一、延迟队列的应用场景
1. 场景:"订单下单成功后,15分钟未支付自动取消"
① 传统处理超时订单
采取定时任务轮训数据库订单,并且批量处理。其弊端也是显而易见的;对服务器、数据库性会有很大的要求,
并且当处理大量订单起来会很力不从心,而且实时性也不是特别好。当然传统的手法还可以再优化一下,
即存入订单的时候就算出订单的过期时间插入数据库,设置定时任务查询数据库的时候就只需要查询过期了的订单,
然后再做其他的业务操作
② RabbitMQ延时队列方案
一台普通的rabbitmq服务器单队列容纳千万级别的消息还是没什么压力的,而且rabbitmq集群扩展支持的也是非常好的,
并且队列中的消息是可以进行持久化,即使我们重启或者宕机也能保证数据不丢失
二、延迟队列中的消息投递和消息消费
1.TTL 和 DLX
rabbitMQ中是没有延时队列的,也没有属性可以设置,只能通过死信交换机(DLX)和设置过期时间(TTL)结合起来实现延迟队列
① TTL
TTL是Time To Live的缩写, 也就是生存时间。
RabbitMq支持对消息和队列设置TTL,对消息这设置是在发送的时候指定,对队列设置是从消息入队列开始计算, 只要超过了队列的超时时间配置, 那么消息会自动清除。
如果两种方式一起使用消息的TTL和队列的TTL之间较小的为准,也就是消息5s过期,队列是10s,那么5s的生效。
默认是没有过期时间的,表示消息没有过期时间;如果设置为0,表示消息在投递到消费者的时候直接被消费,否则丢弃。设置消息的过期时间用 x-message-ttl 参数实现,单位毫秒。 设置队列的过期时间用 x-expires 参数,单位毫秒,注意,不能设置为0。 消息:生产者 -> 交换机 消息在生产者制造消息的时候就开始计算了TTL TTL=5 队列:生产者 -> 交换机 -> 路由键 -> 队列 当消息送达到队列的时候才开始计算TTL TTL=10
② DLX和死信队列
DLX即Dead-Letter-Exchange(死信交换机),它其实就是一个正常的交换机,能够与任何队列绑定。
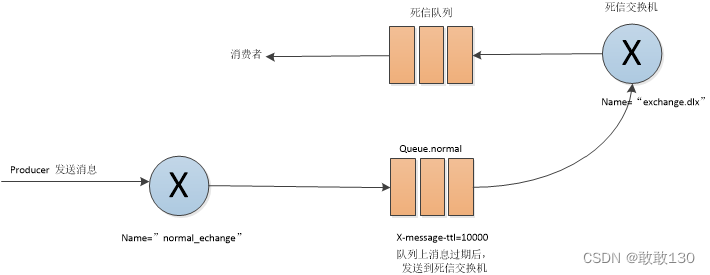
死信队列是指队列(正常)上的消息(过期)变成死信后,能够发送到另外一个交换机(DLX),然后被路由到一个队列上, 这个队列,就是死信队列 成为死信一般有以下几种情况: 消息被拒绝(basic.reject or basic.nack)且带requeue=false参数 消息的TTL-存活时间已经过期 队列长度限制被超越(队列满)死信队列产生流程:
注1:如果队列上存在死信, RabbitMq会将死信消息投递到设置的DLX上去 , 注2:通过在队列里设置x-dead-letter-exchange参数来声明DLX,如果当前DLX是direct类型还要声明 x-dead-letter-routing-key参数来指定路由键,如果没有指定,则使用原队列的路由键
③ 延迟队列
通过DLX和TTL模拟出延迟队列的功能,即,消息发送以后,不让消费者拿到,而是等待过期时间,变成死信后,发送给死信交换机再路由到死信队列进行消费
注1:延迟队列(即死信队列)产生流程见“images/01 死信队列产生流程.png”
④ 开发步骤
1.生产者创建一个正常消息,并添加消息过期时间/死信交换机/死信路由键这3个参数
关键代码1
new Queue(name, durable, exclusive, autoDelete, arguments);
new Queue(NORMAL_QUEUE, true, false, false, map)
参数说明:
name:队列名字
durable:true则持久队列
exclusive:如果我们声明一个排他队列(该队列将仅由声明者的连接使用),则为true
autoDelete:服务器不再使用时应删除队列,则为true
arguments:用于声明队列的参数
map.put("x-message-ttl", 10000);//message在该队列queue的存活时间最大为10秒
map.put("x-dead-letter-exchange", DELAY_EXCHANGE); //x-dead-letter-exchange参数是设置该队列的死信交换器(DLX)
map.put("x-dead-letter-routing-key", DELAY_ROUTING_KEY);//x-dead-letter-routing-key参数是给这个DLX指定路由键
关键代码2
new DirectExchange(NORMAL_EXCHANGE, true, false);
2.消费者A
正常情况下,由消费者A去消费队列“normal-queue”中的消息,但实际上没有,而是等消息过期
3.消费者B
消息过期后,变成死信,根据配置会被投递到DLX,然后根据死信路由键投到死信队列(即延时队列)中
打开我们的虚拟机和连接工具,还有IDEA,确保我们的环境没有问题。
RabbitmqDLXConfig.java
package com.jwj.rabbitmqprovider.config;
import org.springframework.amqp.core.Binding;
import org.springframework.amqp.core.BindingBuilder;
import org.springframework.amqp.core.DirectExchange;
import org.springframework.amqp.core.Queue;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
/**
* @author 敢敢
* @site www.javajwj.com
* @company xxx公司
* @create 2022-12-16 21:02
*/
@Configuration
public class RabbitmqDLXConfig {
// Ctrl+Shift+x:转换为大写
public static final String NORMAL_QUEUE="normal_queue";
