本示例使用 cmake 3.29.0, gcc14.1.0(必要), ninja1.12.0
vscode c/c++插件版本1.20.5
这个版本的插件仍不支持c++ module的代码补全,但可以通过宏欺骗C++ IntelliSense并使用代码补全。
在cmake中使用c++模块
# in CMakeLists.txt
...
file(GLOB MODSRC *.ixx)
target_sources(modules
PUBLIC
FILE_SET CXX_MODULES FILES
${MODSRC}
)
target_compile_features(modules PUBLIC cxx_std_20)
add_executable(${PROJECT_NAME} main.cpp)
target_link_libraries(${PROJECT_NAME} modules)
...
使用cmake成功构建项目后,编译器可以正常编译但vsdcode不支持代码补全,非常难用。
实现代码补全
vscode只支持头文件的代码补全, 所以模块的实现需要放在头文件中,而在模块文件中导入头文件并编译。
目录结构:
.
├── build
├── CMakeLists.txt
├── core.h
├── core.ixx
└── main.cpp
core.h
...
#ifndef BUILD_IN_MODULE // 通过此宏区别使用模块构建还是传统头文件引入
#define EXPORT
#else
#define EXPORT export
#endif
#ifndef BUILD_IN_MODULE // 若不使用模块则导入头文件, 否则不导入任何头文件(头文件在模块文件中导入)
#include <iostream>
#endif
EXPORT struct YourStruct{
void func(){
std::cout << "hello world\n";
}
};
EXPORT void foo(){
std::cout << "foo()\n";
}
...
core.ixx
module;
