1. Hbase安装
**1.1 **安装zookeeper、 hbase
解压至/opt/soft,并分别改名
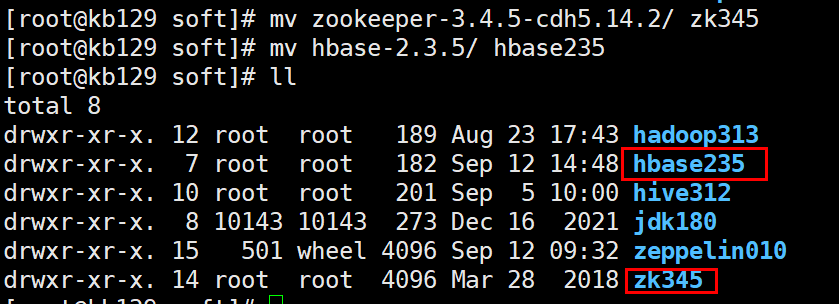
配置环境变量并source生效
#ZK
export ZOOKEEPER_HOME=/opt/soft/zk345
export PATH=$ZOOKEEPER_HOME/bin:$PATH
#HBASE_HOME
export HBASE_HOME=/opt/soft/hbase235
export PATH=$HBASE_HOME/bin:$PATH
hbase235/conf****目录下的
编辑hbase-env.sh:[root@kb129 conf]# vim ./hbase-env.sh
export JAVA_HOME=/opt/soft/jdk180
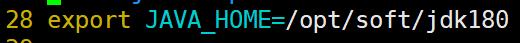

编辑hbase-site.xml
[root@kb129 conf]# vim ./hbase-site.xml
<property>
<name>hbase.rootdir</name>
<value>hdfs://192.168.142.129:9000/hbase</value>
</property>
<property>
<name>hbase.cluster.distributed</name>
<value>true</value>
</property>
<property>
<name>hbase.zookeeper.property.dataDir</name>
<value>/opt/soft/zk345/zkdata</value>
</property>
<property>
<name>hbase.zookeeper.property.clientPort</name>
<value>2181</value>
</property>
拷贝配置文件准备配置zookeeper
[root@kb129 conf]# pwd
/opt/soft/zk345/conf
[root@kb129 conf]# cp zoo_sample.cfg zoo.cfg
创建目录
[root@kb129 conf]# mkdir /opt/soft/zk345/logs
[root@kb129 conf]# mkdir /opt/soft/zk345/zkdata
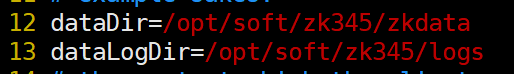
编辑配置文件,增加目录指向
[root@kb129 conf]# vim ./zoo.cfg
dataDir=/opt/soft/zk345/zkdata
dataLogDir=/opt/soft/zk345/logs
server.0=192.168.142.129:2287:3387

追加节点id
[root@kb129 conf]# cd ../zkdata/
[root@kb129 zkdata]# echo "0">myid
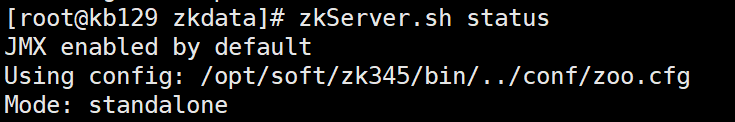
启动zookeeper
[root@kb129 zkdata]# zkServer.sh start
启动hbase
(启动前解决Hbase和hadoop中log4j的jar包冲突报错问题:将Hbase中的jar包改名就不会读取,解决掉冲突报错:mv /opt/soft/hbase235/lib/client-facing-thirdparty/slf4j-log4j12-1.7.30.jar /opt/soft/hbase235/lib/client-facing-thirdparty/slf4j-log4j12-1.7.30.jar.bak)
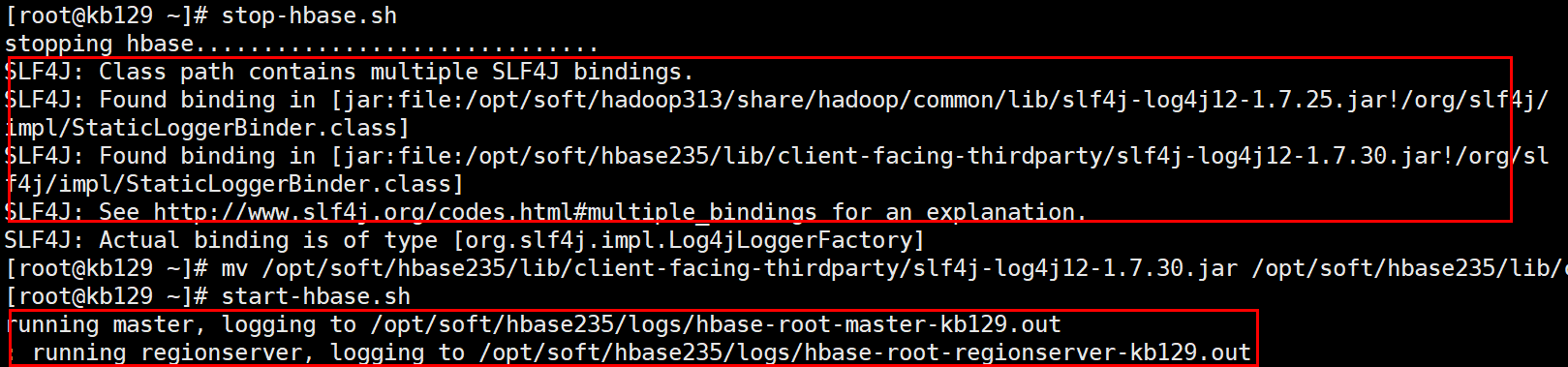
[root@kb129 zkdata]# start-hbase.sh


hbase宕机恢复操作(此操作会删除hbase中数据,慎用!!!)
