
概述
定义
- 传统定义: 一个分布式的, 基于发布订阅模式的消息队列, 主要应用于大数据实时处理领域
- 新定义: 开源的分布式事件流平台, 被用于数据管道/流分析/数据集成
消息队列的使用场景
传统消息队列的主要应用场景包括:
削峰:
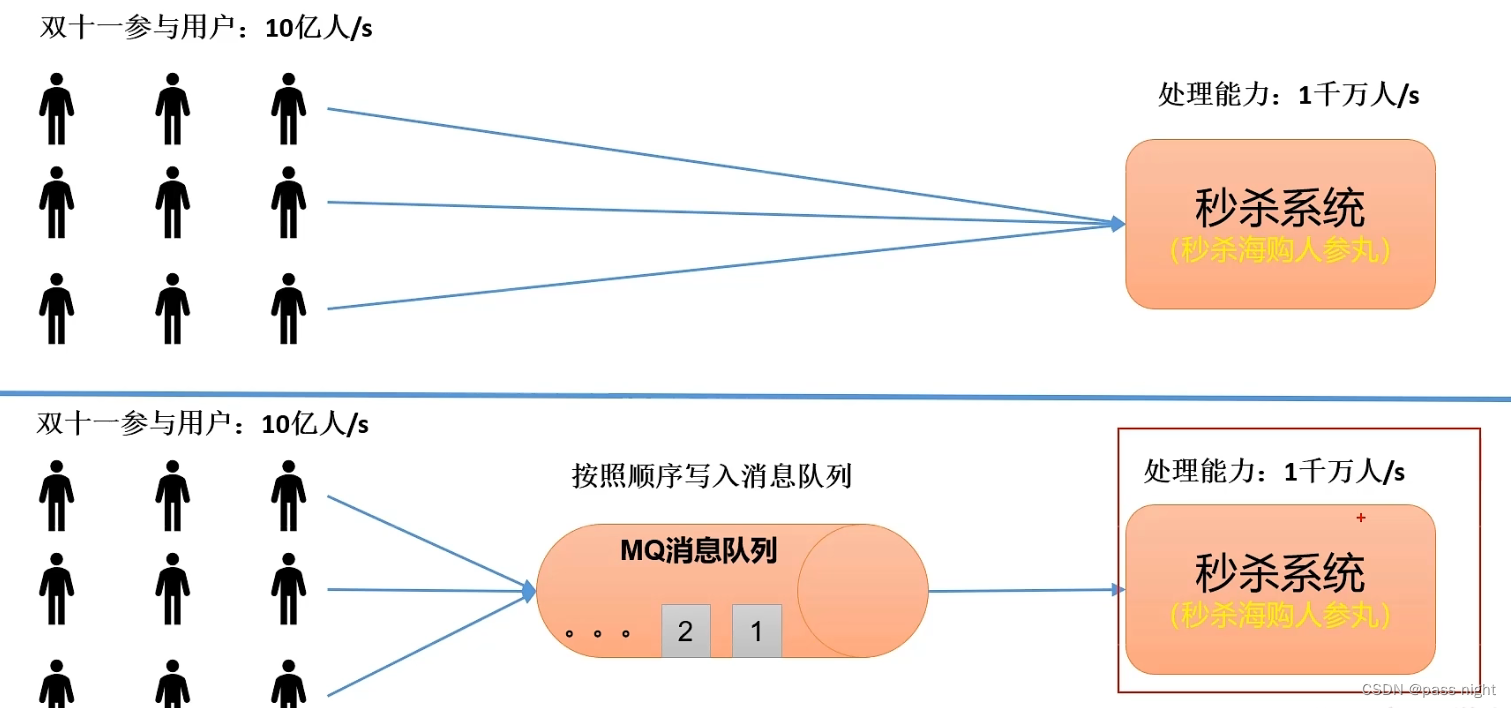
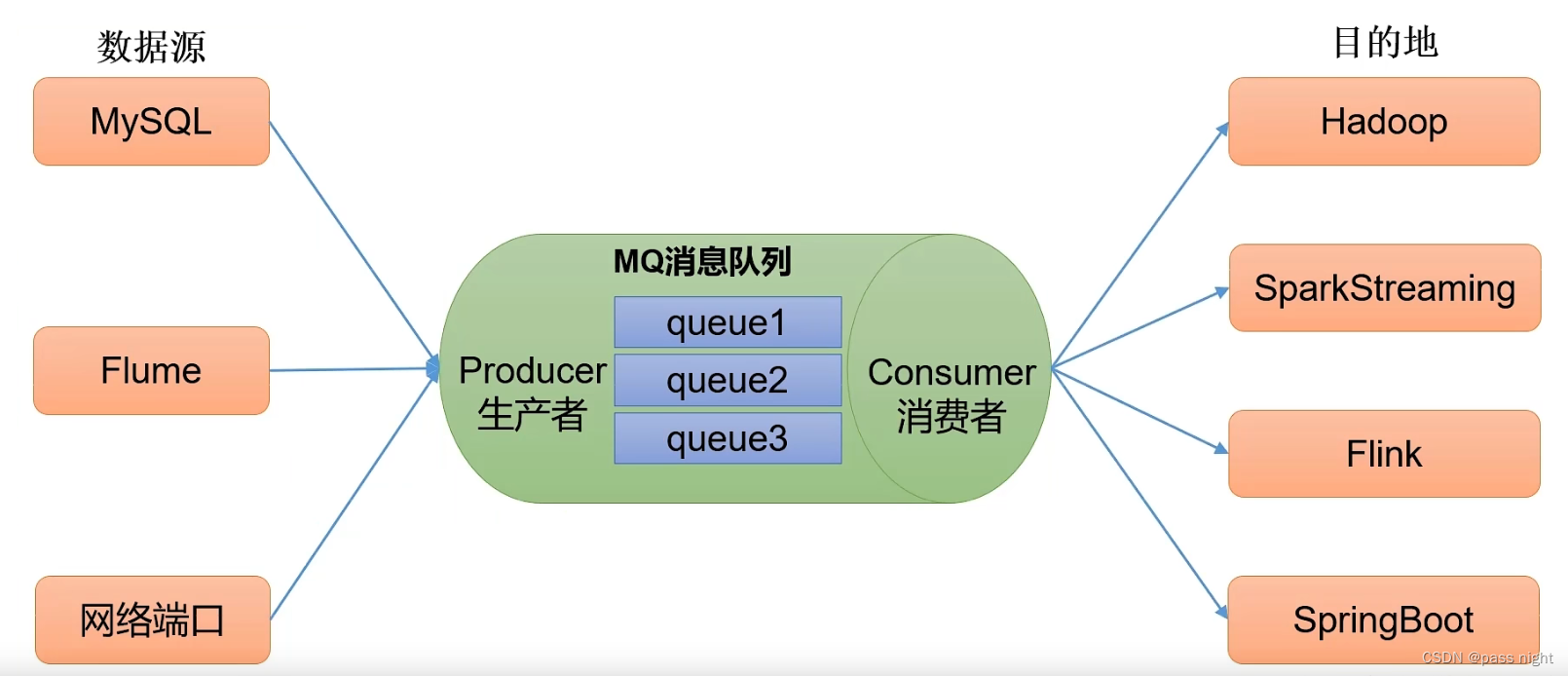
解耦:
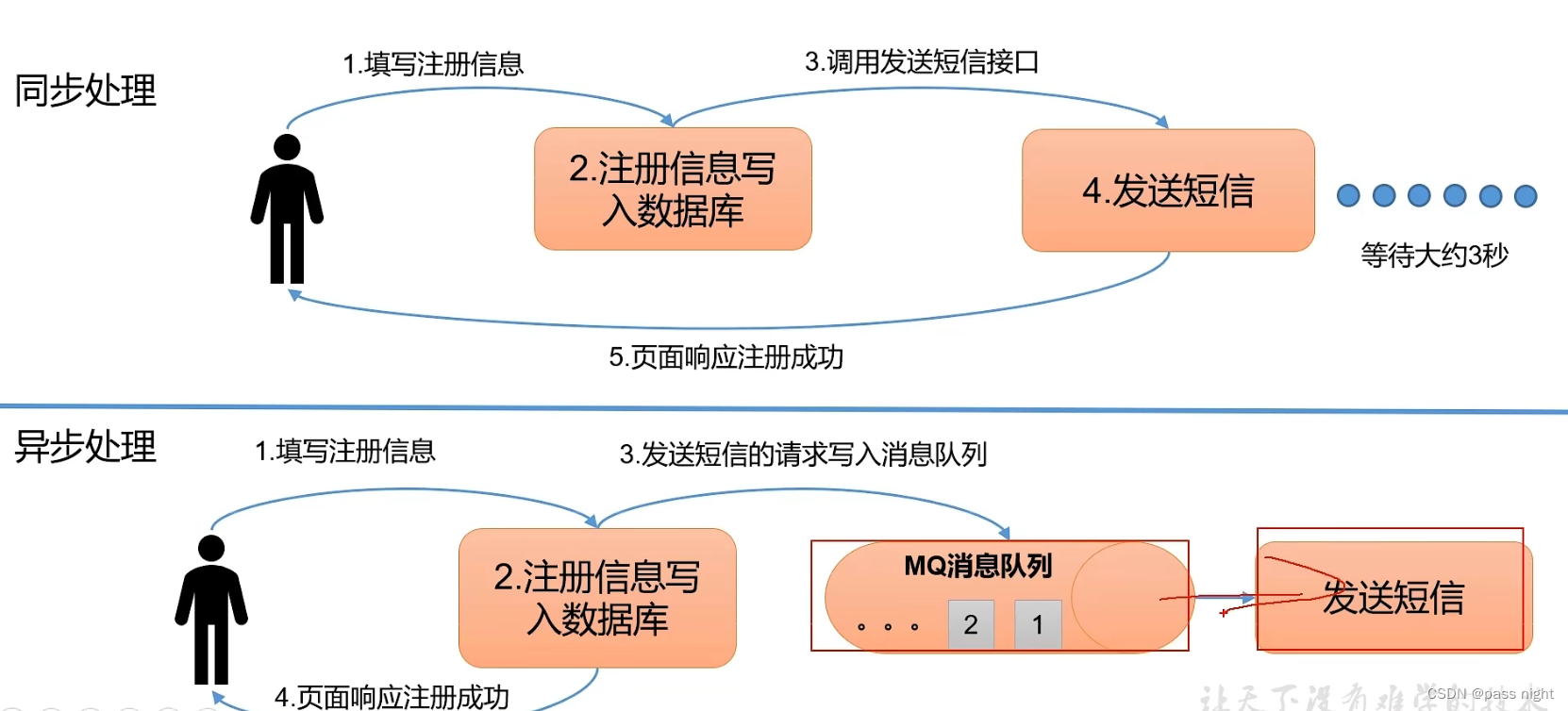
异步:
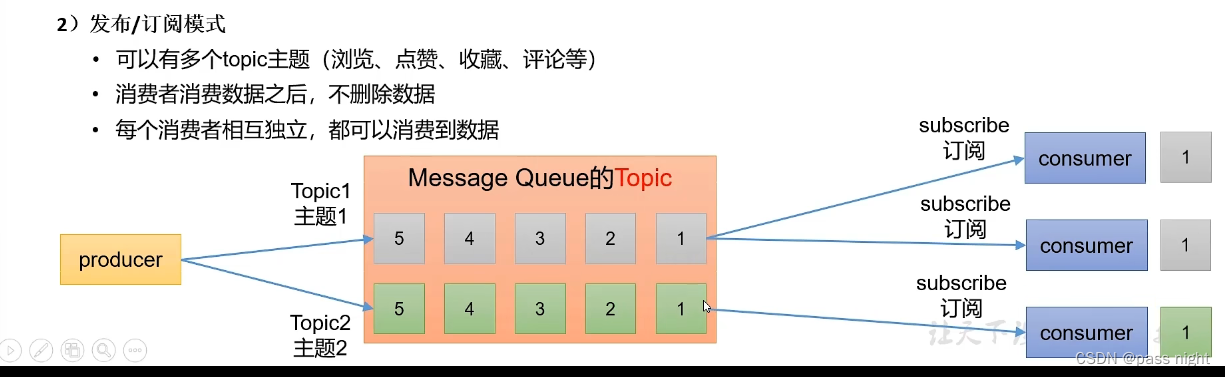
两种模式
点对点模式
发布/订阅模式
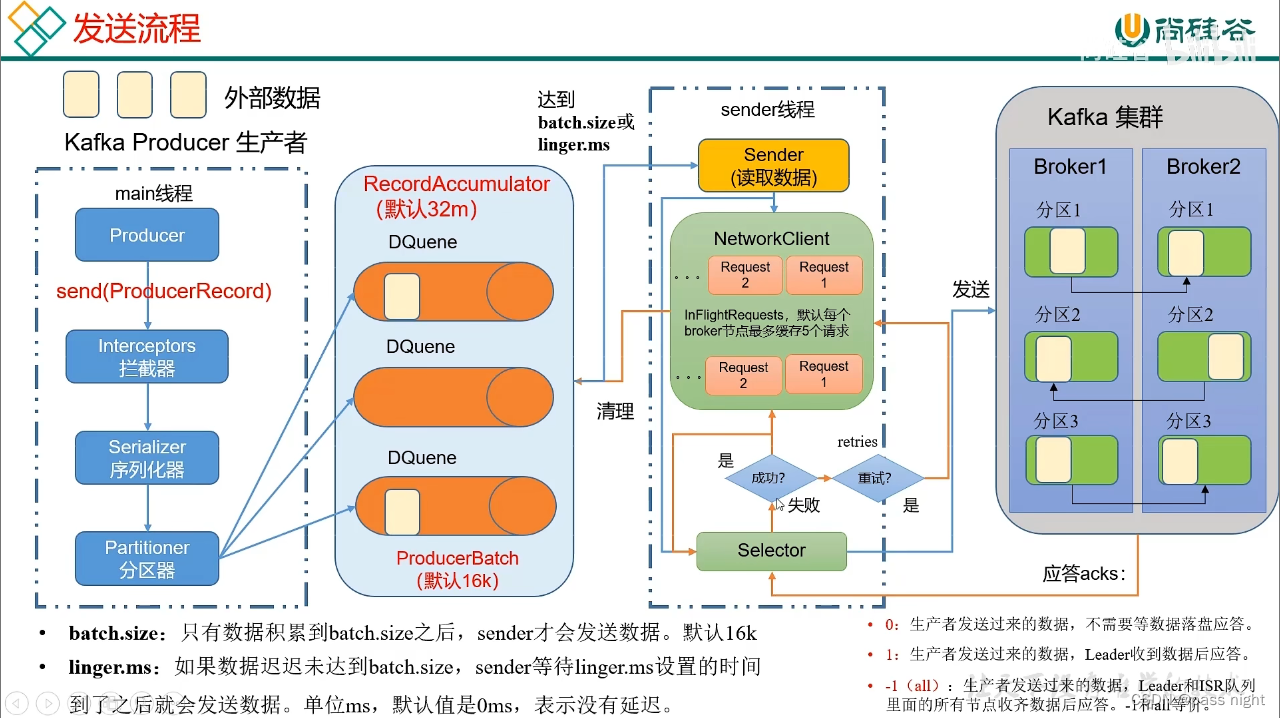
基础架构

- 一个
topic分为多个partition - 为了配合存储分区的设计, 消费者
consumer也分成了group一个分区的数据, 只能由一个消费者消费 - 为了提高可用性, 为每个
Partition提供副本 - Kafka使用
Zookeeper实现分布式管理
基本使用
部署
由于每台机器要装一个
Kafka
容器, 这里使用
Kubernetes
的
DaemonSet
来实现
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: DaemonSet
metadata:name: kafka
labels:app: kafka
spec:selector:matchLabels:app: kafka
template:metadata:labels:app: kafka
spec:containers:-name: kafka
image: bitnami/kafka
# env:# - name: JMX_PORT# value: "9010"ports:-name: client
containerPort:9092hostPort:20015-name: jmx
containerPort:9010hostPort:20016volumeMounts:-name: time
mountPath: /etc/localtime
-name: data
mountPath: /bitnami/kafka
volumes:-name: time
hostPath:path: /etc/localtime
type: File
-name: data
hostPath:path: /opt/docker/kafka/data
type: Directory
以下是三个节点所需要修改的配置文件
# server.passnight.local
broker.id=0
listeners=PLAINTEXT://0.0.0.0:9092
advertised.listeners=PLAINTEXT://server.passnight.local:20015
log.dirs=/bitnami/kafka/logs
# replica.passnight.local
broker.id=1
listeners=PLAINTEXT://0.0.0.0:9092
advertised.listeners=PLAINTEXT://server.passnight.local:20015
log.dirs=/bitnami/kafka/logs
# follower.passnight.local
broker.id=2
listeners=PLAINTEXT://0.0.0.0:9092
advertised.listeners=PLAINTEXT://server.passnight.local:20015
log.dirs=/bitnami/kafka/logs
这里主要要注意以下几点:
- 同
Zookeeper一样,listener的ip要置为0.0.0.0; 不能置为节点ip/127.0.0.1或其他ip broker.id要全局唯一advertised.listeners是外部访问地址, 应该置为外部ip和容器暴露的端口- 这里没有打开
jmx, 打开后会报错端口已经被占用
在Kafka-Manager中添加集群

配置topic
进入容器
passnight@passnight-s600:~$ dockerexec-it kafka bash
Kafka
基本操作
查看
kafka-topics
帮助文档
I have no name!@b0d8083f09f5:/$ kafka-topics.sh
Create, delete, describe, or change a topic.
