SpringBoot 集成 RabbitMQ
1.应用实例
- 需求说明/图解
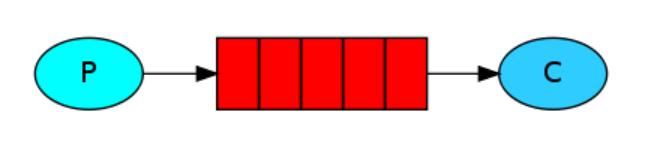
-P : 消息的发送者/生产者
-C : 消息的接受者/消费者
-中间表示队列

- 完成步骤
- 添加依赖
<!--rabbitmq-需要的 AMQP 依赖--><dependency><groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId><artifactId>spring-boot-starter-amqp</artifactId></dependency>
- 修改yaml配置
spring:#rabbitmq 配置rabbitmq:host: 192.168.79.202
username: guest
password: guest
#虚拟主机virtual-host: /
#端口port:5672listener:simple:#消费者最小数量concurrency:10#消费者最大数量max-concurrency:10#限制消费者,每次只能处理一条消息,处理完才能继续下一条消息prefetch:1#启动时是否默认启动容器,默认为 trueauto-startup:true#被拒绝时重新进入队列的default-requeue-rejected:truetemplate:retry:#启用消息重试机制,默认为 falseenabled:true#初始重试间隔时间initial-interval: 1000ms
#重试最大次数,默认为 3 次max-attempts:3#重试最大时间间隔,默认 10000msmax-interval: 10000ms
#重试的间隔乘数,#配置 2 的话,第一次等 1s,第二次等 2s,第三次等 4smultiplier:1#在 RabbitMQ 中,initial-interval 和 max-interval 是用于指定消息重试机制的两个参数,#它们的区别如下:#1. initial-interval(初始间隔时间):表示第一次重试的时间间隔,也就是在消息第一次处#理失败后,等待多长时间再尝试重新发送消息。这个参数的默认值是 1 秒。#2.max-interval(最大间隔时间):表示重试过程中的最大时间间隔,也就是每次重试时,#最长等待多长时间再尝试重新发送消息。这个参数的默认值是 10 秒。
