1.3 应用场景:
①适用于较小规模的系统,实时性要求较高的场景。
②适用于轻量级的任务调度和消息通知场景,适合短期延迟任务,不适合长期任务,例如订单超时未支付等。
### 2. Kafka
2.1 优点:
①Kafka的优点在于其高并发、高吞吐量和可扩展性强,同时支持分片。
②可靠性高,支持分布式和消息持久化。
③消费者可以随时回溯消费。
④支持多个消费者并行消费、消费者组等机制。
2.2 缺点:
①没有原生的延迟队列功能,需要使用topic和消费者组来实现,实现延迟队列需要额外的开发工作。
②消费者需要主动拉取数据,可能会导致延迟,精度不是特别高。
在此案例中代码已经实现了,直接拿来使用就可以了。
2.3 应用场景:
适用于大规模的数据处理,实时性要求较高的,高吞吐量的消息处理场景。
### 3. RabbitMQ
3.1 优点:
①RabbitMQ的延迟队列是通过RabbitMQ的插件实现的,易于部署和使用。
②RabbitMQ的延迟队列支持消息重试和消息顺序处理,可靠性较高。
③支持消息持久化和分布式。
④支持优先级队列和死信队列。
⑤提供了丰富的插件和工具。
3.2 缺点:
①RabbitMQ的延迟队列性能较低,不适用于高吞吐量的场景。
②性能较低,不适合高并发场景。
③实现延迟队列需要额外的配置,但是配置就很简单了。
3.3应用场景:
适用于中小型的任务调度和消息通知,对可靠性要求高的场景。
### 4. RocketMQ
4.1 优点:
①RocketMQ的延迟队列是RocketMQ原生支持的,易于使用和部署。
②RocketMQ的延迟队列支持消息重试和消息顺序处理,可靠性较高。
③高性能和高吞吐量,支持分布式和消息持久化。
④RocketMQ使用简单,性能好,并且支持延迟队列功能。
4.2 缺点:
①RocketMQ的延迟队列不支持动态添加或删除队列。
②RocketMQ的延迟队列需要保证消息的顺序,可能会导致消息延迟。
