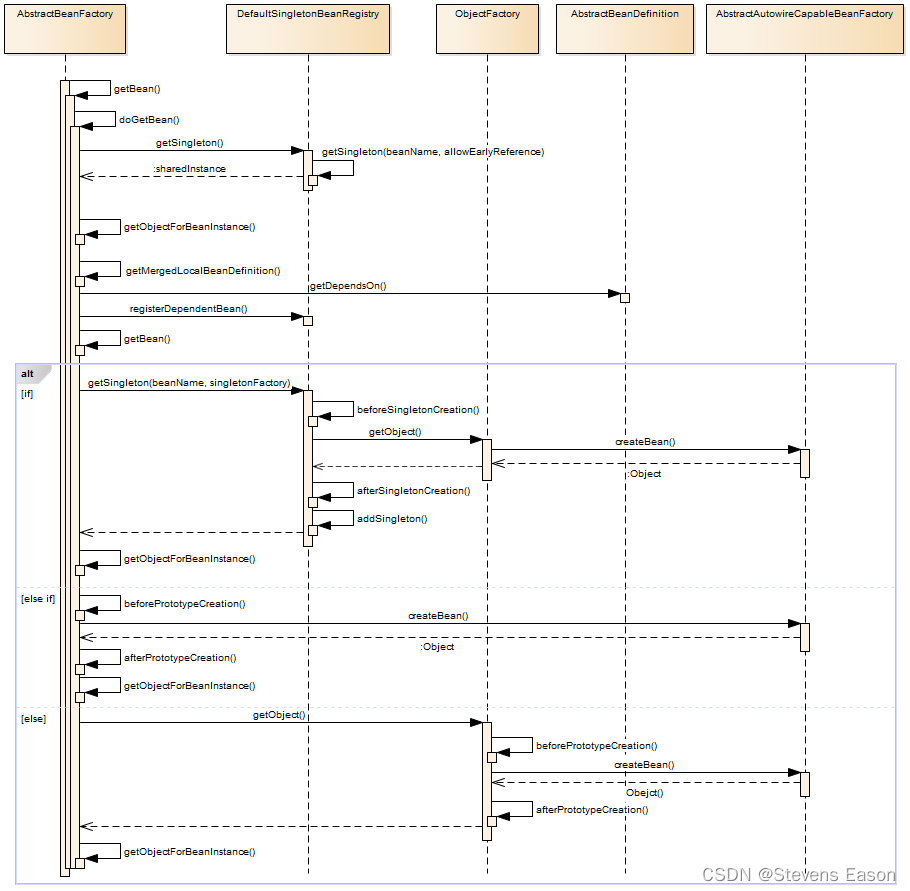
org.springframework.beans.factory.support.AbstractBeanFactory
protected <T> T doGetBean(final String name, final Class<T> requiredType, final Object[] args, boolean typeCheckOnly) throws BeansException {
// 将别名解析为规范Bean名称,如果是FactoryBean还需删除前缀
final String beanName = transformedBeanName(name);
Object bean;
// 检查缓存是否有对象
// 循环依赖解决的关键入口
Object sharedInstance = getSingleton(beanName);
if (sharedInstance != null && args == null) {
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
// 该Bean是否正在创建中
if (isSingletonCurrentlyInCreation(beanName)) {
// logger.debug(.....) 打印日志(略)
}
else {
// logger.debug(.....) 打印日志(略)
}
}
bean = getObjectForBeanInstance(sharedInstance, name, beanName, null);
}
else {
// 如果已经创建了Bean实例则抛出异常,因为可能在循环引用中
if (isPrototypeCurrentlyInCreation(beanName)) {
throw new BeanCurrentlyInCreationException(beanName);
}
// 检查工厂中是否存在Bean定义
BeanFactory parentBeanFactory = getParentBeanFactory();
if (parentBeanFactory != null && !containsBeanDefinition(beanName)) {
// Not found -> check parent.
String nameToLookup = originalBeanName(name);
if (args != null) {
// Delegation to parent with explicit args.
return (T) parentBeanFactory.getBean(nameToLookup, args);
}
else {
// No args -> delegate to standard getBean method.
return parentBeanFactory.getBean(nameToLookup, requiredType);
}
}
if (!typeCheckOnly) {
markBeanAsCreated(beanName);
}
try {
// 合并BeanDefinition。合并主要是因为BeanDefinition可能存在parent BeanDefinition
// 所以要依据合并后的BeanDefinition来实例化和初始化
final RootBeanDefinition mbd = getMergedLocalBeanDefinition(beanName);
// 检查合并后的BeanDefinition。主要是检查是否是abstract
checkMergedBeanDefinition(mbd, beanName, args);
// 获取依赖信息
String[] dependsOn = mbd.getDependsOn();
if (dependsOn != null) {
// 确保当前Bean依赖的Bean初始化
for (String dep : dependsOn) {
if (isDependent(beanName, dep)) {
// throw异常(略)
}
try {
// 注册依赖Bean
registerDependentBean(dep, beanName);
// 获取依赖Bean
getBean(dep);
} catch (NoSuchBeanDefinitionException ex) {
// throw异常(略)
}
}
}
// 创建Bean实例
// 如果是单例对象
if (mbd.isSingleton()) {
// 使用匿名对象工厂来创建Bean
sharedInstance = getSingleton(beanName, new ObjectFactory<Object>() {
@Override
public Object getObject() throws BeansException {
try {
// 创建Bean
return createBean(beanName, mbd, args);
}
catch (BeansException ex) {
// 从单例缓存中显式删除实例。在创建过程可能将它提前引用缓存中,以方便循环引用解析。
// 还要删除所有对该Bean临时引用的Bean
destroySingleton(beanName);
throw ex;
}
}
});
bean = getObjectForBeanInstance(sharedInstance, name, beanName, mbd);
}
// 如果是Prototype对象
else if (mbd.isPrototype()) {
// It's a prototype -> create a new instance.
Object prototypeInstance = null;
try {
// 记录到当前创建的原型对象缓存
beforePrototypeCreation(beanName);
// 创建Bean
prototypeInstance = createBean(beanName, mbd, args);
}
finally {
// 创建完毕,从当前创建的原型对象缓存移除
afterPrototypeCreation(beanName);
}
bean = getObjectForBeanInstance(prototypeInstance, name, beanName, mbd);
}
// 既不是Singleton也不是Prototype,可能是自定义scope的对象
else {
// 获取Scope名称
String scopeName = mbd.getScope();
// 根据名称解析出对应的Scope对象
final Scope scope = this.scopes.get(scopeName);
if (scope == null) {
throw new IllegalStateException("No Scope registered for scope name '" + scopeName + "'");
}
try {
Object scopedInstance = scope.get(beanName, new ObjectFactory<Object>() {
@Override
public Object getObject() throws BeansException {
// 记录到当前创建的原型对象缓存
beforePrototypeCreation(beanName);
try {
// 创建Bean
return createBean(beanName, mbd, args);
}
finally {
// 创建完毕,从当前创建的原型对象缓存移除
afterPrototypeCreation(beanName);
}
}
});
bean = getObjectForBeanInstance(scopedInstance, name, beanName, mbd);
}
catch (IllegalStateException ex) {
// throw异常(略)
}
}
}
catch (BeansException ex) {
cleanupAfterBeanCreationFailure(beanName);
throw ex;
}
}
// 所需的类型与实际Bean实例类型进行匹配转换
if (requiredType != null && bean != null && !requiredType.isInstance(bean)) {
try {
// 转换成需要的类型
return getTypeConverter().convertIfNecessary(bean, requiredType);
}
catch (TypeMismatchException ex) {
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Failed to convert bean '" + name + "' to required type '" +
ClassUtils.getQualifiedName(requiredType) + "'", ex);
}
throw new BeanNotOfRequiredTypeException(name, requiredType, bean.getClass());
}
}
return (T) bean;
}
org.springframework.beans.factory.support.DefaultSingletonBeanRegistry
// 根据Bean注册名称返回单例对象,检查已经实例化的单例,并允许提前曝光当前创建的单例对象(解析循环引用)
protected Object getSingleton(String beanName, boolean allowEarlyReference) {
Object singletonObject = this.singletonObjects.get(beanName);
if (singletonObject == null && isSingletonCurrentlyInCreation(beanName)) {
synchronized (this.singletonObjects) {
singletonObject = this.earlySingletonObjects.get(beanName);
if (singletonObject == null && allowEarlyReference) {
ObjectFactory<?> singletonFactory = this.singletonFactories.get(beanName);
if (singletonFactory != null) {
singletonObject = singletonFactory.getObject();
this.earlySingletonObjects.put(beanName, singletonObject);
this.singletonFactories.remove(beanName);
}
}
}
}
return (singletonObject != NULL_OBJECT ? singletonObject : null);
}
// 根据Bean注册名称返回单例对象。如果尚未注册,则创建并注册一个新的
public Object getSingleton(String beanName, ObjectFactory<?> singletonFactory) {
Assert.notNull(beanName, "'beanName' must not be null");
// 注意synchronized
synchronized (this.singletonObjects) {
// 根据Bean名称从单例缓存中获取实例
Object singletonObject = this.singletonObjects.get(beanName);
if (singletonObject == null) {
if (this.singletonsCurrentlyInDestruction) {
// 抛出异常。原因:工厂单例销毁时不允许创建Bean实例
// throw new BeanCreationNotAllowedException(.......);
}
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Creating shared instance of singleton bean '" + beanName + "'");
}
// 创建前检查,主要检查两项。如果不成功抛出异常
// 1. 正在创建缓存inCreationCheckExclusions中不包含该Bean
// 2. 待创建缓存singletonsCurrentlyInCreation中可以添加该Bean
beforeSingletonCreation(beanName);
boolean newSingleton = false;
boolean recordSuppressedExceptions = (this.suppressedExceptions == null);
if (recordSuppressedExceptions) {
this.suppressedExceptions = new LinkedHashSet<Exception>();
}
try {