- 在RabbitMQ配置类中创建队列
importorg.springframework.amqp.core.Binding;importorg.springframework.amqp.core.BindingBuilder;importorg.springframework.amqp.core.FanoutExchange;importorg.springframework.amqp.core.Queue;importorg.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;importorg.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;@ConfigurationpublicclassRabbitMQConfig{//定义队列名privatestaticfinalString QUEUE ="queue";//创建队列/**
* 1. 配置队列
* 2. 队列名为 queue
* 3. true 表示: 持久化 (不填,默认为true,默认持久化)
* durable: 队列是否持久化。 队列默认是存放到内存中的,rabbitmq 重启则丢失,
* 若想重启之后还存在则队列要持久化,
* 保存到 Erlang 自带的 Mnesia 数据库中,当 rabbitmq 重启之后会读取该数据库
* @return
*/@BeanpublicQueuequeue(){returnnewQueue(QUEUE,true);}}
- 创建消息发送者
/**
* 消息发送者
*/@Slf4j@ServicepublicclassMQSender{@ResourceprivateRabbitTemplate rabbitTemplate;//方法:发送消息publicvoidsend(Object msg){
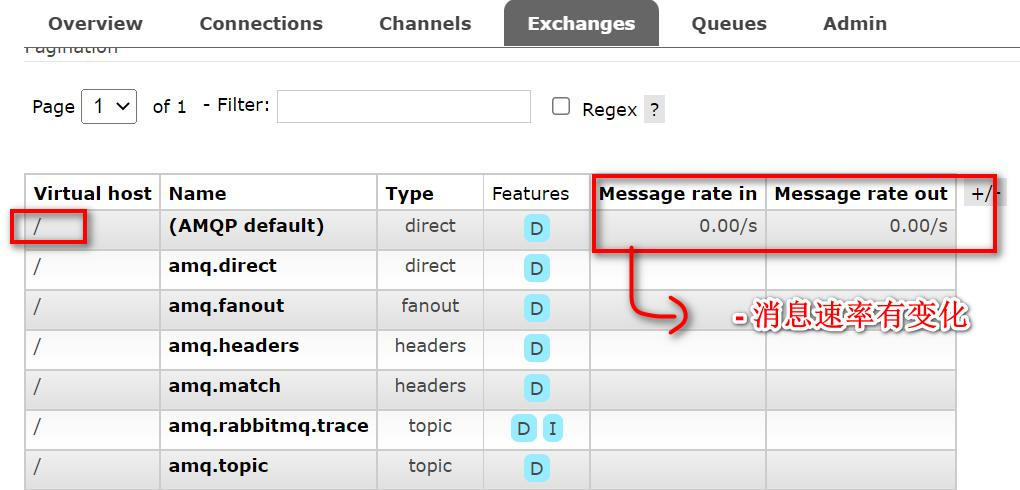
