一、CSS定位布局
CSS定位布局,是通过【position】属性设置的,position属性可以有如下五个取值:
【position】属性取值:
- static:静态定位。
- relative:相对定位。
- fixed:固定定位。
- absolute:绝对定位。
- sticky:粘性定位。
给元素设置【position】属性之后,设置元素的定位方式,然后再通过【top、left、right、bottom】四个属性设置定位的位置。
注意:如果设置了position属性,但是没有设置【top、left、right、bottom】属性,那么position属性不会生效。
1.1、static静态定位
static静态定位,这种是元素默认的定位方式,也就说,没有设置position属性,和设置了【position:static;】属性,这个元素的显示效果是一样的。【top、left、right、bottom】四个属性对于static静态定位来说,是没有效果的。
1.2、relative相对定位
relation相对定位,这个属性是相对于元素自身位置定位的,也就是说,某个元素使用相对定位之后,它是以没有使用相对定位之前显示的位置为参考点,上下左右移动多少距离,下面看个案例。
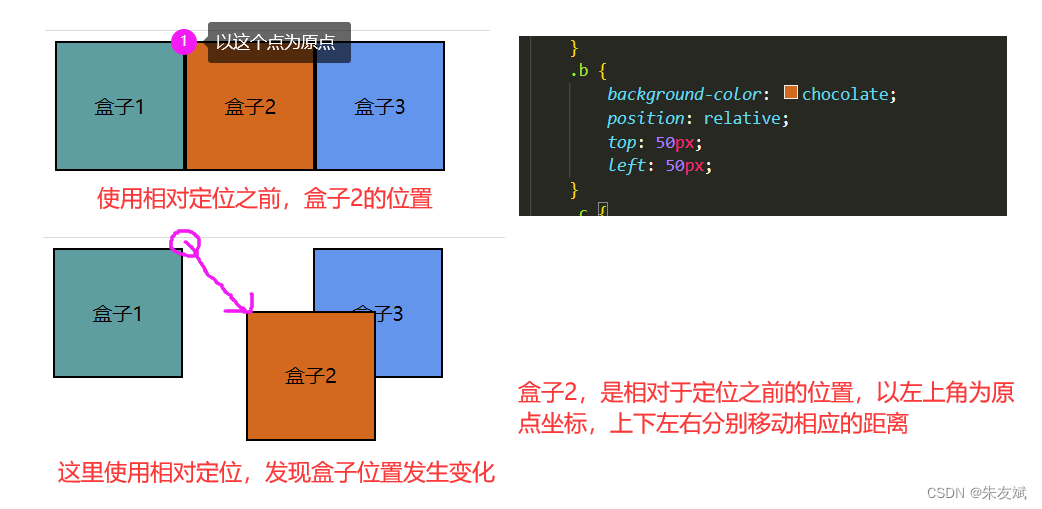
相对定位的特点:
- 相对定位,是以元素自身为参考系。
- 相对定位,默认会覆盖其他没有定位的元素。
- 相对定位,要使用了【top、left、right、bottom】属性才会生效。
- 相对定位,元素定位之前的空间位置还是保留的,不会被其他元素占据。
- 注意:相对定位是没有脱离文档流的(从相对定位的元素还保留之前的元素空间也可以知道,脱离文档流必定不会占据之前的元素空间)。
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>position定位</title>
<style>
div > div {
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
text-align: center;
line-height: 100px;
float: left;
border: 2px solid black;
}
.a {
background-color: cadetblue;
}
.b {
background-color: chocolate;
position: relative;
top: 50px;
left: 50px;
}
.c {
background-color: cornflowerblue;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div>
<div class="a">盒子1</div>
<div class="b">盒子2</div>
<div class="c">盒子3</div>
</div>
</body>
</html>
1.3、fixed固定定位
fixed固定定位,它是相对于浏览器窗口进行定位的,当页面发生滚动的时候,fixed固定定位不会被影响,固定定位始终是固定在一个位置。
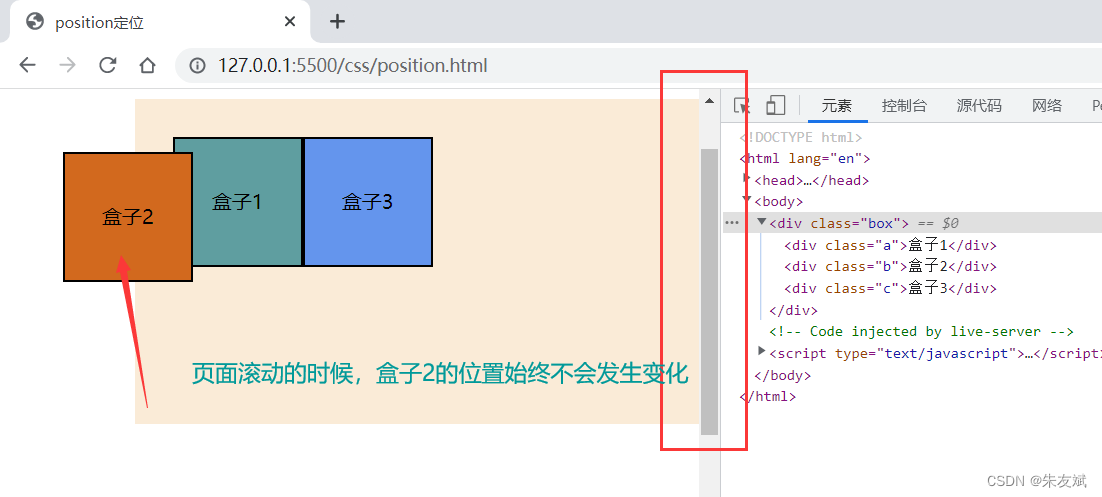
案例代码:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>position定位</title>
<style>
body {
padding: 100px;
height: 2000px;
}
body > div {
width: 400px;
height: 200px;
background-color: antiquewhite;
}
div > div {
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
text-align: center;
line-height: 100px;
float: left;
border: 2px solid black;
}
.box {