// 从工厂中获取单例对象
singletonObject = singletonFactory.getObject();
// 创建成功则为true
newSingleton = true;
}
catch (IllegalStateException ex) {
// 如果出现异常,则从单例缓存中获取
singletonObject = this.singletonObjects.get(beanName);
if (singletonObject == null) {
throw ex;
}
}
catch (BeanCreationException ex) {
if (recordSuppressedExceptions) {
for (Exception suppressedException : this.suppressedExceptions) {
ex.addRelatedCause(suppressedException);
}
}
throw ex;
}
finally {
if (recordSuppressedExceptions) {
this.suppressedExceptions = null;
}
// 创建后检查,仍然是两项检查:
// 1. 正在创建缓存inCreationCheckExclusions中不包含该Bean
// 2. 待创建缓存singletonsCurrentlyInCreation中可以移除该Bean
afterSingletonCreation(beanName);
}
// 创建成功同步几个重要的缓存
if (newSingleton) {
// 同步缓存:
// 1. singletonObjects中添加单例对象
// 2. singletonFactories移除该Bean
// 3. earlySingletonObjects移除该Bean
// 4. registeredSingletons添加该BeanName
addSingleton(beanName, singletonObject);
}
}
return (singletonObject != NULL_OBJECT ? singletonObject : null);
}
}
Bean创建
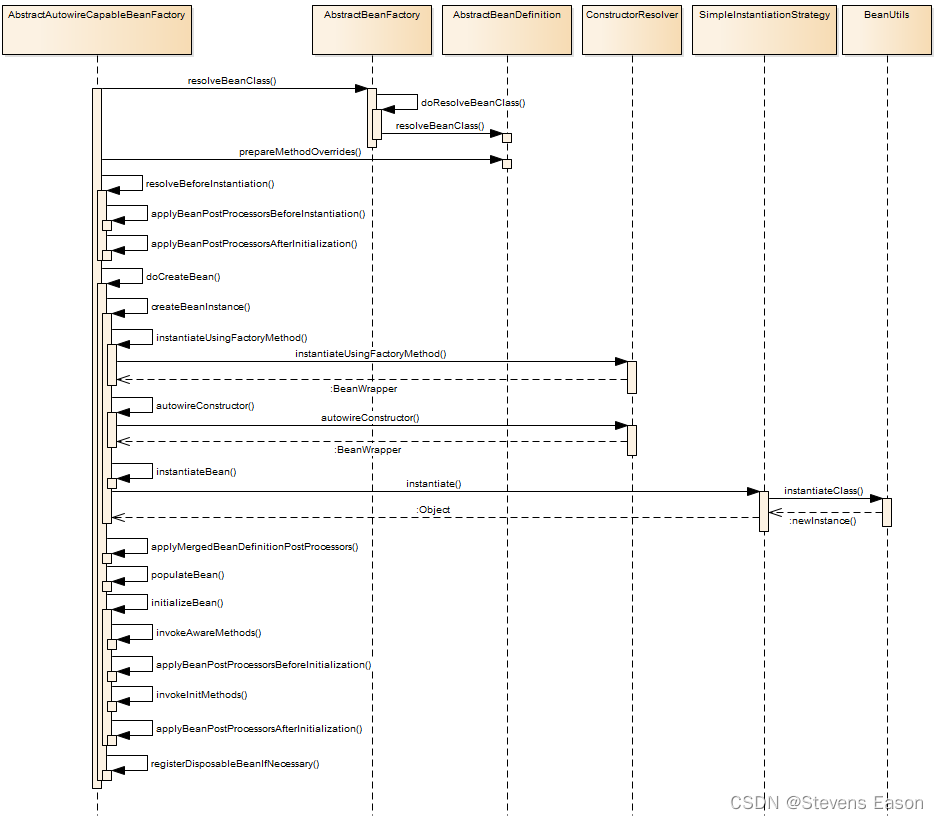
org.springframework.beans.factory.support.AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory
// 创建实例,填充实例,应用后处理器
protected Object createBean(String beanName, RootBeanDefinition mbd, Object[] args) throws BeanCreationException {
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Creating instance of bean '" + beanName + "'");
}
// 合并的BeanDefinition
RootBeanDefinition mbdToUse = mbd;
// 确保解析并加载Bean的Class
Class<?> resolvedClass = resolveBeanClass(mbd, beanName);
// 如果解析的类在合并的BeanDefinition不存在,则克隆Bean定义
if (resolvedClass != null && !mbd.hasBeanClass() && mbd.getBeanClassName() != null) {
mbdToUse = new RootBeanDefinition(mbd);
// 设置Bean的Class
mbdToUse.setBeanClass(resolvedClass);
}
try {
// Spring将lookup-method和replace-method统称为override method,这里主要就是处理这2个函数
mbdToUse.prepareMethodOverrides();
}
catch (BeanDefinitionValidationException ex) {
throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException(mbdToUse.getResourceDescription(),
beanName, "Validation of method overrides failed", ex);
}
try {
// 该函数的作用是给 BeanPostProcessors 后置处理器返回一个代理对象的机会
// 这里是实现AOP处理的重要地方
// AOP是通过BeanPostProcessor机制实现的,而接口InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor是实现代理的重点
Object bean = resolveBeforeInstantiation(beanName, mbdToUse);
if (bean != null) {
return bean;
}
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
throw new BeanCreationException(mbdToUse.getResourceDescription(), beanName,
"BeanPostProcessor before instantiation of bean failed", ex);
}
// 如果后处理器返回的Bean为空,则调用doCreateBean执行创建Bean的过程
Object beanInstance = doCreateBean(beanName, mbdToUse, args);
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Finished creating instance of bean '" + beanName + "'");
}
return beanInstance;
}
// 实际创建指定的Bean
protected Object doCreateBean(final String beanName, final RootBeanDefinition mbd, final Object[] args)
throws BeanCreationException {
// BeanWrapper 是一个用于包装Bean实例的接口,通过这个接口可以设置/获取Bean实例的属性
BeanWrapper instanceWrapper = null;
if (mbd.isSingleton()) {
// 从未完成的实例缓存中获取
instanceWrapper = this.factoryBeanInstanceCache.remove(beanName);
}
// 如果缓存中不存在,则执行创建(三种方式)
if (instanceWrapper == null) {
// 创建 bean 实例,并将实例封装在BeanWrapper中返回。createBeanInstance中包含三种创建方式:
// 1.工厂方法创建Bean实例
// 2.通过构造方法自动注入(autowire by constructor)的方式创建
// 3.通过无参构造方法方法创建
// 如果Bean配置了lookup-method和replace-method,则使用CGLIB增强Bean实例
instanceWrapper = createBeanInstance(beanName, mbd, args);
}
// 获取包装的Bean实例
final Object bean = (instanceWrapper != null ? instanceWrapper.getWrappedInstance() : null);
// 获取包装的Class
Class<?> beanType = (instanceWrapper != null ? instanceWrapper.getWrappedClass() : null);
// 待解析的目标类型
mbd.resolvedTargetType = beanType;
// 允许BeanPostProcessor修改合并的BeanDefinition。这里主要是合并Bean的定义信息
// Autowired等注解就是在这一步完成预解析,并且将注解需要的信息放入缓存
synchronized (mbd.postProcessingLock) {
if (!mbd.postProcessed) {
try {
// 应用MergedBeanDefinitionPostProcessor后处理器
applyMergedBeanDefinitionPostProcessors(mbd, beanType, beanName);
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
throw new BeanCreationException(mbd.getResourceDescription(), beanName,
"Post-processing of merged bean definition failed", ex);
}
mbd.postProcessed = true;
}
}
// earlySingletonExposure 是一个重要的变量,用于表示是否提前暴露单例Bean,用于解决循环依赖。
// earlySingletonExposure 由三个条件组成:是否是单例、是否允许循环引用、当前Bean是否处于创建的状态中
boolean earlySingletonExposure = (mbd.isSingleton() && this.allowCircularReferences &&
isSingletonCurrentlyInCreation(beanName));
if (earlySingletonExposure) {
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Eagerly caching bean '" + beanName +
"' to allow for resolving potential circular references");
}
// 避免循环依赖,在Bean初始化完成前添加ObjectFactory到singletonFactories缓存。
addSingletonFactory(beanName, new ObjectFactory<Object>() {
@Override
public Object getObject() throws BeansException {
// 此回调使后处理器有机会提前曝光Bean(即在目标Bean完全初始化之前)。通常是为了解决循环依赖
return getEarlyBeanReference(beanName, mbd, bean);
}
});
}
// 下面是初始化Bean的流程
Object exposedObject = bean;
try {
// 使用BeanDefinintion的属性值填充Bean实例
populateBean(beanName, mbd, instanceWrapper);
if (exposedObject != null) {
// 初始化Bean
// 如果Bean实现了BeanNameAware、BeanClassLoaderAware、BeanFactoryAware接口则设置
// 应用BeanPostProcessor后处理器
// 执行自定义init-method方法
exposedObject = initializeBean(beanName, exposedObject, mbd);
}
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
if (ex instanceof BeanCreationException && beanName.equals(((BeanCreationException) ex).getBeanName())) {
throw (BeanCreationException) ex;
}
else {
throw new BeanCreationException(
mbd.getResourceDescription(), beanName, "Initialization of bean failed", ex);
}
}
if (earlySingletonExposure) {
// 从提前曝光的Bean缓存中查询,目的是验证是否存在循环依赖
// 如果存在循环依赖,在这里earlySingletonReference不为空
Object earlySingletonReference = getSingleton(beanName, false);
// 在检测到循环依赖的情况下,earlySingletonReference不会为null
if (earlySingletonReference != null) {
// 如果exposedObject没有在initializeBean初始化方法中被改变,说明没有被增强
// 初始化之后的Bean等于原始的bean说明不是proxy对象
if (exposedObject == bean) {
exposedObject = earlySingletonReference;
