文章目录
1 类模板语法
类模板的作用:建立一个通用类,类中的成员数据类型可以不具体制定,用一个虚拟的类型来代表
语法:
template<typenameT>
类
解释:
template
声明创建模板
typename
表明其后面的符号是一种数据类型,可以用
class
代替
T
是通用的数据类型,名称可以替换,通常为大写字母
示例:
//类模板template<classNameType,classAgeType>classPerson{public:Person(NameType name, AgeType age){this->m_Age = age;this->m_Name = name;}voidshowPerson(){
cout <<"name: "<<this->m_Name <<"age: "<<this->m_Age << endl;}
NameType m_Name;
AgeType m_Age;};voidtest01(){
Person<string,int>p1("孙悟空",999);
p1.showPerson();}intmain(){test01();system("pause");return0;}
2 类模板与函数模板的区别
类模板与函数模板区别主要有两点:
- 类模板没有自动类型推导的使用方式
- 类模板在模板参数列表中可以有默认参数
示例:
//类模板与函数模板的区别template<classNameType,classAgeType=int>//指定默认参数classPerson{public:Person(NameType name, AgeType age){this->m_Age = age;this->m_Name = name;}voidshowPerson(){
cout <<"name: "<<this->m_Name <<" age: "<<this->m_Age << endl;}
NameType m_Name;
AgeType m_Age;};voidtest01(){//Person p("孙悟空", 1000);错误的,类模板无法用自动类型推导
Person<string,int>p("孙悟空",1000);//正确,只能用显式指定类型推导
p.showPerson();}voidtest02(){
Person<string>p("猪八戒",999);//类模板在参数列表中有默认参数}intmain(){test01();system("pause");return0;}
3 类模板中成员函数创建时机
类模板中成员函数和普通类中成员函数创建时机是有区别的:
- 普通类中的成员函数一开始就可以创建
- 类模板中的成员函数在调用时才创建
示例:
//类模板中成员函数的创建时机classPerson1{public:voidshowPerson1(){
cout <<"Person1 show"<< endl;}};classPerson2{public:voidshowPerson2(){
cout <<"Person2 show"<< endl;}};template<classT>classMyclass{public:
T obj;//类模板中的成员函数在调用的时候才创建,所以不会报错voidfunc1(){
obj.showPerson1();}voidfunc2(){
obj.showPerson2();}};voidtest01(){
Myclass<Person1>m;
m.func1();//m.func2(); 无法调用}intmain(){test01();system("pause");return0;}
4 类模板对象做函数参数
学习目标:类模板实例化出的对象,向函数传参的方式
一共有三种传入方式:
- 指定传入的类型:直接显示对象的数据类型
- 参数模板化:将对象中的参数变为模板进行传递
- 整个类模板化:将这个对象类型模板化进行传递
示例:
//类模板对象做函数参数template<classT1,classT2>classPerson{public:Person(T1 name,T2 age){this->m_Age = age;this->m_Name = name;}voidshowPerson(){
cout <<"name: "<<this->m_Name <<" age:"<<this->m_Age << endl;}
T1 m_Name;
T2 m_Age;};//1、指定传入类型voidprintPerson1(Person<string,int>&p){
p.showPerson();}voidtest01(){
Person<string,int>p("孙悟空",199);printPerson1(p);}// 2、参数模板化template<classT1,classT2>voidprintPerson2(Person<T1,T2>&p){
p.showPerson();
cout <<"T1的类型为:"<<typeid(T1).name()<< endl;
cout <<"T2的类型为:"<<typeid(T2).name()<< endl;}voidtest02(){
Person<string,int>p("猪八戒",90);printPerson2(p);}// 3、整个类模板化template<classT>voidprintPerson3(T &p){
p.showPerson();
cout <<"T的类型为:"<<typeid(T).name()<< endl;}voidtest03(){
Person<string,int>p("唐僧",60);printPerson3(p);}intmain(){test01();test02();test03();system("pause");return0;}
运行结果: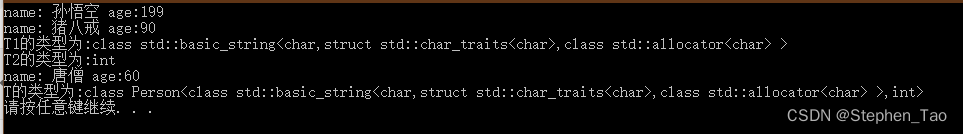
注:使用比较广泛的是指定传入类型的传参方式
5 类模板与继承
当类模板碰到继承时,需要注意以下几点:
- 当子类继承的父类是一个类模板时,子类在声明的时候,要指定出父类中
T的类型 - 如果不指定,编译器无法给子类分配内存
- 如果想灵活指定出父类中