Option Description
------ -----------
--alter Alter the number of partitions and
replica assignment. Update the
configuration of an existing topic
via --alter is no longer supported
here (the kafka-configs CLI supports
altering topic configs with a --
bootstrap-server option).
--at-min-isr-partitions ifset when describing topics, only
show partitions whose isr count is
equal to the configured minimum.
--bootstrap-server <String: server to REQUIRED: The Kafka server to connect
connect to> to.
--command-config <String: command Property file containing configs to be
config property file> passed to Admin Client. This is used
only with --bootstrap-server option
for describing and altering broker
configs.
--config<String: name=value> A topic configuration override for the
topic being created or altered. The
following is a list of valid
configurations:
cleanup.policy
compression.type
delete.retention.ms
file.delete.delay.ms
flush.messages
flush.ms
follower.replication.throttled.
replicas
index.interval.bytes
leader.replication.throttled.replicas
local.retention.bytes
local.retention.ms
max.compaction.lag.ms
max.message.bytes
message.downconversion.enable
message.format.version
message.timestamp.difference.max.ms
message.timestamp.type
min.cleanable.dirty.ratio
min.compaction.lag.ms
min.insync.replicas
preallocate
remote.storage.enable
retention.bytes
retention.ms
segment.bytes
segment.index.bytes
segment.jitter.ms
segment.ms
unclean.leader.election.enable
See the Kafka documentation for full
details on the topic configs. It is
supported only in combination with --
create if --bootstrap-server option
is used (the kafka-configs CLI
supports altering topic configs with
a --bootstrap-server option).
--create Create a new topic.
--delete Delete a topic
--delete-config <String: name> A topic configuration override to be
removed for an existing topic (see
the list of configurations under the
--config option). Not supported with
the --bootstrap-server option.
--describe List details for the given topics.
--exclude-internal exclude internal topics when running
list or describe command. The
internal topics will be listed by
default
--help Print usage information.
--if-exists ifset when altering or deleting or
describing topics, the action will
only execute if the topic exists.
--if-not-exists ifset when creating topics, the
action will only execute if the
topic does not already exist.
--list List all available topics.
--partitions<Integer: # of partitions> The number of partitions for the topic
being created or altered (WARNING:
If partitions are increased for a
topic that has a key, the partition
logic or ordering of the messages
will be affected). If not supplied
for create, defaults to the cluster
default.
--replica-assignment <String: A list of manual partition-to-broker
broker_id_for_part1_replica1 : assignments for the topic being
broker_id_for_part1_replica2 , created or altered.
broker_id_for_part2_replica1 :
broker_id_for_part2_replica2 , ...>
--replication-factor <Integer: The replication factor for each
replication factor> partition in the topic being
created. If not supplied, defaults
to the cluster default.
--topic<String: topic> The topic to create, alter, describe
or delete. It also accepts a regular
expression, except for--create
option. Put topic name in double
quotes and use the '\' prefix to
escape regular expression symbols; e.
g. "test\.topic".
--topic-id <String: topic-id> The topic-id to describe.This is used
only with --bootstrap-server option
for describing topics.
--topics-with-overrides ifset when describing topics, only
show topics that have overridden
configs
--unavailable-partitions ifset when describing topics, only
show partitions whose leader is not
available
--under-min-isr-partitions ifset when describing topics, only
show partitions whose isr count is
less than the configured minimum.
--under-replicated-partitions ifset when describing topics, only
show under replicated partitions
--version Display Kafka version.
基本操作
I have no name!@b0d8083f09f5:/$ kafka-topics.sh --bootstrap-server 127.0.0.1:9092 --list# 查看有哪些主题
I have no name!@b0d8083f09f5:/$ kafka-topics.sh --bootstrap-server 127.0.0.1:9092 --topic fist --create--partitions1 --replication-factor 1# 创建主题"topic", 分区1, 副本1
Created topic fist.
I have no name!@b0d8083f09f5:/$ kafka-topics.sh --bootstrap-server 127.0.0.1:9092 --topic fist --describe# 查看主题详细信息
Topic: fist TopicId: qZfeWB7mRl6iGWOJPql3mQ PartitionCount: 1 ReplicationFactor: 1 Configs: max.message.bytes=10000000
Topic: fist Partition: 0 Leader: 1004 Replicas: 1004 Isr: 1004
I have no name!@b0d8083f09f5:/$ kafka-topics.sh --bootstrap-server 127.0.0.1:9092 --topic fist --alter--partitions4# 修改分区数为4
I have no name!@b0d8083f09f5:/$ kafka-topics.sh --bootstrap-server 127.0.0.1:9092 --topic fist --describe# 现在有4个人分区了
Topic: fist TopicId: qZfeWB7mRl6iGWOJPql3mQ PartitionCount: 4 ReplicationFactor: 1 Configs: max.message.bytes=10000000
Topic: fist Partition: 0 Leader: 1004 Replicas: 1004 Isr: 1004
Topic: fist Partition: 1 Leader: 1004 Replicas: 1004 Isr: 1004
Topic: fist Partition: 2 Leader: 1004 Replicas: 1004 Isr: 1004
Topic: fist Partition: 3 Leader: 1004 Replicas: 1004 Isr: 1004
I have no name!@b0d8083f09f5:/$ kafka-topics.sh --bootstrap-server 127.0.0.1:9092 --topic fist --alter--partitions2# 分区只能增加, 不能减少
Error while executing topic command: Topic currently has 4 partitions, which is higher than the requested 2.
[2023-08-12 11:01:05,935] ERROR org.apache.kafka.common.errors.InvalidPartitionsException: Topic currently has 4 partitions, which is higher than the requested 2.
(kafka.admin.TopicCommand$)
Kafka
生产者/消费者基本操作
生产者文档
I have no name!@b0d8083f09f5:/$ kafka-console-producer.sh
Missing required option(s)[bootstrap-server]
Option Description
------ -----------
--batch-size <Integer: size> Number of messages to send in a single
batch if they are not being sent
synchronously. please note that this
option will be replaced if max-
partition-memory-bytes is also set(default: 16384)
--bootstrap-server <String: server to REQUIRED unless --broker-list
connect to>(deprecated) is specified. The server
(s) to connect to. The broker list
string in the form HOST1:PORT1,HOST2:
PORT2.
--broker-list <String: broker-list> DEPRECATED, use --bootstrap-server
instead; ignored if --bootstrap-
server is specified. The broker
list string in the form HOST1:PORT1,
HOST2:PORT2.
--compression-codec [String: The compression codec: either 'none',
compression-codec]'gzip', 'snappy', 'lz4', or 'zstd'.
If specified without value, then it
defaults to 'gzip'--help Print usage information.
--line-reader <String: reader_class> The class name of the class to use for
reading lines from standard in. By
default each line is read as a
separate message. (default: kafka.
tools.
ConsoleProducer$LineMessageReader)
--max-block-ms <Long: max block on The max time that the producer will
send> block for during a send request.
(default: 60000)
--max-memory-bytes <Long: total memory The total memory used by the producer
in bytes> to buffer records waiting to be sent
to the server. This is the option to
control `buffer.memory`in producer
configs. (default: 33554432)
--max-partition-memory-bytes <Integer: The buffer size allocated for a
memory in bytes per partition> partition. When records are received
which are smaller than this size the
producer will attempt to
optimistically group them together
until this size is reached. This is
the option to control `batch.size`in producer configs. (default: 16384)
--message-send-max-retries <Integer> Brokers can fail receiving the message
for multiple reasons, and being
unavailable transiently is just one
of them. This property specifies the
number of retries before the
producer give up and drop this
message. This is the option to
control `retries`in producer
configs. (default: 3)
--metadata-expiry-ms <Long: metadata The period of timein milliseconds
expiration interval> after which we force a refresh of
metadata even if we haven't seen any
leadership changes. This is the
option to control `metadata.max.age.
ms`in producer configs. (default:
300000)
--producer-property <String: A mechanism to pass user-defined
producer_prop> properties in the form key=value to
the producer.
--producer.config<String: config file> Producer config properties file. Note
that [producer-property] takes
precedence over this config.
--property<String: prop> A mechanism to pass user-defined
properties in the form key=value to
the message reader. This allows
custom configuration for a user-
defined message reader.
Default properties include:
parse.key=false
parse.headers=false
ignore.error=false
key.separator=\t
headers.delimiter=\t
headers.separator=,
headers.key.separator=:
null.marker= When set, any fields
(key, value and headers) equal to
this will be replaced by null
Default parsing pattern when:
parse.headers=true and parse.key=true:
"h1:v1,h2:v2...\tkey\tvalue"parse.key=true:
"key\tvalue"parse.headers=true:
"h1:v1,h2:v2...\tvalue"
--reader-config <String: config file> Config properties filefor the message
reader. Note that [property] takes
precedence over this config.
--request-required-acks <String: The required `acks` of the producer
request required acks> requests (default: -1)
--request-timeout-ms <Integer: request The ack timeout of the producer
timeout ms> requests. Value must be non-negative
and non-zero. (default: 1500)
--retry-backoff-ms <Long> Before each retry, the producer
refreshes the metadata of relevant
topics. Since leader election takes
a bit of time, this property
specifies the amount of time that
the producer waits before refreshing
the metadata. This is the option to
control `retry.backoff.ms`in
producer configs. (default: 100)
--socket-buffer-size <Integer: size> The size of the tcp RECV size. This is
the option to control `send.buffer.
bytes`in producer configs.
(default: 102400)--sync If set message send requests to the
brokers are synchronously, one at a
time as they arrive.
--timeout<Long: timeout_ms> If set and the producer is running in
asynchronous mode, this gives the
maximum amount of time a message
will queue awaiting sufficient batch
size. The value is given in ms. This
is the option to control `linger.ms`in producer configs. (default: 1000)--topic<String: topic> REQUIRED: The topic id to produce
messages to.
--version Display Kafka version.
消费者文档
I have no name!@b0d8083f09f5:/$ kafka-console-consumer.sh
This tool helps to read data from Kafka topics and outputs it to standard output.
Option Description
------ -----------
--bootstrap-server <String: server to REQUIRED: The server(s) to connect to.
connect to>
--consumer-property <String: A mechanism to pass user-defined
consumer_prop> properties in the form key=value to
the consumer.
--consumer.config<String: config file> Consumer config properties file. Note
that [consumer-property] takes
precedence over this config.
--enable-systest-events Log lifecycle events of the consumer
in addition to logging consumed
messages. (This is specific for
system tests.)--formatter<String: class> The name of a class to use for
formatting kafka messages for
display. (default: kafka.tools.
DefaultMessageFormatter)
--formatter-config <String: config Config properties file to initialize
file> the message formatter. Note that
[property] takes precedence over
this config.
--from-beginning If the consumer does not already have
an established offset to consume
from, start with the earliest
message present in the log rather
than the latest message.
--group<String: consumer group id> The consumer group id of the consumer.
--help Print usage information.
--include<String: Java regex (String)> Regular expression specifying list of
topics to include for consumption.
--isolation-level <String> Set to read_committed in order to
filter out transactional messages
which are not committed. Set to
read_uncommitted to read all
messages. (default: read_uncommitted)
--key-deserializer <String:
deserializer for key>
--max-messages <Integer: num_messages> The maximum number of messages to
consume before exiting. If not set,
consumption is continual.
--offset<String: consume offset> The offset to consume from (a non-
negative number), or 'earliest'which means from beginning, or
'latest'which means from end
(default: latest)--partition<Integer: partition> The partition to consume from.
Consumption starts from the end of
the partition unless '--offset' is
specified.
--property<String: prop> The properties to initialize the
message formatter. Default
properties include:
print.timestamp=true|falseprint.key=true|falseprint.offset=true|falseprint.partition=true|falseprint.headers=true|falseprint.value=true|falsekey.separator=<key.separator>line.separator=<line.separator>headers.separator=<line.separator>null.literal=<null.literal>key.deserializer=<key.deserializer>value.deserializer=<value.
deserializer>header.deserializer=<header.
deserializer>
Users can also pass in customized
properties for their formatter;more
specifically, users can pass in
properties keyed with 'key.
deserializer.', 'value.
deserializer.' and 'headers.
deserializer.' prefixes to configure
their deserializers.
--skip-message-on-error If there is an error when processing a
message, skip it instead of halt.
--timeout-ms <Integer: timeout_ms> If specified, exitif no message is
available for consumption for the
specified interval.
--topic<String: topic> The topic to consume on.
--value-deserializer <String:
deserializer for values>--version Display Kafka version.
--whitelist<String: Java regex DEPRECATED, use --include instead;(String)> ignored if--include specified.
Regular expression specifying list
of topics to include for consumption.
