
半 是 温 柔 半 是 风 , 一 生 从 容 一 生 花
1.原理介绍
通常在确定指标权重时往往更多关注的是数据本身,而数据之间的波动性大小也是一种信息,或是数据之间的相关关系大小,也是一种信息,可利用数据波动性大小或数据相关关系大小计算权重。
CRITIC权重法是一种基于数据波动性的客观赋权法。其思想在于两项指标,分别是波动性(对比强度)和冲突性(相关性)指标。对比强度使用标准差进行表示,如果数据**标准差越大**说明**波动越大**,**权重会越高**;冲突性使用相关系数进行表示,如果指标之间的**相关系数值越大**,说明**冲突性越小**,那么其**权重也就越低**。权重计算时,对比强度与冲突性指标相乘,并且进行归一化处理,即得到最终的权重。
CRITIC权重法适用于数据稳定性可视作一种信息,并且分析的指标或因素之间有着一定的关联关系的数据。
2.步骤详解
2.1 获取数据
假设现有一组数据,有m个待评价对象,n个评价指标,构成原始数据矩阵X:
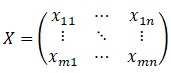
2.2 数据标准化
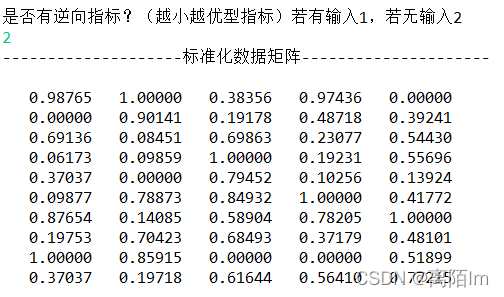
数据标准化的主要目的就是消除量纲影响,使所以数据能用统一的标准去衡量。
对于正向指标:
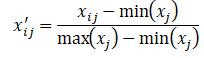
对于逆向指标:
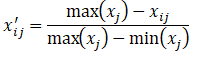
2.3 计算信息承载量
波动性:

冲突性:
计算冲突性时要用到指标的相关性矩阵,计算公式如下:
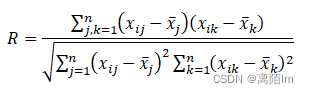
则,冲突性计公式:

信息量:
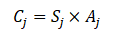
2.4 计算权重
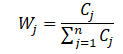
3.案例分析
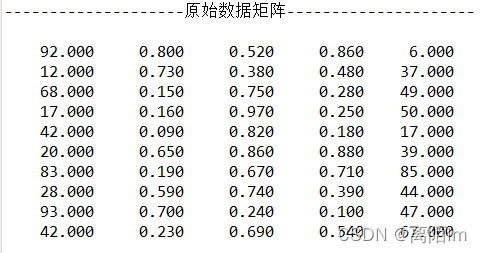
以下是某医院连续十天内的部分数据,其中某些指标的稳定性是一种信息,而且指标之间本身就可能有着相关性。
编号出院人数入出院诊断符合率治疗有效率平均床位使用率病床周转次数1920.80.520.8662120.730.380.48373680.150.750.28494170.160.970.25505420.090.820.18176200.650.860.88397830.190.670.71858280.590.740.39449930.70.240.14710420.230.690.5467
3.1 数据获取
/**
* 从Excel表格读取数据,列为评价指标行为待评价样本
*
* 假设有m个待评价样本,n个评价指标
*
* @param filepath 表格存储位置
* @return componentMartix 返回原始矩阵
*/
public double[][] read(String filepath) throws IOException, BiffException,WriteException {
//创建输入流
InputStream stream = new FileInputStream(filepath);
//获取Excel文件对象
Workbook rwb = Workbook.getWorkbook(stream);
//获取文件的指定工作表 默认的第一个
Sheet sheet = rwb.getSheet("Sheet1");
int rows = sheet.getRows();
int cols = sheet.getColumns();
double[][] componentMatrix = new double[rows][cols];//原始矩阵
//row为行
for(int i=0;i<sheet.getRows();i++) {
for(int j=0;j<sheet.getColumns();j++) {
String[] str = new String[sheet.getColumns()];
Cell cell = null;
cell = sheet.getCell(j,i);
str[j] = cell.getContents();
componentMatrix[i][j] = Double.valueOf(str[j]);
}
}
return componentMatrix;//返回原始矩阵
}
输出:
3.2 数据标准化
/**
* 数据标准化处理,消除量纲影响
* @param componentMatrix 输入原始矩阵
* @return normalizedMatrix 返回标准化后的矩阵
*/
public double[][] normalized(double[][] componentMatrix) {
double[][] normalizedMatrix = new double[componentMatrix.length][componentMatrix[0].length];
List<Integer> neg = new ArrayList<Integer>();//存储逆向指标所在列
double[] max = Max(componentMatrix);
double[] min = Min(componentMatrix);
int a;
for(int i=0; i < componentMatrix.length; i++) {
for(int j=0; j < componentMatrix[0].length; j++) {
normalizedMatrix[i][j] = (componentMatrix[i][j] - min[j])/(max[j] - min[j]);
}
}
System.out.println("是否有逆向指标?(越小越优型指标)若有输入1,若无输入2");
a = input.nextInt();
if(a ==1 ) {