(1)执行stop-hbase.sh关闭hbase进程,或通过kill杀死进程
(2)确保hadoop和zookeeper正常运行状态下,进入zookeeper客户端:zkCli.sh
(3)删除hbase:rmr /hbase,删除后:ls / ,查看是否已经删除
(4)进入hdfs系统,删除hbase指向目录/hbase
(5)执行start-hbase.sh,成功恢复hbase
2.Hbase shell相关操作
[root@kb129 conf]# hbase shell
创建命名空间
hbase(main):001:0> create_namespace 'kb23'
查看命名空间
**hbase(main):001:0>list _namespace **
 ** **
** **
创建表
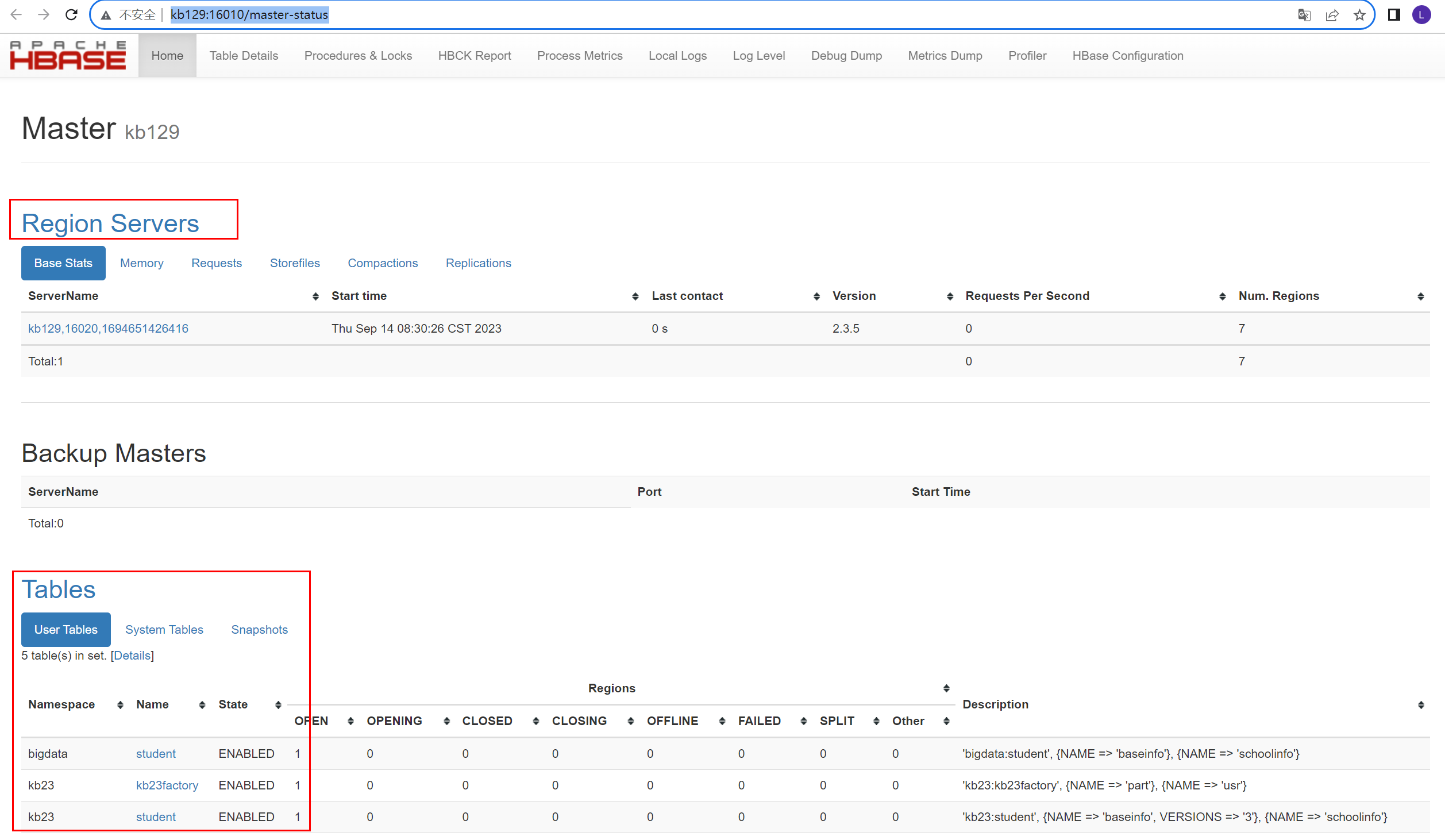
hbase(main):007:0> create 'bigdata:student','baseinfo','schoolinfo'
查看表
hbase(main):008:0> list_namespace_tables 'bigdata'
查看描述
hbase(main):009:0> desc 'bigdata:student'
删除表之前先禁用表
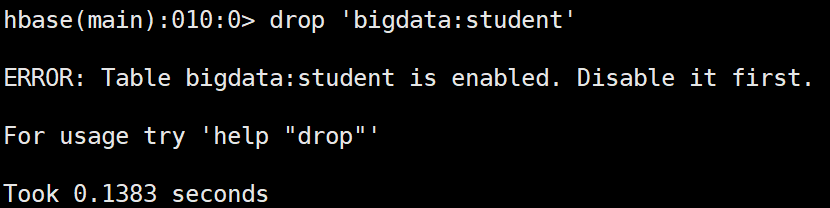
禁用表
hbase(main):011:0> disable 'bigdata:student'
查看是否禁用/启用
hbase(main):011:0> is_disabled/is_enabled 'bigdata:student'
启用表
hbase(main):011:0> enable 'bigdata:student'
插入数据(原有数据的话会覆盖)
hbase(main):006:0> put 'bigdata:student','rowkey1','baseinfo:name','tom'
查看指定rowkey的所有数据
hbase(main):008:0> get 'bigdata:student','rowkey1'
**COLUMN CELL **
** baseinfo:age timestamp=2023-09-13T14:21:26.095, value=30 **
** baseinfo:name timestamp=2023-09-13T14:21:22.385, value=tom **
查看指定列族数据
hbase(main):011:0> get 'bigdata:student','rowkey1','baseinfo'
**COLUMN CELL **
** baseinfo:age timestamp=2023-09-13T14:21:26.095, value=30 **
** baseinfo:name timestamp=2023-09-13T14:21:22.385, value=tom **
查看指定列族中某列数据
hbase(main):012:0> get 'bigdata:student','rowkey1','baseinfo:name'
**COLUMN CELL **
** baseinfo:name timestamp=2023-09-13T14:21:22.385, value=tom**
添加列族
hbase(main):021:0> alter 'kb23:student','teacherinfo'
删除列族
hbase(main):023:0> alter 'kb23:student',{NAME=>'teacherinfo',METHOD=>'delete'}
