1.查看服务器已安装的所有内核版本
awk -F\' '$1=="menuentry " {print i++ " : " $2}' /etc/grub2.cfg
0 : CentOS Linux (3.10.0-1160.83.1.el7.x86_64) 7 (Core)
1 : CentOS Linux (3.10.0-1160.80.1.el7.x86_64) 7 (Core)
2 : CentOS Linux (3.10.0-1127.el7.x86_64) 7 (Core)
3 : CentOS Linux (3.10.0-1160.83.1.el7.x86_64.debug) 7 (Core)
4 : CentOS Linux (3.10.0-1160.80.1.el7.x86_64.debug) 7 (Core)
5 : CentOS Linux (0-rescue-0e5781d77781441b97290d7bad5663e2) 7 (Core)
2.修改版本配置
vi /etc/default/grub
GRUB_TIMEOUT=5GRUB_DISTRIBUTOR="$(sed's, release .*$,,g' /etc/system-release)"GRUB_DEFAULT=3GRUB_DISABLE_SUBMENU=true
GRUB_TERMINAL_OUTPUT="console"GRUB_CMDLINE_LINUX="crashkernel=auto rhgb quiet intel_iommu=on iommu=pt"GRUB_DISABLE_RECOVERY="true"
将配置文件中的
GRUB_DEFAULT
的值改为上面查看的对应值ID,根据自己的所需修改;我这里要改为
CentOS Linux (3.10.0-1160.80.1.el7.x86_64) 7 (Core)
则修改为:
GRUB_DEFAULT=1

3.编译配置
grub2-mkconfig -o /boot/grub2/grub.cfg
4.重启系统
编译完成之后需要重新系统方则生效
reboot
5.重启后查看内核版本
等待重启完成命令查看当前内核版本
uname -a
uname -r
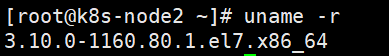
完成版本切换。
版权归原作者 A-刘晨阳 所有, 如有侵权,请联系我们删除。