System.out.println("输入逆向指标所在列(以“/”结尾):");
while(!input.hasNext("/")) {
neg.add(Integer.valueOf(input.nextInt()));
}
for(int i=0; i < componentMatrix.length; i++) {
for(int j=0; j < neg.size(); j++) {
normalizedMatrix[i][neg.get(j)] =
(max[neg.get(j)]-componentMatrix[i][neg.get(j)])/(max[neg.get(j)] - min[neg.get(j)]);
}
}
}
return normalizedMatrix;
}
输出:
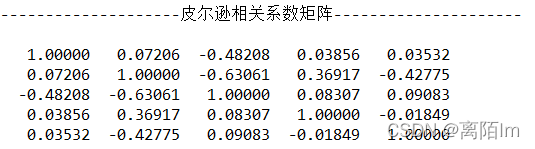
3.3 计算相关系数
/**
* 计算相关系数矩阵
* @param normalizedMatrix 标准化后数据
* @return pearson 皮尔逊相关系数矩阵
*/
public double[][] correlation(double[][] normalizedMatrix){
double[][] pearson = new double[normalizedMatrix[0].length][normalizedMatrix[0].length];//皮尔逊相关系数矩阵
double[] avr = Average(normalizedMatrix);//每列平均值
double[] s = new double[normalizedMatrix[0].length];
for(int j=0;j < normalizedMatrix[0].length;j++) {
double sum = 0;
for(int i=0;i < normalizedMatrix.length;i++){
sum += Math.pow(normalizedMatrix[i][j] - avr[j], 2);
}
s[j] = Math.sqrt(sum/(normalizedMatrix[0].length - 1));
}
double[][] cxy = new double[normalizedMatrix[0].length][normalizedMatrix[0].length];
for(int j=0;j<normalizedMatrix[0].length;j++) {
for(int k=0;k<normalizedMatrix[0].length;k++) {
double sum = 0;
for(int i=0;i<normalizedMatrix.length;i++) {
sum += (normalizedMatrix[i][j] - avr[j])*(normalizedMatrix[i][k] - avr[k]);
}
cxy[j][k] = sum/(pearson.length - 1);
pearson[j][k] = cxy[j][k]/(s[j]*s[k]);
}
}
return pearson;
}
输出:
3.4 计算信息承载量
/**
* 计算每个指标的信息承载量
* @param normalizedMatrix 标准化后的矩阵
* @param pearson 皮尔逊相关系数矩阵
* @return informationVolume 每个指标的信息承载量
*/
public double[] information(double[][] normalizedMatrix,double[][] pearson) {
double[] informationVolume = new double[normalizedMatrix[0].length];
double[] avr = Average(normalizedMatrix);//每列平均值
//计算对比强度(标准差)
double[] s = new double[normalizedMatrix[0].length];
for(int j=0;j < normalizedMatrix[0].length;j++) {
double sum = 0;
for(int i=0;i < normalizedMatrix.length;i++){
sum += Math.pow(normalizedMatrix[i][j] - avr[j], 2);
}
s[j] = Math.sqrt(sum/(normalizedMatrix[0].length - 1));
}
//计算冲突性
double[] r = new double[normalizedMatrix[0].length];
for(int j=0;j<normalizedMatrix[0].length;j++) {
double sum = 0;
for(int i=0;i<normalizedMatrix[0].length;i++) {
sum += 1 - pearson[i][j];
}
r[j] = sum;
}
//计算信息量
for(int j=0;j<normalizedMatrix[0].length;j++) {
informationVolume[j] = s[j]*r[j];
}
return informationVolume;
}
输出:
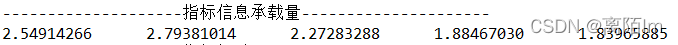
3.5 计算权重
/**
* 计算权重
* @param informationVolume 每个指标的信息量
* @return weight 返回每个指标的权重
*/
public double[] weight(double[] informationVolume) {
double[] weight = new double[informationVolume.length];
double sum = 0;