log.info("发送消息-"+ msg);//没有指定交换机会走默认的交换机,AMQP default//AMQP default是一个direct路由模式的交换机
rabbitTemplate.convertAndSend("queue",msg);}}
- 创建消息接收者
/**
* 消息接收者
*/@Service@Slf4jpublicclassMQReceiver{//方法:接收消息@RabbitListener(queues ="queue")publicvoidreceive(Object msg){
log.info("接收到消息--"+ msg);}}
- 创建controller进行测试
@ControllerpublicclassRabbitMQHandler{//装配MQSender@ResourceprivateMQSender mqSender;//方法:调用消息生产者,发送消息@RequestMapping("/mq")@ResponseBodypublicvoidmq(){
mqSender.send("hello llp");}}
2.完成测试
- 配置 RabbitMQ 所在的 Linux, 开放 5672 端口, 因为 Java 访问 RabbitMQ, 走的是 5672测试前,将 Mysql, Redis,RabbitMQ 启动。
- 防火墙开启端口访问
firewall-cmd --zone=public --add-port=5672/tcp --permanent
- 开启后需要重启防火墙才生效
firewall-cmd --reload
- 执行 firewall-cmd --list-ports 查看端口
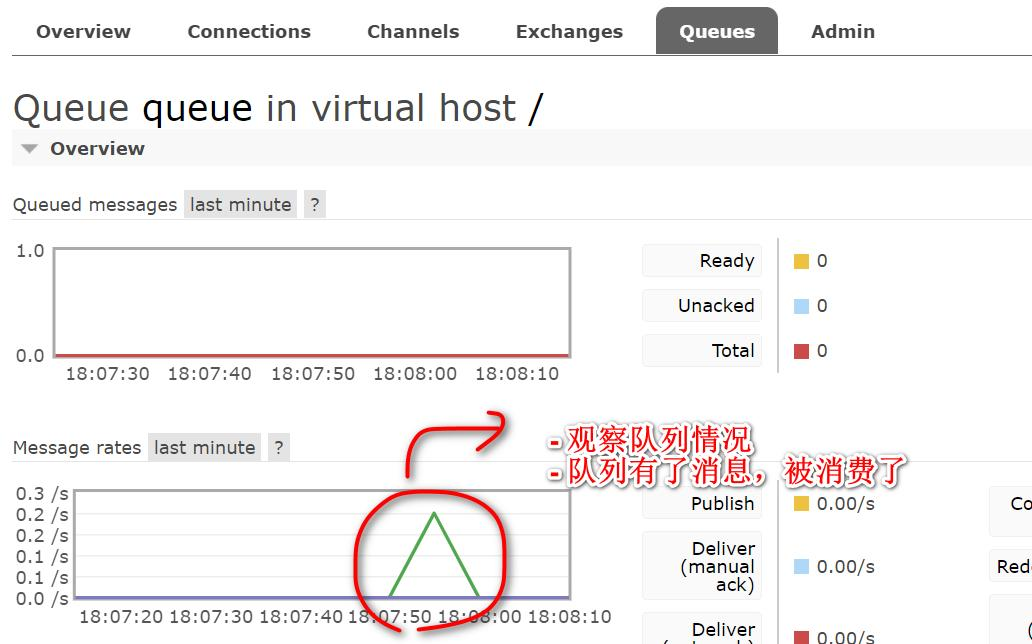
- 启动项目, 再观察 RabbitMQ 管控台
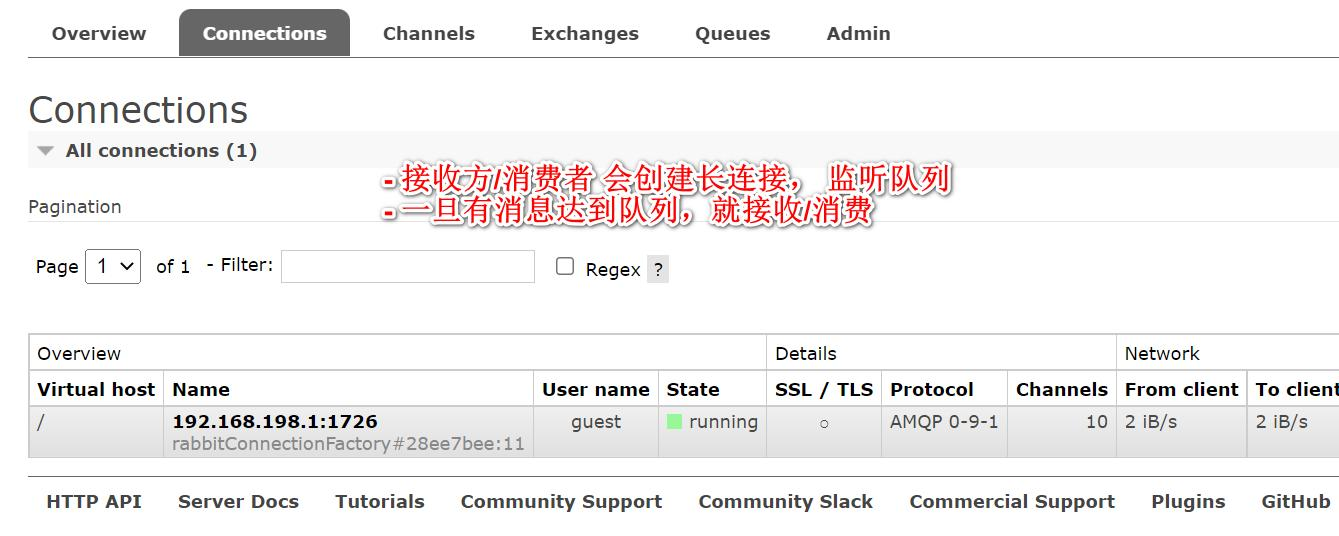
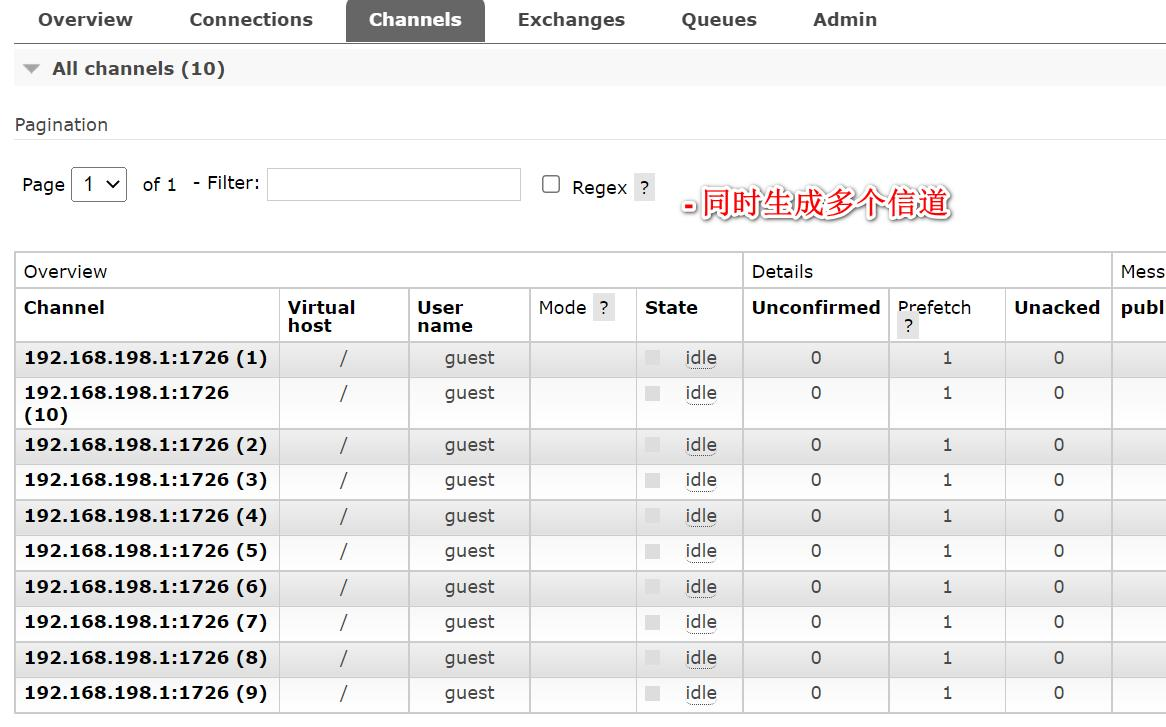
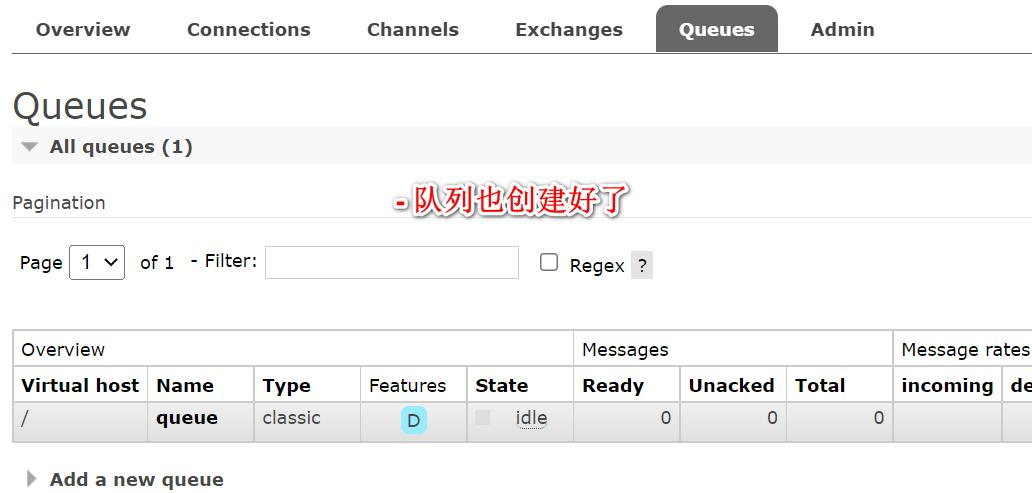
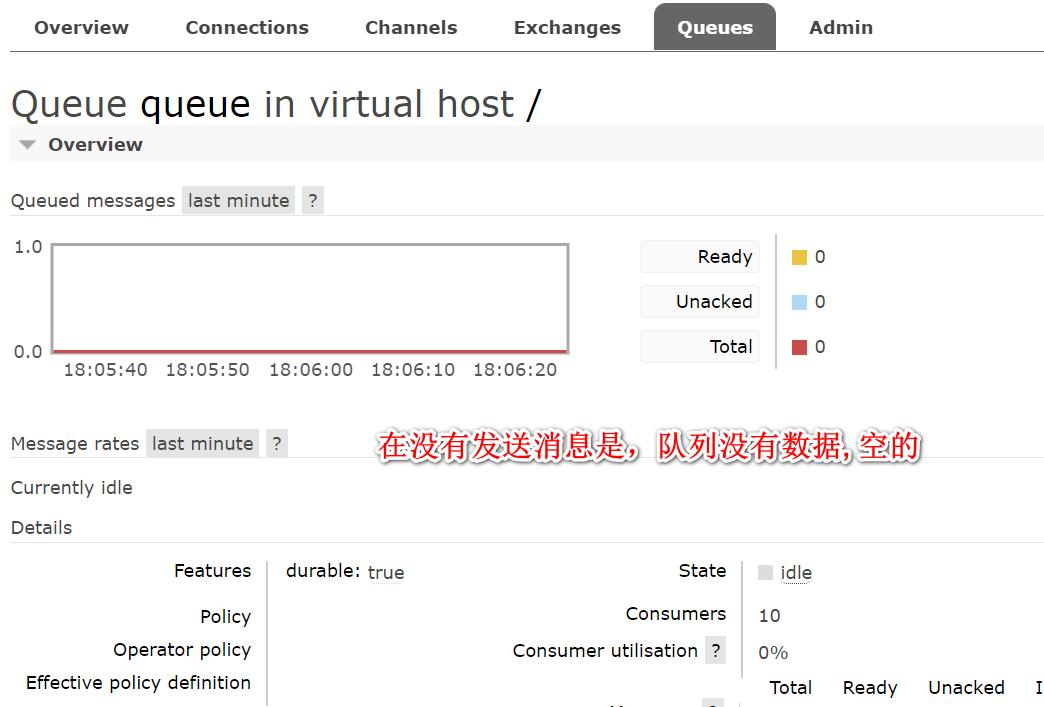
观察后端输出