基本操作
I have no name!@b0d8083f09f5:/$ kafka-console-producer.sh --bootstrap-server localhost:9092 --topic first # 连接生产者Console
I have no name!@b0d8083f09f5:/$ kafka-console-consumer.sh --bootstrap-server localhost:9092 --topic first # 连接消费者

消费者就能看到生产者生产的消息了
I have no name!@b0d8083f09f5:/$ kafka-console-consumer.sh --bootstrap-server localhost:9092 --topic first --from-beginning # 查看所有历史数据
hello
hello
hello from producer
Kafka生产者
异步发送
classAsyncProducer{publicstaticvoidmain(String[] args){Properties properties =newProperties();// 连接集群(server.passnight.local:20015)
properties.put(ProducerConfig.BOOTSTRAP_SERVERS_CONFIG,"server.passnight.local:20015");// 配置Key/Value序列化类
properties.put(ProducerConfig.KEY_SERIALIZER_CLASS_CONFIG,StringSerializer.class.getName());
properties.put(ProducerConfig.VALUE_SERIALIZER_CLASS_CONFIG,StringSerializer.class.getName());try(KafkaProducer<String,String> kafkaProducer =newKafkaProducer<>(properties)){for(int i =0; i <5; i++){// 发送数据
kafkaProducer.send(newProducerRecord<>("first",String.format("value %d", i)),newCallback(){@OverridepublicvoidonCompletion(RecordMetadata metadata,Exception exception){if(exception ==null){System.out.printf("主题: %s, 分区: %s%n", metadata.topic(), metadata.partition());}}});}}}}
在控制台中打开
Consumer
; 可以看到数据已经被接收到了
passnight@passnight-s600:/usr/local/kafka/kafka_2.13-3.5.1/bin$ ./kafka-console-consumer.sh --bootstrap-server server.passnight.local:20015 --topic first
value 0
value 1
value 2
value 3
value 4
并且回调函数也成功执行, 数据被打印在控制台当中
主题: first, 分区: 0
主题: first, 分区: 0
主题: first, 分区: 0
主题: first, 分区: 0
主题: first, 分区: 0
同步发送
classSyncProducer{publicstaticvoidmain(String[] args){Properties properties =newProperties();// 连接集群(server.passnight.local:20015)
properties.put(ProducerConfig.BOOTSTRAP_SERVERS_CONFIG,"server.passnight.local:20015");// 配置Key/Value序列化类
properties.put(ProducerConfig.KEY_SERIALIZER_CLASS_CONFIG,StringSerializer.class.getName());
properties.put(ProducerConfig.VALUE_SERIALIZER_CLASS_CONFIG,StringSerializer.class.getName());try(KafkaProducer<String,String> kafkaProducer =newKafkaProducer<>(properties)){for(int i =0; i <5; i++){// 发送数据RecordMetadata metadata = kafkaProducer.send(newProducerRecord<>("first",String.format("value %d", i))).get();System.out.printf("metadata: %s%n", metadata.toString());}}catch(ExecutionException|InterruptedException e){thrownewRuntimeException(e);}}}
可以看到消费者成功接收到数据
passnight@passnight-s600:/usr/local/kafka/kafka_2.13-3.5.1/bin$ ./kafka-console-consumer.sh --bootstrap-server server.passnight.local:20015 --topic first
value 0
value 1
value 2
value 3
value 4
并且发送成功后返回的元数据也成功打印
metadata: first-0@45
metadata: first-0@46
metadata: first-0@47
metadata: first-0@48
metadata: first-0@49
分区
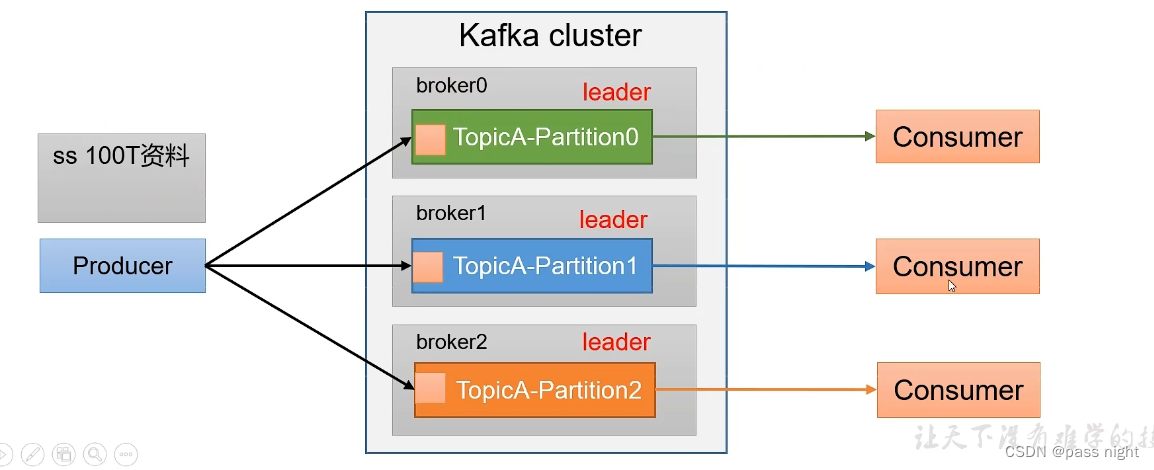
分区的优点:
- 便于合理使用存储资源, 可以将数据分为多个区, 然后将数据存储在多个Broker上; 从而达到负载均衡地效果
- 提高并行度: 生产者可以以分区为单位发送数据, 消费者也可以以分区为单位进行数据消费
Kafka默认分区器
以下内容是从Kafka的
DefaultPartiioner
拷贝过来的, 它解释了Kafka的分区算法:
- The default partitioning strategy:
- If a partition is specified in the record, use it
- If no partition is specified but a key is present choose a partition based on a hash of the key
- If no partition or key is present choose the sticky partition that changes when the batch is full.
- See KIP-480 for details about sticky partitioning.
因此, 在默认情况下:
- 若指明分区则将数据写入对应分区
- 若指明了
key之后, Kafka根据Key的Hash值进行分区 - 若都没有指定, Kafka会采用粘性分区随机使用一个分区, 并尽可能使用该分区, 直到该分区的batch已满或已完成
下面例子中指定了特定分区:
classPartitionProducer{publicstaticvoidmain(String[] args){Properties properties =newProperties();// 连接集群(server.passnight.local:20015)
properties.put(ProducerConfig.BOOTSTRAP_SERVERS_CONFIG,"server.passnight.local:20015,replica.passnight.local:20015,follower.passnight.local:20015");// 配置Key/Value序列化类
properties.put(ProducerConfig.KEY_SERIALIZER_CLASS_CONFIG,StringSerializer.class.getName());
properties.put(ProducerConfig.VALUE_SERIALIZER_CLASS_CONFIG,StringSerializer.class.getName());try(KafkaProducer<String,String> kafkaProducer =newKafkaProducer<>(properties)){for(int i =0; i <5; i++){// 发送数据
kafkaProducer.send(newProducerRecord<>("first",2,"",String.format("value %d", i)),newCallback(){@OverridepublicvoidonCompletion(RecordMetadata metadata,Exception exception){if(exception ==null){System.out.printf("主题: %s, 分区: %s%n", metadata.topic(), metadata.partition());}}});}}}}
Kafka将数据发送到了指定的分区
主题: first, 分区: 2
主题: first, 分区: 2
主题: first, 分区: 2
主题: first, 分区: 2
主题: first, 分区: 2
注意这之前需要在Kafka-Manager中添加分区
自定义分区器
classCustomerPartitionProducer{publicstaticclassHelloPartitionerimplementsPartitioner{// 注意这个要生命为public类型@Overridepublicintpartition(String topic,Object key,byte[] keyBytes,Object value,byte[] valueBytes,Cluster cluster){String msg = value.toString();return msg.contains("hello")?0:1;}@Overridepublicvoidclose(){}@Overridepublicvoidconfigure(Map<String,?> configs){}}publicstaticvoidmain(String[] args){Properties properties =newProperties();
properties.put(ProducerConfig.BOOTSTRAP_SERVERS_CONFIG,"server.passnight.local:20015,replica.passnight.local:20015,follower.passnight.local:20015");
properties.put(ProducerConfig.KEY_SERIALIZER_CLASS_CONFIG,StringSerializer.class.getName());
properties.put(ProducerConfig.VALUE_SERIALIZER_CLASS_CONFIG,StringSerializer.class.getName());// 使用自定义分区器
properties.put(ProducerConfig.PARTITIONER_CLASS_CONFIG,HelloPartitioner.class.getName());String[] messages =newString[]{"hello message","greeting","hello","no more"};try(KafkaProducer<String,String> kafkaProducer =newKafkaProducer<>(properties)){for(String message : messages){// 发送数据
kafkaProducer.send(newProducerRecord<>("first",String.format("%s", message)),(metadata, exception)->{if(exception ==null){System.out.printf("主题: %s, 值: %s, 分区: %s%n", metadata.topic(), message, metadata.partition());}});}}}}
上述分区器将含有
hello
的分区到
0
, 不含的分区到
1
; 打印结果如下:
主题: first, 值: greeting, 分区: 1
主题: first, 值: no more, 分区: 1
主题: first, 值: hello message, 分区: 0
主题: first, 值: hello, 分区: 0
性能
影响Kafka主要有以下几个方面:
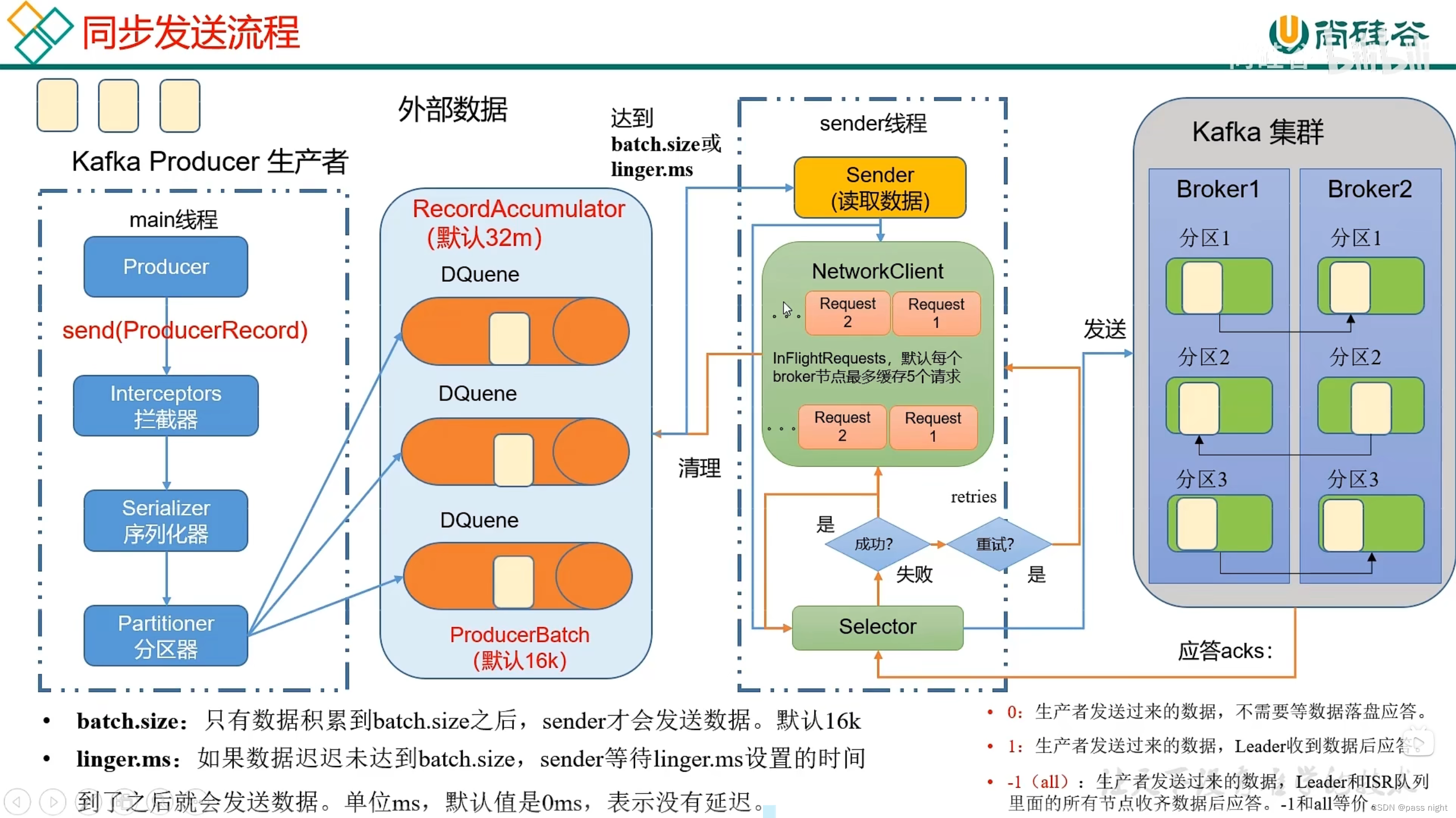
batch.size: 批次大小, 影响每批的大小; 只有当批次缓冲满了之后, 才会发送消息; 增大会提高吞吐量但会也会提高延迟linger.ms: 等待时间, 默认为0毫秒, 若缓冲区没满但是达到了等待时间, 也会发送消息; 若调大则会等待批次中的消息积压, 增大单批次的数据量; 但是会增大延迟 需要同步提高批次大小compression.type: 压缩, 若对数据进行压缩, 单次可以运送的数据增大RecordAccumulator: 缓冲区大小, 也需要和批次大小相适配, 否则会导致传输不能满足等待时间和批次大小
下面是一个设置上述参数的例子:
classParameterProducer{publicstaticvoidmain(String[] args){Properties properties =newProperties();// 连接集群(server.passnight.local:20015)
properties.put(ProducerConfig.BOOTSTRAP_SERVERS_CONFIG,"server.passnight.local:20015,replica.passnight.local:20015,follower.passnight.local:20015");// 配置Key/Value序列化类
properties.put(ProducerConfig.KEY_SERIALIZER_CLASS_CONFIG,StringSerializer.class.getName());
properties.put(ProducerConfig.VALUE_SERIALIZER_CLASS_CONFIG,StringSerializer.class.getName());// 性能相关参数
properties.put(ProducerConfig.BUFFER_MEMORY_CONFIG,64*1024*1024);// 批次大小, 32M->64M
properties.put(ProducerConfig.BATCH_SIZE_CONFIG,16*1024);// 默认是16k, 这里保留默认值
properties.put(ProducerConfig.LINGER_MS_CONFIG,1);// 等待时间, 0ms->1ms
properties.put(ProducerConfig.COMPRESSION_TYPE_CONFIG,CompressionType.SNAPPY.name);// 使用snappy压缩try(KafkaProducer<String,String> kafkaProducer =newKafkaProducer<>(properties)){for(int i =0; i <5; i++){// 发送数据
kafkaProducer.send(newProducerRecord<>("first",String.format("value %d", i)),(metadata, exception)->{if(exception ==null){System.out.printf("主题: %s, 分区: %s%n", metadata.topic(), metadata.partition());}});}}}}
控制台打印出发送结果:
主题: first, 分区: 34
主题: first, 分区: 34
主题: first, 分区: 34
主题: first, 分区: 34
主题: first, 分区: 34
数据可靠性
可以根据Kafka的
ack
来判断数据是否成功落盘; 因此可以配置
ack
应答级别来控制可靠性
ack=0: 生产者不需要等待数据应答, 无任何可靠性保证ack=1: 生产者发送数据, Leader收到数据后应答, 在下述情况中可能会导致数据丢失: 1. Leader完成同步但是还没同步副本后宕机, 此时生产者因为收到ack认为数据已经落盘, 若数据没有同步到任何Follower, 数据便会丢失ack=-1: 只有等待所有ISR队列中的节点(部分Follower)完成与Leader的同步后, Leader才会返回ACK, 因为若需要所有Follower同步可能存在下面问题: 1. 某个Follower宕机, Leader无法接收所有Follower的ACK, 这样会导致Leader一直等待2. 为了解决这个问题, Kafka维护了一个集合in-sync replica set(ISR)保存所有正常同步的节点; 若Follower长时间未向Leader发送心跳, Follower会被踢出ISR; 该时间阈值可以通过replica.lag.time.max.ms配置3. 这样配置, 若ISR中应答的最小副本量为1或分区的副本设置为1, 同ack=1一样, 仍然有丢数的风险4. 但是可能会导致数据重复的问题: 在完成数据同步后, Leader宕机, Producer未收到ACK重试, 导致重发, 进而导致数据重复- 为了保证数据完全可靠, 需要满足: 1. ACK级别为-12. 分区副本数 ≥ 2 \ge 2 ≥23. ISR应答的最小副本数量 ≥ 2 \ge 2 ≥2
- 现实情况中: 1.