public static final String NORMAL_EXCHANGE="normal_exchange";
public static final String NORMAL_ROUTING_KEY="normal_routing_key";
public static final String DLX_QUEUE="dlx_queue";
public static final String DLX_EXCHANGE="dlx_exchange";
public static final String DLX_ROUTING_KEY="dlx_routing_key";
// 普通的交换机及队列
@Bean
public Queue normalQueue(){
// 在正常队列中,要添加参数,2:25发送的消息,要在2:40发送到死信交换机中
Map map = new HashMap();
// map.put("x-message-ttl", 1000*60*15);//message在该队列queue的存活时间最大为10秒
map.put("x-message-ttl", 10000);
map.put("x-dead-letter-exchange", DLX_EXCHANGE); //x-dead-letter-exchange参数是设置该队列的死信交换器(DLX)
map.put("x-dead-letter-routing-key", DLX_ROUTING_KEY);//x-dead-letter-routing-key参数是给这个DLX指定路由键
return new Queue(NORMAL_QUEUE,true,false,false,map);
}
@Bean
public DirectExchange normalDirectExchange(){
return new DirectExchange(NORMAL_EXCHANGE);
}
@Bean
public Binding normalBinding(){
return BindingBuilder.bind(normalQueue())
.to(normalDirectExchange())
.with(NORMAL_ROUTING_KEY);
}
// 死信交换机及队列
@Bean
public Queue dlxQueue(){
return new Queue(DLX_QUEUE);
}
@Bean
public DirectExchange dlxDirectExchange(){
return new DirectExchange(DLX_EXCHANGE);
}
@Bean
public Binding dlxBinding(){
return BindingBuilder.bind(dlxQueue())
.to(normalDirectExchange())
.with(DLX_ROUTING_KEY);
}
}
SendMessageController.java
package com.jwj.rabbitmqprovider.controller;
import com.jwj.rabbitmqprovider.config.RabbitmqDLXConfig;
import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.core.RabbitTemplate;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
import java.time.LocalDateTime;
import java.time.format.DateTimeFormatter;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
/**
* @author 敢敢
* @site www.javajwj.com
* @company xxx公司
* @create 2022-12-16 21:47
*/
@RestController
public class SendMessageController {
@Autowired
private RabbitTemplate rabbitTemplate;
@RequestMapping("/sendDirect")
public Map sendDirect(String routingKey){
Map msg=new HashMap();
msg.put("msg","直连交换机 jwj-direct-Exchange 发送的消息");
msg.put("time", LocalDateTime.now().format(DateTimeFormatter.ofPattern("yyyy-MM-dd hh-mm-ss")));
rabbitTemplate.convertAndSend("jwj-direct-Exchange",
routingKey,
msg);
Map res=new HashMap();
res.put("code",200);
res.put("msg","成功");
return res;
}
@RequestMapping("/sendTopic")
public Map sendTopic(String routingKey){
Map msg=new HashMap();
msg.put("msg","主题交换机 jwj-topic-Exchange 发送的消息");
msg.put("time", LocalDateTime.now().format(DateTimeFormatter.ofPattern("yyyy-MM-dd hh-mm-ss")));
rabbitTemplate.convertAndSend("jwj-topic-Exchange",
routingKey,
msg);
Map res=new HashMap();
res.put("code",200);
res.put("msg","成功");
return res;
}
@RequestMapping("/sendFanout")
public Map sendFanout(){