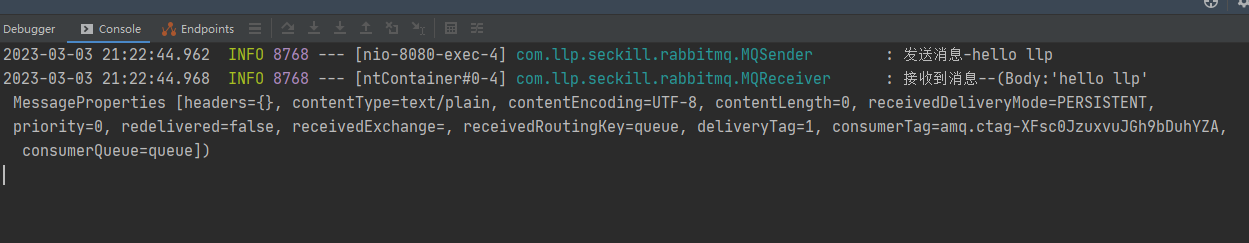
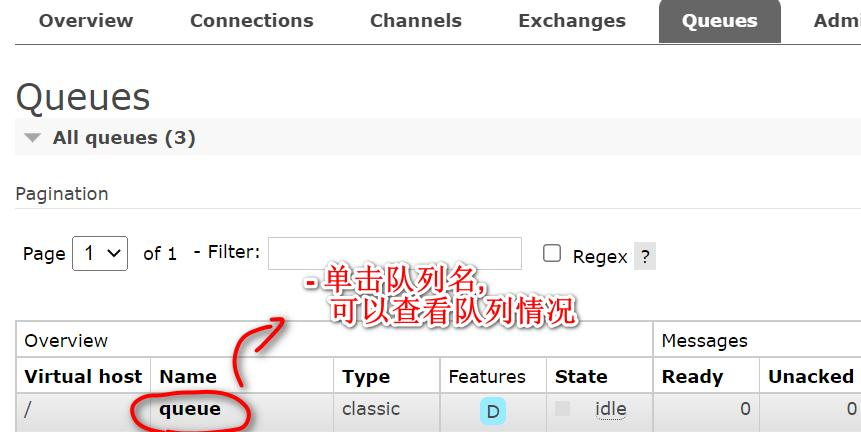
当前案例, 走的是默认交换机 (AMQP Default)
RabbitMQ 使用模式
1. Fanout-广播模式
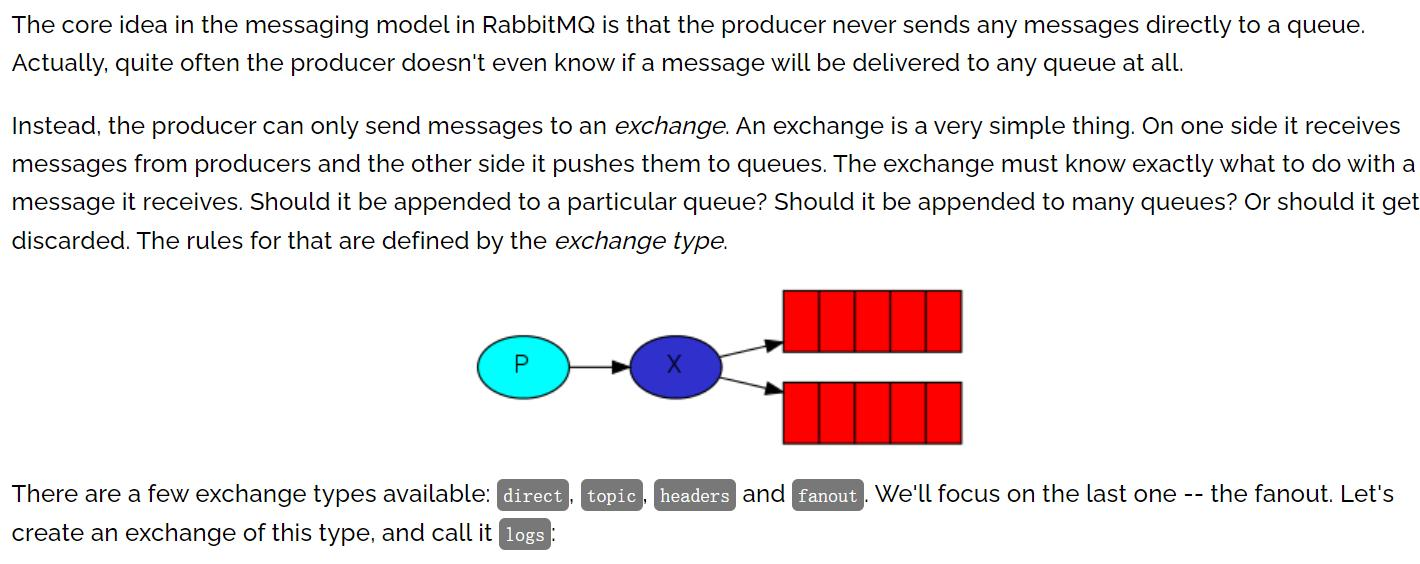
Fanout简介
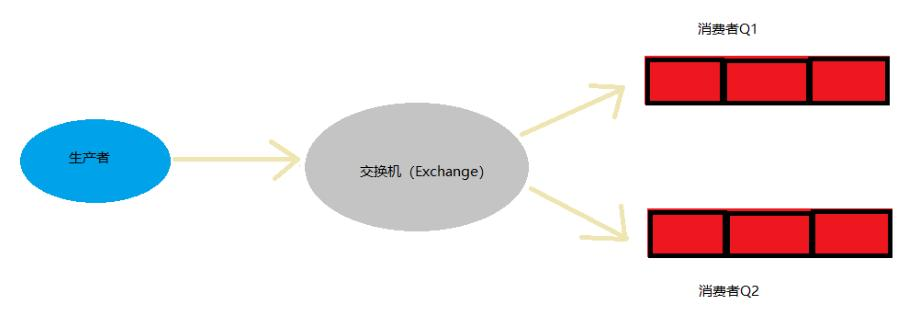
- fanout 就是广播模式, 就是把交换机(Exchange)里的消息发送给所有绑定该交换机的 队列,忽略 routingKey(也就是路由)。
- 示意图
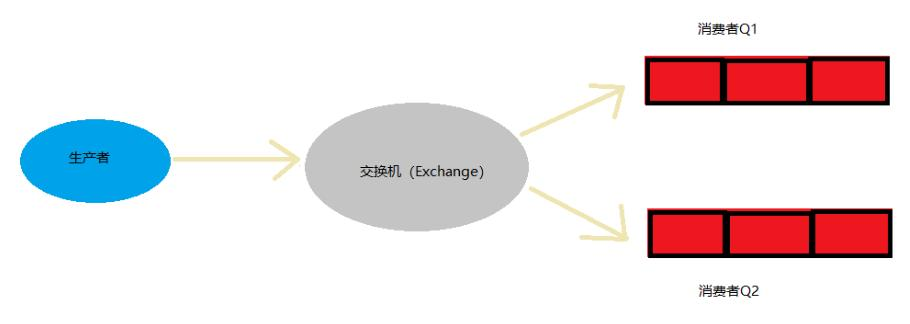
解读上图:
- 生产者把消息发送给指定的交换机
- 再把交换机的消息发送给所有绑定该交换机的队列, 忽略 routingKey/路由
应用实例
- 需求说明/图解
- 执行效果
代码实现
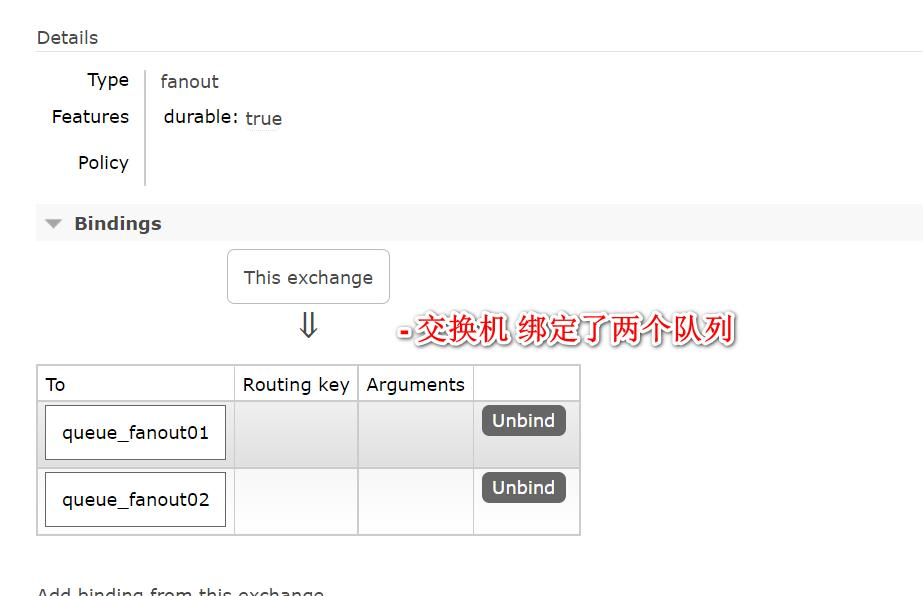
添加队列和交换机,绑定队列和交换机
@ConfigurationpublicclassRabbitMQConfig{privatestaticfinalString QUEUE1 ="queue_fanout01";privatestaticfinalString QUEUE2 ="queue_fanout02";privatestaticfinalString EXCHANGE ="fanoutExchange";//--------fanout广播模式---------/**
* 1. 配置队列
* 2. 队列名为 queue
* 3. true 表示: 持久化 (不填,默认为true,默认持久化)
* durable: 队列是否持久化。 队列默认是存放到内存中的,rabbitmq 重启则丢失,
* 若想重启之后还存在则队列要持久化,
* 保存到 Erlang 自带的 Mnesia 数据库中,当 rabbitmq 重启之后会读取该数据库
* @return