padding: 30px;
}
.a {
background-color: cadetblue;
}
.b {
background-color: chocolate;
position: fixed;
top: 50px;
left: 50px;
}
.c {
background-color: cornflowerblue;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="box">
<div class="a">盒子1</div>
<div class="b">盒子2</div>
<div class="c">盒子3</div>
</div>
</body>
</html>
固定定位特点:
- 固定定位,是特殊的绝对定位,所以固定定位有绝对定位的特点。
- 固定定位,屏幕滚动时候,固定定位的元素位置不会发生变化。
- 固定定位,是脱离文档流的。
1.4、absolute绝对定位
(1)默认绝对定位参考点
absolute绝对定位,默认情况下,元素使用绝对定位之后,它是相对于浏览器屏幕左上角为参考点进行定位的,准确点说,是相对于浏览器内容可见区域的左上角为原点。
设置元素的【position】属性值等于【absolute】绝对定位之后,如果没有设置【top,left、right、bottom】属性,那么就会默认都是0,这个时候元素就会移动到浏览器屏幕可见区域的左上角位置。
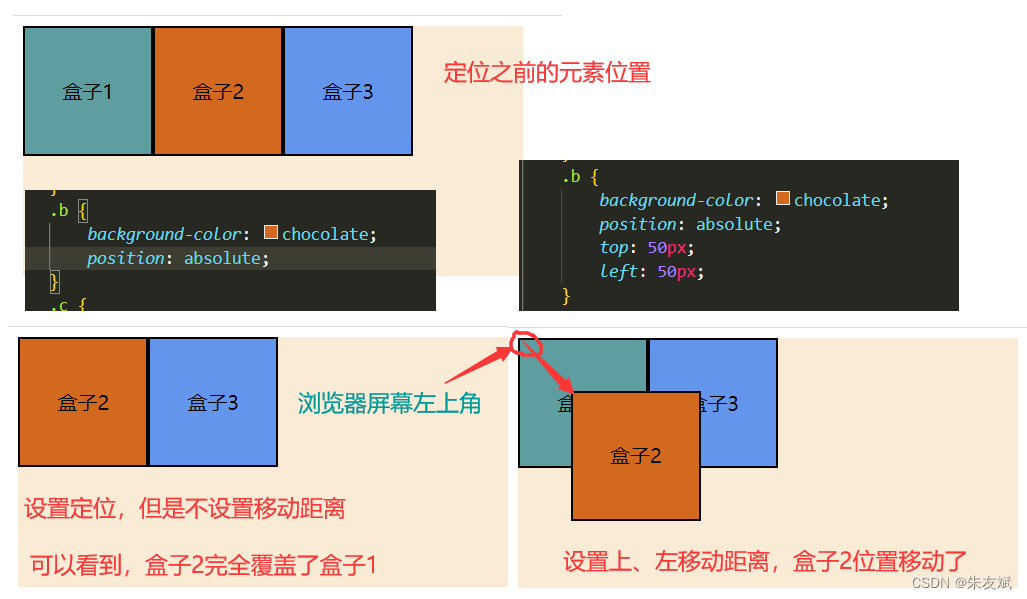
案例代码:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>position定位</title>
<style>
body > div {
width: 400px;
height: 200px;
background-color: antiquewhite;
}
div > div {
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
text-align: center;
line-height: 100px;
float: left;
border: 2px solid black;
}
.a {
background-color: cadetblue;
}
.b {
background-color: chocolate;
position: absolute;
top: 50px;
left: 50px;
}
.c {
background-color: cornflowerblue;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div>
<div class="a">盒子1</div>
<div class="b">盒子2</div>
<div class="c">盒子3</div>
</div>
</body>
</html>
(2)设置绝对定位参考点
CSS也支持相对于某个元素,进行绝对定位,也就是说,可以自定义当前元素是以哪个元素为参考点,从而完成绝对定位。要相对于父元素使用绝对定位,那么就必须给父元素设置【position】属性,属性值取【relative、absolute、fixed、sticky】四种都可以。
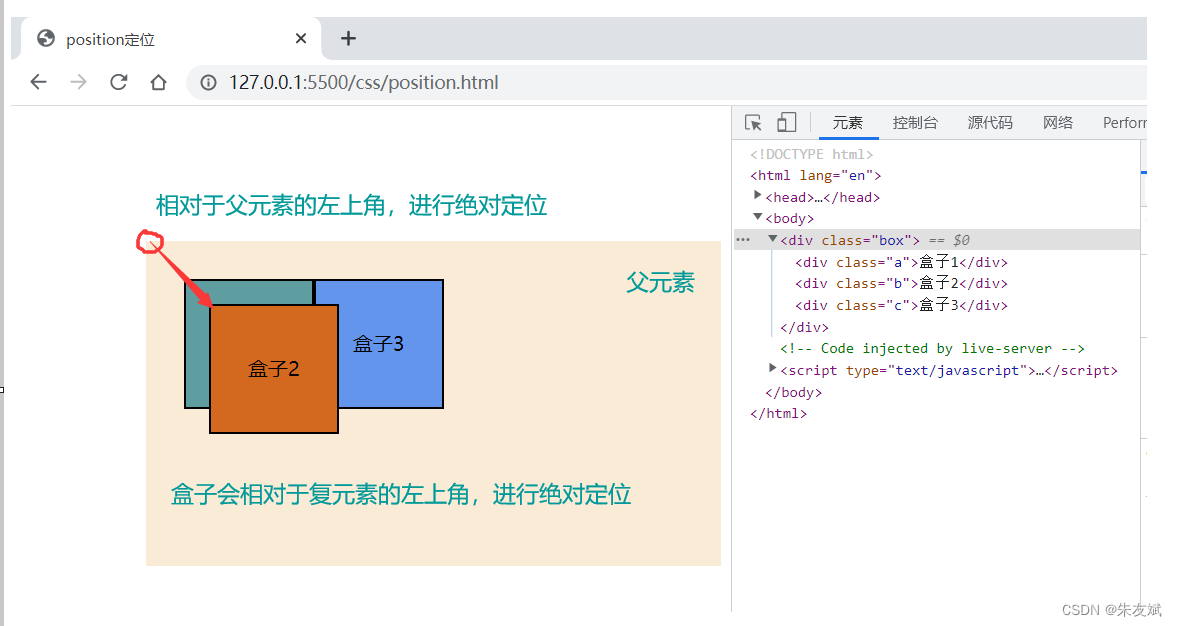
案例代码:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>position定位</title>
<style>
body {
padding: 100px;
}
body > div {
width: 400px;
height: 200px;
background-color: antiquewhite;
}
div > div {
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
text-align: center;
line-height: 100px;
float: left;