更改版本个数(VERSIONS默认为1)
hbase(main):026:0> alter 'kb23:student',{NAME=>'baseinfo',VERSIONS=>3}
全表扫描
hbase(main):027:0> scan 'kb23:student'
删除指定列族中的列
hbase(main):055:0> delete 'kb23:student','rowkey2','baseinfo:name'
删除所有rowkey2信息
hbase(main):060:0> deleteall 'kb23:student','rowkey2'
查看不同版本信息
hbase(main):070:0> get 'kb23:student','rowkey1',COLUMN=>'baseinfo:name',VERSIONS=>3
查看范围内rowkey的数据(左闭右开)
hbase(main):094:0> scan 'kb23:student', {COLUMNS => 'baseinfo:name', STARTROW => 'rowkey',STOPROW=> 'rowkey3'}
查看时使用limit
hbase(main):096:0> scan 'kb23:student', {COLUMNS => 'baseinfo:name', STARTROW => 'rowkey',STOPROW=> 'rowkey3', VERSIONS=> 3, LIMIT=> 1}
过滤查找value包含11开头的信息(可查到多个版本)
hbase(main):099:0> scan 'kb23:student',FILTER=>"ValueFilter(=,'binary:11')"
过滤查找value包含andemen开头的信息(可查到多个版本)
hbase(main):102:0> scan 'kb23:student',FILTER=>"ValueFilter(=,'substring:andemen')"
过滤查找列名birth开头的信息(可查到多个版本)
hbase(main):104:0> scan 'kb23:student',FILTER=>"ColumnPrefixFilter('birth')"
多条件AND查询
hbase(main):110:0> scan 'kb23:student',FILTER=>"ColumnPrefixFilter('birth') AND ValueFilter(=,'substring:200')"
AND****或OR查询
hbase(main):005:0>scan 'kb23:student',FILTER=>"ColumnPrefixFilter('birth') AND (ValueFilter(=,'substring:200')) OR ValueFilter(=,'substring:20')"
3.Hbase运行原理
*3.1 HBase***物理架构 **

*1***)StoreFile **
保存实际数据的物理文件,StoreFile以Hfile的形式存储在HDFS上。每个Store会有一个或多个StoreFile(HFile),数据在每个StoreFile中都是有序的。
2****)MemStore
写缓存,由于HFile中的数据要求是有序的,所以数据是先存储在MemStore中,排好序后,等到达刷写时机才会刷写到HFile,每次刷写都会形成一个新的HFile。
3****)WAL
由于数据要经MemStore排序后才能刷写到HFile,但把数据保存在内存中会有很高的概率导致数据丢失,为了解决这个问题,数据会先写在一个叫做Write-Ahead logfile的文件中,然后再写入MemStore中。所以在系统出现故障的时候,数据可以通过这个日志文件重建。