ack=0几乎不适用2.ack=1: 可以用于传输日志, 允许丢失个别数据3.ack=-1: 用于传输部分重要数据
以下是一个在Java代码中配置的例子
classReliableProducer{publicstaticvoidmain(String[] args){Properties properties =newProperties();// 连接集群(server.passnight.local:20015)
properties.put(ProducerConfig.BOOTSTRAP_SERVERS_CONFIG,"server.passnight.local:20015,replica.passnight.local:20015,follower.passnight.local:20015");// 配置Key/Value序列化类
properties.put(ProducerConfig.KEY_SERIALIZER_CLASS_CONFIG,StringSerializer.class.getName());
properties.put(ProducerConfig.VALUE_SERIALIZER_CLASS_CONFIG,StringSerializer.class.getName());// 性能相关参数
properties.put(ProducerConfig.ACKS_CONFIG,"1");// 配置ack=1, 当Leader落盘后完成传输
properties.put(ProducerConfig.RETRIES_CONFIG,3);// 重试次数, Integer.MAX_VALUE -> 1try(KafkaProducer<String,String> kafkaProducer =newKafkaProducer<>(properties)){for(int i =0; i <5; i++){// 发送数据
kafkaProducer.send(newProducerRecord<>("first",String.format("value %d", i)),(metadata, exception)->{if(exception ==null){System.out.printf("主题: %s, 分区: %s%n", metadata.topic(), metadata.partition());}});}}}}
数据重复
数据传递也有以下几个等级:
- 至少一次(At Least Once): Ack=-1/分区副本数 ≥ 2 \ge 2 ≥2/ISR应答的最小副本数量 ≥ 2 \ge 2 ≥2
- 最多一次(At Most Once): Ack=0
- 精确一次(Exactly Once): 幂等性+至少一次
幂等性

- 定义: 幂等性指无论Producer无论向Broker重复发送多少次数据, Broker都只会持久化一条, 保证了不重复
- 重复数据的判断标准: 以<PID, Partition, SeqNumber>为主键 1. PID: Kafka每次重启都会分配一个新的2. Partition 表示分区号3. SeqNumber: 单调自增的数字4. 因此幂等性保证了: 单分区/单会话不重复
- Kafka通过
enable.idempotence来配置, 默认为true即开启
生产者事务
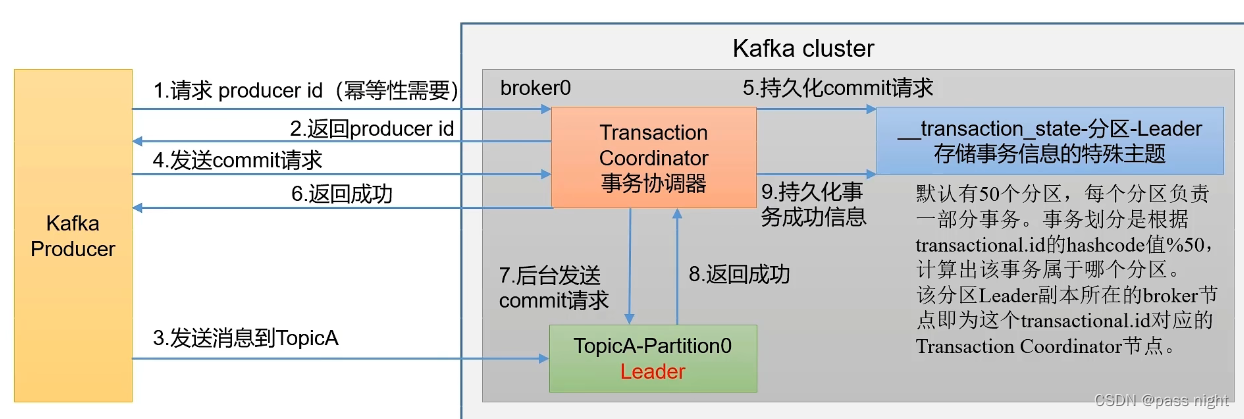
- 定义: 端到端仅有一次, 既可以实现多个
topic多个partition的原子写入 精确一次不保证多分区多主题的原子写入 - 前提: 若要开启生产者事务, 一定要开启幂等性
- 实现方法: 1. 实现幂等性2. 事务协调器: 协调事务; 所有broker都有, 由生产者的
transaction.id决定事务处于哪个分区, 再由对应分区的Leader节点提供事务协调器
当没有开启事务的时候
classTransactionalProducer{publicstaticvoidmain(String[] args){Properties properties =newProperties();
properties.put(ProducerConfig.BOOTSTRAP_SERVERS_CONFIG,"server.passnight.local:20015,replica.passnight.local:20015,follower.passnight.local:20015");
properties.put(ProducerConfig.KEY_SERIALIZER_CLASS_CONFIG,StringSerializer.class.getName());
properties.put(ProducerConfig.VALUE_SERIALIZER_CLASS_CONFIG,StringSerializer.class.getName());// 开启事务必须指定事务id// properties.put(ProducerConfig.TRANSACTIONAL_ID_CONFIG, "transactional_id_01");KafkaProducer<String,String> kafkaProducer =newKafkaProducer<>(properties);try{// kafkaProducer.initTransactions(); // 初始化事务// kafkaProducer.beginTransaction();for(int i =0; i <5; i++){
kafkaProducer.send(newProducerRecord<>("first",String.format("value %d", i)));if(i ==3){int a =1/0;// 触发异常, 放弃事务}}// kafkaProducer.commitTransaction(); // 提交事务}catch(Exception e){// kafkaProducer.abortTransaction();// 异常则放弃事务thrownewRuntimeException(e);}finally{
kafkaProducer.close();}}}
消费者接受到了部分数据
passnight@passnight-s600:/usr/local/kafka/kafka_2.13-3.5.1/bin$ ./kafka-console-consumer.sh --bootstrap-server replica.passnight.local:20015 --topic first
value 0
value 1
value 2
value 3
开启事务后
classTransactionalProducer{publicstaticvoidmain(String[] args){Properties properties =newProperties();
properties.put(ProducerConfig.BOOTSTRAP_SERVERS_CONFIG,"server.passnight.local:20015,replica.passnight.local:20015,follower.passnight.local:20015");
properties.put(ProducerConfig.KEY_SERIALIZER_CLASS_CONFIG,StringSerializer.class.getName());
properties.put(ProducerConfig.VALUE_SERIALIZER_CLASS_CONFIG,StringSerializer.class.getName());// 开启事务必须指定事务id
properties.put(ProducerConfig.TRANSACTIONAL_ID_CONFIG,"transactional_id_01");KafkaProducer<String,String> kafkaProducer =newKafkaProducer<>(properties);try{
kafkaProducer.initTransactions();// 初始化事务
kafkaProducer.beginTransaction();for(int i =0; i <5; i++){
kafkaProducer.send(newProducerRecord<>("first",String.format("value %d", i)));if(i ==3){int a =1/0;// 触发异常, 放弃事务}}
kafkaProducer.commitTransaction();// 提交事务}catch(Exception e){
kafkaProducer.abortTransaction();// 异常则放弃事务thrownewRuntimeException(e);}finally{
kafkaProducer.close();}}}
消费者没有接收到任何数据
passnight@passnight-s600:/usr/local/kafka/kafka_2.13-3.5.1/bin$ ./kafka-console-consumer.sh --bootstrap-server replica.passnight.local:20015 --topic first
数据有序
- 单分区有序:1. Kafka某个分区中的数据生成一个偏移量, 而消费者会根据偏移量消费数据, 所以在单分区内数据的存储是有序的
- 多分区有序1. 因为Kafka在单分区内消息时有序的, 因此只要在生产者保证需要保证顺序的消息被路由到同一个分区即可 (如使用哈希分区)2. 在异常情况下, 若A消息先被收到, 但A消息因执行异常B先执行导致消息乱序, 需要通过开启
max.in.flightrequests.pre.connection来开启同步重试来保证严格有序 - 窗口: 将所有数据都拉下来后排序, 完成排序后再消费
- 设置
max.in.flightrequests.pre.connection=1: 只有当前消息应答后才能发送小一条 1.x版本之前 - 设置
max.in.flightrequests.pre.connection小于5, 并开启幂等性; 因为kafka集群会缓存最近5个请求 1.x版本之后
Kafka Broker
Kafka Broker工作流程
Zookeeper中记录信息
Kafka中的信息都存储在Zookeeper中, 因此可以在Zookeeper中查看Zookeeper信息; 我们可以使用
PrettyZookeeper
查看Zookeeper中的信息; 其中主要要了解的节点有:
/kafka/brokers/ids: 记录有哪些服务器// /kafka/brokers/ids/0{"listener_security_protocol_map":{"PLAINTEXT":"PLAINTEXT"},"endpoints":["PLAINTEXT://server.passnight.local:20015"],"jmx_port":-1,"features":{},"host":"server.passnight.local","timestamp":"1694323239360","port":20015,"version":5}/kafka/brokers/topics/first/partitions/0/state: 记录谁是Leader, 哪些服务可用:// topic: first, partition: 0对应的信息{"controller_epoch":11,"leader":1,"version":1,"leader_epoch":0,"isr":[1]}/kafka/consumers: 消费者信息/kafka/controller: 辅助leader选举的信息:// /kafka/controller{"version":2,"brokerid":0,"timestamp":"1694323244719","kraftControllerEpoch":-1}
Kafka副本
- 副本的作用: 提高数据可靠性
- 副本的数量: 默认为1个, 生产环境一般配置为2个, 既保证了可靠性, 也不会太浪费磁盘空间和网络带宽
- 副本的分类: 副本分为: Leader和Follower, Kafka生产者只会将数据发送给Leader, 而Follower会从Leader同步数据
- 所有副本AR(Assigned Replicas): AR = ISR + OSR 1. ISR(in sync replica): 表示正常与Leader同步的Follower的集合, 超时时间可以用
replica.lag.time.max.ms设置, 默认为30s; 当Leader故障后, 就会从ISR中选举新的Leader2. OSR(Out-of-Sync Replicas): Follower与Leader同步超时的副本
Kafka Broker总体工作流程
选举流程
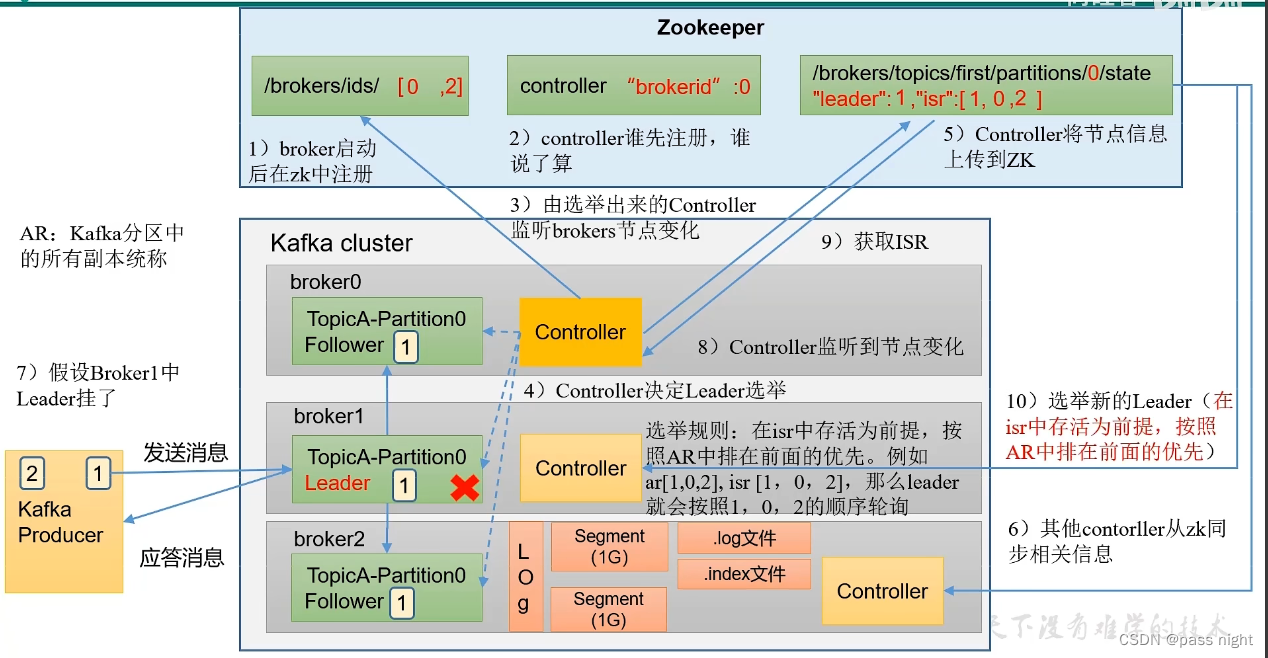
- Kafka Broker中的Controller争先写入Zookeeper的
controller节点, 优先写入者决定选举 - 按照AR中的排序顺序, 对在isr中存活的节点轮询, 最先轮询到可用的节点为Leader
- 将可用的信息同步到Zookeeper, 其他的节点再从Zookeeper中拉取信息
Leader/Follower故障处理
- LEO(Log End Offset): 每个副本的最后一个offset, LEO就是最新的offset+1
- HW(High Watermark): 所有副本中最小的LEO 也是消费者可见的最大的offset
Follower故障处理
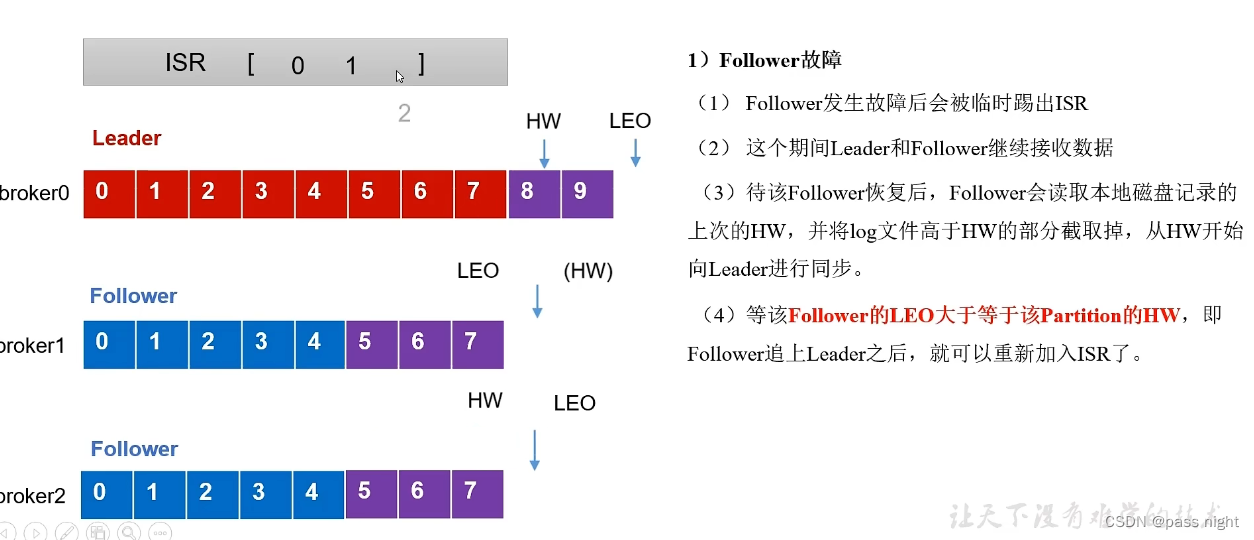
- 将Follower踢出ISR
- ISR中的Leader和Follower正常工作; HW和LEO都会正常前移
- 待该follower恢复后, 会读取本地磁盘, 恢复HW, 并将高于HW的数据截取因为会认为这些数据未验证; 之后与Leader同步
- 等待Follower的LEO大于或等于Partition的HW, 即Follower追上Leader之后, 可以重新加入ISR
Leader故障处理
- Leader故障, Leader被从ISR中剔除, 系统从ISR中选举出一个新的Leader
- Follower将各自文件高于Leader的部分截取掉, 然后从新的Leader中同步数据 这样只能保证数据的一致性, 不能保证数据不丢失或不重复
文件读写流程
Kafka文件存储
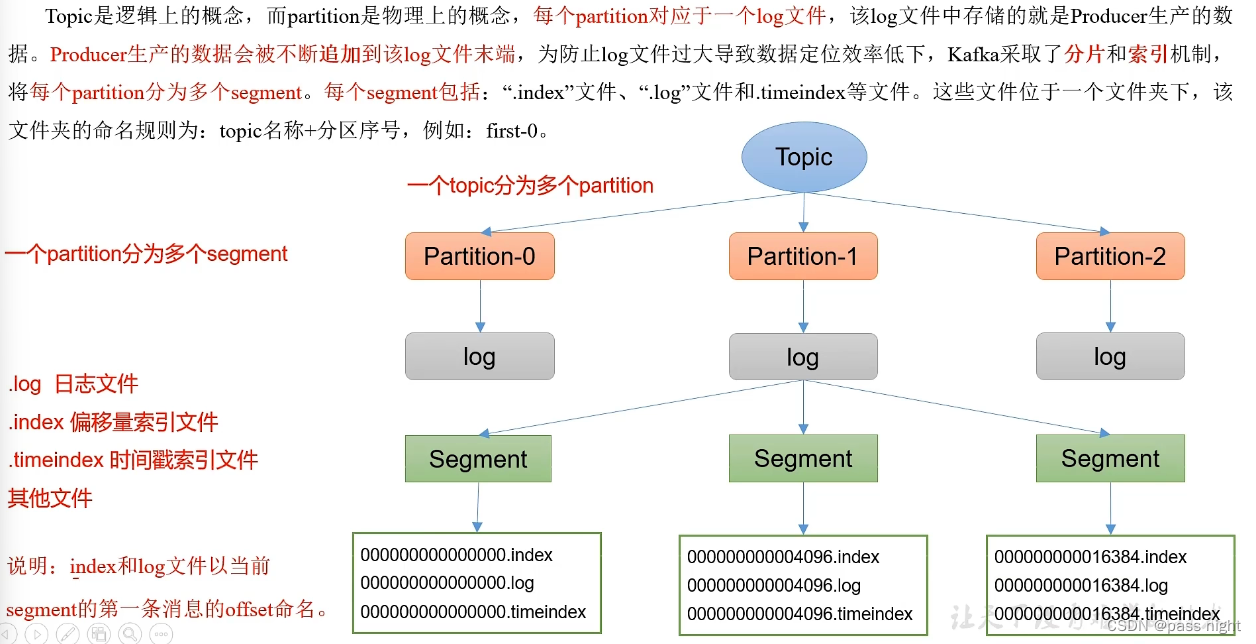
- Topic是一个逻辑上的概念
- Partition是一个物理上的概念, 每个Partition对应一个log文件
- 该log文件存储了Producer产生的数据, Producer产生的数据会不断被追加到log文件末端
- 为了防止log文件过大导致数据定位效率低下, Kafka采用了分片和索引机制, 每个Partition分为多个segment
- 每个segment包含1.
index文件: 偏移量索引文件, 以前一个文件最大的索引命名; index是稀疏索引, 每往log文件写入4kb数据, 才会往index文件写入一条索引, 可以通过log.index.interval.bytes设置2.log文件: 日志文件3.timeindex: 时间戳索引文件; segment只会保存一定时间, 超过后会被删除4. 等文件 - 这些文件位于一个文件夹下, 该文件夹的命名规则为
