1. 背景
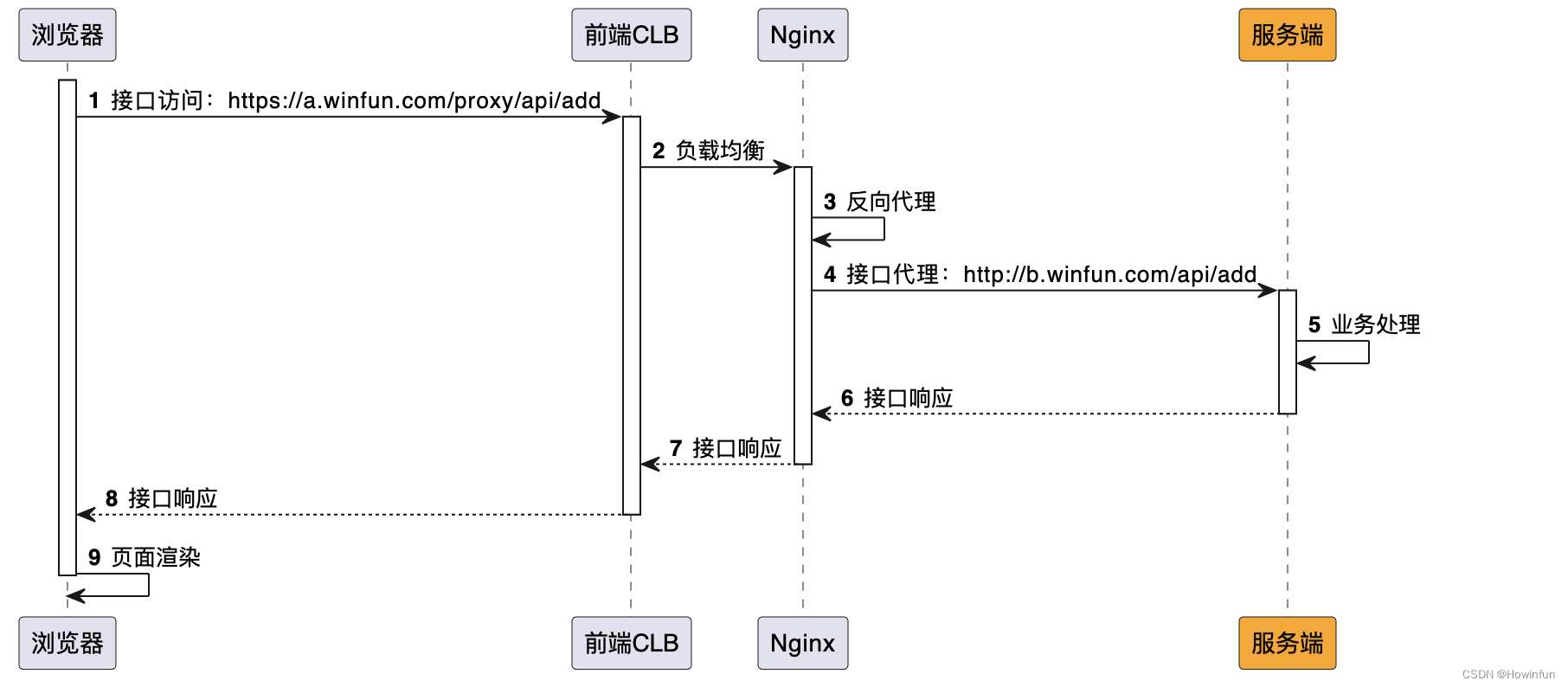
页面通过域名A【https://a.winfun.com】访问接口,域名A通过Nginx服务进行反向代理,代理到域名B【http://b.winfun.com】,然后进行业务逻辑执行。
时序图:
nginx配置:
server {
listen 31001;
server_name localhost;
proxy_intercept_errors on;
error_page 404 /404.html;
error_page 500502503504 /500.html;
index index.html ;
charset utf-8;
location /proxy/ {
rewrite ^/proxy/(.*) /$1break;
proxy_pass http://b.winfun.com;}
location / {
root /usr/local/nginx/html/;
try_files $uri /index.html;}}
2. 403跨域
接口返回Http状态为403,出现跨域问题。

3. Postman模拟
3.1. 模拟
为了方便测试,我们直接将接口放到Postman中进行模拟测试,并带上相关请求头,接口还是返回403,这个没疑问
3.2. 请求头
在请求头搬迁时,发现了几个可疑的请求头,包含:origin、sec-fetch-mode、sec-fetch-site
其中
sec-fetch-mode
显示cors,表示是跨域请求;而
sec-fetch-stie
显示的是same-origin。
orign
显示的是和接口调用同样的域名。

3.3. 猜测
1、sec-fetch- 请求头*
首先将 sec-fetch-mode 也改成 same-origin,接口还是返回403❌,看来sec-fetch-*只是起一定的描述作用。

2、origin 请求头
跨域问题的出现都是因为请求不符合同源策略,虽然接口调用中,origin请求头和接口请求的域名都是一样的,但其实到了nginx服务,是会反向代理到另外一个域名的;我们此时将origin请求头的域名改为反向代理后的域名,接口返回成功✅

4、nginx配置调整
origin请求头是浏览器根据请求附上请求信息里面的,所以我们可以通过nginx的proxy_set_header来修改origin请求头。
server {
listen 31001;
server_name localhost;
proxy_intercept_errors on;
error_page 404 /404.html;
error_page 500 502 503 504 /500.html;
index index.html ;
charset utf-8;
location /proxy/ {
rewrite ^/proxy/(.*) /$1 break;
proxy_set_header origin 'http://b.winfun.com';
proxy_pass http://b.winfun.com;
}
location / {
root /usr/local/nginx/html/;
try_files $uri /index.html;
}}
页面接口响应成功!
版权归原作者 Howinfun 所有, 如有侵权,请联系我们删除。