4****)BlockCache
读缓存,每次查询出的数据会缓存在BlockCache中,方便下次查询。
**3.2 **写流程

1)Client先访问zookeeper,获取hbase:meta表位于哪个Region Server。
2)访问对应的Region Server,获取hbase:meta表,根据写请求的namespace:table/rowkey,查询出目标数据位于哪个Region Server中的哪个Region中。并将该table的region信息以及meta表的位置信息缓存在客户端的meta cache,方便下次访问。
3)与目标Region Server进行通讯;
4)将数据顺序写入(追加)到WAL;
5)将数据写入对应的MemStore,数据会在MemStore进行排序;
6)向客户端发送ack;
7)等达到MemStore的刷写时机后,将数据刷写到HFile。
3.3 MemStore Flush

MemStore****刷写时机:
**1.**当某个memstroe的大小达到了hbase.hregion.memstore.flush.size(默认值128M),其所在region的所有memstore都会刷写。
当memstore的大小达到了
hbase.hregion.memstore.flush.size***(默认值128M) hbase.hregion.memstore.block.multiplier(默认值4)时,会阻止继续往该memstore写数据。
**2.**当region server中memstore的总大小达到
java_heapsizehbase.regionserver.global.memstore.size**(默认值0.4)hbase.regionserver.global.memstore.size.lower.limit(默认值0.95),
region****会按照其所有memstore的大小顺序(由大到小)依次进行刷写。直到region server中所有memstore的总大小减小到上述值以下。
当region server中memstore的总大小达到
java_heapsizehbase.regionserver.global.memstore.size***(默认值0.4)时,会阻止继续往所有的memstore写数据。
**3. **到达自动刷写的时间,也会触发memstore flush。自动刷新的时间间隔由该属性进行配置hbase.regionserver.optionalcacheflushinterval(默认1小时)。
**4.**当WAL文件的数量超过hbase.regionserver.max.logs,region会按照时间顺序依次进行刷写,直到WAL文件数量减小到hbase.regionserver.max.log以下(该属性名已经废弃,现无需手动设置,最大值为32)。
**3.4 **读流程


1)Client先访问zookeeper,获取hbase:meta表位于哪个Region Server。
2)访问对应的Region Server,获取hbase:meta表,根据读请求的namespace:table/rowkey,查询出目标数据位于哪个Region Server中的哪个Region中。并将该table的region信息以及meta表的位置信息缓存在客户端的meta cache,方便下次访问。
3)与目标Region Server进行通讯;
4)分别在MemStore和Store File(HFile)中查询目标数据,并将查到的所有数据进行合并。此处所有数据是指同一条数据的不同版本(time stamp)或者不同的类型(Put/Delete)。