}
else if (!this.allowRawInjectionDespiteWrapping && hasDependentBean(beanName)) {
// 确定是否已经给指定的beanName称注册了依赖
String[] dependentBeans = getDependentBeans(beanName);
Set<String> actualDependentBeans = new LinkedHashSet<String>(dependentBeans.length);
for (String dependentBean : dependentBeans) {
if (!removeSingletonIfCreatedForTypeCheckOnly(dependentBean)) {
actualDependentBeans.add(dependentBean);
}
}
// Bean创建后其依赖的Bean一定也是已经创建的
// 如果actualDependentBeans不为空,则表示依赖的Bean并没有被创建完,即存在循环依赖
if (!actualDependentBeans.isEmpty()) {
// 抛出异常
// throw new BeanCurrentlyInCreationException(....)
}
}
} }
// Register bean as disposable.
// 如果Bean实现了Disposable,则注册该Bean为
try {
registerDisposableBeanIfNecessary(beanName, bean, mbd);
}
catch (BeanDefinitionValidationException ex) {
throw new BeanCreationException(
mbd.getResourceDescription(), beanName, "Invalid destruction signature", ex);
}
return exposedObject;
}
// 创建Bean实例
protected BeanWrapper createBeanInstance(String beanName, RootBeanDefinition mbd, Object[] args) {
// Make sure bean class is actually resolved at this point.
Class<?> beanClass = resolveBeanClass(mbd, beanName);
if (beanClass != null && !Modifier.isPublic(beanClass.getModifiers()) && !mbd.isNonPublicAccessAllowed()) {
// 抛出异常
// throw new BeanCreationException(.....);
}
// 如果工厂方法不为空
if (mbd.getFactoryMethodName() != null) {
// 使用工厂方法创建实例
return instantiateUsingFactoryMethod(beanName, mbd, args);
}
// Shortcut when re-creating the same bean...
boolean resolved = false;
boolean autowireNecessary = false;
if (args == null) {
synchronized (mbd.constructorArgumentLock) {
if (mbd.resolvedConstructorOrFactoryMethod != null) {
resolved = true;
autowireNecessary = mbd.constructorArgumentsResolved;
}
}
}
if (resolved) {
if (autowireNecessary) {
return autowireConstructor(beanName, mbd, null, null);
}
else {
return instantiateBean(beanName, mbd);
}
}
// Candidate constructors for autowiring?
Constructor<?>[] ctors = determineConstructorsFromBeanPostProcessors(beanClass, beanName);
if (ctors != null || mbd.getResolvedAutowireMode() == AUTOWIRE_CONSTRUCTOR ||
mbd.hasConstructorArgumentValues() || !ObjectUtils.isEmpty(args)) {
return autowireConstructor(beanName, mbd, ctors, args);
}
// 调用实例化策略接口来实例化Bean,这里使用无参构造
return instantiateBean(beanName, mbd);
}
// 实例化Bean
protected BeanWrapper instantiateBean(final String beanName, final RootBeanDefinition mbd) {
try {
Object beanInstance;
final BeanFactory parent = this;
if (System.getSecurityManager() != null) {
beanInstance = AccessController.doPrivileged(new PrivilegedAction<Object>() {
@Override
public Object run() {
return getInstantiationStrategy().instantiate(mbd, beanName, parent);
}
}, getAccessControlContext());
}
else {
// InstantiationStrategy负责进行实例化
// SimpleInstantiationStrategy是一个简单的用于Bean实例化的类。如:由Bean类的默认构造函数、带参构造函数或者工厂方法等来实例化Bean。不支持方法注入。
// CglibSubclassingInstantiationStrategy如果方法需要被覆盖来实现“方法注入”,使用CGLIB动态生成子类
beanInstance = getInstantiationStrategy().instantiate(mbd, beanName, parent);
}
// 实例化后的Bean使用BeanWrapper包装。BeanWrapper可以设置以及访问被包装对象的属性值
BeanWrapper bw = new BeanWrapperImpl(beanInstance);
// 初始化BeanWrapper包装包含了2个工作:设置ConversionService和CustomerEditor
initBeanWrapper(bw);
return bw;
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
throw new BeanCreationException(
mbd.getResourceDescription(), beanName, "Instantiation of bean failed", ex);
}
}
// 初始化Bean
protected Object initializeBean(final String beanName, final Object bean, RootBeanDefinition mbd) {
if (System.getSecurityManager() != null) {
AccessController.doPrivileged(new PrivilegedAction<Object>() {
@Override
public Object run() {
invokeAwareMethods(beanName, bean);
return null;
}
}, getAccessControlContext());
}
else {
// 设置Aware
invokeAwareMethods(beanName, bean);
}
Object wrappedBean = bean;
if (mbd == null || !mbd.isSynthetic()) {
// 调用初始化前处理器
wrappedBean = applyBeanPostProcessorsBeforeInitialization(wrappedBean, beanName);
}
try {
// 执行自定义初始化方法
invokeInitMethods(beanName, wrappedBean, mbd);
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
throw new BeanCreationException(
(mbd != null ? mbd.getResourceDescription() : null),
beanName, "Invocation of init method failed", ex);
}
if (mbd == null || !mbd.isSynthetic()) {
// 调用初始化后处理器
wrappedBean = applyBeanPostProcessorsAfterInitialization(wrappedBean, beanName);
}
return wrappedBean;
}
解决循环引用
// 注册名称返回单例对象,检查已经实例化的单例,并允许提前引用当前创建的单例对象(解析循环引用)
protected Object getSingleton(String beanName, boolean allowEarlyReference) {
// 从单例缓存中根据Bean名字获取单例对象
Object singletonObject = this.singletonObjects.get(beanName);
// 如果单例对象为空,并且单例对象正在创建中
if (singletonObject == null && isSingletonCurrentlyInCreation(beanName)) {
// 注意synchronized关键字
synchronized (this.singletonObjects) {
// 从earlySingletonObjects缓存中通过Bean名称获取对象
singletonObject = this.earlySingletonObjects.get(beanName);
// 如果单例对象仍然为空,并且允许提前引用为true
// allowEarlyReference参数含义:是否允许提前曝光
if (singletonObject == null && allowEarlyReference) {
// 从singletonFactories中根据Bean名称获取对应的单例工厂
ObjectFactory<?> singletonFactory = this.singletonFactories.get(beanName);
if (singletonFactory != null) {
// 通过工厂创建单例对象(此时还未进行依赖注入)
singletonObject = singletonFactory.getObject();
// 把创建的单例对象放到提前引用的缓存
this.earlySingletonObjects.put(beanName, singletonObject);
// 移除该单例对象的工厂
this.singletonFactories.remove(beanName);
}
}
}
}
}
代码中出现的缓存:
- singletonObjects:初始化完成的单例对象缓存;
- earlySingletonObjects:提前曝光的单例对象缓存;
- singletonFactories:单例Bean的工厂函数对象缓存;
- singletonsCurrentlyInCreation:即将创建的单例集合
第七步 初始化消息源
Spring中定义一个MessageSource接口,以用于支持信息的国际化和包含参数的信息的替换。ApplicationContext接口扩展了MessageSource接口,因而提供了消息处理的功能(i18n或者国际化)。与HierarchicalMessageSource一起使用,还能够处理嵌套的消息,这些是Spring提供的处理消息的基本接口。
public interface MessageSource {
// 用来从MessageSource获取消息的基本方法。如果在指定的locale中没有找到消息,则使用默认的消息
// args中的参数将使用标准类库中的MessageFormat来替换消息中的值
String getMessage(String code, Object[] args, String default, Locale loc):
// 与上一个方法相同,不同之处在于:没有指定默认值。如果没找到消息,会抛出一个NoSuchMessageException异常。
