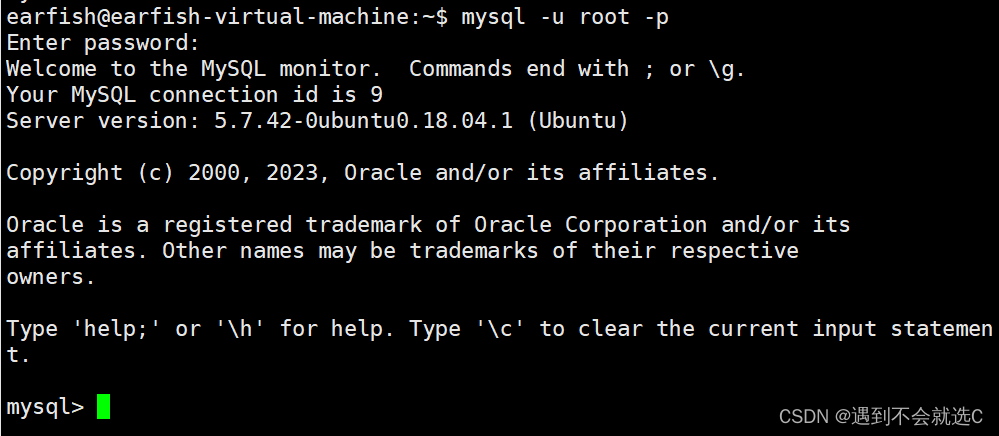
一、登录进入MySQL
mysql -u username -p;//登录
二、MySQL数据库的查看、创建、删除、重命名、拷贝操作
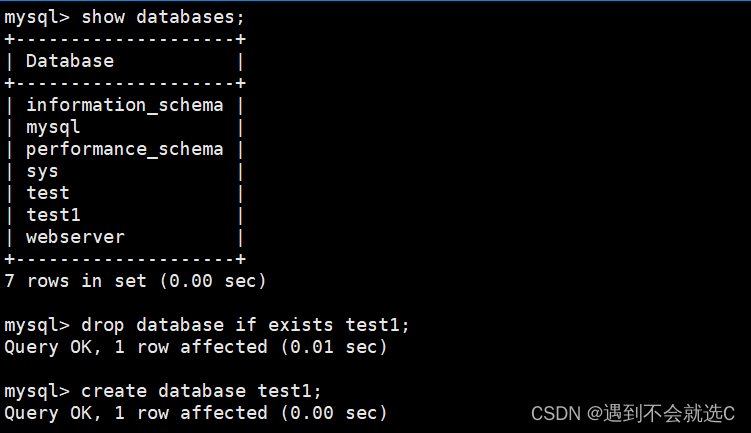
show databases;//查看所有数据库
create database test;//创建数据库test
use test;//使用数据库test
drop database [if exists] test;//删除数据库test可使用if exists保证安全
create database test1;//通过拷贝数据库test进行重命名操作,较为安全
rename table test.user to test1.user;//拷贝数据库test的表user到test1
rename database test to test1;//重命名数据库,不安全且已经被摒弃
三、数据库下表的创建、删除、查看、修改(增加、删除、更新字段/列,修改字段/列名)
对表进行操作时必须要加table 具体表名,当我们需要修改数据表名或者修改数据表字段时,就需要使用到 MySQL ALTER 命令。
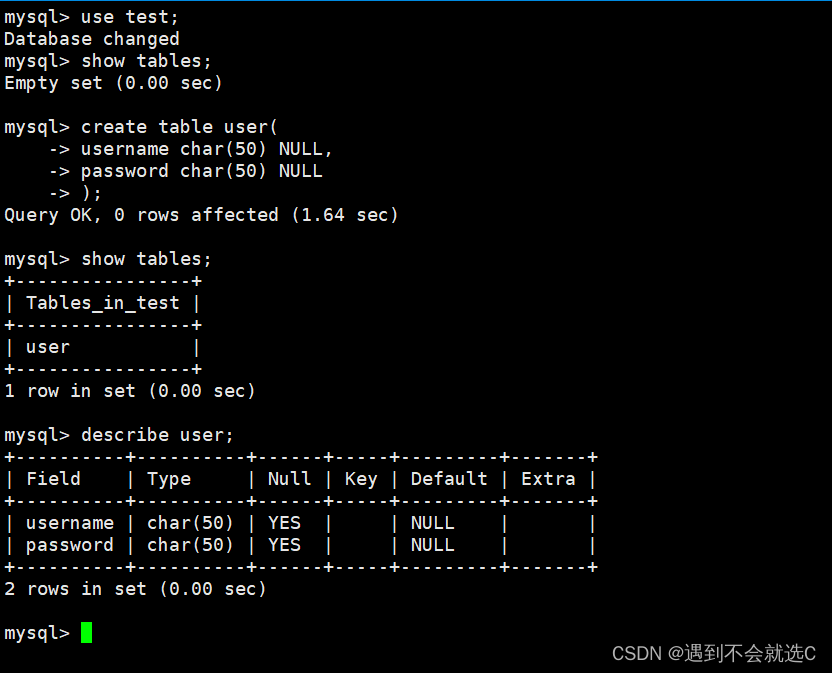
show tables;//查看数据库test所有表
//在test数据库下创建表user,规定其数据结构
create table user(
username char(50) NULL,
password char(50) NULL
);
rename table user to users;//重命名表user为users
describe user;//查看表user的结构
drop table [if exists] user;//删除数据库test的表user
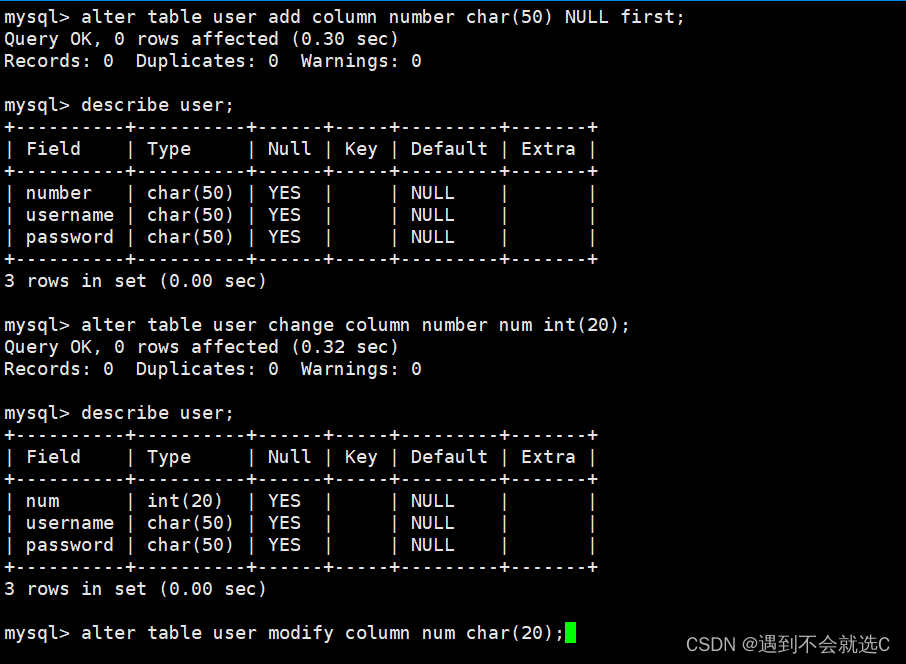
alter table user add column number char(20) NULL;//在表user增加字段number,column可省略,NULL后加first则直接在头增加,否则默认在尾部
alter table user add column number char(20) NULL after password;//规定位置,在表user的password字段后增加字段number
alter table user add column number char(20) NULL before username;//规定位置,在表user的username字段前增加字段number
alter table user change column number num int(20) NULL;//修改表user字段number为num,同时修改其数据类型
alter table user modify column num char(20);//更改表user的num字段的数据类型为char
alter table user drop column num;//删除字段num
四、表中数据的插入、删除、查找、更新
对表中数据的操作不用加table直接使用其具体表名即可,select查询语句后跟期待得到的数据,*代表全部数据,where进行相应的筛选,not则取反或用!也可。
select * from user where username is (not) null;//限定查找username为空或不为空的数据