③在节点崩溃后,RocketMQ有可能发生消息丢失。
4.3 应用场景:
①适用于大规模的数据处理,对性能和吞吐量要求较高的场景。
②适合于任务量较大、需要延迟消息和定时消息的场景。例如电商平台、社交软件等。
③适用于分布式任务调度和高可靠性消息通知场景。
## 四、Kafka延时队列背景
1. 基于以上四种实现延时队列的分析来,选择对应的技术方案的基础上呢,不同公司的mq的基础设施不同,如果只有Kafka,也没必要引入RabbitMQ和RocketMq来实现,引入新的组件也会顺便带来新的问题。
2. 网上搜Kafka实现延时队列有很多文章,很多文章说使用Kafka内部的时间轮,支持延时操作,但这是Kafka自己内部使用的,时间轮只是一个工具类,用户无法将其作为延迟队列来使用。
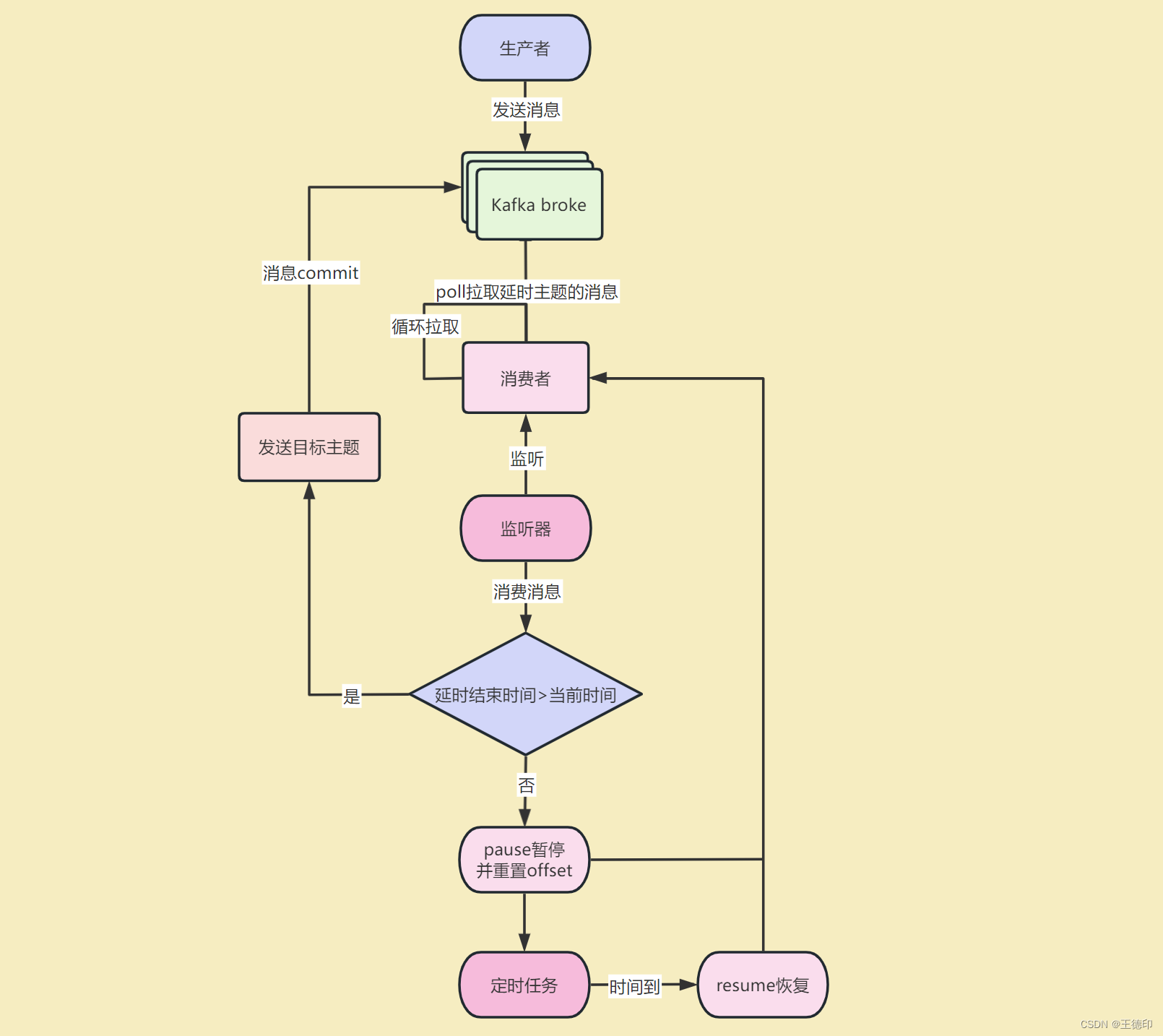
3. Kafka延时队列的最佳实践,**使用Kafka消费者的暂停和恢复机制来实现**。
## 五、Kafka延时队列实现思路
1. 解决一个问题前首先要明确问题,如何让Kafka有延时队列的功能呢?
2. 就是在Kafka消费者消费的时候延时消费,不久搞定了嘛
3. 那如何延时消费呢,网上有些文章使用Thread.sleep进行延时消费这是不靠谱的(亲身实践),sleep的时间超过了Kafka配置的max.poll.records时间,消费者无法及时提交offset,kafka就会认为这个消费者已经挂了,会进行rebalance也就是重新分配分区给消费者,以保证每个分区只被一个消费者消费
4. 也有同学说了,为了不发生rebalance,那可以增加max.poll.records时间啊,但是这样的话,如果要sleep几天的时间,难道max.poll.records要写几天的时间嘛,有违Kafka的设计原理了,那怎么办呢?