String getMessage(String code, Object[] args, Locale loc) throws NoSuchMessageException;
// 与上面的方法不同之处在于:将code、args等属性封装到MessageSourceResolvable中
String getMessage(MessageSourceResolvable resolvable, Locale locale) throws NoSuchMessageException;
}
MessageSource类图
Spring提供了两个MessageSource实现:ResourceBundleMessageSource和StaticMessageSource。它们都继承HierarchicalMessageSource能够处理嵌套的消息。

ResourceBundleMessageSource会用得更多一些。StaticMessageSource很少被使用,但能以编程的方式向源添加消息。
类或接口
描述
HierarchicalMessageSource
MessageSource子接口,提供解析层级消息的能力。该接口的目的是设置父MessageSource用于当前对象无法解析消息时,由父MessageSource尝试解析。
DelegatingMessageSource
空的MessageSource,它将所有处理转发给父MessageSource。如果没有父MessageSource,它不会处理任何消息。用户未指定MessageSource时,Spring默认使用该类。该类的功能比较简单:将字符串和参数数组格式化为一个消息字符串
AbstractMessageSource
支持“配置文件”方式的抽象类,内部提供一个与区域设置无关的公共消息配置文件,消息代码为关键字
AbstractResourceBasedMessageSource
基于资源并实现了MessageSource接口的抽象类,同时提供了一些参数配置的方法
ResourceBundleMessageSource
该类通过beanName指定一个资源名(包括类路径的全限定资源名),或通过beanNames指定一组资源名。不同的区域获取加载资源文件,达到国际化信息的目的。该类依赖JDK的ResourceBundle,并结合了JDK MessageFormat提供的标准消息解析。被访问的ResourceBundle和为每个消息生成的MessageFormat都会被缓存。
ReloadableResourceBundleMessageSource
同ResourceBundleMessageSource。该类参与Spring ApplicationContex的资源加载。它使用java.util.Properties作为其消息的自定义数据结构,通过PropertiesPersister策略从Spring Resource中加载它们。该策略不仅能够根据时间戳的更改重新加载文件,而且还能够使用特定的字符编码加载属性文件。
StaticMessageSource
MessageSource的简单实现,允许以编程方式注册消息,提供基本的国际化支持(通常用于测试)
使用示例
Xml配置文件
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<bean id="messageSource"
class="org.springframework.context.support.ResourceBundleMessageSource">
<property name="basenames">
<list>
<value>locale.messages</value>
<value>locale.exceptions</value>
</list>
</property>
</bean>
</beans>
messageSource配置
# exceptions_en_US.properties文件
exceptions.illegal = The user {0} attempted to login, time: {1}
# exceptions_zh_CN.properties文件
exceptions.illegal = \u975e\u6cd5\u7528\u6237{0}\u5c1d\u8bd5\u767b\u5f55, \u65f6\u95f4\uff1a{1}
# message_en_US.properties文件
id.ilegal = userid {0} is illegal! time: {1}
password.empty = username{0}'s password is empty!
# message_zh_CN.properties文件
id.ilegal = \u7528\u6237\u7f16\u53f7{0}\u975e\u6cd5\u767b\u5f55\uff01{1}
password.empty = \u7528\u6237\u540d{0}\u7684\u5bc6\u7801\u4e0d\u80fd\u4e3a\u7a7a\uff01
注意:中文messageSource文件需要把中文转为Ascii
源码解读
getMessage()时序图
该段源码主要目的
当一个ApplicationContext被加载时,它会自动在context中查找已定义为MessageSource类型的Bean。此Bean的名称须为messageSource。
如果找到,那么所有对上述方法的调用将被委托给该Bean。否则ApplicationContext会在其父类中查找是否含有同名的Bean。如果有,就把它作为MessageSource。如果最终没有找到任何的消息源,实例化一个空的DelegatingMessageSource,使它能够接受上述方法的调用。
protected void initMessageSource() {
// 获取BeanFactory
ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = getBeanFactory();
// beanFactory中是否包含名字为messageSource的Bean
if (beanFactory.containsLocalBean(MESSAGE_SOURCE_BEAN_NAME)) {
// 创建MessageSource类型的Bean
this.messageSource = beanFactory.getBean(MESSAGE_SOURCE_BEAN_NAME, MessageSource.class);
// 判断messageSource是否有parent MessageSource
if (this.parent != null && this.messageSource instanceof HierarchicalMessageSource) {
// 设置MessageSource的parent MessageSource.
HierarchicalMessageSource hms = (HierarchicalMessageSource) this.messageSource;
if (hms.getParentMessageSource() == null) {
// 如果未注册任何父MessageSource,则仅将父上下文的MessageSource设置为父MessageSource
hms.setParentMessageSource(getInternalParentMessageSource());
}
}
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Using MessageSource [" + this.messageSource + "]");
}
}
// beanFactory中不包含名字为messageSource的Bean
else {
// 新建DelegatingMessageSource对象
DelegatingMessageSource dms = new DelegatingMessageSource();
// 设置DelegatingMessageSource的parent MessageSource
dms.setParentMessageSource(getInternalParentMessageSource());
this.messageSource = dms;
// 向BeanFactory中注册MessageSource
beanFactory.registerSingleton(MESSAGE_SOURCE_BEAN_NAME, this.messageSource);
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Unable to locate MessageSource with name '" + MESSAGE_SOURCE_BEAN_NAME +
"': using default [" + this.messageSource + "]");
}
}
}
第八步 初始化事件广播
protected void initApplicationEventMulticaster() {
ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = getBeanFactory();
// 检查配置中是否有applicationEventMulticaster的Bean定义
if (beanFactory.containsLocalBean(APPLICATION_EVENT_MULTICASTER_BEAN_NAME)) {
// 如果有则获取(实例化Bean)
this.applicationEventMulticaster =
beanFactory.getBean(APPLICATION_EVENT_MULTICASTER_BEAN_NAME, ApplicationEventMulticaster.class);
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Using ApplicationEventMulticaster [" + this.applicationEventMulticaster + "]");
}
}
else {
// 如果没有手动创建SimpleApplicationEventMulticaster的实例
this.applicationEventMulticaster = new SimpleApplicationEventMulticaster(beanFactory);
// 把创建的SimpleApplicationEventMulticaster注册到BeanFactory
beanFactory.registerSingleton(APPLICATION_EVENT_MULTICASTER_BEAN_NAME, this.applicationEventMulticaster);
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Unable to locate ApplicationEventMulticaster with name '" +
APPLICATION_EVENT_MULTICASTER_BEAN_NAME +
"': using default [" + this.applicationEventMulticaster + "]");
}
}
}
ApplicationContext中的事件处理是通过ApplicationEvent抽象类和ApplicationListener接口实现的。将实现ApplicationListener接口的Bean部署到上下文中,那么每次将ApplicationEvent发布到ApplicationContext时,该Bean都会得到通知。本质上,这是标准的观察者设计模式。
观察者模式
- Subject:抽象主题类。保存对所有观察者对象的引用,每个主题都可以有任意数量的观察者。该接口可以添加和删除观察者对象
- ConcreteSubject:具体主题。将状态保存到具体观察者对。在主题内部发生改变时,给所有登记的观察者发出通知。
- Observer:抽象观察者。为所有具体的观察者定义接口,在得到主题通知时更新自己。
- ConcreteObserver:具体观察者。实现更新接口,以使自身状态和主题状态同步。
具体实现
抽象被观察者接口
public interface Subject {
// 添加观察者
public void addObserver(Observer o);
// 删除观察者
public void removeObserver(Observer o);
// 通知观察者
public void notifyObserver();
}
抽象观察者接口
public interface Observer {
// 当被观察者调用notify()方法时,观察者的update()方法会被回调
public void update(String message);
}
定义被观察者,实现了Observerable接口,对Observerable接口的三个方法进行了具体实现,同时有一个List集合,用以保存注册的观察者,等需要通知观察者时,遍历该集合即可。
/**
* 被观察者
* 实现了Subject接口,对Subject接口的三个方法进行了具体实现
*/
public class ConcreteSubject implements Subject {
// 保存观察者的集合
private List<Observer> list;