topic名称+分区序号如first-0 - 该文件可以使用
kafka-run-class.sh来查看:# 查看索引文件passnight@passnight-s600:/opt/docker/kafka/data$ /usr/local/kafka/kafka_2.13-3.5.1/bin/kafka-run-class.sh kafka.tools.DumpLogSegments --files ./logs/first-11/00000000000000000000.indexDumping ./logs/first-11/00000000000000000000.indexoffset: 0 position: 0# 查看日志文件passnight@passnight-s600:/opt/docker/kafka/data$ /usr/local/kafka/kafka_2.13-3.5.1/bin/kafka-run-class.sh kafka.tools.DumpLogSegments --files ./logs/first-11/00000000000000000000.logDumping ./logs/first-11/00000000000000000000.logLog starting offset: 0baseOffset: 0 lastOffset: 0 count: 1 baseSequence: -1 lastSequence: -1 producerId: 0 producerEpoch: 1 partitionLeaderEpoch: 0 isTransactional: true isControl: true deleteHorizonMs: OptionalLong.empty position: 0 CreateTime: 1694349261255 size: 78 magic: 2 compresscodec: none crc: 2496089419 isvalid: true
文件清除策略
kafka可以保存消息一段时间, 具体可以通过以下配置:
- 保存时间(不同单位): 1.
log.retention.hours: 默认7天(默认值为168), 单位为小时, 优先级最低2.log.retention.minutes: 分钟3.log.retention.ms: 毫秒, 最高优先级 log.retnetion.check.interval.ms: 检查周期, 默认为5分钟- Kafka中对于过期的日志有两种处理方式(删除和压缩), 可以通过
log.cleanup.policy=delete配置 1. 删除有两种策略: 1. 基于时间(默认打开): 以segment中所有记录中最大的时间戳作为文件的时间戳这是为了防止部分过期部分没过期的segment被删除2. 基于大小(默认关闭): 超过所设置的所有日志总大小, 删除最小的segment, 根据log.retention.bytes配置, 默认为-1, 表示无穷大2. 压缩策略(通过log.cleanup.policy=compact打开: 1. 对于相同的Key不同的Value值, 只保留最新的版本2. 但压缩后的数据不再是连续的, *假设要拿offset=6的信息, 最后因为offset=6被压缩了, 只能拿offset=7的数据
高效读写技术的实现
- Kafka是分布式集群, 采用分区数据, 并行度高
- Kafka采用稀疏索引, 可以快速定位要消费的数据
- 顺序写入磁盘: producer生产的数据写入log的过程, 一直是通过追加的形式加到文件末端; 因为是顺序读写, 可以最大化发挥某些硬盘的性能
- 零拷贝技术: 减少了用户态/内核态切换及用户态/内核态间无效的数据拷贝
- 页缓存技术: 操作系统提供页缓存, 缓存磁盘IO数据
Broker 相关基本操作
分区副本分配
# 创建一个新的topic: `second`; 由16个分区, 3个副本
passnight@passnight-s600:/usr/local/kafka/kafka_2.13-3.5.1/bin$ ./kafka-topics.sh --bootstrap-server replica.passnight.local:20015 --create--topic second --partitions16 --replication-factor 3
Created topic second.
# 使用describe命令查看所有副本, 可以看到副本/leader存在`1,0,2`的周期性; Kafka会均匀将将分区放在不同的服务器上
passnight@passnight-s600:/usr/local/kafka/kafka_2.13-3.5.1/bin$ ./kafka-topics.sh --bootstrap-server replica.passnight.local:20015 --describe--topic second
Topic: second TopicId: 6oBdeLc9Qu2yoGnByrBLkg PartitionCount: 16 ReplicationFactor: 3 Configs:
Topic: second Partition: 0 Leader: 1 Replicas: 1,0,2 Isr: 1,0,2
Topic: second Partition: 1 Leader: 0 Replicas: 0,2,1 Isr: 0,2,1
Topic: second Partition: 2 Leader: 2 Replicas: 2,1,0 Isr: 2,1,0
Topic: second Partition: 3 Leader: 1 Replicas: 1,2,0 Isr: 1,2,0
Topic: second Partition: 4 Leader: 0 Replicas: 0,1,2 Isr: 0,1,2
Topic: second Partition: 5 Leader: 2 Replicas: 2,0,1 Isr: 2,0,1
Topic: second Partition: 6 Leader: 1 Replicas: 1,0,2 Isr: 1,0,2
Topic: second Partition: 7 Leader: 0 Replicas: 0,2,1 Isr: 0,2,1
Topic: second Partition: 8 Leader: 2 Replicas: 2,1,0 Isr: 2,1,0
Topic: second Partition: 9 Leader: 1 Replicas: 1,2,0 Isr: 1,2,0
Topic: second Partition: 10 Leader: 0 Replicas: 0,1,2 Isr: 0,1,2
Topic: second Partition: 11 Leader: 2 Replicas: 2,0,1 Isr: 2,0,1
Topic: second Partition: 12 Leader: 1 Replicas: 1,0,2 Isr: 1,0,2
Topic: second Partition: 13 Leader: 0 Replicas: 0,2,1 Isr: 0,2,1
Topic: second Partition: 14 Leader: 2 Replicas: 2,1,0 Isr: 2,1,0
Topic: second Partition: 15 Leader: 1 Replicas: 1,2,0 Isr: 1,2,0
有的时候由于每台服务器性能不一致; 按照Kafka默认的分配方式并不是最优的, 因此需要手动调整分区副本
# 创建一个4分区, 2副本的主题
passnight@passnight-s600:/usr/local/kafka/kafka_2.13-3.5.1/bin$ ./kafka-topics.sh --bootstrap-server replica.passnight.local:20015 --create--topic three --partitions4 --replication-factor 2
Created topic three.
# 查看注意分布
passnight@passnight-s600:/usr/local/kafka/kafka_2.13-3.5.1/bin$ ./kafka-topics.sh --bootstrap-server replica.passnight.local:20015 --describe--topic three
Topic: three TopicId: _E1mdzhSTWSOzsN7399tTg PartitionCount: 4 ReplicationFactor: 2 Configs:
Topic: three Partition: 0 Leader: 2 Replicas: 2,1 Isr: 2,1
Topic: three Partition: 1 Leader: 1 Replicas: 1,0 Isr: 1,0
Topic: three Partition: 2 Leader: 0 Replicas: 0,2 Isr: 0,2
Topic: three Partition: 3 Leader: 2 Replicas: 2,0 Isr: 2,0
passnight@passnight-s600:/usr/local/kafka/kafka_2.13-3.5.1$ sudovim reset-replication-factor.json
输入以下内容
{"version":1,"partitions":[{"topic":"three","partition":0,"replicas":[0,1]},{"topic":"three","partition":1,"replicas":[0,1]},{"topic":"three","partition":2,"replicas":[1,0]},{"topic":"three","partition":3,"replicas":[1,0]}]}
并执行
passnight@passnight-s600:/usr/local/kafka/kafka_2.13-3.5.1$ ./bin/kafka-reassign-partitions.sh --bootstrap-server replica.passnight.local:20015 --reassignment-json-file reset-replication-factor.json --execute
Current partition replica assignment
{"version":1,"partitions":[{"topic":"three","partition":0,"replicas":[2,1],"log_dirs":["any","any"]},{"topic":"three","partition":1,"replicas":[1,0],"log_dirs":["any","any"]},{"topic":"three","partition":2,"replicas":[0,2],"log_dirs":["any","any"]},{"topic":"three","partition":3,"replicas":[2,0],"log_dirs":["any","any"]}]}
Save this to use as the --reassignment-json-file option during rollback
Successfully started partition reassignments for three-0,three-1,three-2,three-3
# 验证是否重分配成功, 发现已经完成重新分配
passnight@passnight-s600:/usr/local/kafka/kafka_2.13-3.5.1/bin$ ./kafka-reassign-partitions.sh --bootstrap-server replica.passnight.local:20015 --reassignment-json-file ../reset-replication-factor.json --verify
Status of partition reassignment:
Reassignment of partition three-0 is completed.
Reassignment of partition three-1 is completed.
Reassignment of partition three-2 is completed.
Reassignment of partition three-3 is completed.
Clearing broker-level throttles on brokers 0,1,2
Clearing topic-level throttles on topic three
# 重新查看, 发现分区已经按照预定义的调整了
passnight@passnight-s600:/usr/local/kafka/kafka_2.13-3.5.1/bin$ ./kafka-topics.sh --bootstrap-server replica.passnight.local:20015 --describe--topic three
Topic: three TopicId: _E1mdzhSTWSOzsN7399tTg PartitionCount: 4 ReplicationFactor: 2 Configs:
Topic: three Partition: 0 Leader: 0 Replicas: 0,1 Isr: 1,0
Topic: three Partition: 1 Leader: 1 Replicas: 0,1 Isr: 1,0
Topic: three Partition: 2 Leader: 0 Replicas: 1,0 Isr: 0,1
Topic: three Partition: 3 Leader: 1 Replicas: 1,0 Isr: 0,1
Leader Partition 自动平衡
- 正常情况, Kafka本身会自动将Leader partition均匀分散在各个节点上, 来保证每个节点的吞吐量是均匀的
- 但若某个broker宕机, 会导致Leader Partition过于集中在部分几台broker上
- 并且即使旧leader重启后, 只能作为follower, 无法重新分担新leader的任务
- 为了解决这个问题, Kafka有一个变量
auto.leader.rebalance.enable, 当broker不平衡的阈值达到这个数值时, 控制器会重新平衡leader 默认值为10% - 同时还可以通过
leaer.imbalance.check.interval.seconds来配置检测leader负载的时间间隔 默认值为300
增加副本因子
# 创建主题4, 副本数为1
passnight@passnight-s600:/usr/local/kafka/kafka_2.13-3.5.1/bin$ ./kafka-topics.sh --bootstrap-server replica.passnight.local:20015 --create--topic four --partitions3 --replication-factor 1
Created topic four.
