前言
本篇博客我们接着来理解一个STL库里的list链表的结构,根据前面数据结构的铺垫,理解这个结构相对比较容易。我们来一起看看吧
💓 个人主页:小张同学zkf
⏩ 文章专栏:C++
若有问题 评论区见📝
🎉欢迎大家点赞👍收藏⭐文章


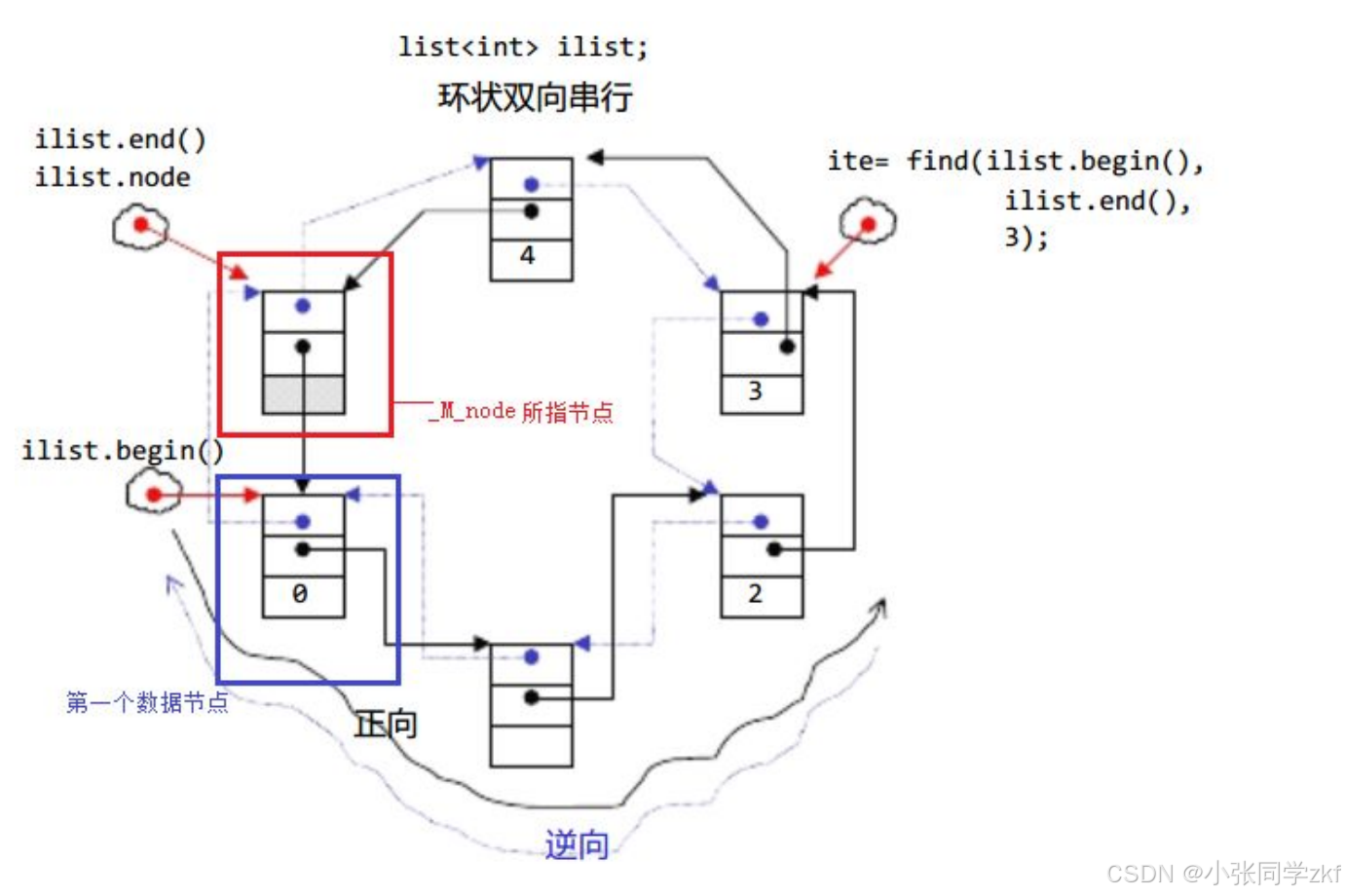
1.list介绍
文档:list
2.list使用
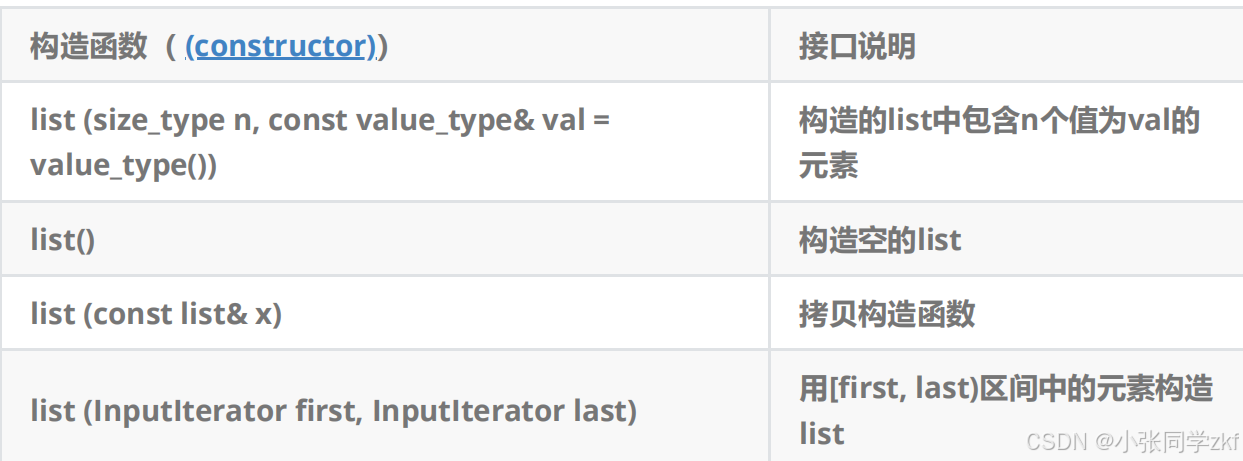
2.1list的构造
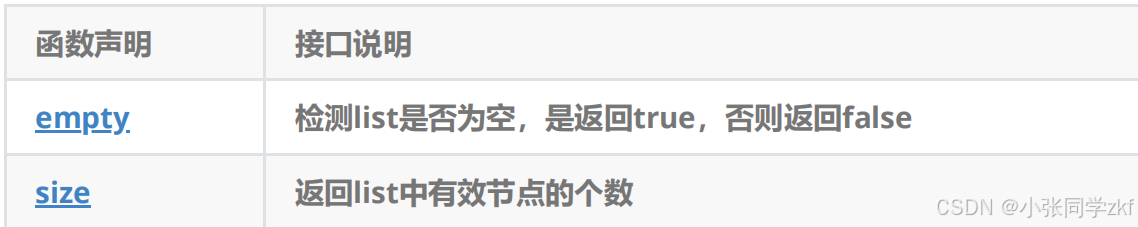
2.2list capacity
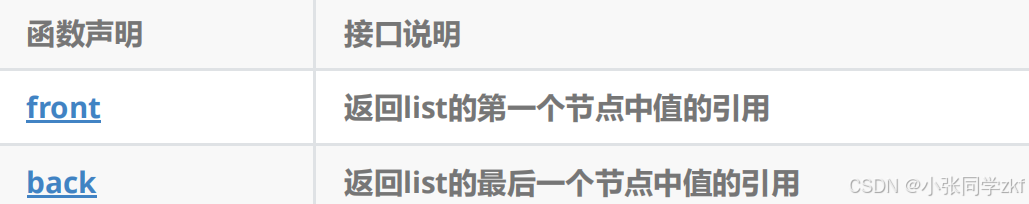
2.3**list element access **
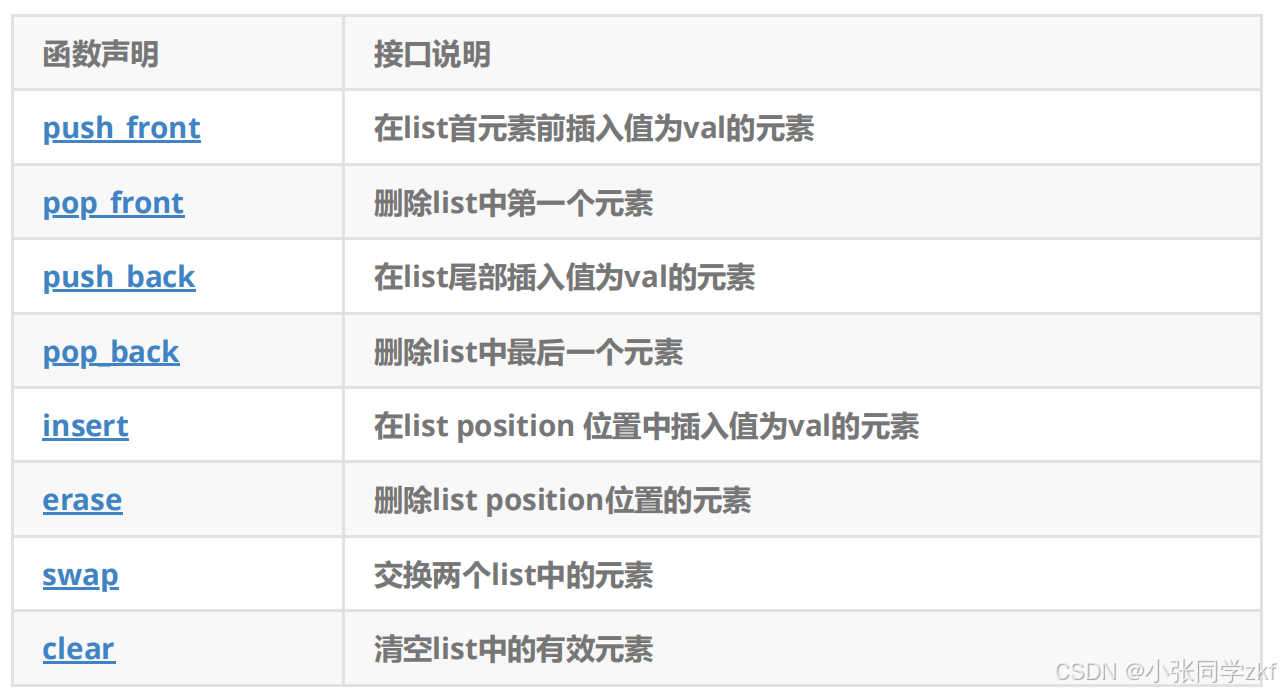
2.4**list modifiers **
3.list迭代器
此处大家可将迭代器暂时理解成类似于指针,迭代器失效即迭代器所指向的节点的无****效,即该节点被删除了。因为list****的底层结构为带头结点的双向循环链表,因此在list中进行插入时是不会导致list的迭代器失效的,只有在删除时才会失效,并且失效的只是指向被删除节点的迭代器,其他迭代器不会受到影响。
void TestListIterator1()
{
int array[] = { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 0 };
list<int> l(array, array+sizeof(array)/sizeof(array[0]));
auto it = l.begin();
while (it != l.end())
{
// erase()函数执行后,it所指向的节点已被删除,因此it无效,在下一次使用it时,必须先给
其赋值
l.erase(it);
++it;
}
}
// 改正
void TestListIterator()
{