private String message;
public ConcreteSubject() {
list = new ArrayList<Observer>();
}
@Override
public void addObserver(Observer o) {
list.add(o);
}
@Override
public void removeObserver(Observer o) {
if(!list.isEmpty())
list.remove(o);
}
//遍历
@Override
public void notifyObserver() {
for(int i = 0; i < list.size(); i++) {
Observer oserver = list.get(i);
oserver.update(message);
}
}
public void setMessage(String s) {
this.message = s;
System.out.println("服务消息: " + s);
//消息更新,通知所有观察者
notifyObserver();
}
}
具体观察者
public class User implements Observer {
private String name;
private String message;
public User(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
@Override
// 实现update方法
public void update(String message) {
this.message = message;
read();
}
public void read() {
System.out.println(name + " 收到推送消息: " + message);
}
}
测试类
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ConcreteSubject cs = new ConcreteSubject();
Observer user1 = new User("Zhangsan");
Observer user2 = new User("Lisi");
Observer user3 = new User("Wangwu");
cs.addObserver(user1);
cs.addObserver(user2);
cs.addObserver(user3);
cs.setMessage("发布了消息1");
System.out.println("----------------------------------------------");
cs.removeObserver(userZhang);
cs.setMessage("发布了消息2");
}
}
事件驱动机制
事件驱动的常见形式便是发布-订阅模式。
在跨进程的通信间,我们通常采用引入 MQ (消息队列) 来实现消息的发布和订阅。目前主流应用的架构中,均采用消息的发布-订阅模式来进行大型分布式系统的解耦。使得数据生产方和使用方分离,同时 MQ 还可起到削峰等作用。
同一进程内很多时候也需要这种事件驱动机制来进行逻辑解耦。
事件机制主要由三个部分组成:
事件对象:事件实体。封装事件源对象和事件,在事件源和监听器之间传递信息
监听器:监听事件对象。事件发生时处理回调
事件源:事件发生的起源。注册监听,对事件进行响应。
Java的事件机制
Java 提供了事件相关的接口定义:
事件对象:EventObject 自定义事件对象需要继承该类
监听器:EventListener 事件监听器接口
事件源:不需要实现任何接口,Java 中也没给出相应的定义
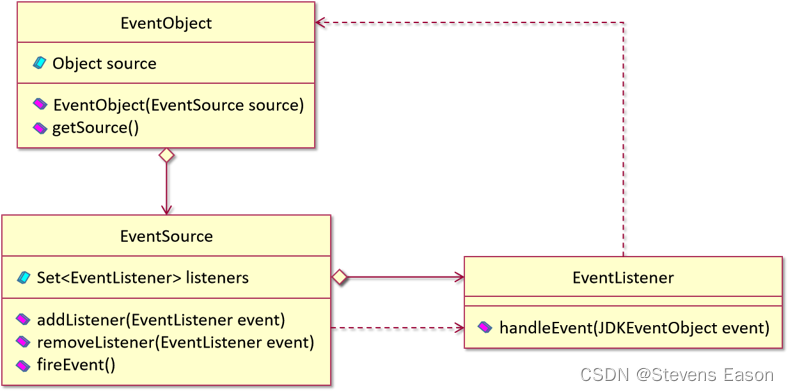
示例
事件对象
public class JDKEventObject extends EventObject {
private Object source;
/**
* Constructs a prototypical Event.
*
* @param source The object on which the Event initially occurred.
* @throws IllegalArgumentException if source is null.
*/
public JDKEventObject(JDKEventSource source) {
super(source);
this.source = source;
}
@Override
public Object getSource() {
return source;
}
}
监听器
public interface JDKEventListener extends EventListener {
public void handleEvent(JDKEventObject event);
}
事件源
public class JDKEventSource {
private Set<EventListener> listeners = new HashSet();
private String message;
public void addListener(EventListener event) {
listeners.add(event);
}
public void removeListener(EventListener event) {
if (listeners.contains(event))
listeners.remove(event);
}
public void fireEvent() {
Iterator<EventListener> iter = listeners.iterator();
while (iter.hasNext()) {
JDKEventListener listener = (JDKEventListener) iter.next();
listener.handleEvent(new JDKEventObject(this));
}
}
}
测试类
public class JDKEventTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
JDKEventSource eventSource = new JDKEventSource();
eventSource.addListener(new JDKEventListener() {
@Override
public void handleEvent(JDKEventObject event) {
System.out.println("事件1......");
}
});
eventSource.addListener(new JDKEventListener() {
@Override
public void handleEvent(JDKEventObject event) {
System.out.println("事件2......");
}
});
eventSource.fireEvent();
}
}
事件处理机制在某种程度上与发布-订阅模式非常相似,事件监听器的角色与观察者类似,事件源则充当了被观察对象。事件源状态触发后,主动发起通知给监听器,监听器完成各种后续处理。
Spring事件机制
Spring内置事件:
事件类
说明
ContextRefreshedEvent
ApplicationContext初始化或刷新时触发该事件。通常在Spring加载或刷新应用上下文时,同事也想刷新预加载的资源,就可以通过监听ContextRefreshedEvent来做这样的事情。这里的“初始化”是指所有Bean均已加载,检测到并激活了BeanPostProcessors,已预先实例化单例并且可以使用ApplicationContext对象。只要上下文尚未关闭,选用的ApplicationContext支持这种“热”刷新(如:XmlWebApplicationContext支持热刷新,但GenericApplicationContext不支持),刷新可以被多次触发。
ContextStartedEvent
ApplicationContext启动时触发该事件。"Started" 意味着所有Lifecycle Bean会获得启动事件。 通常,此事件用于在显式停止后重新启动Bean时,也可以用于启动尚未配置为自动启动的组件。
ContextStoppedEvent
ApplicationContext被停止时触发该事件。"Stopped"是指所有Lifecycle Bean都收到一个明确的停止事件。已停止的上下文可以通过start()调用重新启动
ContextClosedEvent
ApplicationContext被关闭时触发该事件。 "Closed" 意味着容器管理的所有单例Bean都被销毁。关闭的上下文表示容器生命周期结束,它不能刷新或重新启动。
RequestHandledEvent
基于Web应用的事件,当一个HTTP请求完成后,触发该事件。该事件仅适用于使用DispatcherServlet的Web应用程序。
容器生命周期
BeanPostProcessor及Bean的初始和销毁回调这些事件都是建立在容器已经成功启动的基础上,如果我们想在容器本身的生命周期。
// 生命周期接口,任何Spring管理的对象都可以实现该接口
public interface Lifecycle {
void start();
void stop();
boolean isRunning();
}
// 管理ApplicationContext生命周期
public interface LifecycleProcessor extends Lifecycle {
void onRefresh();
void onClose();
}
public interface SmartLifecycle extends Lifecycle, Phased {
// Lifecycle Bean是否自动启动
boolean isAutoStartup();
// 停止的时候执行回调,默认超时时间30秒
void stop(Runnable callback);
}
// Phased最小的对象首先启动,停止时,顺序和启动时相反
public interface Phased {
// SmartLifecycle的实现类默认Phase为0
int getPhase();
}
常规的Lifecycle接口只在容器上下文显式的调用start()/stop()方法时,才会去回调Lifecycle实现类的start/stop方法逻辑。并不意味着在上下文刷新时自动启动。
另外,LifeCycle Bean在销毁之前不能保证会收到停止通知。正常关闭时,所有Lifecycle Bean在销毁回调之前首先会收到停止通知,但是在上下文的生命周期内进行热刷新或中止刷新尝试时,只会调用destroy方法。
// 实现Lifecycle的测试类
public class TestLifeCycle implements Lifecycle {
private boolean running = false;
public TestLifeCycle() {
System.out.println("TestLifeCycle.......");
}
@Override
public void start() {
System.out.println("TestLifeCycle.start().......");
running = true;
}
@Override
public void stop() {
System.out.println("TestLifeCycle.start().......");
running = false;
}
@Override
public boolean isRunning() {
return running;
}
}
// 实现SmartLifecycle的测试类
public class TestSmartLifecycle implements SmartLifecycle {
private boolean running = false;
public TestSmartLifecycle() {
System.out.println("TestSmartLifecycle.......");
}
@Override
public boolean isAutoStartup() {
return true;
}
@Override
public int getPhase() {
return 10000;
}
@Override
public void start() {
System.out.println("TestSmartLifecycle.start().......");
running = true;
}
@Override
public void stop() {
System.out.println("TestSmartLifecycle.stop().......");
running = false;
}
@Override
public void stop(Runnable callback) {
System.out.println("TestSmartLifecycle.stop(Runnable callback).......");
running = false;
}
@Override
public boolean isRunning() {
return running;
}
}
事件机制