for(int i=0;i<informationVolume.length;i++) {
sum += informationVolume[i];
}
for(int i=0;i<informationVolume.length;i++) {
weight[i] = informationVolume[i]/sum;
}
return weight;
}
输出:
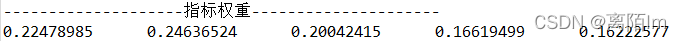
4.算法改进
从上述计算步骤可以看出 CRITIC 法存在以下可以 改进和完善的地方 :(1)相关系数有正有负,对于绝对值相同的相关系数其反映指 标间的相关性程度大小应是一样的 ,因此在反映指标 之间的对比强度时用 (1−|rij|) 代替原方法中的 (1−rij) 更 适合 ;(2)CRITIC 法虽能有效考虑指标数据间的相关性(冲突性)和对比强度 (波动性),但未考虑指标数据间的离散程度。因此,需要对 CRITIC 法进行改进,以使改进的 CRITIC 法能够充分考虑指标数据本身的三大属性。
改进后的计算公式如下:
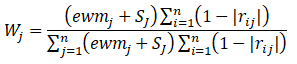
其中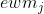代表用熵权法计算得到的指标熵值(不会计算的可以点击阅读文章“权重计算方法二:熵权法(EWM)”),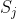为对比强度,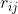为第i个指标与第j个指标的相关系数。
/**
* 改进算法
* @param normalizedMatrix 标准化后的矩阵
* @param pearson 皮尔逊相关系数矩阵
* @param ewm 熵权法求得的指标熵值
* @return
*/
public double[] weight1(double[][] normalizedMatrix,double[][] pearson,double[] ewm) {
double[] informationVolume = new double[normalizedMatrix[0].length];
double[] avr = Average(normalizedMatrix);//每列平均值
double[] weight = new double[normalizedMatrix[0].length];
double[] pear = new double[normalizedMatrix[0].length];
//计算对比强度(标准差)
double[] s = new double[normalizedMatrix[0].length];
for(int j=0;j < normalizedMatrix[0].length;j++) {
double sum = 0;
for(int i=0;i < normalizedMatrix.length;i++){
sum += Math.pow(normalizedMatrix[i][j] - avr[j], 2);
}
s[j] = Math.sqrt(sum/(normalizedMatrix[0].length - 1));
}
double total = 0;
for(int j=0;j<normalizedMatrix[0].length;j++) {
for(int i=0;i<normalizedMatrix[0].length;i++) {
pear[j] += Math.abs(pearson[i][j]);
}
total += ewm[j] + s[j];
}
for(int j=0;j<normalizedMatrix[0].length;j++) {
informationVolume[j] = ((ewm[j] + s[j])*pear[j])/(total + pear[j]);
}
double sum = 0;
for(int i=0;i<informationVolume.length;i++) {
sum += informationVolume[i];
}
for(int i=0;i<informationVolume.length;i++) {
weight[i] = informationVolume[i]/sum;
}
return weight;
}
输出:

** 改进前后结果对比:**
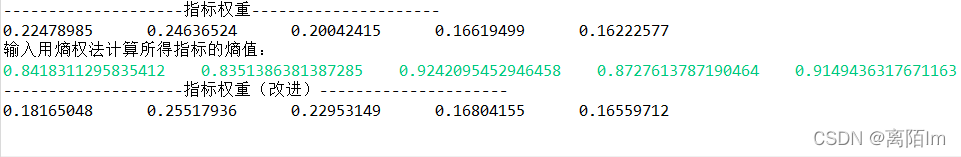
通过观察可以发现改进后得到的权重基本与改进前得到的权重一致,但部分指标改进前后权重有较大变化,但基本保持在5%以内。
5.完整代码
5.1 方法类 CRITIC.java
package critic;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Scanner;
import jxl.Cell;
import jxl.Sheet;
import jxl.Workbook;
import jxl.read.biff.BiffException;
import jxl.write.WriteException;
public class CRITIC {
Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in);
//矩阵每列最大值
public double[] Max(double[][] m) {
double max[] = new double[m[0].length];
for(int j=0;j < m[0].length;j++) {
max[j] = m[0][j];
for(int i=0;i < m.length;i++) {
if(m[i][j] >= max[j]) {
max[j] = m[i][j];
}
}
}
return max;
}
//矩阵每列最小值
public double[] Min(double[][] m) {