T的类型,子类也需为类模板
示例:
//类模板与继承template<classT>classBase{
T m;};//class Son: public Base //错误,必须要知道父类中的T类型,才能继承给子类classSon:publicBase<int>{};voidtest01(){
Son s1;}//如果想灵活指定父类中T的类型,子类也需要变成类模板template<classT1,classT2>classSon2:publicBase<T2>{public:Son2(){
cout <<"T1的类型为:"<<typeid(T1).name()<< endl;
cout <<"T2的类型为:"<<typeid(T2).name()<< endl;}
T1 obj;};voidtest02(){
Son2<int,char> s2;}intmain(){test02();system("pause");return0;}
6 类模板成员函数类外实现
示例:
//类模板成员类外实现template<classT1,classT2>classPerson{public:Person(T1 name, T2 age);/*{
this->m_Name = name;
this->m_Age = age;
}*/voidshowPerson();/*{
cout << "姓名:" << this->m_Name << " 年龄:" << this->m_Age << endl;
}*/
T1 m_Name;
T2 m_Age;};//构造函数的类外实现template<classT1,classT2>Person<T1, T2>::Person(T1 name, T2 age){this->m_Name = name;this->m_Age = age;}//成员函数的类外实现template<classT1,classT2>voidPerson<T1, T2>::showPerson(){
cout <<"姓名:"<<this->m_Name <<" 年龄:"<<this->m_Age << endl;}voidtest01(){
Person<string,int>p("Tom",30);
p.showPerson();}intmain(){test01();system("pause");return0;}
7 类模板分文件编写
如果工程中需要利用多个类模板,那么将这些类模板都写在同一个文件中将会导致代码可读性变差,所以有必要对类模板进行分文件编写,但是类模板的分文件编写面临着一些问题,以下是类模板分文件编写面临的问题及解决方法。
问题:类模板中成员函数创建时机是在调用阶段,导致分文件编写时链接不到
解决:
- 解决方式1:直接包含
.cpp源文件 - 解决方式2:将声明和实现写到同一个文件中,并更改后缀名为
.hpp,hpp是约定的名称,并不是强制的
示例1:(未进行分文件编写)
template<classT1,classT2>classPerson{public:Person(T1 name, T2 age);/*{
this->m_Name = name;
this->m_Age = age;
}*/voidshowPerson();/*{
cout << "姓名:" << this->m_Name << " 年龄:" << this->m_Age << endl;
}*/
T1 m_Name;
T2 m_Age;};//构造函数的类外实现template<classT1,classT2>Person<T1, T2>::Person(T1 name, T2 age){this->m_Name = name;this->m_Age = age;}//成员函数的类外实现template<classT1,classT2>voidPerson<T1, T2>::showPerson(){
cout <<"姓名:"<<this->m_Name <<" 年龄:"<<this->m_Age << endl;}voidtest01(){
Person<string,int>p("Tom",30);
p.showPerson();}intmain(){test01();system("pause");return0;}
实例2:(进行分文件编写,利用
.cpp
)
1.创建头文件
person.h
,写一些声明
#pragmaonce#include<iostream>usingnamespace std;#include<string>template<classT1,classT2>classPerson{public:Person(T1 name, T2 age);voidshowPerson();
T1 m_Name;
T2 m_Age;};
2.创建
person.cpp
,写具体实现
#include"person.h"//构造函数的类外实现template<classT1,classT2>Person<T1, T2>::Person(T1 name, T2 age){this->m_Name = name;this->m_Age = age;}//成员函数的类外实现template<classT1,classT2>voidPerson<T1, T2>::showPerson(){
cout <<"姓名:"<<this->m_Name <<" 年龄:"<<this->m_Age << endl;}
函数编写main
错误代码:
#include<iostream>usingnamespace std;#include<string>#include"person.h"voidtest01(){
Person<string,int>p("Tom",30);
p.showPerson();}intmain(){test01();system("pause");return0;}
注:因为如果包含
person.h
文件,那么编译器将会看到
person.h
中的代码。但是由于类模板中的成员函数一开始是不创建的,导致编译器没有看到
person.cpp
中的代码,所以执行
test01
时,无法解析其中的代码。
正确代码:(不常用)