Spring事件机制中除了事件对象和监听者者两个角色之外,“事件广播器”则负责把事件转发给监听者:
类名
描述
ApplicationEvent
Spring提供的事件类,继承自 EventObject 类
ApplicationListener
事件监听者,该类接收一个泛型,供 ApplicationEventPublisher 在发布事件时选择 EventListener
ApplicationEventPublisher
封装事件发布功能的接口,通知所有在 Spring 中注册的该事件的监听者进行处理
ApplicationEventPublisherAware
Spring 提供的 Aware 接口之一,实现该接口的 Bean 可以获取 ApplicationEventPublisher 并进行发布事件
ApplicationEventMulticaster
管理多个ApplicationListener对象并向其发布事件的接口
示例
Spring 中,不需要我们手动进行监听器注册。ApplicationListener 对象一旦在 Spring 容器中被注册,Spring 会进行监听器的注册,实现事件的监听。
服务类
// Spring容器检测到Service实现了ApplicationEventPublisherAware接口,会自动调用setApplicationEventPublisher
public class SpringService implements ApplicationEventPublisherAware {
private List<String> nameList;
private ApplicationEventPublisher publisher;
@Override
public void setApplicationEventPublisher(ApplicationEventPublisher publisher) {
this.publisher = publisher;
}
public void setNameList(List<String> list) {
this.nameList = list;
}
// 要发布自定义ApplicationEvent,需要在ApplicationEventPublisher上调用publishEvent方法
public void sendMessage(String name) {
if (nameList.contains(name)) {
publisher.publishEvent(new SpringEvent(this, name));
return;
}
}
}
监听器
// 要接收自定义的ApplicationEvent,需要实现ApplicationListener监听器
public class SpringListener implements ApplicationListener<SpringEvent> {
String notifier;
public void setNotifier(String notifier) {
this.notifier = notifier;
}
@Override
public void onApplicationEvent(SpringEvent event) {
System.out.println("onApplicationEvent: "+ notifier);
}
}
事件类
public class SpringEvent extends ApplicationEvent {
String name;
/**
* Create a new ApplicationEvent.
*
* @param source the object on which the event initially occurred (never {@code null})
*/
public SpringEvent(Object source, String name) {
super(source);
this.name = name;
}
}
第九步 初始化主题
protected void onRefresh() throws BeansException {
// For subclasses: do nothing by default.
}
SpringMVC框架主题可以设置应用程序的整体外观,从而增强用户体验。主题是静态资源的集合,通常有css样式表和图片构成,这些css样式和图片会直接影响应用程序的视觉样式。
要在Web应用中使用主题,必须实现ThemeSource接口,WebApplicationContext接口就扩展了ThemeSource,但将其职责委托给专用的实现。
默认委托将是ResourceBundleThemeSource,该实现从类路径的根加载主题属性文件。要使用自定义ThemeSource或需要配置ResourceBundleThemeSource的属性,可以在应用程序上下文中注册使用保留名称'themeSource'的Bean,Web应用程序上下文会自动检测到具有'themeSource'名称的Bean并使用它。
主题使用示例
SpringMVC配置文件
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xmlns:mvc="http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc" xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc/spring-mvc.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop.xsd">
<mvc:default-servlet-handler />
<mvc:annotation-driven />
<context:component-scan base-package="xxx.xxx" />
<!-- 视图解析 -->
<bean class="org.springframework.web.servlet.view.InternalResourceViewResolver">
<property name="prefix" value="/" />
<property name="suffix" value=".jsp" />
</bean>
<!-- Theme主题资源 -->
<bean id="themeSource" class="org.springframework.ui.context.support.ResourceBundleThemeSource">
<property name="basenamePrefix" value="theme." />
</bean>
<!-- Theme主题解析器 -->
<bean id="themeResolver" class="org.springframework.web.servlet.theme.CookieThemeResolver">
<property name="defaultThemeName" value="blue" />
</bean>
<!-- Theme主题拦截器 -->
<mvc:interceptors>
<bean id="themeInterceptor" class="org.springframework.web.servlet.theme.ThemeChangeInterceptor">
<property name="paramName" value="theme" />
</bean>
</mvc:interceptors>
</beans>
主题资源文件
blue.properties和gray.properties两个属性配置文件存放到resources资源目录下面。
blue.properties
------------------------------
blue.properties
------------------------------
# css对应位置
styleSheet=/css/blue.css
# 图片对应位置
background=images/blue.png
gray.properties
------------------------------
gray.properties
------------------------------
# css对应位置
styleSheet=/css/gray.css
# 图片对应位置
background=images/gray.png
前端页面
JSP代码中引用主题文件的键。在JSP中,通常使用spring:theme标签来执行此操作,该标签与spring:message标签的使用方法非常相似。
<%@page contentType="text/html" pageEncoding="UTF-8"%>
<%@ taglib prefix="spring" uri="http://www.springframework.org/tags"%>
<html>
<head>
<link rel="stylesheet" href="<spring:theme code='styleSheet'/>" type="text/css"/>
<title>Title</title>
</head>
<body style="background: url(<spring:theme code='background'/>)">
<a href="?theme=blue">blue</a> - <a href="?theme=gray">gray</a>
</body>
</html>
源码解析
public static ThemeSource initThemeSource(ApplicationContext context) {
// 判断容器中是否包含"themeSource"的Bean
if (context.containsLocalBean(THEME_SOURCE_BEAN_NAME)) {
// 如果包含则实例化这个themSource
ThemeSource themeSource = context.getBean(THEME_SOURCE_BEAN_NAME, ThemeSource.class);
// 设置themeSource的父themeSource
if (context.getParent() instanceof ThemeSource && themeSource instanceof HierarchicalThemeSource) {
// 用来表示层级关系的ThemeSource对象
HierarchicalThemeSource hts = (HierarchicalThemeSource) themeSource;
if (hts.getParentThemeSource() == null) {
hts.setParentThemeSource((ThemeSource) context.getParent());
}
}
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Using ThemeSource [" + themeSource + "]");
}
return themeSource;
}
else {
// 如果context中不包含"themeSource"的定义
HierarchicalThemeSource themeSource = null;
// 如果context的parent是ThemeSource实例,则设置该contexnt的父ThemeSource
if (context.getParent() instanceof ThemeSource) {
// 实例化一个DelegatingThemeSource
themeSource = new DelegatingThemeSource();
themeSource.setParentThemeSource((ThemeSource) context.getParent());
}
else {
// 否则,实例化一个ResourceBundleThemeSource
themeSource = new ResourceBundleThemeSource();
}
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Unable to locate ThemeSource with name '" + THEME_SOURCE_BEAN_NAME +
"': using default [" + themeSource + "]");
}
return themeSource;
}
}
第十步 注册事件监听
protected void registerListeners() {
// 注册静态指定的监听器
for (ApplicationListener<?> listener : getApplicationListeners()) {
getApplicationEventMulticaster().addApplicationListener(listener);
}
// 从BeanFactory中获取listener的名称,并注册
String[] listenerBeanNames = getBeanNamesForType(ApplicationListener.class, true, false);
for (String listenerBeanName : listenerBeanNames) {