insert into user(num, username, password) values('1', 'user1', '123456');//向表user插入数据
insert into user(num, username, password)
values
('1', 'user1', '123456'),
('2', 'user2', '12345'),
('3', 'user3', '1234');//向表user插入多条数据
delete from user;//删除表user所有数据,不改变其表结构
delete from user where num='1';//删除表user中所有num为1的数据
update user set username='user01',password='01' where num='1';//更新表user中num为1的username和password
select * from user;//查询user表中所有数据
select username from user;//查询表user中字段username的所有数据
select * from user where username = 'user1';//查询表user中username为user1的所有数据
select * from user where not username = 'user1';//查询表user中username不为user1的所有数据或用username!='user1'
select * from user order by num;//查询所有数据并按照num的升序排序
select * from user order by num desc;//查询所有数据并按照num的降序排序
select * from user where num >1 and num < 10;//限定查找num在1-10之间的信息
select * from user where num >1 or usename ='user2';//限定查找num大于1以及username=='user2'的数据,or合并两个查询语句
select * from user where num >1
union //union合并两个查询结果取并集,同上or,intersect取交集、except取差集,可以自动过滤重复字段,不过滤其后加all即可
select * from user where username='user2';
select * from user where num in (2,4,6);//限定查找num为2,4,6的信息
select * from user where num between 1 and 10;//限定查找num在1-10之间的信息
select * from user where username like '刘%';// %表示任意个字符,限定查找username开头为刘的数据
select * from user where username like '%刘%';//限定查找username中包含刘的数据
select * from user where username like '刘_';// _表示任意一个字符,限定查找username开头为刘且只有两个姓的数据

五、正则表达式查找
LIKE命令查找的通配符只有%表示任意个字符以及_表示任意一个字符,而使用正则表达式查找需要用命令REGEXP/RLIKE,结合通配符使用:
- .:匹配任意单个字符。
- ^:匹配开始。
- $:匹配结束。
- A|B:表示匹配A或者B
- [abc]:匹配a/b/c中的任意一个字符。
- [a-z]:匹配范围内的任意一个字符。