*/@BeanpublicQueuequeue1(){returnnewQueue(QUEUE1);}@BeanpublicQueuequeue2(){returnnewQueue(QUEUE2);}//创建交换机@BeanpublicFanoutExchangeexchange(){returnnewFanoutExchange(EXCHANGE);}//将队列和交换机进行绑定@BeanpublicBindingbinding01(){//将队列queue1和交换机进行绑定returnBindingBuilder.bind(queue1()).to(exchange());}@BeanpublicBindingbinding02(){//将队列queue1和交换机进行绑定returnBindingBuilder.bind(queue2()).to(exchange());}}
消息发送者
/**
* 消息发送者
*/@Slf4j@ServicepublicclassMQSender{@ResourceprivateRabbitTemplate rabbitTemplate;//fanout广播模式发送消息publicvoidsendFanout(Object msg){
log.info("发送消息-"+ msg);//因为是fanout广播模式,不需要指定路由,这里路由赋空值处理
rabbitTemplate.convertAndSend("fanoutExchange","",msg);}}
消息接收者
/**
* 消息接收者
*/@Service@Slf4jpublicclassMQReceiver{//queues对应接收消息的队列@RabbitListener(queues ="queue_fanout01")publicvoidreceive1(Object msg){
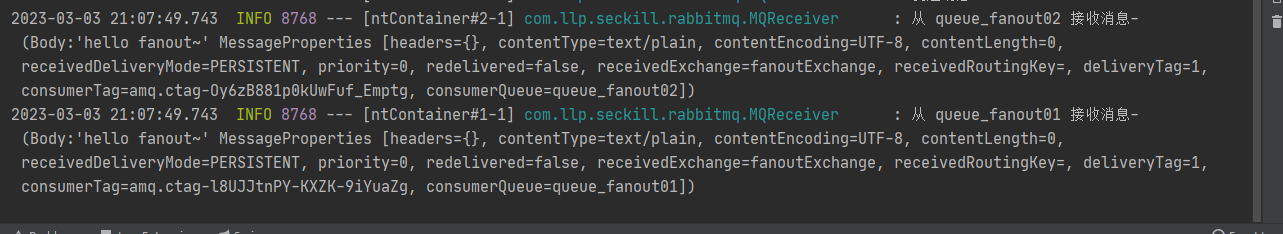
log.info("从 queue_fanout01 接收消息-"+ msg);}@RabbitListener(queues ="queue_fanout02")publicvoidreceive2(Object msg){
log.info("从 queue_fanout02 接收消息-"+ msg);}}
controller层测试类