double min[] = new double[m[0].length];
for(int j=0;j < m[0].length;j++) {
min[j] = m[0][j];
for(int i=0;i < m.length;i++) {
if(m[i][j] <= min[j]) {
min[j] = m[i][j];
}
}
}
return min;
}
//矩阵每列平均值
public double[] Average(double[][] m) {
double avr[] = new double[m[0].length];
for(int j=0;j < m[0].length;j++) {
double sum = 0;
for(int i=0;i < m.length;i++) {
sum += m[i][j];
}
avr[j] = sum/m.length;
}
return avr;
}
//输出二维矩阵
public void matrixoutput(double[][] x) {
for(int i=0;i<x.length;i++) {
for(int j=0;j<x[0].length;j++) {
System.out.print(x[i][j]+" ");
}
System.out.println();
}
}
//输出一维矩阵
public void matrixoutput1(double[] x) {
for(int i=0;i<x.length;i++) {
System.out.print(String.format("%.8f\t", x[i]));
}
System.out.println();
}
/**
* 从Excel表格读取数据,列为评价指标行为待评价样本
*
* 假设有m个待评价样本,n个评价指标
*
* @param filepath 表格存储位置
* @return componentMartix 返回原始矩阵
*/
public double[][] read(String filepath) throws IOException, BiffException,WriteException {
//创建输入流
InputStream stream = new FileInputStream(filepath);
//获取Excel文件对象
Workbook rwb = Workbook.getWorkbook(stream);
//获取文件的指定工作表 默认的第一个
Sheet sheet = rwb.getSheet("Sheet1");
int rows = sheet.getRows();
int cols = sheet.getColumns();
double[][] componentMatrix = new double[rows][cols];//原始矩阵
//row为行
for(int i=0;i<sheet.getRows();i++) {
for(int j=0;j<sheet.getColumns();j++) {
String[] str = new String[sheet.getColumns()];
Cell cell = null;
cell = sheet.getCell(j,i);
str[j] = cell.getContents();
componentMatrix[i][j] = Double.valueOf(str[j]);
}
}
return componentMatrix;//返回原始矩阵
}
/**
* 数据标准化处理,消除量纲影响
* @param componentMatrix 输入原始矩阵
* @return normalizedMatrix 返回标准化后的矩阵
*/
public double[][] normalized(double[][] componentMatrix) {
double[][] normalizedMatrix = new double[componentMatrix.length][componentMatrix[0].length];
List<Integer> neg = new ArrayList<Integer>();//存储逆向指标所在列
double[] max = Max(componentMatrix);
double[] min = Min(componentMatrix);
int a;
for(int i=0; i < componentMatrix.length; i++) {
for(int j=0; j < componentMatrix[0].length; j++) {
normalizedMatrix[i][j] = (componentMatrix[i][j] - min[j])/(max[j] - min[j]);
}
}
System.out.println("是否有逆向指标?(越小越优型指标)若有输入1,若无输入2");
a = input.nextInt();
if(a ==1 ) {
System.out.println("输入逆向指标所在列(以“/”结尾):");
while(!input.hasNext("/")) {
neg.add(Integer.valueOf(input.nextInt()));
}
for(int i=0; i < componentMatrix.length; i++) {
for(int j=0; j < neg.size(); j++) {
normalizedMatrix[i][neg.get(j)] =
(max[neg.get(j)]-componentMatrix[i][neg.get(j)])/(max[neg.get(j)] - min[neg.get(j)]);
}
}
}
return normalizedMatrix;
}
/**
* 计算相关系数矩阵
* @param normalizedMatrix 标准化后数据
* @return pearson 皮尔逊相关系数矩阵
*/