5. 这时候Kafka的pause暂停消费和resume恢复消费就登场了,pause暂停某个分区之后消费者不会再poll拉取该分区的消息,直到resume恢复该分区之后才会重新poll消息。
6. **我已经做好了Kafka延时队列的封装,以后只需要一行代码就可以实现延时队列了**,代码核心使用Kafka消费者的pause函数(暂停)和resume函数(恢复)+线程池+定时任务+事件监听机制+工厂模式
## 六、Kafka延时队列架构图
## 七、kafka延时任务代码实现
以下代码只列出了核心实现,完整代码已经给大家整理好了,可以关注【**微信公众号**】微信搜索【**老板来一杯java**】,然后【**加群**】直接获取源码,在自己项目中引入即用!
**源码目录:**
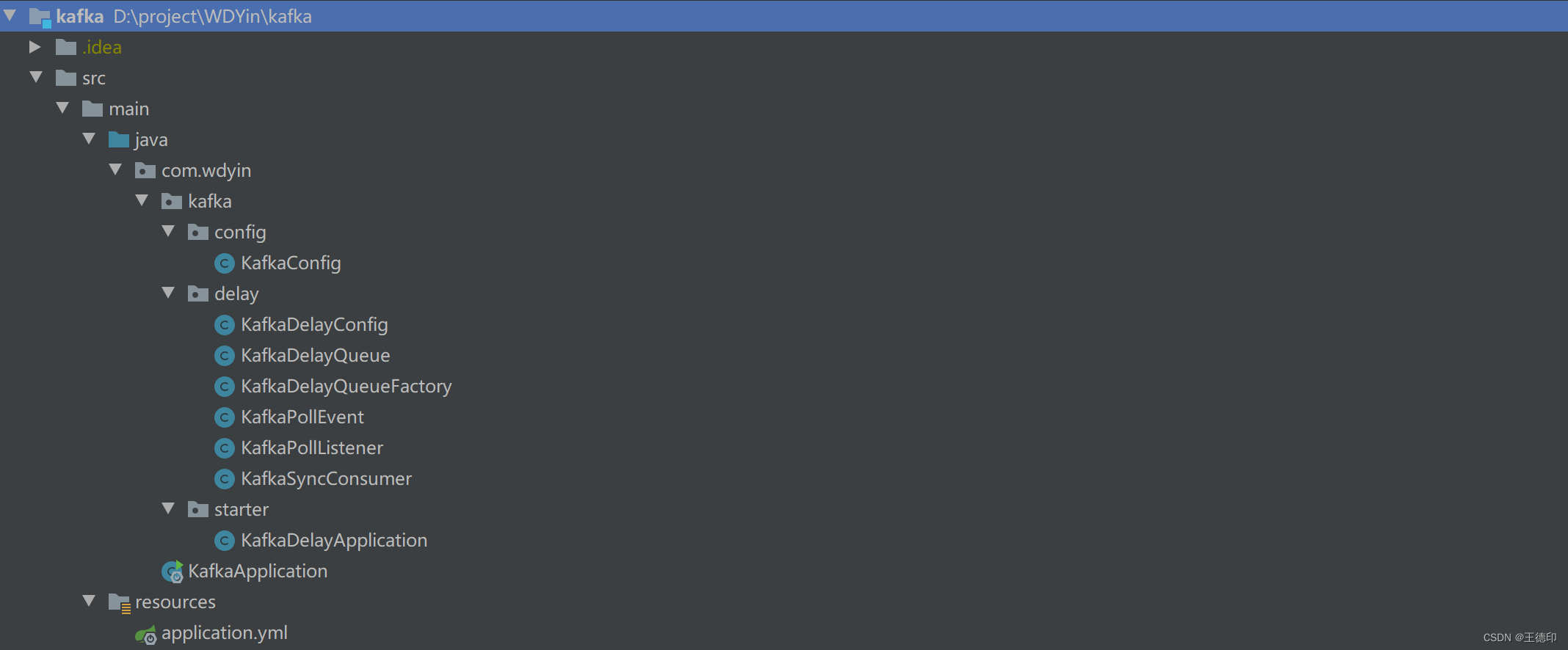
### 1. KafkaDelayQueue:Kafka延迟队列
定义一个Kafka延期队列,包含的内容:KafkaDelayQueue,其中有延迟队列配置,主题,消费组,延迟时间,目标主题,KafkaSyncConsumer,ApplicationContext,poll线程池,delay线程池等等
package com.wdyin.kafka.delay;
import lombok.Getter;
import lombok.Setter;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.apache.kafka.clients.consumer.ConsumerRecords;
import org.apache.kafka.common.TopicPartition;
import org.slf4j.Logger;
import org.slf4j.LoggerFactory;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.scheduling.concurrent.ThreadPoolTaskScheduler;
import java.time.Duration;
import java.util.Collections;
import java.util.concurrent.ThreadPoolExecutor;
/**
- kafka延时队列
- @Author WDYin
- @Date 2022/7/2
**/
@Slf4j
@Getter
@Setter
class KafkaDelayQueue<K, V> {
private String topic;
private String group;
private Integer delayTime;
private String targetTopic;
private KafkaDelayConfig kafkaDelayConfig;
private KafkaSyncConsumer<K, V> kafkaSyncConsumer;
private ApplicationContext applicationContext;
private ThreadPoolTaskScheduler threadPoolPollTaskScheduler;
private ThreadPoolTaskScheduler threadPoolDelayTaskScheduler;
......