@ControllerpublicclassRabbitMQHandler{//装配MQSender@ResourceprivateMQSender mqSender;//调用消息生产者,发送消息到交换机@RequestMapping("/mq/fanout")@ResponseBodypublicvoidfanout(){
mqSender.sendFanout("hello fanout~");}}
完成测试
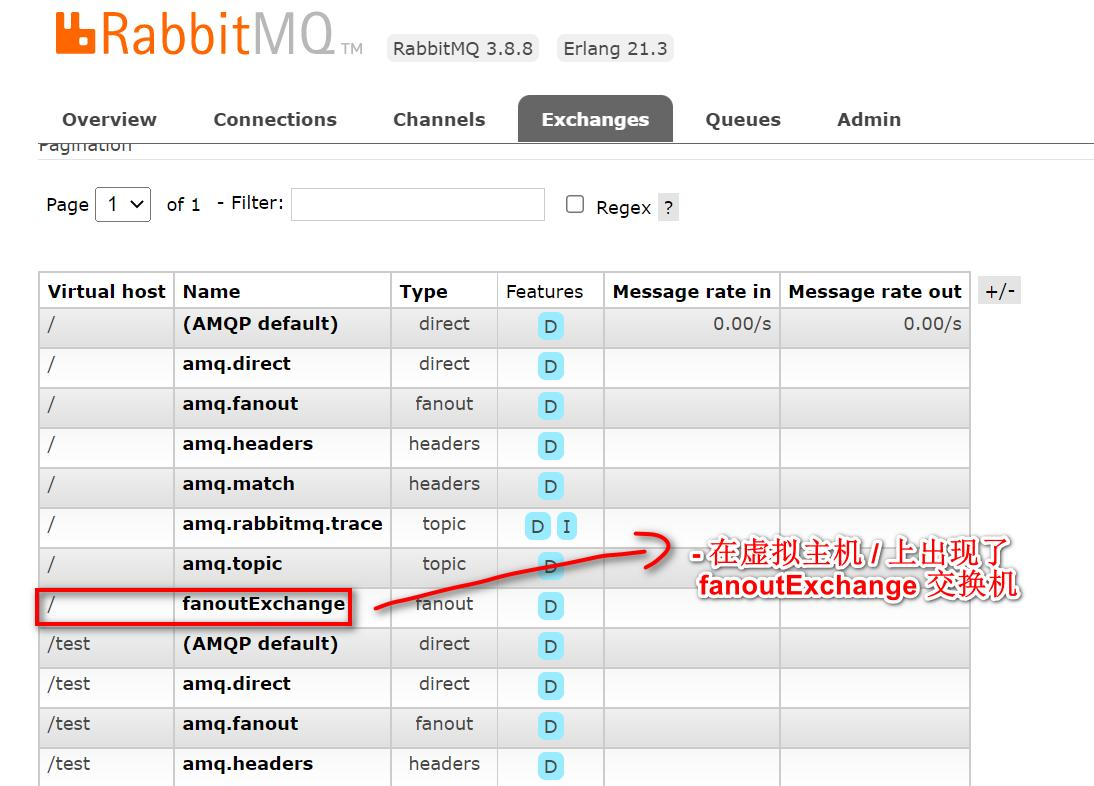
- 点击交换机 fanoutExchange, 查看绑定情况
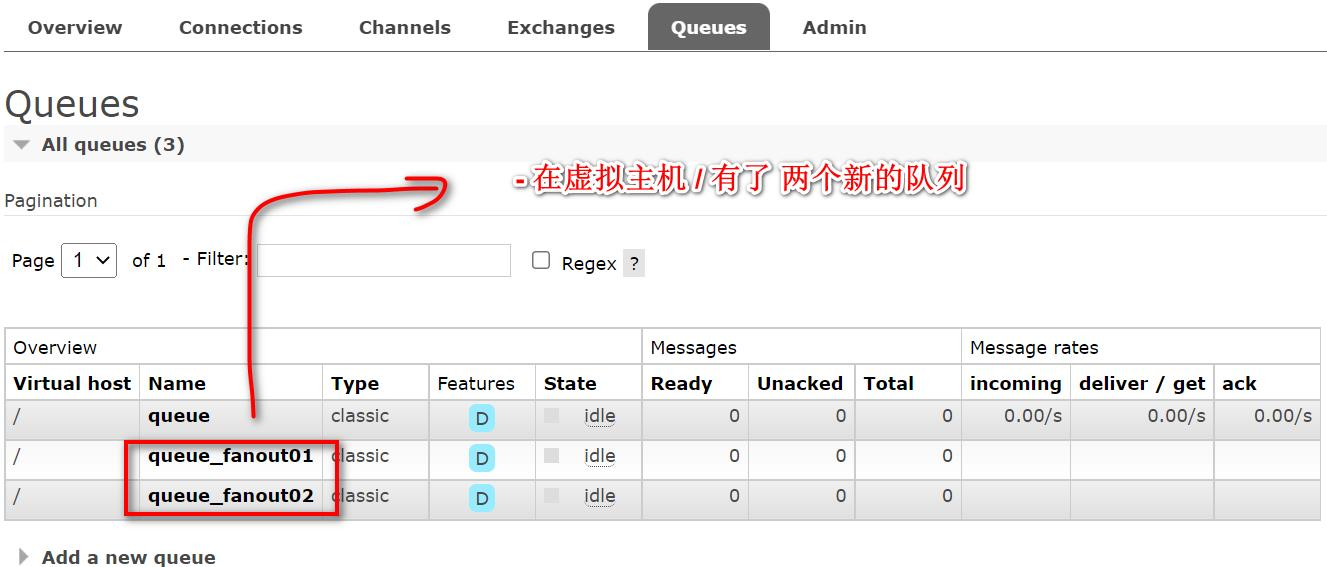
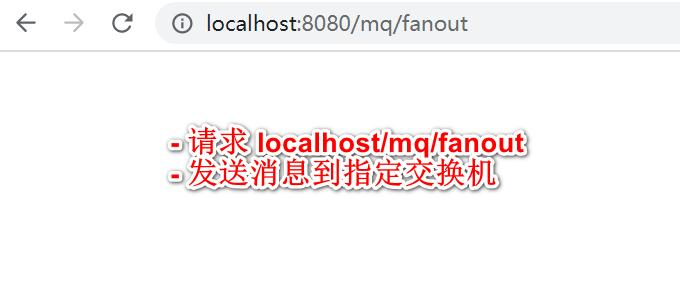
观察后台输出
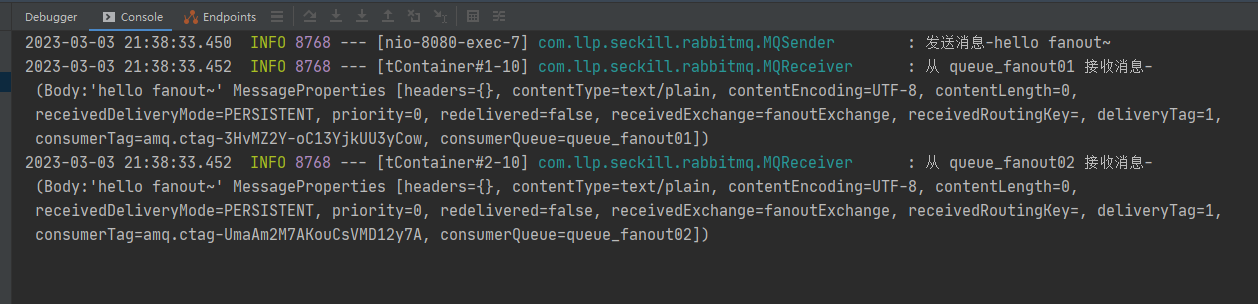
点击队列名,查看队列情况
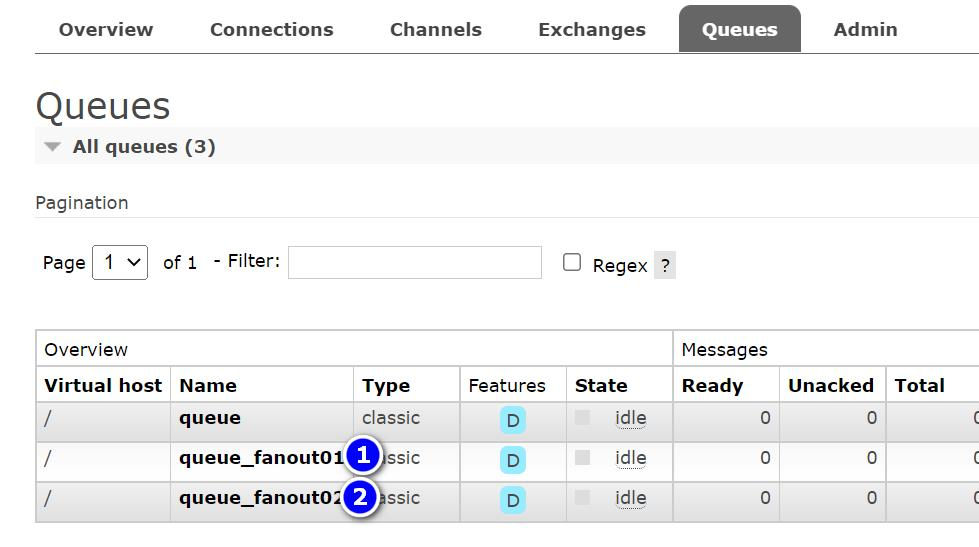
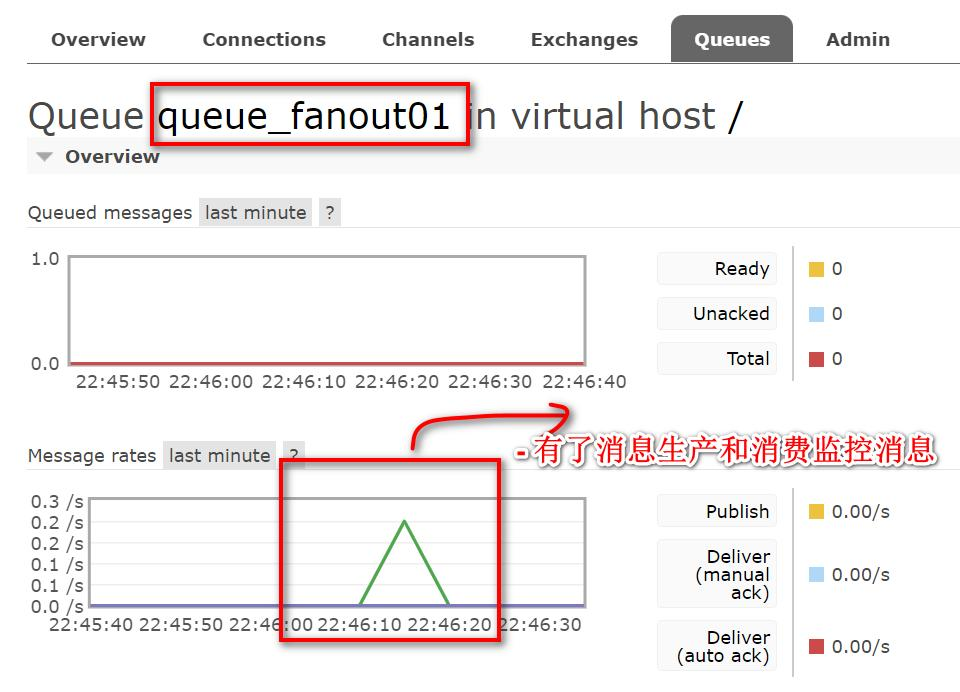
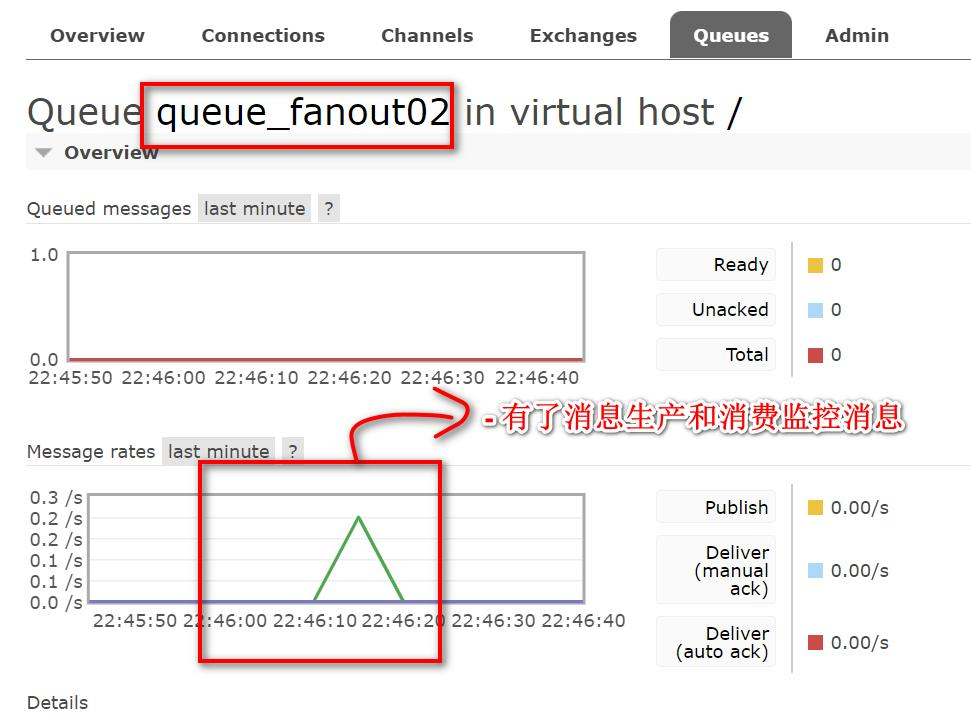
2.Direct-路由模式
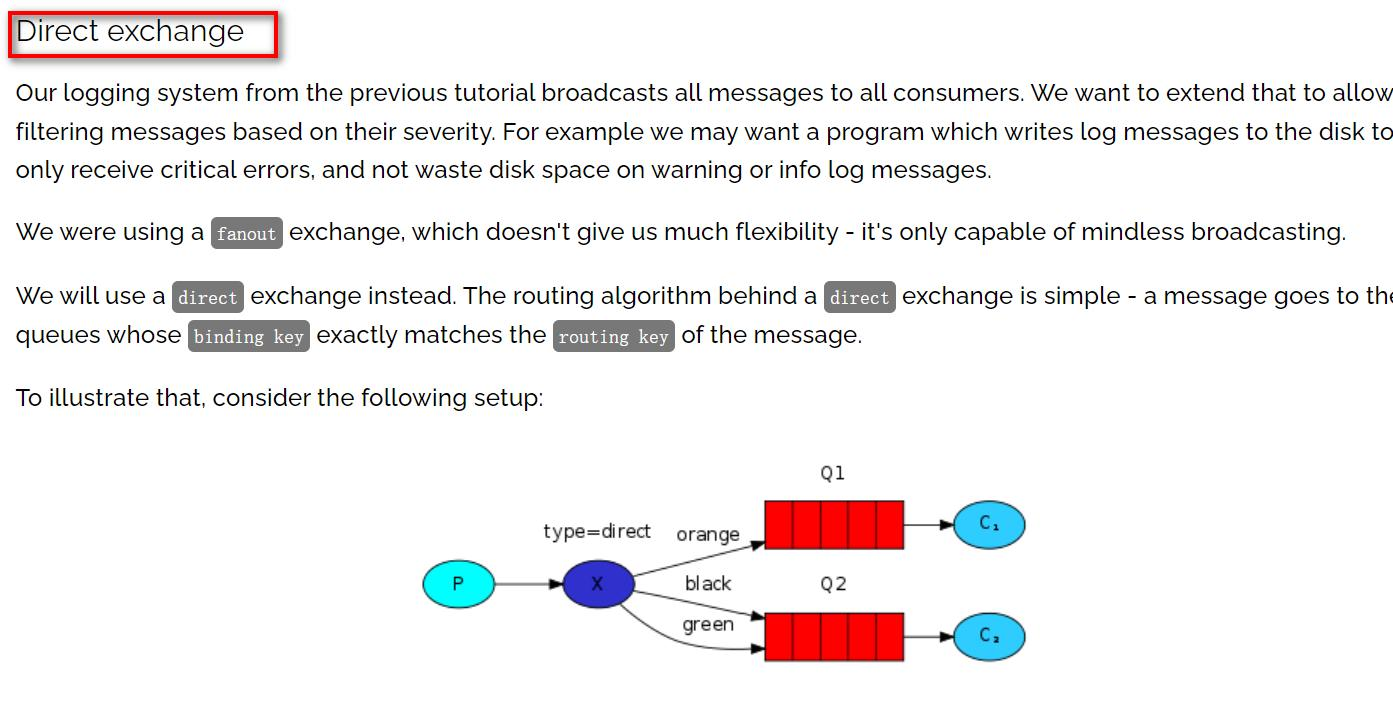
Direct简介
- direct 就是路由模式, 路由模式是在使用交换机的同时,生产者指定路由发送数据, 消费者绑定路由接受数据。
- 与广播模式不同的是,广播模式只要是绑定了交换机的队列都会收到生产者向交换 机推送过来的数据。而路由模式下加了一个路由设置,生产者向交换机发送数据时,会 声明发送给交换机下的哪个路由,并且只有当消费者的队列绑定了交换机并且声明了路 由,才会收到数据
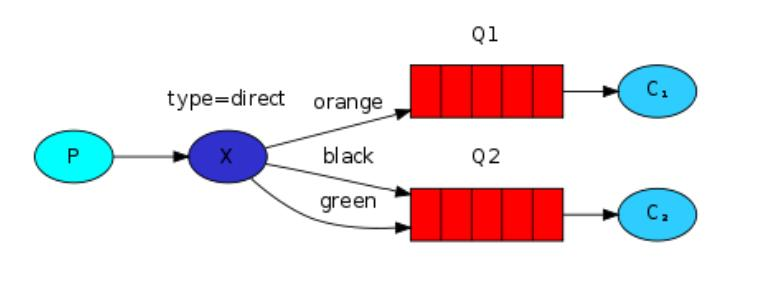
- 示意图
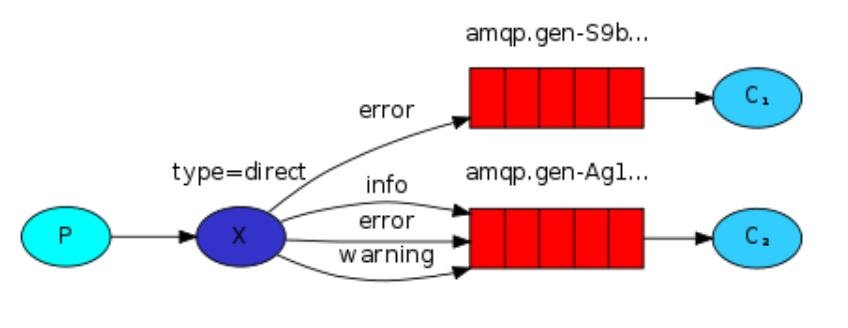
- P:消息的生产者
- X:交换机
- 红色:队列
- C1,C2:消息消费者
- error,info,warning:路由
应用实例
- 需求说明/图解
- 执行效果
代码实现
声明队列、交换机、路由