border: 2px solid black;
}
.box {
padding: 30px;
/* 设置 position 属性,让子元素可以使用绝对定位 */
position: relative;
}
.a {
background-color: cadetblue;
}
.b {
background-color: chocolate;
position: absolute;
top: 50px;
left: 50px;
}
.c {
background-color: cornflowerblue;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="box">
<div class="a">盒子1</div>
<div class="b">盒子2</div>
<div class="c">盒子3</div>
</div>
</body>
</html>
绝对定位特点:
- 绝对定位,默认是以屏幕左上角为参考点。
- 绝对定位,是会脱离文档流,不会占据元素的位置。
- 绝对定位,默认会覆盖没有定位的元素。
- 相对父元素的绝对定位,会按照最近的设置了【position】属性的祖先元素进行绝对定位(就近原则)。
1.5、sticky粘性定位
sticky粘性定位,这个定位属性是【position:sticky;】,需要至少设置【top、left、right、bottom】四个属性之一,否则不生效。sticky粘性定位,可以看作是:【static静态定位】和【fixed固定定位】的结合体,最开始默认是static静态定位,当相对于父元素满足定位条件的时候,sticky粘性定位就会由static静态定位转变为fixed固定定位。
(1)sticky粘性定位失效的原因
sticky粘性定位不生效的原因可能有如下几个原因:
- 父元素不能添加【overflow:hidden;】或者【overflow:auto;】属性值。
- 元素自身必须设置【top、left、right、bottom】四个属性之一,否则就相当于静态定位。
- 父元素的高度必须大于使用了sticky粘性定位元素的高度。
- sticky定位只能够在其父元素里面生效。
(2)sticky案例
案例效果:

案例代码:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>position定位</title>
<style>
body {
padding: 100px;
height: 2000px;
}
.box>div {
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
text-align: center;
line-height: 100px;
float: left;
border: 2px solid black;
}
.a {
background-color: cadetblue;
}
.b {
background-color: chocolate;
}
.c {
background-color: cornflowerblue;
}
.box4 {
width: 100%;
height: 60px;
text-align: center;
background-color: darkkhaki;
clear: both;
/* 设置粘性定位 */
position: sticky;
top: 50px; /* 当距离父容器顶部50px时候,转换为固定定位 */
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="box">
<div class="a">盒子1</div>
<div class="b">盒子2</div>
<div class="c">盒子3</div>
</div>
<div class="box4">
盒子4,采用sticky粘性定位
</div>
</body>
</html>
以上,就是CSS中的五种定位方式,其中会脱离文档流的只有【绝对定位】。
版权归原作者 朱友斌 所有, 如有侵权,请联系我们删除。