5)将查询到的新的数据块(Block,HFile数据存储单元,默认大小为64KB)缓存到Block Cache。
6)将合并后的最终结果返回给客户端。
3.5 StoreFile Compaction
由于memstore每次刷写都会生成一个新的HFile,且同一个字段的不同版本(timestamp)和不同类型(Put/Delete)有可能会分布在不同的HFile中,因此查询时需要遍历所有的HFile。为了减少HFile的个数,以及清理掉过期和删除的数据,会进行StoreFile Compaction。
Compaction****分为两种,分别是Minor Compaction和Major Compaction。Minor Compaction会将临近的若干个较小的HFile合并成一个较大的HFile,并清理掉部分过期和删除的数据。Major Compaction会将一个Store下的所有的HFile合并成一个大HFile,并且会清理掉所有过期和删除的数据。

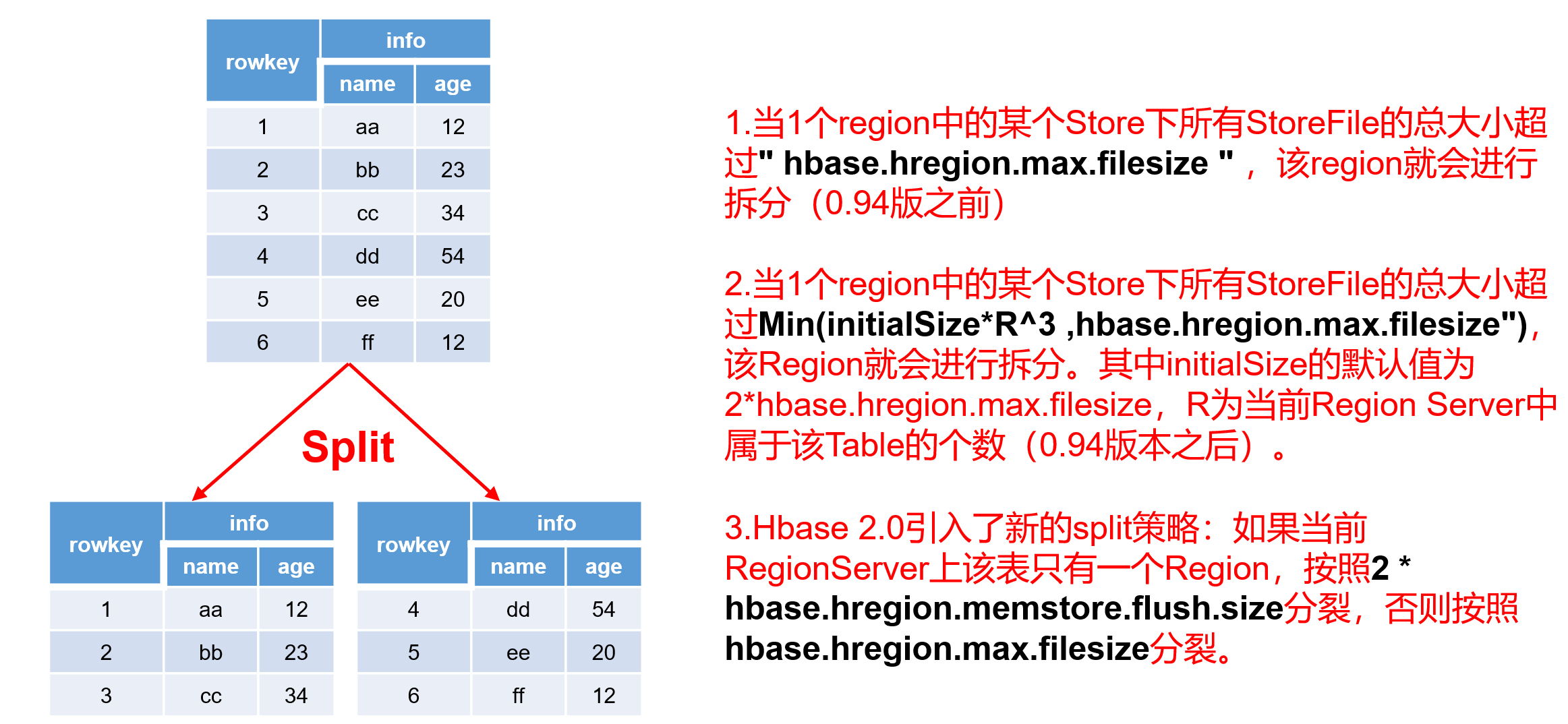
3.6 Region Split
默认情况下,每个Table起初只有一个Region,随着数据的不断写入,Region会自动进行拆分。刚拆分时,两个子Region都位于当前的Region Server,但处于负载均衡的考虑,HMaster有可能会将某个Region转移给其他的Region Server。
Region Split****时机:
**1.**当1个region中的某个Store下所有StoreFile的总大小超过hbase.hregion.max.filesize (10G),该Region就会进行拆分(0.94版本之前)。
**2.*当1个region中的某个Store下所有StoreFile的总大小超过Min(initialSizeR^3 ,hbase.hregion.max.filesize"),该Region就会进行拆分。其中initialSize的默认值为2*hbase.hregion.memstore.flush.size,R为当前Region Server中属于该Table的Region个数(0.94版本之后)。
具体的切分策略为:
**第一次split:1^3 * 256 = 256MB **
**第二次split:2^3 * 256 = 2048MB **
**第三次split:3^3 * 256 = 6912MB **
**第四次split:4^3 * 256 = 16384MB > 10GB,因此取较小的值10GB **
后面每次split的size都是10GB了。
3.Hbase 2.0****引入了新的split策略:如果当前RegionServer上该表只有一个Region,按照2 * hbase.hregion.memstore.flush.size分裂,否则按照hbase.hregion.max.filesize分裂。
4.hive映射hbase
hive****中创建表格,关联hbase中的表
(1)

create external table student(
id string,
stuname string,
birthdate string,
age int,
schoolname string,
location string
)
stored by 'org.apache.hadoop.hive.hbase.HBaseStorageHandler' with
serdeproperties