select * from user where username rlike '^刘';// 限定查找username开头为刘的数据
select * from user where username rlike '刘';//限定查找username中包含刘的数据
select * from user where username rlike '^刘.$';//限定查找username开头为刘且名字仅两个字的数据
select * from user where username rlike '[刘王]';//限定查找username中包含刘、王的数据
select * from user where username rlike '刘|王';//限定查找username中包含刘、王的数据
六、聚合函数与子查询应用
MySQL中可以通过相应的聚合函数对数据进行操作,聚合函数不能和where同时使用,可以使用having来替代where:
- COUNT():返回行数,当获取具体字段的行数时不包括NULL
- AVG() :返回平均值
- MAX():返回最大值
- MIN():返回最小值
- SUM():求和
select count(*) from user;//获取整个表的行数,包括NULL
select avg(num) as avg_num from user;//获取num平均值,使用as取别名方便阅读,也可直接去掉as效果一致
select gender,count(gender) from user group by gender;//查询性别以及性别个数并按照性别gender分组
select age,count(age) from user group by age having count(age)>5;// having命令对分组后的数据进行相应的处理,查询年龄以及各年龄的个数并按照年龄分组,并显示出分组后大于5个人的年龄段
select age,count(age) from user group by age having count(age)>5 order by count(age) desc limit 3;//查询年龄以及各年龄的个数并按照年龄分组,并筛选出年龄段数量大于5的前3个分组并按照人数多少进行降序排序,也可设置偏移limit 2,3表示从偏移量为2即第3个开始的前3个分组
select * form user where age>(select avg(age) from user);//子查询,查询大于平均值的age
create table old_age select * form user where age>(select avg(age) from user);//子查询创建表
insert into old_age select * form user where age between (select avg(age) from user) and 50;//子查询插入表
select exists (select * from user where age>100)//exists结果仅0和1,存在和不存在
七、表关联
查询多个表中的数据,关联的表中有相同的字段才可进行关联。
select * from user inner join log on user.num = log.user_num;//通过num和user_num字段关联表user和log
//也可使用where进行连接
select * from user u,log l where u.num = l.user_num;//u和l分别是规定的user和log的别名
- 内连接 inner join :返回两个表中都有的数据