Map msg=new HashMap();
msg.put("msg","扇形交换机 jwj-fanout-Exchange 发送的消息");
msg.put("time", LocalDateTime.now().format(DateTimeFormatter.ofPattern("yyyy-MM-dd hh-mm-ss")));
rabbitTemplate.convertAndSend("jwj-fanout-Exchange",
null,
msg);
Map res=new HashMap();
res.put("code",200);
res.put("msg","成功");
return res;
}
@RequestMapping("/sendDLX")
public Map sendDLX(){
Map msg=new HashMap();
msg.put("msg","死信交换机 jwj-fanout-Exchange 发送的消息");
msg.put("time", LocalDateTime.now().format(DateTimeFormatter.ofPattern("yyyy-MM-dd hh-mm-ss")));
rabbitTemplate.convertAndSend(RabbitmqDLXConfig.NORMAL_EXCHANGE,
RabbitmqDLXConfig.NORMAL_ROUTING_KEY,
msg);
Map res=new HashMap();
res.put("code",200);
res.put("msg","成功");
return res;
}
}
运行效果如图所示:
DLXReceiver.java
package com.jwj.rabbitmqconsumer.config;
import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.annotation.RabbitHandler;
import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.annotation.RabbitListener;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import java.util.Map;
@Component
@RabbitListener(queues = {"dlx_queue"})
public class DLXReceiver {
// @RabbitListener(queues = {"direct-queue"})
@RabbitHandler
public void handler(Map msg){
// "修改订单的状态的业务逻辑写在这"
System.out.println("死信队列中接受到的消息:"+msg);
}
}
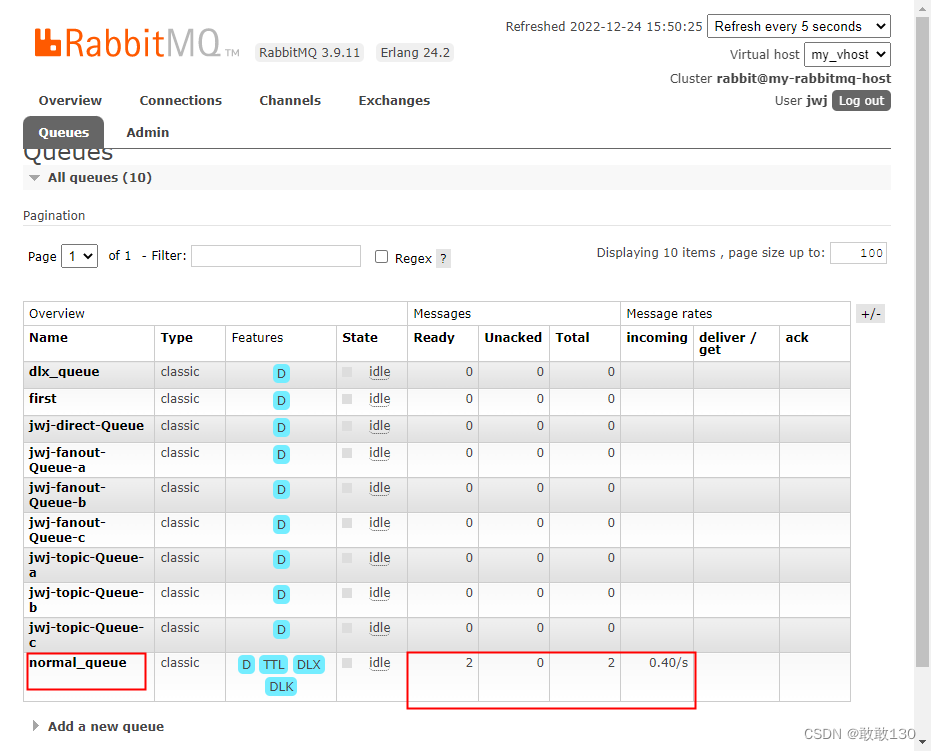
运行结果如下所示:

⑤ json转换
生产者
@Bean public RabbitTemplate createRabbitTemplate(ConnectionFactory connectionFactory, Jackson2JsonMessageConverter jackson2JsonMessageConverter) { RabbitTemplate rabbitTemplate = new RabbitTemplate(connectionFactory); rabbitTemplate.setMessageConverter(jackson2JsonMessageConverter());//指定json转换器 return rabbitTemplate; } @Bean public Jackson2JsonMessageConverter jackson2JsonMessageConverter(){ return new Jackson2JsonMessageConverter(); }消费者:
@Bean public SimpleRabbitListenerContainerFactory rabbitListenerContainerFactory(ConnectionFactory connectionFactory, Jackson2JsonMessageConverter jackson2JsonMessageConverter) { SimpleRabbitListenerContainerFactory factory = new SimpleRabbitListenerContainerFactory(); factory.setConnectionFactory(connectionFactory); factory.setMessageConverter(jackson2JsonMessageConverter()); return factory; } @Bean public Jackson2JsonMessageConverter jackson2JsonMessageConverter(){ return new Jackson2JsonMessageConverter(); }附录一:英文
delay:延迟的
normal:正常
exchange、route、queue
Receiver
⑥ 回顾
应用场景:支付下单的场景
买商品下单,会有待支付到已支付,或者待支付已取消的过程,该过程会有一个时间间隔15min
难点:数据库中有大量的订单处于待支付状态,每一笔订单的过期时间是不一样的,什么时候检查呢?
传统方案:轮询------>缺陷性能极差,对硬件设备要求极高
TTL:Time to live
DLX:dead letterexchange死信交换机
14:11投递消息,最终会在14:26路由到死信交换机,再路由死信队列中
代码层面:
在实例化queue的时候,绑定参数,绑定map集合
map集合中设置ttl时间,以及绑定的dlx exchange名称,以及dlx的routing key
版权归原作者 敢敢130 所有, 如有侵权,请联系我们删除。