('hbase.columns.mapping'=':key,baseinfo:name,baseinfo:birthday,baseinfo:age,schoolinfo:name,schoolinfo:location')
tblproperties ('hbase.table.name'='kb23:student');
select * from student;
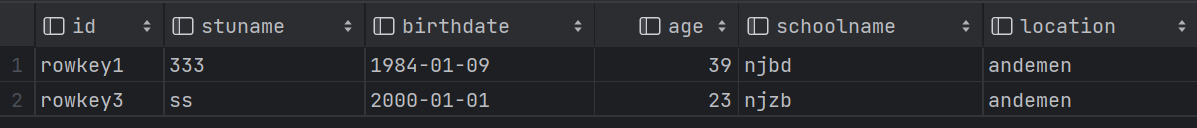
(2)rowkey之间不同字段
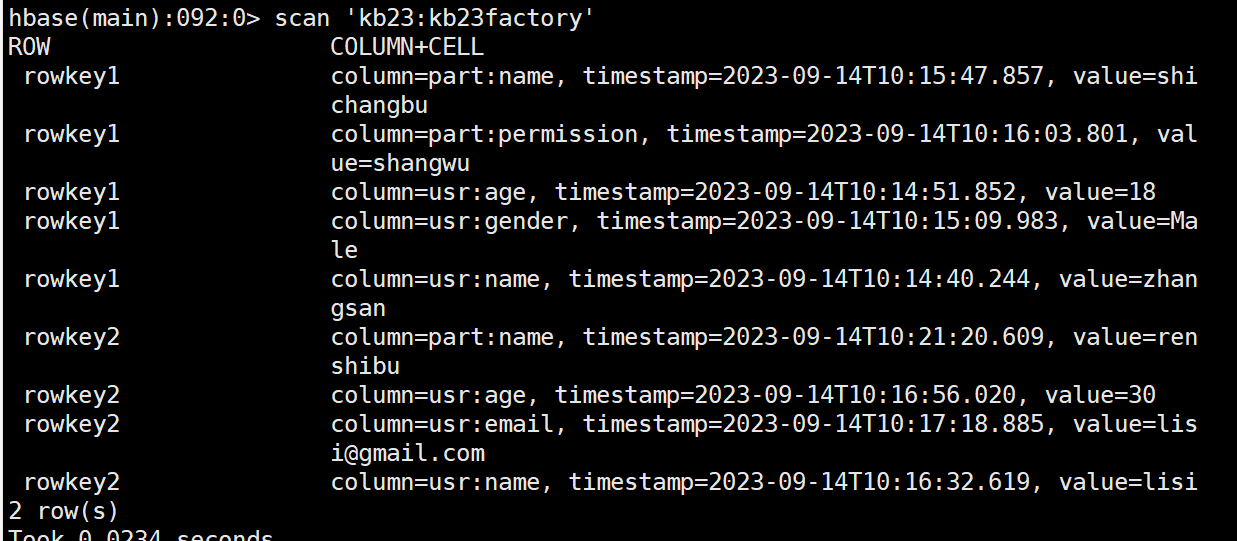
create external table kb23factory(
id string,
usrname string,
age string,
gender string,
email string,
partname string,
permission string
)
stored by 'org.apache.hadoop.hive.hbase.HBaseStorageHandler' with
serdeproperties
('hbase.columns.mapping'=':key,usr:name,usr:age,usr:gender,usr:email,part:name,part:permission')
tblproperties ('hbase.table.name'='kb23:kb23factory');
select * from kb23factory;

5.Hbase API
5.1 pom****依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.hbase</groupId>
<artifactId>hbase-client</artifactId>
<version>2.3.5</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.hbase</groupId>
<artifactId>hbase-common</artifactId>
<version>2.3.5</version>
</dependency>
**5.2 **增删改查等具体操作
import org.apache.hadoop.conf.Configuration;
import org.apache.hadoop.hbase.HBaseConfiguration;
import org.apache.hadoop.hbase.HColumnDescriptor;
import org.apache.hadoop.hbase.HTableDescriptor;
import org.apache.hadoop.hbase.TableName;
import org.apache.hadoop.hbase.client.*;
import org.apache.hadoop.hbase.filter.BinaryComparator;
import org.apache.hadoop.hbase.filter.CompareFilter;
import org.apache.hadoop.hbase.filter.FamilyFilter;
import org.apache.hadoop.hbase.util.Bytes;
import org.junit.After;
import org.junit.Before;
import org.junit.Test;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.ArrayList;
/**
* Unit test for simple App.