getApplicationEventMulticaster().addApplicationListenerBean(listenerBeanName);
}
// 发布早期事件
Set<ApplicationEvent> earlyEventsToProcess = this.earlyApplicationEvents;
this.earlyApplicationEvents = null;
if (earlyEventsToProcess != null) {
for (ApplicationEvent earlyEvent : earlyEventsToProcess) {
getApplicationEventMulticaster().multicastEvent(earlyEvent);
}
}
}
事件广播类图 
类
说明
ApplicationEventMulticaster
管理多个监听器并向其发布事件对象的接口
AbstractApplicationEventMulticaster
提供监听器注册/管理功能的抽象实现
SimpleApplicationEventMulticaster
将所有事件多播到所有已注册的监听器,让监听器忽略它们不感兴趣的事件。默认情况下,所有监听器在线程中被调用。
源码解读
public void addApplicationListener(ApplicationListener<?> listener) {
synchronized (this.retrievalMutex) {
Object singletonTarget = AopProxyUtils.getSingletonTarget(listener);
// 如果代理的目标监听器也已经注册到多播器,为了避免两次都调用相同的监听器
// 从多播器移除目标监听器
if (singletonTarget instanceof ApplicationListener) {
this.defaultRetriever.applicationListeners.remove(singletonTarget);
}
this.defaultRetriever.applicationListeners.add(listener);
this.retrieverCache.clear();
}
}
@Override
public void addApplicationListenerBean(String listenerBeanName) {
synchronized (this.retrievalMutex) {
this.defaultRetriever.applicationListenerBeans.add(listenerBeanName);
this.retrieverCache.clear();
}
}
// 获取喝Event匹配的事件类型,不匹配的排除在外
protected Collection<ApplicationListener<?>> getApplicationListeners(
ApplicationEvent event, ResolvableType eventType) {
// 获取事件源
Object source = event.getSource();
// 获取事件类型
Class<?> sourceType = (source != null ? source.getClass() : null);
// 使用事件源和事件类型构造缓存Key
ListenerCacheKey cacheKey = new ListenerCacheKey(eventType, sourceType);
// 在缓存中通过Key查找是否存在缓存
ListenerRetriever retriever = this.retrieverCache.get(cacheKey);
if (retriever != null) {
// 如果缓存中存在,则直接返回
return retriever.getApplicationListeners();
}
// 通过类是否在classLoader或者parent classLoader中来判断类是否是可以缓存的
if (this.beanClassLoader == null ||
(ClassUtils.isCacheSafe(event.getClass(), this.beanClassLoader) &&
(sourceType == null || ClassUtils.isCacheSafe(sourceType, this.beanClassLoader)))) {
// 同步缓存
synchronized (this.retrievalMutex) {
// 通过Key获取缓存
retriever = this.retrieverCache.get(cacheKey);
if (retriever != null) {
// 缓存不为空,则返回
return retriever.getApplicationListeners();
}
// 构造ListenRetriever
retriever = new ListenerRetriever(true);
Collection<ApplicationListener<?>> listeners =
retrieveApplicationListeners(eventType, sourceType, retriever);
this.retrieverCache.put(cacheKey, retriever);
return listeners;
}
}
else {
// 无ListenerRetriever缓存,不需要同步
return retrieveApplicationListeners(eventType, sourceType, null);
}
}
// 检索指定事件和源类型的监听器
private Collection<ApplicationListener<?>> retrieveApplicationListeners(
ResolvableType eventType, Class<?> sourceType, ListenerRetriever retriever) {
// List为要返回的监听器
List<ApplicationListener<?>> allListeners = new ArrayList<ApplicationListener<?>>();
Set<ApplicationListener<?>> listeners;
Set<String> listenerBeans;
synchronized (this.retrievalMutex) {
// 使用成员变量defaultRetriever初始化listeners
listeners = new LinkedHashSet<ApplicationListener<?>>(this.defaultRetriever.applicationListeners);
// 使用成员变量defaultRetriever初始化listenerBeans
listenerBeans = new LinkedHashSet<String>(this.defaultRetriever.applicationListenerBeans);
}
for (ApplicationListener<?> listener : listeners) {
// 确定监听器是否支持指定的事件
if (supportsEvent(listener, eventType, sourceType)) {
if (retriever != null) {
// 有缓存的情况(有传参决定)
retriever.applicationListeners.add(listener);
}
allListeners.add(listener);
}
}
if (!listenerBeans.isEmpty()) {
BeanFactory beanFactory = getBeanFactory();
for (String listenerBeanName : listenerBeans) {
try {
// BeanFactory中获取Class
Class<?> listenerType = beanFactory.getType(listenerBeanName);
if (listenerType == null || supportsEvent(listenerType, eventType)) {
// 从BeanFactory中获取listener
ApplicationListener<?> listener =
beanFactory.getBean(listenerBeanName, ApplicationListener.class);
// allListeners中不包含该监听器,并确定监听器是否支持指定的事件
if (!allListeners.contains(listener) && supportsEvent(listener, eventType, sourceType)) {
if (retriever != null) {
// 有缓存的情况(有传参决定)
retriever.applicationListenerBeans.add(listenerBeanName);
}
allListeners.add(listener);
}
}
}
catch (NoSuchBeanDefinitionException ex) {
// Singleton listener instance (without backing bean definition) disappeared -
// probably in the middle of the destruction phase
}
}
}
// 对Listener进行排序
AnnotationAwareOrderComparator.sort(allListeners);
return allListeners;
}
第十一步 完成初始化
// 完成Context的BeanFactory初始化,并完成所有剩余的单例Bean的初始化
protected void finishBeanFactoryInitialization(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory) {
// 为context上下文初始化conversion service
if (beanFactory.containsBean(CONVERSION_SERVICE_BEAN_NAME) &&
beanFactory.isTypeMatch(CONVERSION_SERVICE_BEAN_NAME, ConversionService.class)) {
beanFactory.setConversionService(
beanFactory.getBean(CONVERSION_SERVICE_BEAN_NAME, ConversionService.class));
}
// 如果之前没有嵌入值解析器注册,则注册默认的嵌入值解析器
// 所谓嵌入值解析器主要用于解析注解属性值
if (!beanFactory.hasEmbeddedValueResolver()) {
beanFactory.addEmbeddedValueResolver(new StringValueResolver() {
@Override
public String resolveStringValue(String strVal) {
return getEnvironment().resolvePlaceholders(strVal);
}
});
}
// 初始化LoadTimeWeaverAware
String[] weaverAwareNames = beanFactory.getBeanNamesForType(LoadTimeWeaverAware.class, false, false);
for (String weaverAwareName : weaverAwareNames) {
getBean(weaverAwareName);
}
// 停止使用TempClassLoader
beanFactory.setTempClassLoader(null);
// 冻结Bean定义配置(Bean定义不会被修改或进一步后处理),因为下一步会实例化对象
beanFactory.freezeConfiguration();
// 实例化所有剩余的单例对象(非懒加载的)
beanFactory.preInstantiateSingletons();
}
源码解读
preInstantiateSingleton
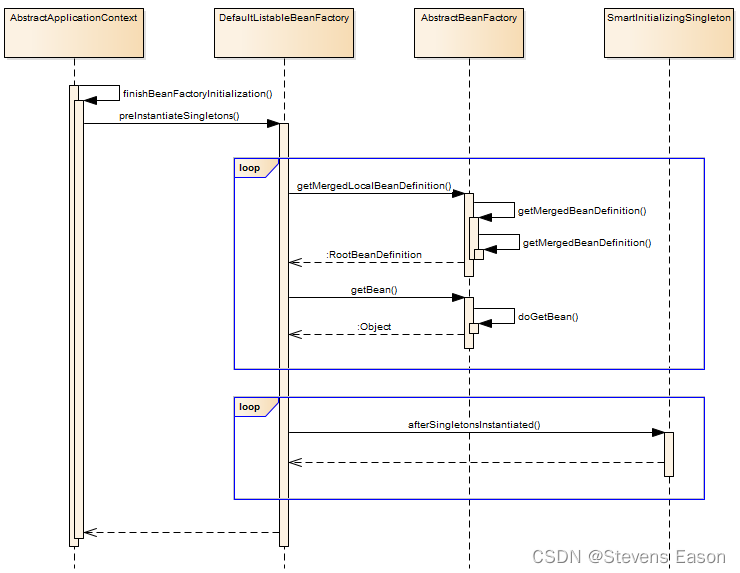
// 确保所有非延迟初始化单例都被实例化
public void preInstantiateSingletons() throws BeansException {
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Pre-instantiating singletons in " + this);
}
// 遍历beanDefinitionNames副本以允许使用init方法注册新的BeanDefinition
List<String> beanNames = new ArrayList<String>(this.beanDefinitionNames);
// Trigger initialization of all non-lazy singleton beans...