int array[] = { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 0 };
list<int> l(array, array+sizeof(array)/sizeof(array[0]));
auto it = l.begin();
while (it != l.end())
{
l.erase(it++); // it = l.erase(it);
}
}
4.list模拟实现
#include<iostream>
#include<assert.h>
using namespace std;
namespace zkf
{
template<class T>
struct list_node
{
T _date;
list_node<T>* _next;
list_node<T>* _prev;
list_node(const T& s=T())
:_date(s)
, _next(nullptr)
, _prev(nullptr)
{}
};
template<class T,class ref,class ptr>
struct list_iterator
{
typedef list_node<T> node;
typedef list_iterator<T,ref,ptr> self;
node* _node;
list_iterator(node* node)
:_node(node)
{}
ref operator*()
{
return _node->_date;
}
self& operator++()
{
_node = _node->_next;
return *this;
}
self& operator--(int)
{
self tmp(*this);
_node = _node->_prev;
return tmp;
}
self& operator++(int)
{
self tmp(*this);
_node = _node->_next;
return tmp;
}
self& operator--()
{
_node = _node->_prev;
return *this;
}
bool operator!=(const self& s)
{
return _node!= s._node;
}
ptr operator->()
{
return &_node->_date;
}
};
template<class T>
class list
{
typedef list_node<T> node;
public:
typedef list_iterator<T,T&,T*> iterator;
typedef list_iterator<T,const T&,const T*> const_iterator;
void empty_init()
{
_head = new node;
_head->_next = _head;
_head->_prev = _head;
_size = 0;
}
list()
{
empty_init();
}
list(const list<T>& s)
{
empty_init();
for (auto& it : s)
{
push_back(it);
}
}
void swap(list<T>& s)
{
std::swap(_head, s._head);
std::swap(_size, s._size);
}
list<T>& operator=(list<T> s)
{
swap(s);
return *this;
}
iterator insert(iterator it, const T& s)
{
node* newnode = new node(s);
node* tail=(it._node)->_prev;
newnode->_prev = tail;
newnode->_next = it._node;
tail->_next = newnode;
(it._node)->_prev = newnode;
++_size;
return newnode;
}
iterator erase(iterator it)