# 修改副本数为3(不能通过命令行参数修改, 只能通过josn重新分配)
passnight@passnight-s600:/usr/local/kafka/kafka_2.13-3.5.1/bin$ sudovim../reset-replication-factor.json
修改json文件为:
{"version":1,"partitions":[{"topic":"four","partition":0,"replicas":[0,1,2]},{"topic":"four","partition":1,"replicas":[0,1,2]},{"topic":"four","partition":2,"replicas":[0,1,2]}]}
执行并查看结果
passnight@passnight-s600:/usr/local/kafka/kafka_2.13-3.5.1/bin$ ./kafka-reassign-partitions.sh --bootstrap-server replica.passnight.local:20015 --reassignment-json-file ../reset-replication-factor.json --verify
Status of partition reassignment:
There is no active reassignment of partition four-0, but replica set is 2 rather than 0,1,2.
There is no active reassignment of partition four-1, but replica set is 1 rather than 0,1,2.
There is no active reassignment of partition four-2, but replica set is 0 rather than 0,1,2.
Clearing broker-level throttles on brokers 0,1,2
Clearing topic-level throttles on topic four
passnight@passnight-s600:/usr/local/kafka/kafka_2.13-3.5.1/bin$ ./kafka-topics.sh --bootstrap-server replica.passnight.local:20015 --describe--topic four
Topic: four TopicId: OJT1_NUOSv-AkGirZgl4RA PartitionCount: 3 ReplicationFactor: 1 Configs:
Topic: four Partition: 0 Leader: 2 Replicas: 2 Isr: 2
Topic: four Partition: 1 Leader: 1 Replicas: 1 Isr: 1
Topic: four Partition: 2 Leader: 0 Replicas: 0 Isr: 0
可以看到副本数已经成功改变
Kafka消费者
消费方式主要分为以下两种消费方式
- pull模式: consumer主动从broker中拉取数据; 这样consumer可以根据自己的处理能力决定拉取的速度; 但如果生产者没有生产数据, 生产者就会陷入空循环
- push模式: producer主动推送数据给consumer
消费者工作流程
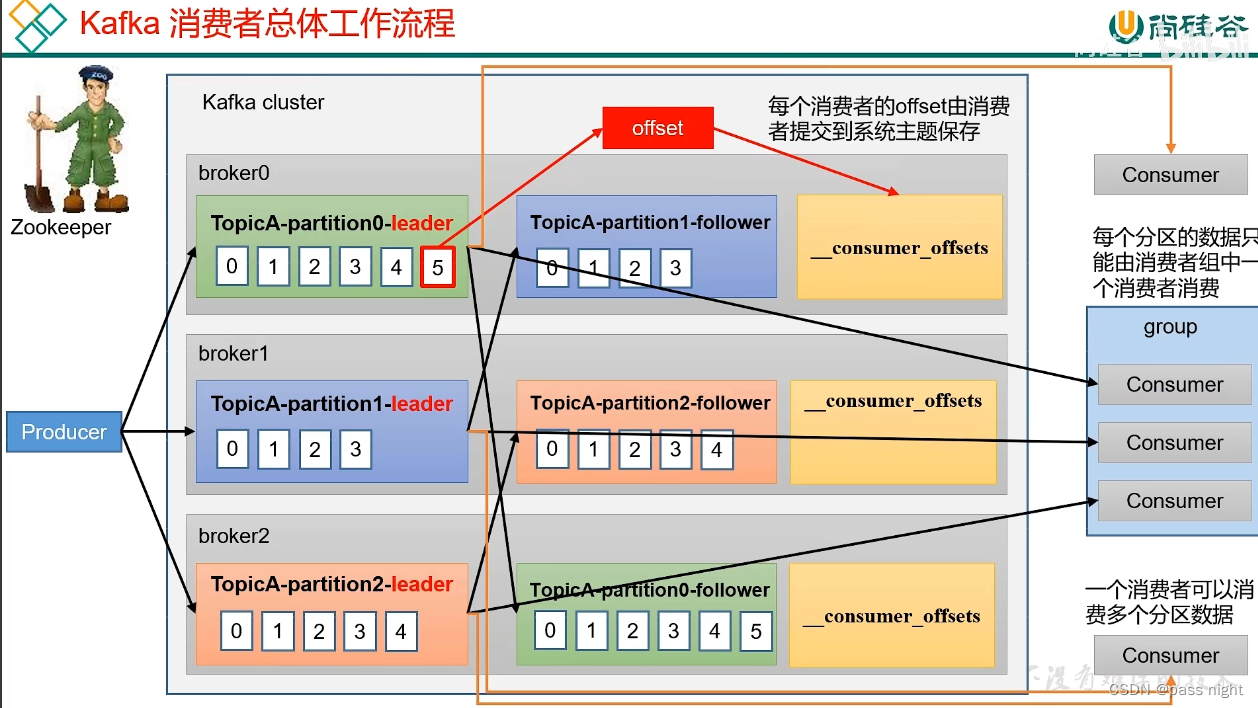
- 生产者生产数据, 并向Leader发送数据
- Follower主动向Leader同步数据
- 消费者可以消费一个或多个分区的数据; 但是消费者组中只能有一个消费者消费一个分区
- Kafka会将消费到的位置offset保存到磁盘中, 这样当消费者宕机重新加入集群后可以继续消费 老版本offset会存储在zookeeper中, 但因为所有消费者都将offset存储到zookeeper中会让zookeeper不堪重负, 所以新版本改到了各个节点
消费者组原理
- 消费者组(Consumer Group): 由多个消费者组成, 其中他们的
groupid相同 1. 消费者组内各个消费者负责消费不同分区的数据, 一个分区只能由一个组内的消费者消费2. 消费者组之间互不影响, 所有的消费者都属于某个消费者组, 因此消费者组是逻辑上的订阅者3. 注意: 一旦消费者超过分区超过分区数量, 则会有一部分消费者闲置, 不接收任何消息
消费者组的初始化流程
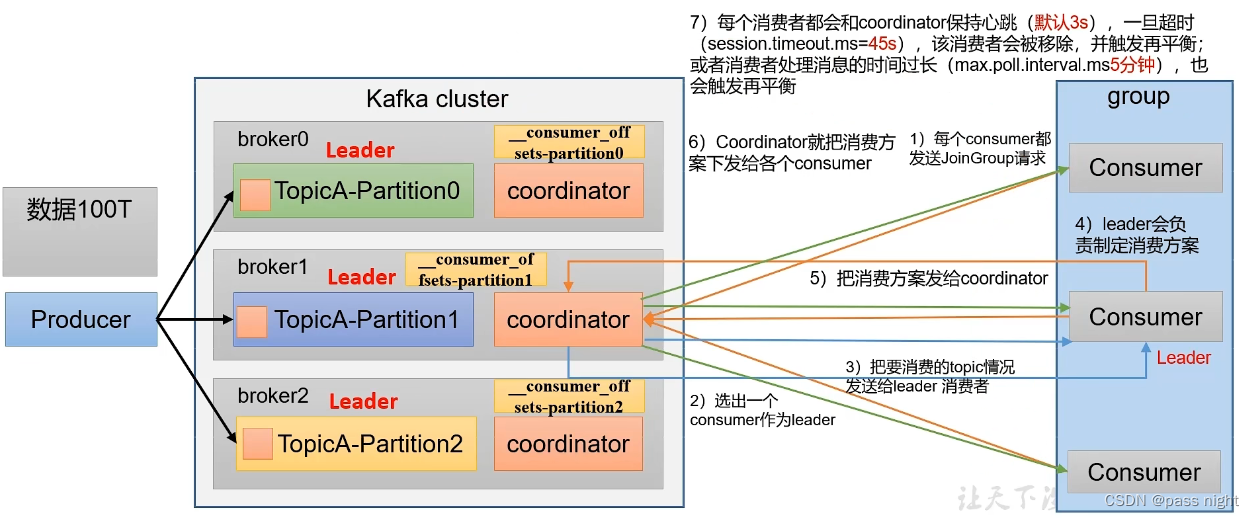
- coordinator: 辅助实现消费者组的初始化和分区的分配; 其选择函数为: h a s h ( g r o u p i d ) % n u m _ _ c o n s u m e r _ o f f s e t s hash(groupid) % num_{__consumer_offsets} hash(groupid)%num__consumer_offsets
- 所有消费者向coordinator发送加入组请求, coordinator会从所有消费者中随机选一个做Leader, 再把要消费的topic信息发送给消费者Leader
- 消费者Leader根据topic信息生成消费方案, 再将消费方案发送给coordinator
- coordinator再将消费方案同步发送给其他的消费者
- 这个过程, 所有消费者会与coordinator进行心跳同步, 超时coordinator会认为消费者离线, 会重新分配任务; 消费者处理消息时间过长也会再触发平衡 前者可以通过
session.timeout.ms=45s配置, 后者可以通过max.poll.interval.ms=5min配置
消费者组的消费流程
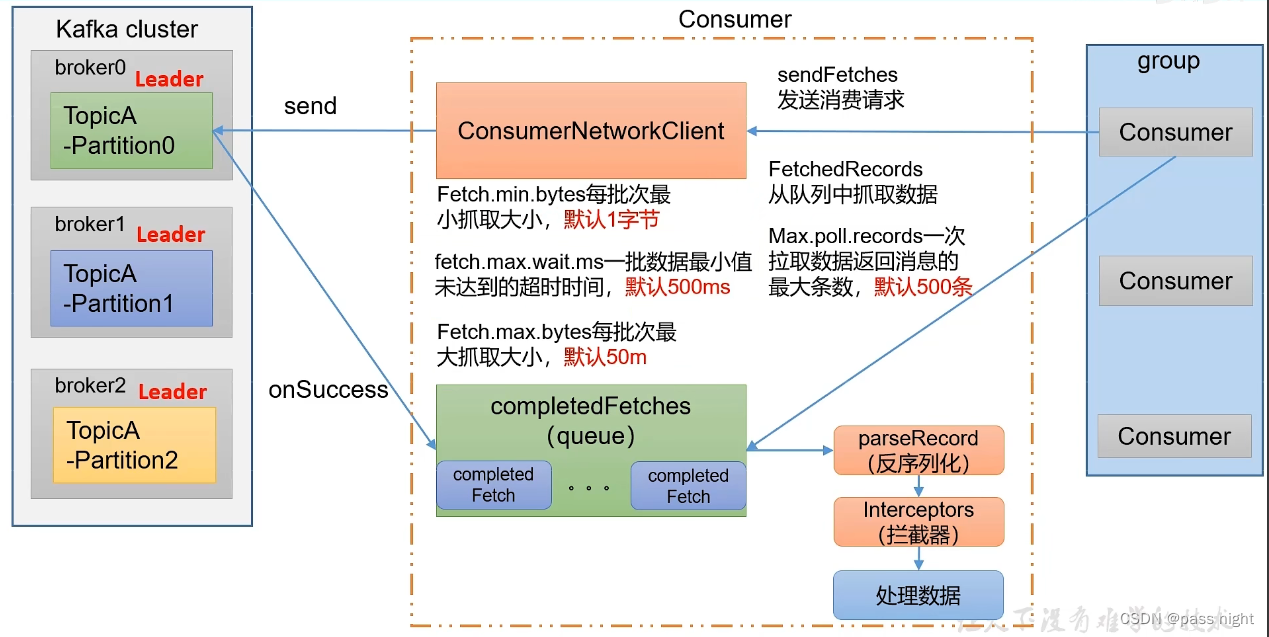
- 创建一个消费者网络连接, 与kafka集群进行通信
- 发送
sendFetches请求, 其中可以配置每批次最小抓取的大小Fetch.min.bytes=1/一批数据最小值未达到的超时时间fetch.max.wait.ms=500和每批次最大抓取大小fetch.max.bytes=50m - Kafka集群在成功接收后, 会执行
onSuccess回调函数, 将数据放到一个队列当中; 消费者会将这些数据反序列化/通过拦截器并拉取消息再处理数据, 其中一次拉取数据返回消息的最大条数为max.poll.records=500条
消费者API
消费者订阅主题
背景: 一个first主题, 有三个分区, 都由一个consumer消费
packagecom.passnight.springboot.kafka.consumer;importlombok.Cleanup;importorg.apache.kafka.clients.consumer.ConsumerConfig;importorg.apache.kafka.clients.consumer.ConsumerRecords;importorg.apache.kafka.clients.consumer.KafkaConsumer;importorg.apache.kafka.common.serialization.StringDeserializer;importjava.time.Duration;importjava.util.Collections;importjava.util.Properties;publicclassConsumer{}classCustomerConsumer{staticboolean stopped =false;publicstaticvoidmain(String[] args){Properties properties =newProperties();
properties.put(ConsumerConfig.BOOTSTRAP_SERVERS_CONFIG,"server.passnight.local:20015,replica.passnight.local:20015,follower.passnight.local:20015");
properties.put(ConsumerConfig.KEY_DESERIALIZER_CLASS_CONFIG,StringDeserializer.class.getName());
properties.put(ConsumerConfig.VALUE_DESERIALIZER_CLASS_CONFIG,StringDeserializer.class.getName());// 必须配置group id, 否则消费者无法正常启动
properties.put(ConsumerConfig.GROUP_ID_CONFIG,"group_test");// 创建一个消费者@CleanupKafkaConsumer<String,String> consumer =newKafkaConsumer<>(properties);// 订阅一个主题
consumer.subscribe(Collections.singleton("first"));// 消费数据while(!stopped){ConsumerRecords<String,String> records = consumer.poll(Duration.ofSeconds(1));
records.forEach(System.out::println);}}}
在控制台中使用
kafka-console-producer.sh
创建一个producer并发送数据
passnight@passnight-s600:/usr/local/kafka/kafka_2.13-3.5.1/bin$ ./kafka-console-producer.sh --bootstrap-server server.passnight.local:20015 --topic first
>hello from producer
之后就能接收到producer发送的数据了
ConsumerRecord(topic = first, partition =34, leaderEpoch =0, offset =6, CreateTime =1694850051405, serialized key size = -1, serialized value size =19, headers = RecordHeaders(headers =[], isReadOnly =false), key = null, value = hello from producer)
消费者订阅分区
消费者使用
assign
函数绑定分区/主题, 然后拉取数据
classPartitionConsumer{staticboolean stopped =false;publicstaticvoidmain(String[] args){Properties properties =newProperties();
properties.put(ConsumerConfig.BOOTSTRAP_SERVERS_CONFIG,"server.passnight.local:20015,replica.passnight.local:20015,follower.passnight.local:20015");
properties.put(ConsumerConfig.KEY_DESERIALIZER_CLASS_CONFIG,StringDeserializer.class.getName());
properties.put(ConsumerConfig.VALUE_DESERIALIZER_CLASS_CONFIG,StringDeserializer.class.getName());// 必须配置group id, 否则消费者无法正常启动
properties.put(ConsumerConfig.GROUP_ID_CONFIG,"group_test");// 创建一个消费者@CleanupKafkaConsumer<String,String> consumer =newKafkaConsumer<>(properties);// 订阅一个主题的某个分区
consumer.assign(Collections.singleton(newTopicPartition("first",0)));// 消费数据while(!stopped){ConsumerRecords<String,String> records = consumer.poll(Duration.ofSeconds(1));
records.forEach(System.out::println);}}}
使用java代码往对应的分区发送数据
classPartitionProducer{publicstaticvoidmain(String[] args){Properties properties =newProperties();// 连接集群(server.passnight.local:20015)
properties.put(ProducerConfig.BOOTSTRAP_SERVERS_CONFIG,"server.passnight.local:20015,replica.passnight.local:20015,follower.passnight.local:20015");// 配置Key/Value序列化类
properties.put(ProducerConfig.KEY_SERIALIZER_CLASS_CONFIG,StringSerializer.class.getName());
properties.put(ProducerConfig.VALUE_SERIALIZER_CLASS_CONFIG,StringSerializer.class.getName());try(KafkaProducer<String,String> kafkaProducer =newKafkaProducer<>(properties)){for(int i =0; i <5; i++){// 发送数据
kafkaProducer.send(newProducerRecord<>("first",0,"",String.format("value %d", i)),(metadata, exception)->{if(exception ==null){System.out.printf("主题: %s, 分区: %s%n", metadata.topic(), metadata.partition());}});}}}}
可以看到数据成功被发送和接收
# Consumer的日志
ConsumerRecord(topic = first, partition =0, leaderEpoch =2, offset =101, CreateTime =1694850576525, serialized key size =0, serialized value size =7, headers = RecordHeaders(headers =[], isReadOnly =false), key = , value = value 0)
ConsumerRecord(topic = first, partition =0, leaderEpoch =2, offset =102, CreateTime =1694850576536, serialized key size =0, serialized value size =7, headers = RecordHeaders(headers =[], isReadOnly =false), key = , value = value 1)
ConsumerRecord(topic = first, partition =0, leaderEpoch =2, offset =103, CreateTime =1694850576536, serialized key size =0, serialized value size =7, headers = RecordHeaders(headers =[], isReadOnly =false), key = , value = value 2)
ConsumerRecord(topic = first, partition =0, leaderEpoch =2, offset =104, CreateTime =1694850576537, serialized key size =0, serialized value size =7, headers = RecordHeaders(headers =[], isReadOnly =false), key = , value = value 3)
ConsumerRecord(topic = first, partition =0, leaderEpoch =2, offset =105, CreateTime =1694850576537, serialized key size =0, serialized value size =7, headers = RecordHeaders(headers =[], isReadOnly =false), key = , value = value 4)# Producer的日志
主题: first, 分区: 0
主题: first, 分区: 0
主题: first, 分区: 0
主题: first, 分区: 0
主题: first, 分区: 0
消费者组
目标: 创建一个由三个消费者组成的消费者组, 然后消费
first
主题
使用以下java代码发送30条数据到不同的分区
classAsyncProducer{publicstaticvoidmain(String[] args){Properties properties =newProperties();// 连接集群(server.passnight.local:20015)
properties.put(ProducerConfig.BOOTSTRAP_SERVERS_CONFIG,"server.passnight.local:20015");// 配置Key/Value序列化类
properties.put(ProducerConfig.KEY_SERIALIZER_CLASS_CONFIG,StringSerializer.class.getName());
properties.put(ProducerConfig.VALUE_SERIALIZER_CLASS_CONFIG,StringSerializer.class.getName());try(KafkaProducer<String,String> kafkaProducer =newKafkaProducer<>(properties)){for(int i =0; i <30; i++){// 发送数据
kafkaProducer.send(newProducerRecord<>("first",String.format("value %d", i)),(metadata, exception)->{if(exception ==null){System.out.printf("主题: %s, 分区: %s%n", metadata.topic(), metadata.partition());}});Thread.sleep(1);}}catch(InterruptedException e){thrownewRuntimeException(e);}}}
可以看到消息被发送到不同的分区中
主题: first, 分区: 0
主题: first, 分区: 0
主题: first, 分区: 0
主题: first, 分区: 0
主题: first, 分区: 0
主题: first, 分区: 0
主题: first, 分区: 0
主题: first, 分区: 0
主题: first, 分区: 0
主题: first, 分区: 34
主题: first, 分区: 34
主题: first, 分区: 34
主题: first, 分区: 34
主题: first, 分区: 34
主题: first, 分区: 34
主题: first, 分区: 34
主题: first, 分区: 34
主题: first, 分区: 34
主题: first, 分区: 40
主题: first, 分区: 40
主题: first, 分区: 40
主题: first, 分区: 32
主题: first, 分区: 32
主题: first, 分区: 32
主题: first, 分区: 32
主题: first, 分区: 32
主题: first, 分区: 32
主题: first, 分区: 32
主题: first, 分区: 32
主题: first, 分区: 36
再使用以下代码接收消息
@Log4j2classGroupedConsumer{staticvolatileboolean stopped =false;staticProperties properties =newProperties();staticCountDownLatch initLatch =newCountDownLatch(3);static{
properties.put(ConsumerConfig.BOOTSTRAP_SERVERS_CONFIG,"server.passnight.local:20015,replica.passnight.local:20015,follower.passnight.local:20015");
properties.put(ConsumerConfig.KEY_DESERIALIZER_CLASS_CONFIG,StringDeserializer.class.getName());
properties.put(ConsumerConfig.VALUE_DESERIALIZER_CLASS_CONFIG,StringDeserializer.class.getName());// 必须配置group id, 否则消费者无法正常启动
properties.put(ConsumerConfig.GROUP_ID_CONFIG,"group_test");}privatestaticclassConsumerThreadextendsThread{@SneakyThrows@Overridepublicvoidrun(){KafkaConsumer<String,String> consumer =newKafkaConsumer<>(properties);// 订阅一个主题的某个分区
consumer.assign(Collections.singleton(newTopicPartition("first",0)));
initLatch.countDown();
initLatch.await();// 消费数据while(!stopped){ConsumerRecords<String,String> records = consumer.poll(Duration.ofSeconds(1));for(ConsumerRecord<String,String> record : records){System.out.printf("%s: %s%n",getName(), record);}}
consumer.close();}ConsumerThread(long n){super();setName(String.format("ConsumerThread-%d", n));}}publicstaticvoidmain(String[] args){IntStream.range(0,3).asLongStream().mapToObj(ConsumerThread::new).forEach(Thread::start);}}
之后便可以看到每个Consumer消费固定的Partition
ConsumerThread-2: ConsumerRecord(topic = first, partition =0, leaderEpoch =2, offset =144, CreateTime =1694852156029, serialized key size = -1, serialized value size =7, headers = RecordHeaders(headers =[], isReadOnly =false), key = null, value = value 0)
ConsumerThread-2: ConsumerRecord(topic = first, partition =0, leaderEpoch =2, offset =145, CreateTime =1694852156038, serialized key size = -1, serialized value size =7, headers = RecordHeaders(headers =[], isReadOnly =false), key = null, value = value 1)