#include<iostream>usingnamespace std;#include<string>#include"person.cpp"voidtest01(){
Person<string,int>p("Tom",30);
p.showPerson();}intmain(){test01();system("pause");return0;}
注:就是将
person.h
文件改成了
person.cpp
代码。编译器首先看到了
person.cpp
文件,因为
person.cpp
文件中有
person.h
文件,编译器又看到了
person.h
文件,所以能够解析
test01
中的代码。但是一般很少直接包含
.cpp
文件的,所以这个方法不常用。
实例3:(分文件编写,利用
.hpp
)
将
person.h
和
person.cpp
的内容写到一起,并将后缀名改为
.hpp
,这是类模板分文件编写最常用的方式
1.编写person.hpp文件:
#pragmaonce#include<iostream>usingnamespace std;#include<string>template<classT1,classT2>classPerson{public:Person(T1 name, T2 age);voidshowPerson();
T1 m_Name;
T2 m_Age;};//构造函数的类外实现template<classT1,classT2>Person<T1, T2>::Person(T1 name, T2 age){this->m_Name = name;this->m_Age = age;}//成员函数的类外实现template<classT1,classT2>voidPerson<T1, T2>::showPerson(){
cout <<"姓名:"<<this->m_Name <<" 年龄:"<<this->m_Age << endl;}
2.编写
main
函数
#include<iostream>usingnamespace std;#include<string>#include"person.hpp"voidtest01(){
Person<string,int>p("Tom",30);
p.showPerson();}intmain(){test01();system("pause");return0;}
8 类模板与友元
全局函数类内实现:直接在类内声明友元即可
全局函数类外实现:需要提前让编译器知道全局函数的存在
1.全局函数的类内实现
template<classT1,classT2>classPerson{//全局函数类内实现friendvoidprintPerson(Person<T1, T2> p){
cout <<"姓名:"<< p.m_Name <<" 年龄:"<< p.m_Age << endl;}public:Person(T1 name, T2 age){this->m_Name = name;this->m_Age = age;}private:
T1 m_Name;
T2 m_Age;};voidtest01(){
Person<string,int>p("Tom",30);printPerson(p);}intmain(){test01();system("pause");return0;}
2.全局函数类外实现
//提前让编译器知道Person类的存在template<classT1,classT2>classPerson;//类外实现template<classT1,classT2>voidprintPerson(Person<T1, T2> p){
cout <<"姓名:"<< p.m_Name <<" 年龄:"<< p.m_Age << endl;}template<classT1,classT2>classPerson{//全局函数类外实现 //加空模板参数列表//如果全局函数是类外实现,需要让编译器提前知道这个函数的存在friendvoidprintPerson<>(Person<T1, T2> p);public:Person(T1 name, T2 age){this->m_Name = name;this->m_Age = age;}private:
T1 m_Name;
T2 m_Age;};voidtest01(){
Person<string,int>p("Tom",30);printPerson(p);}intmain(){test01();system("pause");return0;}
注:需要注意各个函数声明之间的顺序。在
Person
类模板中有友元的声明
friend void printPerson<>(Person<T1, T2> p)
,因为类模板中友元的类外实现需要让编译器提前知道这个函数,所以需要将
printPerson
函数写在前面。而
printPerson
函数中又涉及
Person
类,所以在
printPerson
函数前面需要提前声明
Person
类模板的存在。
总结:建议全局函数做类内实现,用法简单,而且编译器可以直接识别。
9 类模板案例
案例描述:
- 可以对内置数据类型以及自定义数据类型的数据进行存储
- 将数组中的数据存储到堆区
- 构造函数中可以传入数组的容量
- 提供对应的拷贝构造函数以及
operator=防止浅拷贝的问题 - 提供尾插法和尾删法对数组中的数据进行增加和删除
- 可以通过下标的方式访问数组中的元素
- 可以获取数组中当前元素个数和数组的容量
MyArray.hpp
文件:
#pragmaonce#include<iostream>usingnamespace std;template<classT>classMyArray{public://构造函数MyArray(int capacity){
cout <<"MyArray有参构造的调用"<< endl;this->m_Capacity = capacity;this->pAdress =new T[this->m_Capacity];this->m_Size =0;}//析构函数~MyArray(){if(this->pAdress !=NULL){