#include <iostream> // core.h 所需的头文件在此处包含
#define BUILD_IN_MODULE // 定义此宏后,包含的core.h中的EXOPRT将变为export关键字
export module core;
#include "core.h"
main.cpp
#ifndef IMPORT_MODULE
#include "core.h"
#else
import core;
#endif
int main() {
...
return 0;
}
此处IMPORT_MODULE宏将在编译时定义, 在CMakeLists.txt中增加:
add_compile_definitions(IMPORT_MODULE)
由于vscode IntelliSense不知道此宏存在,所以其前端编译器导入了头文件并提供代码补全,而由于IMPORT_MODULE已定义,g++编译时使用import core;而不是#include<core.h>。
效果
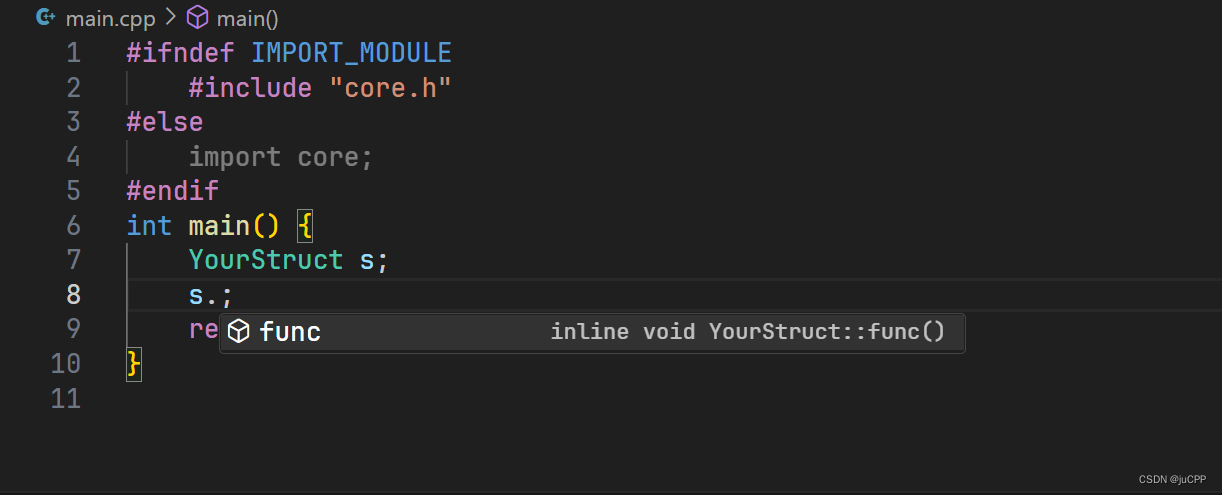
可以正常debug: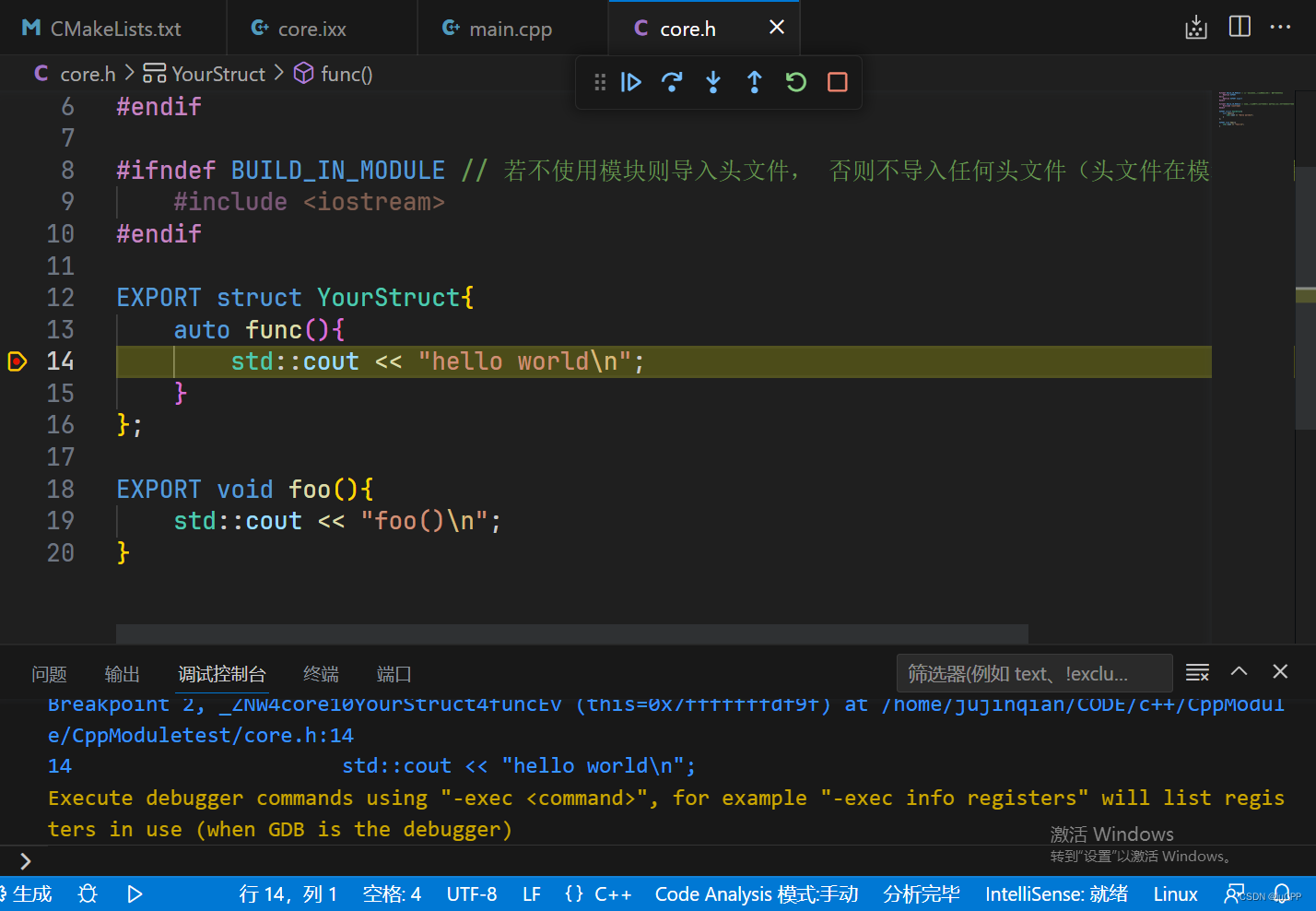
在不定义IMPORT_MODULE宏的状态下,core.h也可以作为正常头文件直接导入并使用。
模块的使用可以极大加速编译,避免对头文件的冗余的扫描,头文件越大,使用模块带来的速度增加越明显。
注意
若vscode正确的导入了CMake中定义的宏,则需要删除.vscode目录下c_cpp_properties.json中的"configurationProvider": "ms-vscode.cmake-tools",或将如下位置字段删除: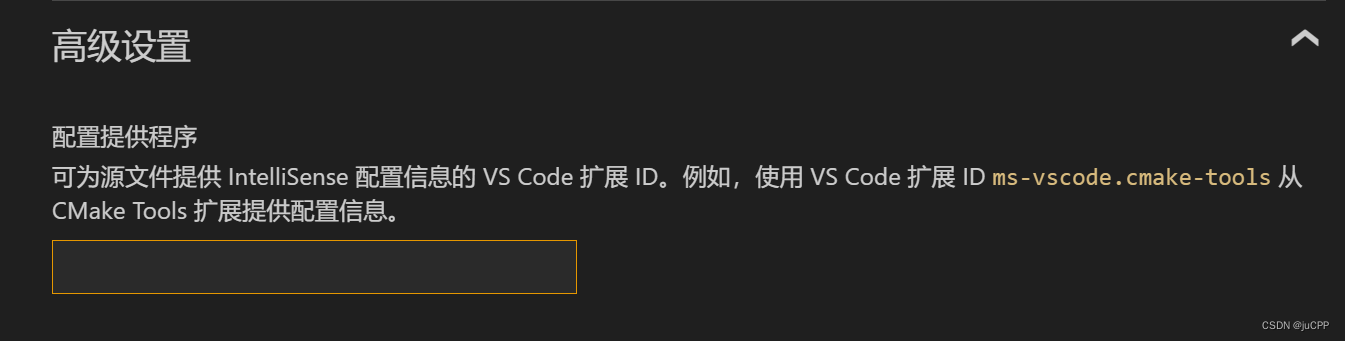
缺点是这样做会导致IntelliSense无法得到你在cmake中自定义的文件包含路径等,你需要在c_cpp_properties.json的includePath中加入它们以获得正确的头文件解析。
版权归原作者 juCPP 所有, 如有侵权,请联系我们删除。