ConsumerThread-2: ConsumerRecord(topic = first, partition =0, leaderEpoch =2, offset =146, CreateTime =1694852156040, serialized key size = -1, serialized value size =7, headers = RecordHeaders(headers =[], isReadOnly =false), key = null, value = value 2)
ConsumerThread-2: ConsumerRecord(topic = first, partition =0, leaderEpoch =2, offset =147, CreateTime =1694852156041, serialized key size = -1, serialized value size =7, headers = RecordHeaders(headers =[], isReadOnly =false), key = null, value = value 3)
ConsumerThread-2: ConsumerRecord(topic = first, partition =0, leaderEpoch =2, offset =148, CreateTime =1694852156042, serialized key size = -1, serialized value size =7, headers = RecordHeaders(headers =[], isReadOnly =false), key = null, value = value 4)
ConsumerThread-2: ConsumerRecord(topic = first, partition =0, leaderEpoch =2, offset =149, CreateTime =1694852156043, serialized key size = -1, serialized value size =7, headers = RecordHeaders(headers =[], isReadOnly =false), key = null, value = value 5)
ConsumerThread-2: ConsumerRecord(topic = first, partition =0, leaderEpoch =2, offset =150, CreateTime =1694852156044, serialized key size = -1, serialized value size =7, headers = RecordHeaders(headers =[], isReadOnly =false), key = null, value = value 6)
ConsumerThread-2: ConsumerRecord(topic = first, partition =0, leaderEpoch =2, offset =151, CreateTime =1694852156045, serialized key size = -1, serialized value size =7, headers = RecordHeaders(headers =[], isReadOnly =false), key = null, value = value 7)
ConsumerThread-2: ConsumerRecord(topic = first, partition =0, leaderEpoch =2, offset =152, CreateTime =1694852156047, serialized key size = -1, serialized value size =7, headers = RecordHeaders(headers =[], isReadOnly =false), key = null, value = value 8)
ConsumerThread-1: ConsumerRecord(topic = first, partition =0, leaderEpoch =2, offset =144, CreateTime =1694852156029, serialized key size = -1, serialized value size =7, headers = RecordHeaders(headers =[], isReadOnly =false), key = null, value = value 0)
ConsumerThread-0: ConsumerRecord(topic = first, partition =0, leaderEpoch =2, offset =144, CreateTime =1694852156029, serialized key size = -1, serialized value size =7, headers = RecordHeaders(headers =[], isReadOnly =false), key = null, value = value 0)
ConsumerThread-1: ConsumerRecord(topic = first, partition =0, leaderEpoch =2, offset =145, CreateTime =1694852156038, serialized key size = -1, serialized value size =7, headers = RecordHeaders(headers =[], isReadOnly =false), key = null, value = value 1)
ConsumerThread-1: ConsumerRecord(topic = first, partition =0, leaderEpoch =2, offset =146, CreateTime =1694852156040, serialized key size = -1, serialized value size =7, headers = RecordHeaders(headers =[], isReadOnly =false), key = null, value = value 2)
ConsumerThread-1: ConsumerRecord(topic = first, partition =0, leaderEpoch =2, offset =147, CreateTime =1694852156041, serialized key size = -1, serialized value size =7, headers = RecordHeaders(headers =[], isReadOnly =false), key = null, value = value 3)
ConsumerThread-1: ConsumerRecord(topic = first, partition =0, leaderEpoch =2, offset =148, CreateTime =1694852156042, serialized key size = -1, serialized value size =7, headers = RecordHeaders(headers =[], isReadOnly =false), key = null, value = value 4)
ConsumerThread-1: ConsumerRecord(topic = first, partition =0, leaderEpoch =2, offset =149, CreateTime =1694852156043, serialized key size = -1, serialized value size =7, headers = RecordHeaders(headers =[], isReadOnly =false), key = null, value = value 5)
ConsumerThread-1: ConsumerRecord(topic = first, partition =0, leaderEpoch =2, offset =150, CreateTime =1694852156044, serialized key size = -1, serialized value size =7, headers = RecordHeaders(headers =[], isReadOnly =false), key = null, value = value 6)
ConsumerThread-1: ConsumerRecord(topic = first, partition =0, leaderEpoch =2, offset =151, CreateTime =1694852156045, serialized key size = -1, serialized value size =7, headers = RecordHeaders(headers =[], isReadOnly =false), key = null, value = value 7)
ConsumerThread-1: ConsumerRecord(topic = first, partition =0, leaderEpoch =2, offset =152, CreateTime =1694852156047, serialized key size = -1, serialized value size =7, headers = RecordHeaders(headers =[], isReadOnly =false), key = null, value = value 8)
ConsumerThread-0: ConsumerRecord(topic = first, partition =0, leaderEpoch =2, offset =145, CreateTime =1694852156038, serialized key size = -1, serialized value size =7, headers = RecordHeaders(headers =[], isReadOnly =false), key = null, value = value 1)
ConsumerThread-0: ConsumerRecord(topic = first, partition =0, leaderEpoch =2, offset =146, CreateTime =1694852156040, serialized key size = -1, serialized value size =7, headers = RecordHeaders(headers =[], isReadOnly =false), key = null, value = value 2)
ConsumerThread-0: ConsumerRecord(topic = first, partition =0, leaderEpoch =2, offset =147, CreateTime =1694852156041, serialized key size = -1, serialized value size =7, headers = RecordHeaders(headers =[], isReadOnly =false), key = null, value = value 3)
ConsumerThread-0: ConsumerRecord(topic = first, partition =0, leaderEpoch =2, offset =148, CreateTime =1694852156042, serialized key size = -1, serialized value size =7, headers = RecordHeaders(headers =[], isReadOnly =false), key = null, value = value 4)
ConsumerThread-0: ConsumerRecord(topic = first, partition =0, leaderEpoch =2, offset =149, CreateTime =1694852156043, serialized key size = -1, serialized value size =7, headers = RecordHeaders(headers =[], isReadOnly =false), key = null, value = value 5)
ConsumerThread-0: ConsumerRecord(topic = first, partition =0, leaderEpoch =2, offset =150, CreateTime =1694852156044, serialized key size = -1, serialized value size =7, headers = RecordHeaders(headers =[], isReadOnly =false), key = null, value = value 6)
ConsumerThread-0: ConsumerRecord(topic = first, partition =0, leaderEpoch =2, offset =151, CreateTime =1694852156045, serialized key size = -1, serialized value size =7, headers = RecordHeaders(headers =[], isReadOnly =false), key = null, value = value 7)
ConsumerThread-0: ConsumerRecord(topic = first, partition =0, leaderEpoch =2, offset =152, CreateTime =1694852156047, serialized key size = -1, serialized value size =7, headers = RecordHeaders(headers =[], isReadOnly =false), key = null, value = value 8)
指定offset消费
Kafka可以配置消费的offset, 具体可以通过
auto.offset.reset=realiest|latest|none
来配置, 默认值是
latest
; 他们的具体功能分别如下:
- earliest: 自动将偏移量重置为最早的偏移量, 功能同控制台中的
--from-beginning - latest(默认值): 自动将偏移量重置为最新的偏移量
- none: 若未找到先前的偏移量, 则向消费者抛出异常
- 在任意位置开始消费: 见下面java代码
下面是一个从任意位置开始消费的例子:
classCustomerOffsetConsumer{staticboolean stopped =false;publicstaticvoidmain(String[] args){Properties properties =newProperties();
properties.put(ConsumerConfig.BOOTSTRAP_SERVERS_CONFIG,"server.passnight.local:20015,replica.passnight.local:20015,follower.passnight.local:20015");
properties.put(ConsumerConfig.KEY_DESERIALIZER_CLASS_CONFIG,StringDeserializer.class.getName());
properties.put(ConsumerConfig.VALUE_DESERIALIZER_CLASS_CONFIG,StringDeserializer.class.getName());
properties.put(ConsumerConfig.GROUP_ID_CONFIG,"group_test");@CleanupKafkaConsumer<String,String> consumer =newKafkaConsumer<>(properties);
consumer.subscribe(Collections.singleton("first"));// 指定开始消费的offsetSet<TopicPartition> assignment = consumer.assignment();// 保证分区已经分配完毕; 若没有分配完毕可能会拿到空值while(assignment.isEmpty()){
consumer.poll(Duration.ofSeconds(1));
assignment = consumer.assignment();}
assignment.forEach(topicPartition -> consumer.seek(topicPartition,150));while(!stopped){ConsumerRecords<String,String> records = consumer.poll(Duration.ofSeconds(1));
records.forEach(System.out::println);}}
可以看到offset大于或等于
150
的消息被再次消费
ConsumerRecord(topic = first, partition =0, leaderEpoch =2, offset =150, CreateTime =1694852156044, serialized key size = -1, serialized value size =7, headers = RecordHeaders(headers =[], isReadOnly =false), key = null, value = value 6)
ConsumerRecord(topic = first, partition =0, leaderEpoch =2, offset =151, CreateTime =1694852156045, serialized key size = -1, serialized value size =7, headers = RecordHeaders(headers =[], isReadOnly =false), key = null, value = value 7)
ConsumerRecord(topic = first, partition =0, leaderEpoch =2, offset =152, CreateTime =1694852156047, serialized key size = -1, serialized value size =7, headers = RecordHeaders(headers =[], isReadOnly =false), key = null, value = value 8)
ConsumerRecord(topic = first, partition =0, leaderEpoch =2, offset =153, CreateTime =1694874743206, serialized key size = -1, serialized value size =13, headers = RecordHeaders(headers =[], isReadOnly =false), key = null, value = hello message)
ConsumerRecord(topic = first, partition =0, leaderEpoch =2, offset =154, CreateTime =1694874743216, serialized key size = -1, serialized value size =5, headers = RecordHeaders(headers =[], isReadOnly =false), key = null, value = hello)
指定开始时间消费
- Kafka不仅可以指定开始的offset, 还可以指定开始的时间
- 其实现方式就是在寻址前, 将时间转换成offset, 再指定开始的offset
以下是示例代码
classCustomerTimeConsumer{staticboolean stopped =false;publicstaticvoidmain(String[] args){Properties properties =newProperties();
properties.put(ConsumerConfig.BOOTSTRAP_SERVERS_CONFIG,"server.passnight.local:20015,replica.passnight.local:20015,follower.passnight.local:20015");
properties.put(ConsumerConfig.KEY_DESERIALIZER_CLASS_CONFIG,StringDeserializer.class.getName());
properties.put(ConsumerConfig.VALUE_DESERIALIZER_CLASS_CONFIG,StringDeserializer.class.getName());
properties.put(ConsumerConfig.GROUP_ID_CONFIG,"group_test");@CleanupKafkaConsumer<String,String> consumer =newKafkaConsumer<>(properties);
consumer.subscribe(Collections.singleton("first"));Set<TopicPartition> assignment = consumer.assignment();while(assignment.isEmpty()){
consumer.poll(Duration.ofSeconds(1));
assignment = consumer.assignment();}// 获取Map<TopicPartition,Long> topicPartitionLongMap = assignment.stream().collect(Collectors.toMap(Function.identity(),
topicPartition ->System.currentTimeMillis()-1*24*3600*1000L));Map<TopicPartition,OffsetAndTimestamp> topicPartitionOffsetAndTimestampMap = consumer.offsetsForTimes(topicPartitionLongMap);
assignment.forEach(topicPartition -> consumer.seek(topicPartition, topicPartitionOffsetAndTimestampMap.get(topicPartition).offset()));while(!stopped){ConsumerRecords<String,String> records = consumer.poll(Duration.ofSeconds(1));
records.forEach(System.out::println);}}}
控制台中打印了前一天开始的所有消息
ConsumerRecord(topic = first, partition =35, leaderEpoch =0, offset =0, CreateTime =1694851421184, serialized key size = -1, serialized value size =9, headers = RecordHeaders(headers =[], isReadOnly =false), key = null, value = value 342)
ConsumerRecord(topic = first, partition =35, leaderEpoch =0, offset =1, CreateTime =1694851421250, serialized key size = -1, serialized value size =9, headers = RecordHeaders(headers =[], isReadOnly =false), key = null, value = value 399)
ConsumerRecord(topic = first, partition =35, leaderEpoch =0, offset =2, CreateTime =1694851421252, serialized key size = -1, serialized value size =9, headers = RecordHeaders(headers =[], isReadOnly =false), key = null, value = value 401)# ....................等等等.........................