}
### 2. KafkaDelayQueueFactory:Kafka延迟队列工厂
Kafka延期队列的工厂,用于及其管理延迟队列
package com.wdyin.kafka.delay;
import lombok.Data;
import org.apache.kafka.clients.consumer.ConsumerConfig;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.util.Assert;
import org.springframework.util.StringUtils;
import java.util.Properties;
/**
- 延时队列工厂
- @author WDYin
- @date 2023/4/17
**/
@Data
public class KafkaDelayQueueFactory {
private KafkaDelayConfig kafkaDelayConfig;
private Properties properties;
private ApplicationContext applicationContext;
private Integer concurrency;
public KafkaDelayQueueFactory(Properties properties, KafkaDelayConfig kafkaDelayConfig) {
Assert.notNull(properties, "properties cannot null");
Assert.notNull(kafkaDelayConfig.getDelayThreadPool(), "delayThreadPool cannot null");
Assert.notNull(kafkaDelayConfig.getPollThreadPool(), "pollThreadPool cannot null");
Assert.notNull(kafkaDelayConfig.getPollInterval(), "pollInterval cannot null");
Assert.notNull(kafkaDelayConfig.getPollTimeout(), "timeout cannot null");
this.properties = properties;
this.kafkaDelayConfig = kafkaDelayConfig;
}
public void listener(String topic, String group, Integer delayTime, String targetTopic) {
if (StringUtils.isEmpty(topic)) {
throw new RuntimeException("topic cannot empty");
}
if (StringUtils.isEmpty(group)) {
throw new RuntimeException("group cannot empty");
}
if (StringUtils.isEmpty(delayTime)) {
throw new RuntimeException("delayTime cannot empty");
}
if (StringUtils.isEmpty(targetTopic)) {
throw new RuntimeException("targetTopic cannot empty");
}
KafkaSyncConsumer<String, String> kafkaSyncConsumer = createKafkaSyncConsumer(group);
KafkaDelayQueue<String, String> kafkaDelayQueue = createKafkaDelayQueue(topic, group, delayTime, targetTopic, kafkaSyncConsumer);
kafkaDelayQueue.send();
}
private KafkaDelayQueue<String, String> createKafkaDelayQueue(String topic, String group, Integer delayTime, String targetTopic, KafkaSyncConsumer<String, String> kafkaSyncConsumer) {
KafkaDelayQueue<String, String> kafkaDelayQueue = new KafkaDelayQueue<>(kafkaSyncConsumer, kafkaDelayConfig);
Assert.notNull(applicationContext, "kafkaDelayQueue need applicationContext");
kafkaDelayQueue.setApplicationContext(applicationContext);
kafkaDelayQueue.setDelayTime(delayTime);
kafkaDelayQueue.setTopic(topic);
kafkaDelayQueue.setGroup(group);
kafkaDelayQueue.setTargetTopic(targetTopic);
return kafkaDelayQueue;
}
private KafkaSyncConsumer<String, String> createKafkaSyncConsumer(String group) {
properties.put(ConsumerConfig.GROUP\_ID\_CONFIG, group);
return new KafkaSyncConsumer<>(properties);
}
}
### 3. KafkaPollListener:Kafka延迟队列事件监听
package com.wdyin.kafka.delay;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.apache.kafka.clients.consumer.ConsumerRecord;
import org.apache.kafka.clients.consumer.ConsumerRecords;