- 左连接 left jion:返回左表所有数据以及右表匹配的数据,右表中没有的数据用NULL填充
- 右连接 right jion:返回右表所有数据以及左表匹配的数据,左表中没有的数据用NULL填充
八、主键与索引
通过建立索引进行查找可以极大提升查找的效率,建立索引后依然使用原字段进行查询,在 MySQL 中,索引分为普通索引INDEX、主键索引PRIMARY KEY 、唯一索引UNIQUE INDEX以及文件索引FULLTEXT INDEX,主键索引是一种特殊的唯一索引,一个表只有一个主键索引,主键索引不允许设立主键的字段有重复值且不允许有空值NULL,在建表的时候指定了主键,就会创建主键索引,只可以建表时或者使用ALTER创建不能使用CREAT创建主键索引、唯一索引规定建立索引的字段的值必须唯一,但允许有空值,一张表中可以有多个唯一索引。文件索引用于全文搜索。仅适用于 CHAR, VARCHAR和TEXT字段。
CREATE (UNIQUE) INDEX user_nums ON user(num);//直接创建索引:为表user的字段num创建索引user_nums
ALTER TABLE user ADD INDEX user_nums (num);//更改表的结构为某个字段添加索引,必须有索引名
ALTER TABLE user ADD PRIMARY KEY(num);//更改表的结构将某个字段设为主键
ALTER TABLE user ADD UNIQUE INDEX user_nums (num);//更改表的结构为某个字段添加索引
CREATE TABLE user (//建表时直接创建索引
num int(20) AUTO_INCREMENT PRIMARY KEY NOT NULL,//主键索引,AUTO_INCREMENT表示自增
username varchar(200) NOT NULL,
password varchar(200) NOT NULL DEFAULT '123'//默认值
//(UNIQUE)INDEX user_nums (num) //(唯一)普通索引
);
show index from user;//查看建立的索引
select * from user where num>100;//使用原字段查询
DROP INDEX user_nums ON user;//删除表user的索引user_nums
ALTER TABLE user DROP INDEX user_nums;//删除表user的索引user_nums,UNIQUE类型也可删除
ALTER TABLE user DROP PRIMARY KEY;//删除表user的主键索引,若有自增则先改变自增,用modify或change重新规定字段类型
九、视图
视图是虚拟存在的表,其本身并不包含数据,作为一个查询语句保存在数据字典中,根据查询语句中的表变化从而动态变化,使用creat view 视图名 as 查询语句进行创建。更改视图需要更改其查询语句
//视图创建
create view top10
as
select * from user order by num desc limit 10;
//更改视图
alter view top10
as
select * from user order by num limit 10;
//删除视图
drop view top10;
本文转载自: https://blog.csdn.net/csdnabcaq/article/details/138050847
版权归原作者 遇到不会就选C 所有, 如有侵权,请联系我们删除。
版权归原作者 遇到不会就选C 所有, 如有侵权,请联系我们删除。