{
assert(it != end());
node* prev = (it._node)->_prev;
node* next = (it._node)->_next;
prev->_next = next;
next->_prev = prev;
delete it._node;
--_size;
return next;
}
void push_back(const T& s)
{
insert(end(), s);
}
void push_front(const T& s)
{
insert(begin(), s);
}
void pop_back()
{
erase(--end());
}
void pop_front()
{
erase(begin());
}
size_t size()const
{
return _size;
}
bool empty()const
{
return _size == 0;
}
iterator begin()
{
return _head->_next;
}
iterator end()
{
return _head;
}
const_iterator begin()const
{
return _head->_next;
}
const_iterator end()const
{
return _head;
}
void clear()
{
iterator it = begin();
while (it != end())
{
it=erase(it);
}
}
~list()
{
clear();
delete _head;
_head = nullptr;
}
private:
node* _head;
size_t _size;
};
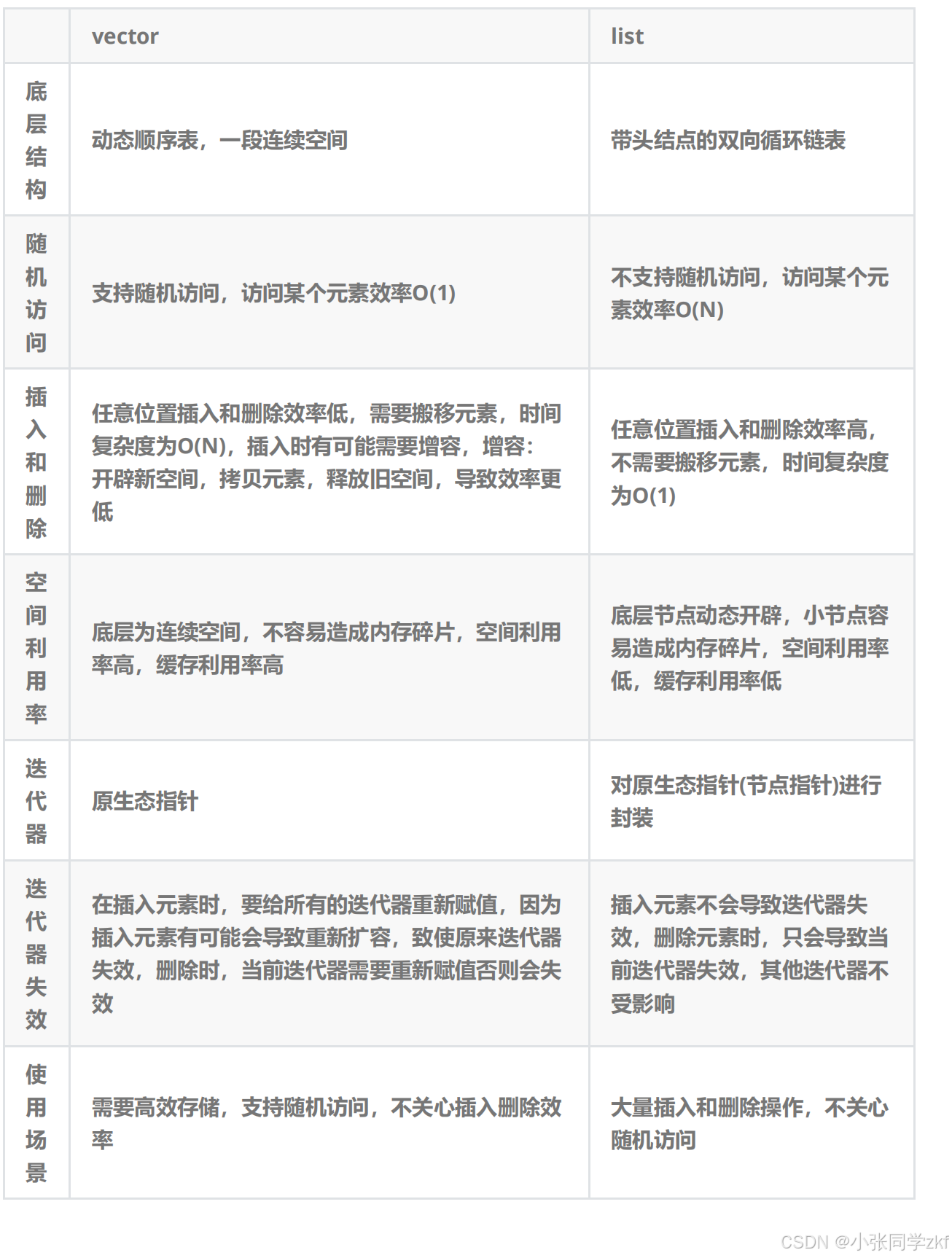
5.list与vector对比
结束语
list总结到这里,下篇准备STL库里的queue和stack
OK,感谢观看!!!
版权归原作者 小张同学zkf 所有, 如有侵权,请联系我们删除。