import org.apache.kafka.clients.consumer.OffsetAndMetadata;
import org.apache.kafka.common.TopicPartition;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationListener;
import org.springframework.kafka.core.KafkaTemplate;
import java.time.Instant;
import java.time.LocalDateTime;
import java.time.ZoneId;
import java.util.*;
/**
- 延时队列监听
- @Author : WDYin
- @Date : 2021/5/7
- @Desc :
*/
@Slf4j
public class KafkaPollListener<K, V> implements ApplicationListener<KafkaPollEvent<K, V>> {
private KafkaTemplate kafkaTemplate;
public KafkaPollListener(KafkaTemplate kafkaTemplate) {
this.kafkaTemplate = kafkaTemplate;
}
@Override
public void onApplicationEvent(KafkaPollEvent<K, V> event) {
ConsumerRecords<K, V> records = (ConsumerRecords<K, V>) event.getSource();
Integer delayTime = event.getDelayTime();
KafkaDelayQueue<K, V> kafkaDelayQueue = event.getKafkaDelayQueue();
KafkaSyncConsumer<K, V> kafkaSyncConsumer = kafkaDelayQueue.getKafkaSyncConsumer();
Set<TopicPartition> partitions = records.partitions();
Map<TopicPartition, OffsetAndMetadata> commitMap = new HashMap<>();
partitions.forEach((partition) -> {
List<ConsumerRecord<K, V>> consumerRecords = records.records(partition);
for (ConsumerRecord<K, V> record : consumerRecords) {
long startTime = (record.timestamp() / 1000) \* 1000;
long endTime = startTime + delayTime;
long now = System.currentTimeMillis();
if (endTime > now) {
kafkaSyncConsumer.pauseAndSeek(partition, record.offset());
kafkaDelayQueue.getThreadPoolPollTaskScheduler().schedule(kafkaDelayQueue.delayTask(partition), new Date(endTime));
break;
}
log.info("{}: partition:{}, offset:{}, key:{}, value:{}, messageDate:{}, nowDate:{}, messageDate:{}, nowDate:{}",
Thread.currentThread().getName() + "#" + Thread.currentThread().getId(), record.topic() + "-" + record.partition(), record.offset(), record.key(), record.value(), LocalDateTime.ofInstant(Instant.ofEpochMilli(startTime), ZoneId.systemDefault()), LocalDateTime.now(), startTime, Instant.now().getEpochSecond());
kafkaTemplate.send(kafkaDelayQueue.getTargetTopic(), record.value());
commitMap.put(partition, new OffsetAndMetadata(record.offset() + 1));
}
});
if (!commitMap.isEmpty()) {
kafkaSyncConsumer.commit(commitMap);
}
}
}
### 4. KafkaDelayConfig:Kafka延时配置
package com.wdyin.kafka.delay;
import lombok.Data;
/**
- 延时队列配置
- @author WDYin
- @date 2023/4/16
**/
@Data
public class KafkaDelayConfig {
private Integer pollInterval;
private Integer pollTimeout;
private Integer pollThreadPool;
private Integer delayThreadPool;
public KafkaDelayConfig() {
}
......
}
## 八. 如何使用kafka延时队列
自己项目中引入以上代码之后,使用KafkaDelayApplication:一个Kafka延迟任务注册程序,注意一个延时主题对应一个延迟时间,后续有新的延迟任务只需要在此注册延迟任务的监听即可!开箱即用!
**使用流程:**
1. 生产者发送消息到【延时主题】——自己写
2. 然后Kafka将消息从【延时主题】经过【延时时间】后发送到【目标主题】——以下代码
版权归原作者 2401_86400247 所有, 如有侵权,请联系我们删除。