// 触发所有非懒加载单例Bean的初始化
for (String beanName : beanNames) {
// 根据Bean的名称获取MergedBeanDefinition
RootBeanDefinition bd = getMergedLocalBeanDefinition(beanName);
if (!bd.isAbstract() && bd.isSingleton() && !bd.isLazyInit()) {
// 判断该beanName是不是一个FactoryBean
if (isFactoryBean(beanName)) {
// 获取FactoryBean实例。通过FactoryBean的getBean方法可以获取FactoryBean创建的Bean实例
final FactoryBean<?> factory = (FactoryBean<?>) getBean(FACTORY_BEAN_PREFIX + beanName);
// 是否希望提前初始化
boolean isEagerInit;
if (System.getSecurityManager() != null && factory instanceof SmartFactoryBean) {
isEagerInit = AccessController.doPrivileged(new PrivilegedAction<Boolean>() {
@Override
public Boolean run() {
return ((SmartFactoryBean<?>) factory).isEagerInit();
}
}, getAccessControlContext());
}
else {
isEagerInit = (factory instanceof SmartFactoryBean &&
((SmartFactoryBean<?>) factory).isEagerInit());
}
if (isEagerInit) {
getBean(beanName);
}
}
else {
// 如果beanName对应的不是FactoryBean,则通过beanName获取Bean实例
getBean(beanName);
}
}
}
// 触发所有实现SmartInitializingSingleton接口的Bean的初始化后回调
for (String beanName : beanNames) {
// 获取对应beanName的实例
Object singletonInstance = getSingleton(beanName);
if (singletonInstance instanceof SmartInitializingSingleton) {
// 判断是否实现了SmartInitializingSingleton接口
final SmartInitializingSingleton smartSingleton = (SmartInitializingSingleton) singletonInstance;
if (System.getSecurityManager() != null) {
AccessController.doPrivileged(new PrivilegedAction<Object>() {
@Override
public Object run() {
smartSingleton.afterSingletonsInstantiated();
return null;
}
}, getAccessControlContext());
}
else {
smartSingleton.afterSingletonsInstantiated();
}
}
}
}
最后一步 完成刷新
protected void finishRefresh() {
// 为上下文初始化生命周期处理器
initLifecycleProcessor();
// 将刷新事件传播到生命周期处理器
getLifecycleProcessor().onRefresh();
// 发布刷新完毕事件到对应的监听器
publishEvent(new ContextRefreshedEvent(this));
// 注册Mbean
LiveBeansView.registerApplicationContext(this);
}
Spring使用BeanPostProcessor来处理可以找到的任何接口实现并调用具体的方法。如果需要自定义功能或其他生命周期行为,Spring并不提供现成的功能,需要自己实现BeanPostProcessor。
除了初始化和销毁回调外,Bean对象还可以实现Lifecycle接口,以便这些Bean可以在容器自身的生命周期驱动下进行start和stop过程。Lifecycle接口为具有生命周期要求的对象定义了基本方法。
当ApplicationContext接收到开始和停止信号时,它会调用那些关联到在该上下文中的所有Lifecycle实现类(如:启动和停止某些后台进程)。
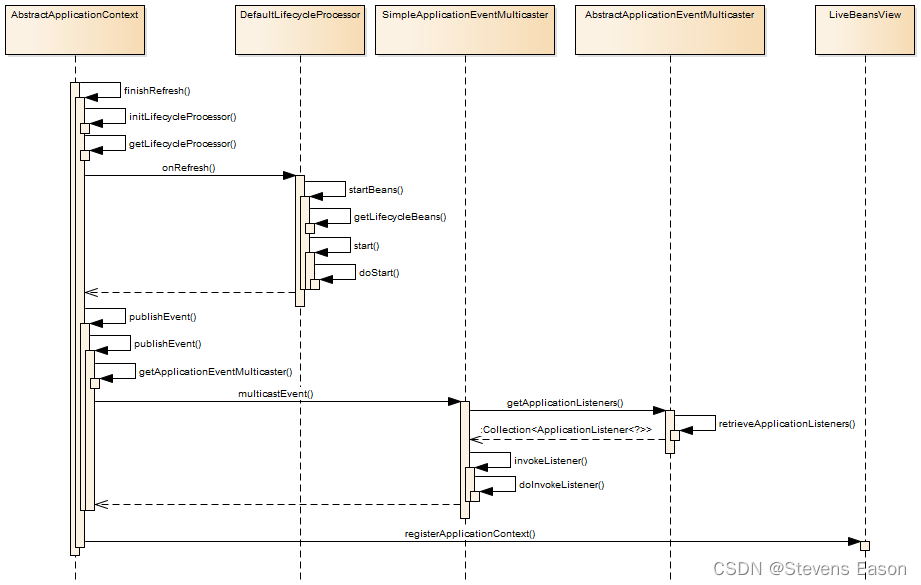
解码解读
org.springframework.context.support.AbstractApplicationContext
// 初始化生命周期处理器
protected void initLifecycleProcessor() {
// 获取BeanFactory
ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = getBeanFactory();
// 判断BeanFactory中是否已经定义过lifecycleProcessor
if (beanFactory.containsLocalBean(LIFECYCLE_PROCESSOR_BEAN_NAME)) {
// 如果定义过lifecycleProcessor,则使用beanFactory中的定义给lifecycleProcessor赋值
this.lifecycleProcessor =
beanFactory.getBean(LIFECYCLE_PROCESSOR_BEAN_NAME, LifecycleProcessor.class);
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
// 日志打印
}
}
else {
// 如果BeanFactory中没有定义lifecycleProcessor,则构造一个DefaultLifecycleProcessor
DefaultLifecycleProcessor defaultProcessor = new DefaultLifecycleProcessor();
// 设置defaultProcessor的BeanFactory
defaultProcessor.setBeanFactory(beanFactory);
this.lifecycleProcessor = defaultProcessor;
// 将defaultProcessor以单例的形式注册到BeanFactory的生命周期管理器
beanFactory.registerSingleton(LIFECYCLE_PROCESSOR_BEAN_NAME, this.lifecycleProcessor);
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Unable to locate LifecycleProcessor with name '" +
LIFECYCLE_PROCESSOR_BEAN_NAME +
"': using default [" + this.lifecycleProcessor + "]");
}
}
}
org.springframework.context.support.DefaultLifecycleProcessor
private void startBeans(boolean autoStartupOnly) {
// 获取所有的Lifecycle接口实现类
Map<String, Lifecycle> lifecycleBeans = getLifecycleBeans();
// 按phase进行分组存储
Map<Integer, LifecycleGroup> phases = new HashMap<Integer, LifecycleGroup>();
for (Map.Entry<String, ? extends Lifecycle> entry : lifecycleBeans.entrySet()) {
Lifecycle bean = entry.getValue();
// 如果参数autoStartupOnly不等于true,或者bean是SmartLifecycle实现类并且autoStartup=true
// autoStartupOnly=true 代表本次刷新为自动启动,触发所有自动启动的SmartLifecycle实现类
// autoStartupOnly=false 代表本次刷新为显式调用,触发所有的Lifecycle实现类启动
if (!autoStartupOnly || (bean instanceof SmartLifecycle && ((SmartLifecycle) bean).isAutoStartup())) {
// 获取Lifecycle Bean的phase,phase默认为0
int phase = getPhase(bean);
// 根据phase获取对应的分组
LifecycleGroup group = phases.get(phase);
if (group == null) {
// 如果没有分组,则新建一个分组
group = new LifecycleGroup(phase, this.timeoutPerShutdownPhase, lifecycleBeans, autoStartupOnly);
// 把phase和对应的group放入到集合
phases.put(phase, group);
}
// 把对应的Lifecycle Bean放到对应的分组中
group.add(entry.getKey(), bean);
}
}
// 遍历分组后的集合
if (!phases.isEmpty()) {
List<Integer> keys = new ArrayList<Integer>(phases.keySet());
// 根据分组phase进行排序
Collections.sort(keys);
for (Integer key : keys) {
// 根据分组顺序依次启动Lifecycle Bean
phases.get(key).start();
}
}
}
// 遍历集合成员,执行Lifecycle实现类的start()函数回调
public void start() {
if (this.members.isEmpty()) {
return;
}
if (logger.isInfoEnabled()) {
logger.info("Starting beans in phase " + this.phase);
}
// 对分组内的member进行排序
Collections.sort(this.members);
for (LifecycleGroupMember member : this.members) {
if (this.lifecycleBeans.containsKey(member.name)) {
// 启动Lifecycle Bean
doStart(this.lifecycleBeans, member.name, this.autoStartupOnly);
}
}
}
private void doStart(Map<String, ? extends Lifecycle> lifecycleBeans, String beanName, boolean autoStartupOnly) {
Lifecycle bean = lifecycleBeans.remove(beanName);
if (bean != null && bean != this) {
// 根据beanName获取相应的依赖Bean
String[] dependenciesForBean = this.beanFactory.getDependenciesForBean(beanName);
// 遍历依赖Bean
for (String dependency : dependenciesForBean) {
// 递归。先回调依赖Bean的start函数(如果依赖Bean是Lifecycle实现类)
doStart(lifecycleBeans, dependency, autoStartupOnly);
}
if (!bean.isRunning() &&
(!autoStartupOnly || !(bean instanceof SmartLifecycle) || ((SmartLifecycle) bean).isAutoStartup())) {
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
// 打印日志
}
try {
// 执行Lifecycle实现类的start()函数回调
bean.start();
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
throw new ApplicationContextException("Failed to start bean '" + beanName + "'", ex);
}
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Successfully started bean '" + beanName + "'");
}
}
}
}
版权归原作者 Stevens Eason 所有, 如有侵权,请联系我们删除。