一、python 中打开文件,
python中读写txt文件,首先得打开文件,即使用open()函数,
lastpath1 = r'D:apache-jmeter-4.0insrcWaveId.txt'
file1 = open(lastpath,'r'')
可以使用不同的模式打开文件,如:r,r+,w,w+,a,a+,它们的区别如下: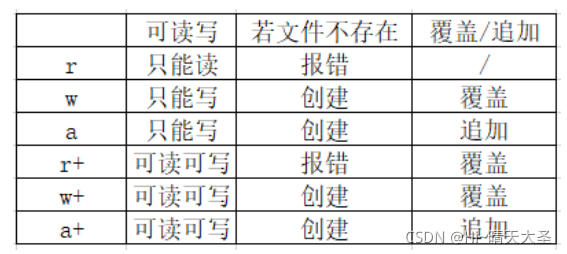
注意:write()会创建文件
二、读取txt文件
python常用的读取文件函数有三种read()、readline()、readlines()*
(1)、read() 一次性读全部内容 一次性读取文本中全部的内容,以字符串的形式返回结果
path1=r'D:Document est.txt'
file1=open(path1,'r')
content1=file1.read()
print(content1)
file1.close() #文件打开,使用完毕后需要关闭
(2)、readline() 读取第一行内容,只读取文本第一行的内容,以字符串的形式返回结果
path2=r'D:Document est.txt'
file2=open(path1,'r')
content2=file2.readline()
print(content2)
file2.close() #文件打开,使用完毕后需要关闭
(3)、readlines()读取文本所有内容,并且以数列的格式返回结果,
path3=r'D:Document est.txt'
file3=open(path3,'r')
content3=file3.readlines()
print(content3)
file3.close() #文件打开,使用完毕后需要关闭
返回结果:
['one
', 'two
', 'three
', 'four
', 'five']
因readlines()会读到换行符,所以一般配合for in使用去除换行符
f = open("test.txt", "r")
for line in f.readlines():
line = line.strip('
') #去掉列表中每一个元素的换行符
print(line)
f.close()
三、txt文件中写入
常用函数:write()
1、文件中写入内容,首先需要打开文件
2.wirte()写入后默认不换行
path2 = r'D:Document est2.txt'
file2 = open(path2,'w+')
file2.write('aaa')
b = 'ccc'
file2.write(b)
四、关闭文件
文件打开最后需要关闭,常用函数为close()
版权归原作者 m0_67401920 所有, 如有侵权,请联系我们删除。