cout <<"MyArray析构的调用"<< endl;delete[]this->pAdress;this->pAdress =NULL;}}//拷贝构造MyArray(const MyArray& arr){
cout <<"MyArray拷贝构造的调用"<< endl;this->m_Capacity = arr.m_Capacity;this->m_Size = arr.m_Size;//深拷贝this->pAdress =new T[arr.m_Capacity];//将arr中的数据都拷贝过来for(int i =0; i <this->m_Size; i++){this->pAdress[i]= arr.pAdress[i];}}//operator= 防止浅拷贝问题
MyArray&operator=(const MyArray& arr){
cout <<"MyArray的operator=调用"<< endl;//先判断原来堆区是否有数据,如果有先释放if(this->pAdress !=NULL){delete[]this->pAdress;this->pAdress =NULL;this->m_Capacity =0;this->m_Size =0;}this->m_Capacity = arr.m_Capacity;this->m_Size = arr.m_Size;//深拷贝this->pAdress =new T[arr.m_Capacity];//将arr中的数据都拷贝过来for(int i =0; i <this->m_Size; i++){this->pAdress[i]= arr.pAdress[i];}return*this;}//尾插法voidPush_Back(const T& val){//判断容量是否等于大小if(this->m_Size ==this->m_Capacity){return;}this->pAdress[this->m_Size]= val;//在数组末尾插入数据this->m_Size++;//更新数组大小}//尾删法voidPop_Back(){//让用户访问不到最后一个元素即为尾删法 if(this->m_Size ==0){return;}this->m_Size--;}//通过下标方式访问数组中的元素
T&operator[](int index)//以引用作为返回值是为了能够做arr[0]=100这样的操作{returnthis->pAdress[index];}//返回数组容量intgetCapacity(){returnthis->m_Capacity;}//返回数组大小intgetSize(){returnthis->m_Size;}private:
T *pAdress;//指针指向堆区开辟的真实数组int m_Capacity;//数组容量int m_Size;//数组大小};
main
文件:
#include<iostream>usingnamespace std;#include"MyArray.hpp"#include<string>voidprintIntArray(MyArray<int>& arr1){for(int i =0; i < arr1.getSize(); i++){
cout << arr1[i]<<" ";}
cout << endl;}voidtest01(){
MyArray<int>arr1(5);
MyArray<int>arr2(arr1);
MyArray<int>arr3(100);
arr3 = arr1;
cout <<"--------------------"<< endl;
MyArray<int>arr4(5);for(int i =0; i <5; i++){//通过尾插法向数组中插入数据
arr4.Push_Back(i);}
cout <<"arr4的打印输出为:"<< endl;printIntArray(arr4);
cout <<"arr4的容量为:"<< arr4.getCapacity()<< endl;
cout <<"arr4的大小为:"<< arr4.getSize()<< endl;
MyArray<int>arr5(arr4);
cout <<"arr5的打印输出为:"<< endl;printIntArray(arr5);//尾删法
arr5.Pop_Back();
cout <<"arr5尾删后的打印输出为:"<< endl;printIntArray(arr5);}//测试自定义类型classPerson{public:Person(){}Person(string name,int age){this->m_Age = age;this->m_Name = name;}
string m_Name;int m_Age;};voidprintPersonArray(MyArray<Person>& arr){for(int i =0; i < arr.getSize(); i++){
cout <<"Name: "<< arr[i].m_Name <<" Age: "<< arr[i].m_Age << endl;}}voidtest02(){
MyArray<Person>arr(10);
Person p1("Tom",12);
Person p2("Jack",15);
Person p3("Bill",17);//数据插入到数组中
arr.Push_Back(p1);
arr.Push_Back(p2);
arr.Push_Back(p3);printPersonArray(arr);
cout <<"arr的容量为:"<< arr.getCapacity()<< endl;
cout <<"arr的大小为:"<< arr.getSize()<< endl;}intmain(){test01();
cout <<"=========="<< endl;test02();system("pause");return0;}
运行结果: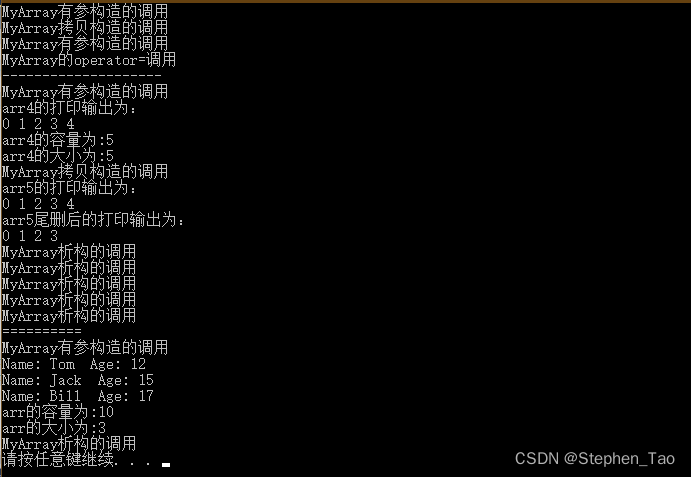
注:本文参考b站黑马程序员c++课程
版权归原作者 Stephen_Tao 所有, 如有侵权,请联系我们删除。