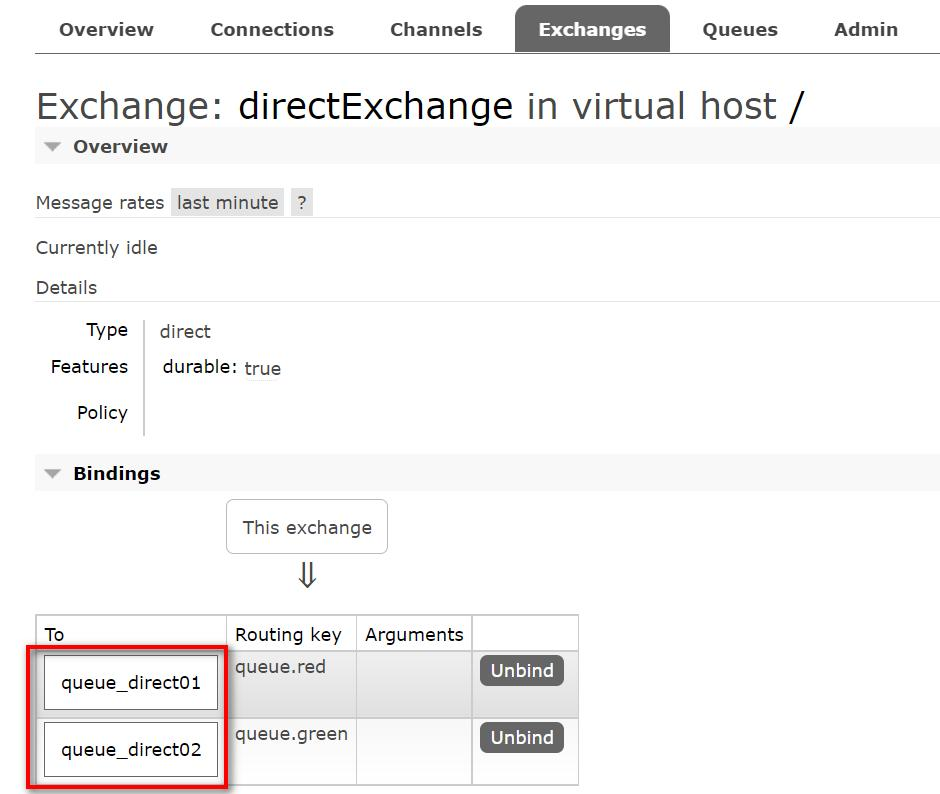
@ConfigurationpublicclassRabbitMQConfig{//directprivatestaticfinalString QUEUE_DIRECT1 ="queue_direct01";privatestaticfinalString QUEUE_DIRECT2 ="queue_direct02";privatestaticfinalString EXCHANGE_DIRECT ="directExchange";//路由privatestaticfinalString routing_key01 ="queue.red";privatestaticfinalString routing_key02 ="queue.green";//--------direct路由模式---------@BeanpublicQueuequeue_direct1(){returnnewQueue(QUEUE_DIRECT1);}@BeanpublicQueuequeue_direct2(){returnnewQueue(QUEUE_DIRECT2);}@BeanpublicDirectExchangeexchange_direct(){returnnewDirectExchange(EXCHANGE_DIRECT);}@BeanpublicBindingbinding_direct1(){//将队列queue_direct1和交换机进行绑定,并给队列绑定路由returnBindingBuilder.bind(queue_direct1()).to(exchange_direct()).with(routing_key01);}@BeanpublicBindingbinding_direct2(){//将队列queue_direct2和交换机进行绑定,并给队列绑定路由returnBindingBuilder.bind(queue_direct2()).to(exchange_direct()).with(routing_key02);}}
消息发送者
/**
* 消息发送者