public double[][] correlation(double[][] normalizedMatrix){
double[][] pearson = new double[normalizedMatrix[0].length][normalizedMatrix[0].length];//皮尔逊相关系数矩阵
double[] avr = Average(normalizedMatrix);//每列平均值
double[] s = new double[normalizedMatrix[0].length];
for(int j=0;j < normalizedMatrix[0].length;j++) {
double sum = 0;
for(int i=0;i < normalizedMatrix.length;i++){
sum += Math.pow(normalizedMatrix[i][j] - avr[j], 2);
}
s[j] = Math.sqrt(sum/(normalizedMatrix[0].length - 1));
}
double[][] cxy = new double[normalizedMatrix[0].length][normalizedMatrix[0].length];
for(int j=0;j<normalizedMatrix[0].length;j++) {
for(int k=0;k<normalizedMatrix[0].length;k++) {
double sum = 0;
for(int i=0;i<normalizedMatrix.length;i++) {
sum += (normalizedMatrix[i][j] - avr[j])*(normalizedMatrix[i][k] - avr[k]);
}
cxy[j][k] = sum/(pearson.length - 1);
pearson[j][k] = cxy[j][k]/(s[j]*s[k]);
}
}
return pearson;
}
/**
* 计算每个指标的信息承载量
* @param normalizedMatrix 标准化后的矩阵
* @param pearson 皮尔逊相关系数矩阵
* @return informationVolume 每个指标的信息承载量
*/
public double[] information(double[][] normalizedMatrix,double[][] pearson) {
double[] informationVolume = new double[normalizedMatrix[0].length];
double[] avr = Average(normalizedMatrix);//每列平均值
//计算对比强度(标准差)
double[] s = new double[normalizedMatrix[0].length];
for(int j=0;j < normalizedMatrix[0].length;j++) {
double sum = 0;
for(int i=0;i < normalizedMatrix.length;i++){
sum += Math.pow(normalizedMatrix[i][j] - avr[j], 2);
}
s[j] = Math.sqrt(sum/(normalizedMatrix[0].length - 1));
}
//计算冲突性
double[] r = new double[normalizedMatrix[0].length];
for(int j=0;j<normalizedMatrix[0].length;j++) {
double sum = 0;
for(int i=0;i<normalizedMatrix[0].length;i++) {
sum += 1 - pearson[i][j];
}
r[j] = sum;
}
//计算信息量
for(int j=0;j<normalizedMatrix[0].length;j++) {
informationVolume[j] = s[j]*r[j];
}
return informationVolume;
}
/**
* 计算权重
* @param informationVolume 每个指标的信息量
* @return weight 返回每个指标的权重
*/
public double[] weight(double[] informationVolume) {
double[] weight = new double[informationVolume.length];
double sum = 0;
for(int i=0;i<informationVolume.length;i++) {
sum += informationVolume[i];
}
for(int i=0;i<informationVolume.length;i++) {
weight[i] = informationVolume[i]/sum;
}
return weight;
}
/**
* 改进算法
* @param normalizedMatrix 标准化后的矩阵
* @param pearson 皮尔逊相关系数矩阵
* @param ewm 熵权法求得的指标熵值
* @return
*/
public double[] weight1(double[][] normalizedMatrix,double[][] pearson,double[] ewm) {
double[] informationVolume = new double[normalizedMatrix[0].length];
double[] avr = Average(normalizedMatrix);//每列平均值
double[] weight = new double[normalizedMatrix[0].length];