分区分配
- 一个Consumer Group由多个Consumer组成, 而一个topic由多个Partition组成, Partition和Consumer之间的分配需要有一定的策略, 主流的分区分配策略有 *他们可以通过
partition.assignment.strategy配置, 默认值是Range+CooperativeSticky*1. Range2. RoundRobin3. Sticky4. CooperativeSticky - 分配策略: 在消费者初始化过程中, 由Leader指定消费方案, Coordinator再接收到Leader制定的消费方案后, 将消费方案广播给Consumer
- 再分配策略: 当某个消费者心跳超时或处理时间过长, Coordinator会直接创建新的策略并广播到消费者组中
Range策略
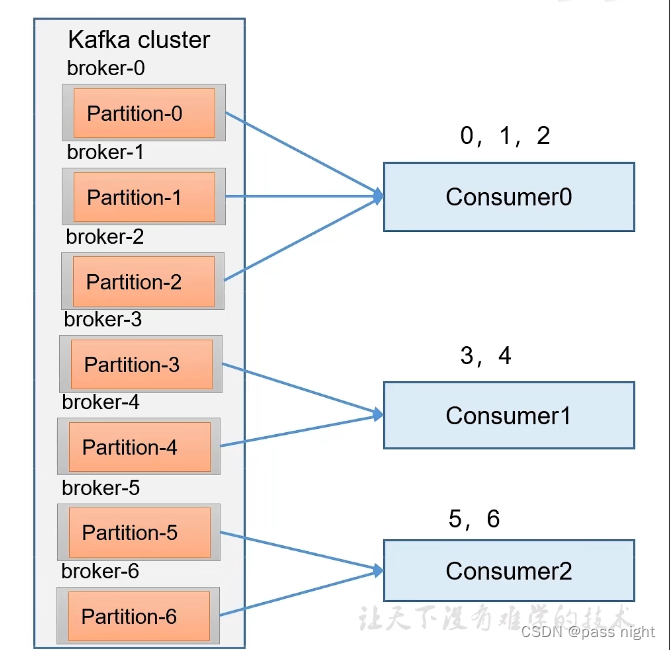
- Range是对每个topic而言的, 一个topic中的分区按照序号排序; 并对消费者按照字典序排序
- 每个消费者分配 p a r t i t i o n c o n s u m e r \frac{partition}{consumer} consumerpartition个分区, 其中排在前面的Consumer多分配除不尽的分区
- 缺点: 若有N个topic, 可能会导致数据倾斜每个多出来的分区都会被分配给排在前面的分区
RoundRobin
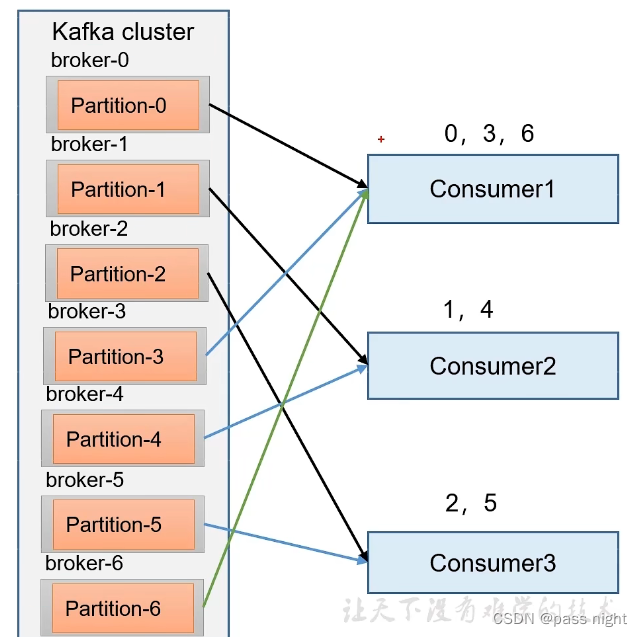
- Range针对的是单个Topic; 而RoundRobin是针对所有的主题
- RoundRobin轮询分区策略将所有的Partition和所有的consumer列出来, 然后按照Hashcode排序, 最后通过轮询换发分配Partition给各个消费者
Sticky
- 粘性分区首先会尽量均衡放置分区到消费者上面, 当同一消费者组中的消费者出现问题的时候, 会尽量保持原有的分区不变化
Offset
- Consumer消费到的位置会保存在offset中,
0.9版版本之后存储在Kafka内置的topic中, 其Key为groupid+topic+分区号, value为offset值,0.9版本之前存储在Zookeeper中; 变化的原因是因为前者性能更好 - 默认情况下是看不到系统主题中的数据, 需要修改
config/consumer.properties中的exculde.internal.topics配置为true才能看到
offset查看
使用
kafka-sonsole-consumer.sh
查看
__consumer_offsets
主题, 里面包含了offset信息
passnight@passnight-s600:/usr/local/kafka/kafka_2.13-3.5.1/bin$ ./kafka-console-consumer.sh --topic __consumer_offsets --bootstrap-server server.passnight.local:20015 --from-beginning --formatter"kafka.coordinator.group.GroupMetadataManager\$OffsetsMessageFormatter"[group_test,first,33]::OffsetAndMetadata(offset=0, leaderEpoch=Optional.empty, metadata=, commitTimestamp=1694849715527, expireTimestamp=None)[group_test,first,12]::OffsetAndMetadata(offset=0, leaderEpoch=Optional.empty, metadata=, commitTimestamp=1694849715527, expireTimestamp=None)# ..............等等等...................
offset自动维护功能
- 为了能够让用户专注于业务逻辑的实现, Kafka提供了自动提交
offset的功能; 需要配置相关参数 1.enable.auto.commit=true: 是否开启自动提交offset功能2.auto.commit.interval.ms=5000: 自动提交offset的间隔 - 在配置了上述参数之后, Kafka每5秒就会自动提交一次offset
在java代码中打开上述参数
classAutoOffsetConsumer{staticboolean stopped =false;publicstaticvoidmain(String[] args){Properties properties =newProperties();
properties.put(ConsumerConfig.BOOTSTRAP_SERVERS_CONFIG,"server.passnight.local:20015,replica.passnight.local:20015,follower.passnight.local:20015");
properties.put(ConsumerConfig.KEY_DESERIALIZER_CLASS_CONFIG,StringDeserializer.class.getName());
properties.put(ConsumerConfig.VALUE_DESERIALIZER_CLASS_CONFIG,StringDeserializer.class.getName());
properties.put(ConsumerConfig.GROUP_ID_CONFIG,"group_test");// 开启自动提交offset的功能 true->true
properties.put(ConsumerConfig.ENABLE_AUTO_COMMIT_CONFIG,true);// true -> true
properties.put(ConsumerConfig.AUTO_COMMIT_INTERVAL_MS_CONFIG,1000);// 5000 -> 1000@CleanupKafkaConsumer<String,String> consumer =newKafkaConsumer<>(properties);
consumer.subscribe(Collections.singleton("first"));while(!stopped){ConsumerRecords<String,String> records = consumer.poll(Duration.ofSeconds(1));
records.forEach(System.out::println);}}}
发送数据
主题: first, 分区: 36
主题: first, 分区: 36
主题: first, 分区: 36
主题: first, 分区: 36
主题: first, 分区: 36
可以看到消息可以正常消费
ConsumerRecord(topic = first, partition =36, leaderEpoch =0, offset =27, CreateTime =1694874800292, serialized key size = -1, serialized value size =7, headers = RecordHeaders(headers =[], isReadOnly =false), key = null, value = value 0)
ConsumerRecord(topic = first, partition =36, leaderEpoch =0, offset =28, CreateTime =1694874800300, serialized key size = -1, serialized value size =7, headers = RecordHeaders(headers =[], isReadOnly =false), key = null, value = value 1)
ConsumerRecord(topic = first, partition =36, leaderEpoch =0, offset =29, CreateTime =1694874800300, serialized key size = -1, serialized value size =7, headers = RecordHeaders(headers =[], isReadOnly =false), key = null, value = value 2)
ConsumerRecord(topic = first, partition =36, leaderEpoch =0, offset =30, CreateTime =1694874800300, serialized key size = -1, serialized value size =7, headers = RecordHeaders(headers =[], isReadOnly =false), key = null, value = value 3)
ConsumerRecord(topic = first, partition =36, leaderEpoch =0, offset =31, CreateTime =1694874800300, serialized key size = -1, serialized value size =7, headers = RecordHeaders(headers =[], isReadOnly =false), key = null, value = value 4)
并且可以在offset的消费端看到更新的offset
[group_test,first,1]::OffsetAndMetadata(offset=22, leaderEpoch=Optional[0], metadata=, commitTimestamp=1694874804756, expireTimestamp=None)[group_test,first,15]::OffsetAndMetadata(offset=14, leaderEpoch=Optional[0], metadata=, commitTimestamp=1694874804756, expireTimestamp=None)
手动提交offset
- 虽然Kafka提供了自动提交的功能, 但开发人员难以把握offset提交时机, 因此Kafka还提供了手动提交offset的API
- 手动提交方式分两种: 1. 同步提交: 必须等待offset提交完毕, 再去消费下一批数据2. 异步提交: 发送完提交offset请求之后, 就可以消费下一批数据了
下面代码是一个手动提交的例子, 具体输出和自动提交类似
classManualOffsetConsumer{staticboolean stopped =false;publicstaticvoidmain(String[] args){Properties properties =newProperties();
properties.put(ConsumerConfig.BOOTSTRAP_SERVERS_CONFIG,"server.passnight.local:20015,replica.passnight.local:20015,follower.passnight.local:20015");
properties.put(ConsumerConfig.KEY_DESERIALIZER_CLASS_CONFIG,StringDeserializer.class.getName());
properties.put(ConsumerConfig.VALUE_DESERIALIZER_CLASS_CONFIG,StringDeserializer.class.getName());
properties.put(ConsumerConfig.GROUP_ID_CONFIG,"group_test");// 关闭自动提交offset的功能 true -> false
properties.put(ConsumerConfig.ENABLE_AUTO_COMMIT_CONFIG,false);// true -> false@CleanupKafkaConsumer<String,String> consumer =newKafkaConsumer<>(properties);
consumer.subscribe(Collections.singleton("first"));while(!stopped){ConsumerRecords<String,String> records = consumer.poll(Duration.ofSeconds(1));
records.forEach(System.out::println);// consumer.commitSync();
consumer.commitAsync();}}}
消费中可能存在的问题
重复消费与漏消费
- 由自动提交offset引起的重复消费: 若consumer消费了一半的数据, 此时offset还没有提交, 重启后会读取到老的offset, 进而导致重复消费
- 由手动提交引起的漏消费: offset被提交但还没有落盘的期间, 消费者宕机, 由于数据未处理而offset已提交, 导致这部分消息漏消费
生产者事务
- 为了实现Consumer的精确一次消费, Kafka消费端需要将消费过程和提交offset过程做原子绑定. 此时需要将Kafka的offset保存到支持事务的自定义介质如MySQL
数据积压
Kafka的数据由于消费不及时而被删除
- 若原因是Kafka消费能力不足, 可以考虑增加Topic分区并增加Consumer数量来提高消费能力
- 若是下游数据处理不及时导致的原因: 可以提高每批次拉取数据的量以提高每批次拉取的数据量, 进而提高每批次处理的数据量 注意要可能要同步修改最大批次
引用
版权归原作者 pass night 所有, 如有侵权,请联系我们删除。