*/
public class AppTest {
private Connection connection = null;
// 获取配置类
private Configuration config = HBaseConfiguration.create();
//创建连接
@Before
public void init() throws IOException {
// 给配置类添加配置
config.set("hbase.zookeeper.quorum", "kb129");
config.set("hbase.zookeeper.property.clientPort", "2181");
// 获取连接
connection = ConnectionFactory.createConnection(config);
}
//打印连接,测试连接
@Test
public void testConnection() throws IOException {
System.out.println(connection);
}
//创建表
@Test
public void createTable() throws IOException {
// 获取admin
Admin admin = connection.getAdmin();
TableName tableName = TableName.valueOf("kb23:test2");
/*HTableDescriptor desc = new HTableDescriptor(tableName);
HColumnDescriptor family1 = new HColumnDescriptor("info");
HColumnDescriptor family2 = new HColumnDescriptor("info2");
desc.addFamily(family1);
desc.addFamily(family2);*/
// 获取descriptor的builder
TableDescriptorBuilder tableDescriptorBuilder = TableDescriptorBuilder.newBuilder(tableName);
// 添加列族
ColumnFamilyDescriptor columnFamilyDescriptor1 = ColumnFamilyDescriptorBuilder.of("baseinfo");
ColumnFamilyDescriptor columnFamilyDescriptor2 = ColumnFamilyDescriptorBuilder.of("schoolinfo");
// 将单个列族的descriptor添加到builder中
tableDescriptorBuilder.setColumnFamily(columnFamilyDescriptor1);
tableDescriptorBuilder.setColumnFamily(columnFamilyDescriptor2);
TableDescriptor descriptor = tableDescriptorBuilder.build();
//创建表
admin.createTable(descriptor);
}
//插入数据
@Test
public void putValue() throws IOException {
// 1.获取table
Table table = connection.getTable(TableName.valueOf("kb23:test1"));
// 2.创建Put对象
Put put = new Put(Bytes.toBytes("liuxin"));
// 3.添加put属性
put.addColumn(Bytes.toBytes("info"), Bytes.toBytes("name"), Bytes.toBytes("刘鑫"));
put.addColumn(Bytes.toBytes("info"), Bytes.toBytes("gender"), Bytes.toBytes("Male"));
put.addColumn(Bytes.toBytes("info"), Bytes.toBytes("height"), Bytes.toBytes("180"));
// 4.put数据
table.put(put);
// 5.关闭资源
table.close();
}
//通过集合插入多条数据
@Test
public void putValueList() throws IOException {
// 1.获取table
Table table = connection.getTable(TableName.valueOf("kb23:test1"));
// 2.创建Put对象
Put zs = new Put(Bytes.toBytes("zhangsan"));
// 3.添加put属性
zs.addColumn(Bytes.toBytes("info"), Bytes.toBytes("name"), Bytes.toBytes("张三"));
zs.addColumn(Bytes.toBytes("info"), Bytes.toBytes("gender"), Bytes.toBytes("Female"));
zs.addColumn(Bytes.toBytes("info"), Bytes.toBytes("height"), Bytes.toBytes("160"));
Put ls = new Put(Bytes.toBytes("lisi"));
// 3.添加put属性
ls.addColumn(Bytes.toBytes("info"), Bytes.toBytes("name"), Bytes.toBytes("李四"));
ls.addColumn(Bytes.toBytes("info"), Bytes.toBytes("gender"), Bytes.toBytes("Male"));
ls.addColumn(Bytes.toBytes("info"), Bytes.toBytes("height"), Bytes.toBytes("180"));
// 4.put数据
ArrayList<Put> puts = new ArrayList<Put>();
puts.add(zs);
puts.add(ls);
table.put(puts);
// 5.关闭资源
table.close();
}
@Test
public void putValueMutator() throws IOException {
BufferedMutatorParams bufferedMutatorParams = new BufferedMutatorParams(TableName.valueOf("kb23:test1 "));
bufferedMutatorParams.setWriteBufferPeriodicFlushTimeoutMs(10000);//设置超时flush时间最大值
bufferedMutatorParams.writeBufferSize(10*1024*1024);//设置缓存大小flush
BufferedMutator bufferedMutator = connection.getBufferedMutator(bufferedMutatorParams) ;
/*// 3.添加put属性
Put zs = new Put(Bytes.toBytes("zhangsan"));
zs.addColumn(Bytes.toBytes("info"), Bytes.toBytes("name"), Bytes.toBytes("张三"));
zs.addColumn(Bytes.toBytes("info"), Bytes.toBytes("gender"), Bytes.toBytes("Female"));
zs.addColumn(Bytes.toBytes("info"), Bytes.toBytes("height"), Bytes.toBytes("160"));
Put ls = new Put(Bytes.toBytes("lisi"));
// 3.添加put属性
ls.addColumn(Bytes.toBytes("info"), Bytes.toBytes("name"), Bytes.toBytes("李四"));
ls.addColumn(Bytes.toBytes("info"), Bytes.toBytes("gender"), Bytes.toBytes("Male"));
ls.addColumn(Bytes.toBytes("info"), Bytes.toBytes("height"), Bytes.toBytes("180"));*/
// 4.put数据
ArrayList<Put> puts = new ArrayList<Put>();
//puts.add(zs);
//puts.add(ls);
bufferedMutator.mutate(puts);
}
//删除数据
@Test
public void delete() throws IOException {
// 1.获取table
Table table = connection.getTable(TableName.valueOf("kb23:test1"));
//删除具体的列
/*Delete delname = new Delete(Bytes.toBytes("lisi"));
delname.addColumn(Bytes.toBytes("info"),Bytes.toBytes("name"));
