String类
一:String类的初始化方式
string str:生成空字符串
string s(str):生成字符串为str的复制品 (拷贝构造)(带参构造)
string s(str, strbegin,strlen):将字符串str中从下标strbegin开始、长度为strlen的部分作为字符串初值
string s(cstr, char_len):以string类型cstr的前char_len个字符串作为字符串s的初值
string s(num ,c):生成num个c字符的字符串
string s(str, strindex):将字符串str中从下标strindex开始到字符串结束的位置作为字符串初值
二:String类的访问方式
一:
string s1 = ("hello world"); 我们可以通过s1[i]的方式来访问
但 s1[i] 的实际写法 s1.operator(i); 因为实际上是对[]进行了运算符重载
二:
1.通过迭代器 iterator
string::iterator it1 = s1.begin();
while (it1 != s1.end()) //这里的end都是字符串最后一个位置的下一个位置
{
cout << *it1 << " ";
it1++;
}
2.这里还有一种叫做反向迭代器(reverse_interator, rbegin(), rend())
string s3("hello");
string::reverse_iterator it2 = s3.rbegin();
while (it2 != s3.rend())
{
cout << *it2 << " ";
++it2;
}
3.auto 范围for //底层就是迭代器
for (auto& e : lt1)
{
cout << e << " ";
}
s1.operator(i) 和 iterator都有 const的情况 const _interator
例如:const string s2(s1);
注意:const _interator是interator指向的数据不能修改 如果是 const interator的话那么就是interator本身不能修改
三:String的大小和容量
1. size()和length():返回string对象的字符个数,他们执行效果相同。
2. max_size():返回string对象最多包含的字符数,超出会抛出length_error异常
3. capacity():重新分配内存之前,string对象能包含的最大字符数
这里对capacity底层作出一些解释:如果字符串占用的空间不大,则占用的是栈空间中的buffer,默认为15个字节,如果超过,就会在堆空间上开辟空间
四:string的插入:push_back() 和 insert()
string s1;
// 尾插一个字符
s1.push_back('a');
s1.push_back('b');
s1.push_back('c');
cout << "s1:" << s1 << endl; // s1:abc
// insert(pos,char) : 在制定的位置pos前插入字符char
//insert方法 慎用效率不高 类似顺序表
string ss("helloworld");
ss.insert(0, "xxxx"); // 时间复杂度 O(n)
五:string拼接字符串:append() & + 操作符
// 方法一:append()
string s1("abc");
s1.append("def");
cout << "s1:" << s1 << endl; // s1:abcdef
// 方法二:+ 操作符
string s2 = "abc";
/*s2 += "def";*/
string s3 = "def";
s2 += s3.c_str();
cout << "s2:" << s2 << endl; // s2:abcdef
六: string的删除:erase()
//删除erase 效率也很低和insert差不多
1. iterator erase(iterator p);//删除字符串中p所指的字符
2. iterator erase(iterator first, iterator last);//删除字符串中迭代器
区间[first,last)上所有字符 左闭右开
3. string& erase(size_t pos = 0, size_t len = npos);//删除字符串中从索引
位置pos开始的len个字符
4. void clear();//删除字符串中所有字符
七: string的字符替换
1. string& replace(size_t pos, size_t n, const char *s);//将当前字符串
从pos索引开始的n个字符,替换成字符串s
2. string& replace(size_t pos, size_t n, size_t n1, char c); //将当前字符串从pos索引开始的n个字符,替换成n1个字符c
3. string& replace(iterator i1, iterator i2, const char* s);//将当前字符串[i1,i2)区间中的字符串替换为字符串s
八:c_str()使用场景
string file("stl.cpp");
// c_str返回string的指针 相同与数组首元素地址
FILE* fout = fopen(file.c_str(), "r"); //只能传const char* c和c++的不同之处 这个时候c_str这个时候就派上用场了
char ch = fgetc(fout);
while (ch != EOF)
{
cout << ch;