double[] pear = new double[normalizedMatrix[0].length];
//计算对比强度(标准差)
double[] s = new double[normalizedMatrix[0].length];
for(int j=0;j < normalizedMatrix[0].length;j++) {
double sum = 0;
for(int i=0;i < normalizedMatrix.length;i++){
sum += Math.pow(normalizedMatrix[i][j] - avr[j], 2);
}
s[j] = Math.sqrt(sum/(normalizedMatrix[0].length - 1));
}
double total = 0;
for(int j=0;j<normalizedMatrix[0].length;j++) {
for(int i=0;i<normalizedMatrix[0].length;i++) {
pear[j] += Math.abs(pearson[i][j]);
}
total += ewm[j] + s[j];
}
for(int j=0;j<normalizedMatrix[0].length;j++) {
informationVolume[j] = ((ewm[j] + s[j])*pear[j])/(total + pear[j]);
}
double sum = 0;
for(int i=0;i<informationVolume.length;i++) {
sum += informationVolume[i];
}
for(int i=0;i<informationVolume.length;i++) {
weight[i] = informationVolume[i]/sum;
}
return weight;
}
}
5.2 主类 CRITICmain.java
package critic;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.Scanner;
import Jama.Matrix;
import jxl.read.biff.BiffException;
import jxl.write.WriteException;
public class CRITICmain {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, BiffException, WriteException {
@SuppressWarnings("resource")
Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in);
CRITIC critic = new CRITIC();
double[][] componentMatrix = critic.read("critic.xls");
System.out.println("--------------------原始数据矩阵---------------------");
Matrix A1 = new Matrix(componentMatrix);
A1.print(8, 3);
//critic.matrixoutput(componentMatrix);
double[][] normalizedMatrix = critic.normalized(componentMatrix);
System.out.println("--------------------标准化数据矩阵---------------------");
Matrix A = new Matrix(normalizedMatrix);
A.print(8, 5);
//critic.matrixoutput(normalizedMatrix);
double[][] pearson = critic.correlation(normalizedMatrix);
System.out.println("--------------------皮尔逊相关系数矩阵---------------------");
Matrix B = new Matrix(pearson);
B.print(8, 5);
//critic.matrixoutput(pearson);
double[] informationVolume = critic.information(normalizedMatrix, pearson);
System.out.println("--------------------指标信息承载量---------------------");
critic.matrixoutput1(informationVolume);
double[] weight = critic.weight(informationVolume);
System.out.println("--------------------指标权重---------------------");
critic.matrixoutput1(weight);
double[] ewm = new double[normalizedMatrix[0].length];//熵权法计算所得指标权重
System.out.println("输入用熵权法计算所得指标的熵值:");
for(int i=0;i<ewm.length ;i++) {
ewm[i] = input.nextDouble();
}
double[] weight1 = critic.weight1(normalizedMatrix,pearson,ewm);
System.out.println("--------------------指标权重(改进)---------------------");
critic.matrixoutput1(weight1);
}
}
版权归原作者 离陌lm 所有, 如有侵权,请联系我们删除。