table.delete(delname);*/
//通过rowkey整个删除
Delete lisi = new Delete(Bytes.toBytes("lisi"));
table.delete(lisi);
}
//查询数据
@Test
public void getValue() throws IOException {
// 1.获取table
Table table = connection.getTable(TableName.valueOf("kb23:test1"));
// 2.获取Get对象
Get zhangsan = new Get(Bytes.toBytes("zhangsan"));
// 3. 获取result
Result result = table.get(zhangsan);
byte[] name = result.getValue(Bytes.toBytes("info"), Bytes.toBytes("name"));
byte[] gender = result.getValue(Bytes.toBytes("info"), Bytes.toBytes("gender"));
byte[] height = result.getValue(Bytes.toBytes("info"), Bytes.toBytes("height"));
System.out.println(Bytes.toString(name) + Bytes.toString(gender) + Bytes.toString(height));
}
//扫描数据
@Test
public void scanValue() throws IOException {
// 1.获取table
Table table = connection.getTable(TableName.valueOf("kb23:test1"));
// 2.创建Scan对象
Scan scan = new Scan();
// 3.扫描数据
scan.addColumn(Bytes.toBytes("info"), Bytes.toBytes("name"));
scan.addColumn(Bytes.toBytes("info"), Bytes.toBytes("gender"));
scan.addColumn(Bytes.toBytes("info"), Bytes.toBytes("height"));
ResultScanner scanner = table.getScanner(scan);
// 4.获取结果
for (Result result : scanner) {
byte[] name = result.getValue(Bytes.toBytes("info"), Bytes.toBytes("name"));
byte[] gender = result.getValue(Bytes.toBytes("info"), Bytes.toBytes("gender"));
byte[] height = result.getValue(Bytes.toBytes("info"), Bytes.toBytes("height"));
System.out.println(Bytes.toString(name) + Bytes.toString(gender) + Bytes.toString(height));
}
}
//过滤器,查找数据
@Test
public void getFilterRowKey() throws IOException {
TableName tableName = TableName.valueOf("kb23:student");
Table table = connection.getTable(tableName);
FamilyFilter familyFilter =
new FamilyFilter(CompareFilter.CompareOp.EQUAL, new BinaryComparator(Bytes.toBytes("baseinfo")));
Scan scan = new Scan();
scan.setFilter(familyFilter);
ResultScanner scanner = table.getScanner(scan);
for (Result result : scanner) {
byte[] name = result.getValue(Bytes.toBytes("baseinfo"), Bytes.toBytes("name"));
byte[] age = result.getValue(Bytes.toBytes("baseinfo"), Bytes.toBytes("age"));
byte[] birthday = result.getValue(Bytes.toBytes("baseinfo"), Bytes.toBytes("birthday"));
System.out.println(Bytes.toString(name) + "\t" + Bytes.toString(age) + "\t" + Bytes.toString(birthday));
System.out.println("----------------------");
}
}
//关闭连接
@After
public void closeConnection() throws IOException {
if (connection != null) {
// 关闭连接
connection.close();
}
}
}
**5.3 **写缓存 HBase客户端的批量写缓存BufferedMutator
HBase****的每一个put操作实际上是一个RPC操作,将客户端的数据传输到服务器再返回结果,这只适用于小数据量的操作,如果数据量多的话,每次put都需要建立一次RPC的连接(TCP连接),而建立连接传输数据是需要时间的,因此减少RPC的调用可以提高数据传输的效率,减少建立连接的时间和IO消耗。
HBase****的客户端API提供了写缓存区,put的数据一开始放在缓存区内,当数量到达指定的容量或者用户强制提交是才将数据一次性提交到HBase的服务器。这个缓冲区可以通过调用 HTable.setAutoFlush(false) 来开启。而新版HBbase的API中使用了BufferedMutator替换了老版的缓冲区,通过BufferedMutator对象提交的数据自动存放在缓冲区中。
BufferedMutator
通过获取 BufferedMutator 对象,并调用 mutator.mutate(List<Mutation> mutations) 方法来进行批量插入数据。可以使用 Put 类型的对象列表作为 mutations 参数进行插入。BufferedMutator 提供了自动管理缓冲区和写入操作的功能,可以提高插入数据的性能。
@Test
public void putValueMutator() throws IOException {
BufferedMutatorParams bufferedMutatorParams = new BufferedMutatorParams(TableName.valueOf("kb23:test1 "));
bufferedMutatorParams.setWriteBufferPeriodicFlushTimeoutMs(10000);//设置超时flush时间最大值
bufferedMutatorParams.writeBufferSize(10*1024*1024);//设置缓存大小flush
BufferedMutator bufferedMutator = connection.getBufferedMutator(bufferedMutatorParams) ;
/*// 3.添加put属性
Put zs = new Put(Bytes.toBytes("zhangsan"));
zs.addColumn(Bytes.toBytes("info"), Bytes.toBytes("name"), Bytes.toBytes("张三"));
zs.addColumn(Bytes.toBytes("info"), Bytes.toBytes("gender"), Bytes.toBytes("Female"));
zs.addColumn(Bytes.toBytes("info"), Bytes.toBytes("height"), Bytes.toBytes("160"));
Put ls = new Put(Bytes.toBytes("lisi"));
// 3.添加put属性
ls.addColumn(Bytes.toBytes("info"), Bytes.toBytes("name"), Bytes.toBytes("李四"));
ls.addColumn(Bytes.toBytes("info"), Bytes.toBytes("gender"), Bytes.toBytes("Male"));
ls.addColumn(Bytes.toBytes("info"), Bytes.toBytes("height"), Bytes.toBytes("180"));*/
// 4.put数据
ArrayList<Put> puts = new ArrayList<Put>();
//puts.add(zs);
//puts.add(ls);
bufferedMutator.mutate(puts);
}
版权归原作者 不吃香菜lw 所有, 如有侵权,请联系我们删除。