ch = fgetc(fout);
}
九: string的大小写转换:tolower() 和toupper() 函数 或者 STL中transform算法
方法一:
#include<iostream>#include<string>usingnamespace std;intmain(){
string s ="ABCDEFG";for(int i =0; i < s.size(); i++){
s[i]=tolower(s[i]);}
cout << s << endl;return0;}
方法二:
#include<iostream>#include<algorithm>#include<string>usingnamespace std;intmain(){
string s ="ABCDEFG";
string result;transform(s.begin(),s.end(),s.begin(),::tolower);
cout << s << endl;return0;}
十: string的查找:find() 和 substr()方法
1. size_t find (constchar* s, size_t pos = 0) const;
//在当前字符串的pos索引位置开始,查找子串s,返回找到的位置索引,
-1表示查找不到子串
2. size_t find (charc, size_t pos = 0) const;
//在当前字符串的pos索引位置开始,查找字符c,返回找到的位置索引,
-1表示查找不到字符
3. size_t rfind (constchar* s, size_t pos = npos) const;
//在当前字符串的pos索引位置开始,反向查找子串s,返回找到的位置索引,
-1表示查找不到子串
4. size_t rfind (charc, size_t pos = npos) const;
//在当前字符串的pos索引位置开始,反向查找字符c,返回找到的位置索引,-1表示查找不到字符
string file("stl.cpp");
size_t pos = file.rfind("."); //从前往后倒着找. 找到返回对应的下标
//string suffix = file.substr(pos, file.size() - pos);
string suffix = file.substr(pos); //有多少取多少
十一:reserve() 和 resize()
reserve为容器预留足够的空间,避免不必要的重复分配,分配空间大于等于函数的参数,影响capacity。
resize调整容器中有效数据区域的尺寸,如果尺寸变小,原来数据多余的截掉。若尺寸变大,不够的数据用该函数第二个参数填充,影响size。
// reserve 不一定会缩容 但会扩容 意义是直接reserve就不用一直倍增扩容了 提前开空间
// reserve 不会初始化 但是resize会
string ss("helloworld");
cout << ss.capacity() << endl;
ss.reserve(100);
cout << ss.capacity() << endl;
// 注意不会改变size 所以不能越界访问
// 这个时候resize就出现了 就可以用下标进行访问了
string str;
str.resize(5, '0');
str[3] = '1';
cout << str[2] << endl;
cout << str.size() << endl;
//自己去验证一下才是最有效的
ss.clear();
ss = "hello world";
ss.resize(15, 'x'); //如果有剩余位置 就在剩余位置填充 不会覆盖原有位置
cout << ss << endl;
cout << ss.size() << " " << s1.capacity() << endl;
十二:to_string 与 stoi 函数
介绍
stoi(),to_string 这两个函数都是对字符串处理的函数,前者是将字符串转化为十进制 int 类型,最后一个是将十进制类型 int、double 等转化为string。
头文件都是:#include <cstring>里的 \colorbox{pink}{头文件都是:\#include <cstring>里的} 头文件都是:#include <cstring>里的
✨to_string作用
将整数转换为字符串
功能:将数字常量(int,double,long等)转换为字符串(string),返回转换好的字符串

测试代码
#include<iostream>#include<cstring>usingnamespace std;intmain(){int num =123456789;
string s =to_string(num);// "123456789"
cout << s << endl;return0;}
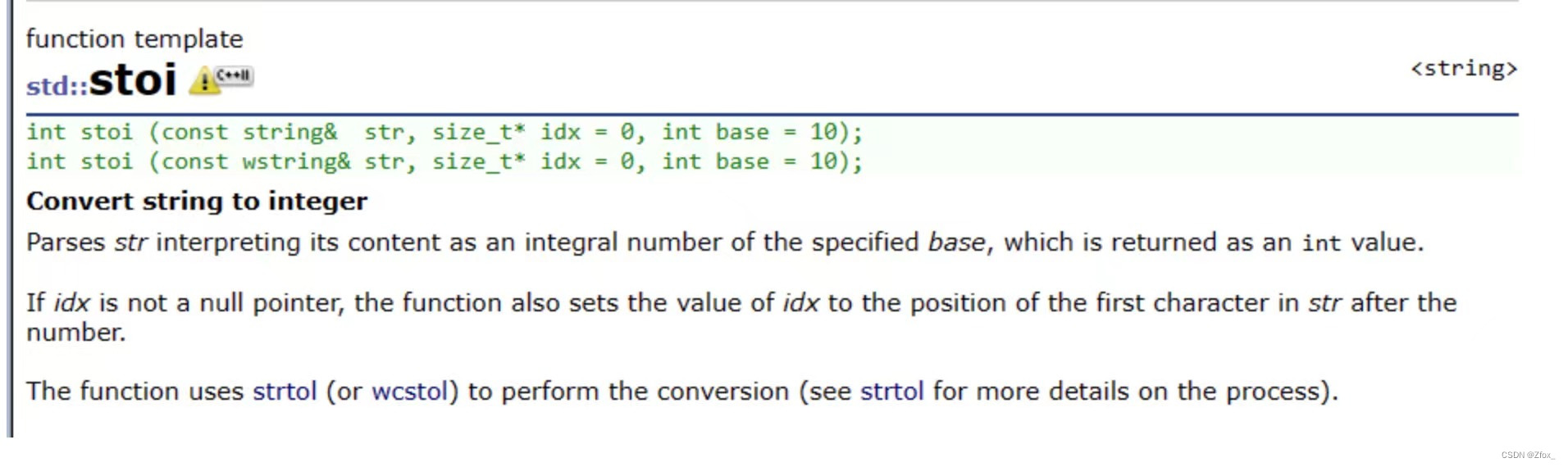
✨stoi作用
将 n 进制的字符串转化为十进制
stoi(字符串,起始位置,n进制(默认10进制)),将 n 进制的字符串转化为十进制
测试代码
#include<iostream>#include<cstring>usingnamespace std;intmain(){
string str ="100";int x =stoi(str,0,2);//将二进制"100"转化为十进制x
cout << x << endl;return0;}
总结:
以上就是string类的常用函数,内容并不全面,详细内容可在官方文档中进行查阅,希望对大家的学习有所帮助,一起进步!
版权归原作者 Zfox_ 所有, 如有侵权,请联系我们删除。