一、安装selenium ,
pip install -U selenium
二、安装chromedriver
http://chromedriver.storage.googleapis.com/index.html
三、chromedriver放在python的安装根目录下面即可,为什么放到python安装的根目录下即可呢,是因为WebDriver的初始化代码里,init,有这个注释
- executable_path - Deprecated: path to the executable. If the default is used it assumes the executable is in the $PATH
实现思路
selenium自动化代码-》XXXdriver.exe-》 浏览器(ie、chrome、firefox)
通过http进行通信的,客户端是python代码或者java代码,服务端是xxxdriver
通信流程:
1、xxxdriver启动,ip+端口监听中
2、selenium webdriver跟xxxdriver建立连接,然后发送http请求
3、xxxdriver收到指令后,驱动浏览器
4、xxxxdriver要把结果返回给selenium webdriver
5、继续发下一个http请求
6、断开连接,关闭驱动服务、关闭浏览器
写一个简单的例子,可以跟一下源码,可以发现原理:是一个http请求,协议是json格式,
本质上来讲把每一个对网页的操作,都是一个接口,json格式、url、请求类型、请求数据,协议名称jsonwireprotocol
from selenium import webdriver
# 打开浏览器,与浏览器建立会话
# 启动chromedriver.exe,并且建立连接,会话ID
driver = webdriver.Chrome()
driver.get("https://www.baidu.com")
1)点击get方法
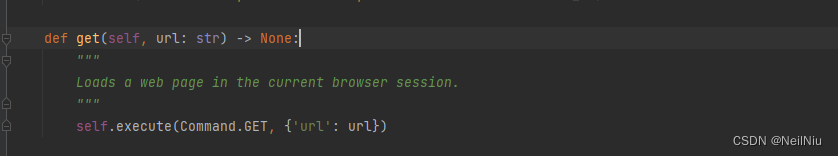
2)然后点击execute方法,主要看response,调用了execute方法
def execute(self, driver_command: str, params: dict = None) -> dict:
"""
Sends a command to be executed by a command.CommandExecutor.
:Args:
- driver_command: The name of the command to execute as a string.
- params: A dictionary of named parameters to send with the command.
:Returns:
The command's JSON response loaded into a dictionary object.
"""
if self.session_id:
if not params:
params = {'sessionId': self.session_id}
elif 'sessionId' not in params:
params['sessionId'] = self.session_id
params = self._wrap_value(params)
response = self.command_executor.execute(driver_command, params)
if response:
self.error_handler.check_response(response)
response['value'] = self._unwrap_value(
response.get('value', None))
return response
# If the server doesn't send a response, assume the command was
# a success
return {'success': 0, 'value': None, 'sessionId': self.session_id}
3)继续点击execute()方法,可以看到最后调用的是request方法
def execute(self, command, params):
"""
Send a command to the remote server.
Any path substitutions required for the URL mapped to the command should be
included in the command parameters.
:Args:
- command - A string specifying the command to execute.
- params - A dictionary of named parameters to send with the command as
its JSON payload.
"""
command_info = self._commands[command]
assert command_info is not None, 'Unrecognised command %s' % command
path = string.Template(command_info[1]).substitute(params)
if isinstance(params, dict) and 'sessionId' in params:
del params['sessionId']
data = utils.dump_json(params)
url = f"{self._url}{path}"
return self._request(command_info[0], url, body=data)
4)点击request方法,可以看到其实就是发起了一个http请求,只要开始我们把参数传对,就会发送正确的http请求。
def _request(self, method, url, body=None):
"""
Send an HTTP request to the remote server.
:Args:
- method - A string for the HTTP method to send the request with.
- url - A string for the URL to send the request to.
- body - A string for request body. Ignored unless method is POST or PUT.
:Returns:
A dictionary with the server's parsed JSON response.
"""
LOGGER.debug(f"{method} {url} {body}")
parsed_url = parse.urlparse(url)
headers = self.get_remote_connection_headers(parsed_url, self.keep_alive)
response = None
if body and method not in ("POST", "PUT"):
body = None
if self.keep_alive:
response = self._conn.request(method, url, body=body, headers=headers)
statuscode = response.status
else:
conn = self._get_connection_manager()
with conn as http:
response = http.request(method, url, body=body, headers=headers)
statuscode = response.status
if not hasattr(response, 'getheader'):
if hasattr(response.headers, 'getheader'):
response.getheader = lambda x: response.headers.getheader(x)
elif hasattr(response.headers, 'get'):
response.getheader = lambda x: response.headers.get(x)
data = response.data.decode('UTF-8')
LOGGER.debug(f"Remote response: status={response.status} | data={data} | headers={response.headers}")
try:
if 300 <= statuscode < 304:
return self._request('GET', response.getheader('location'))
if 399 < statuscode <= 500:
return {'status': statuscode, 'value': data}
content_type = []
if response.getheader('Content-Type'):
content_type = response.getheader('Content-Type').split(';')
if not any([x.startswith('image/png') for x in content_type]):
try:
data = utils.load_json(data.strip())
except ValueError:
if 199 < statuscode < 300:
status = ErrorCode.SUCCESS
else:
status = ErrorCode.UNKNOWN_ERROR
return {'status': status, 'value': data.strip()}
# Some drivers incorrectly return a response
# with no 'value' field when they should return null.
if 'value' not in data:
data['value'] = None
return data
else:
data = {'status': 0, 'value': data}
return data
finally:
LOGGER.debug("Finished Request")
response.close()
1、退出会话,关闭浏览器,关闭chromedriver
driver.quit(),这个退出
driver.close(),关闭当前的窗口
版权归原作者 NeilNiu 所有, 如有侵权,请联系我们删除。