*/@Slf4j@ServicepublicclassMQSender{@ResourceprivateRabbitTemplate rabbitTemplate;publicvoidsendDirect1(Object msg){
log.info("发送消息-"+ msg);
rabbitTemplate.convertAndSend("directExchange","queue.red",msg);}publicvoidsendDirect2(Object msg){
log.info("发送消息-"+ msg);
rabbitTemplate.convertAndSend("directExchange","queue.green",msg);}}
消息接收者
/**
* 消息接收者
*/@Service@Slf4jpublicclassMQReceiver{@RabbitListener(queues ="queue_direct01")publicvoidqueue_direct1(Object msg){
log.info("从 queue_direct1 接收消息-"+ msg);}@RabbitListener(queues ="queue_direct02")publicvoidqueue_direct2(Object msg){
log.info("从 queue_direct2 接收消息-"+ msg);}}
controller测试
@ControllerpublicclassRabbitMQHandler{//装配MQSender@ResourceprivateMQSender mqSender;//direct 模式@GetMapping("/mq/direct01")@ResponseBodypublicvoiddirect01(){
mqSender.sendDirect1("hello aimee");}//direct 模式@GetMapping("/mq/direct02")@ResponseBodypublicvoiddirect02(){
mqSender.sendDirect2("hello llp");}}
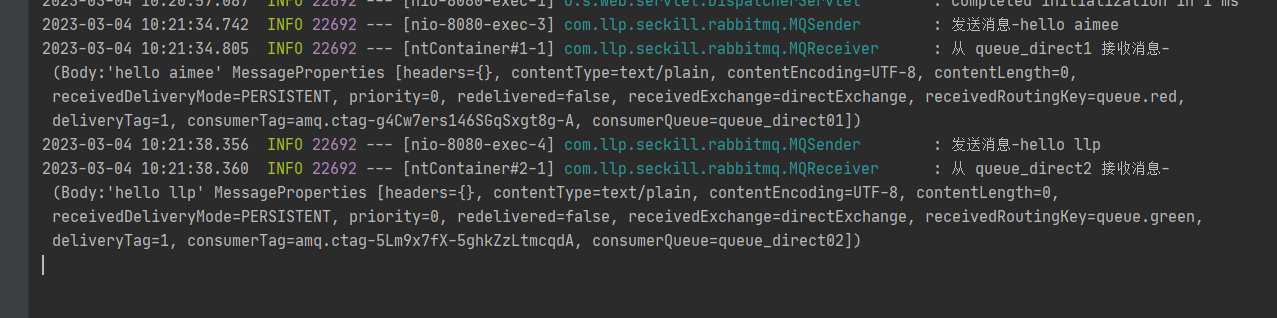
完成测试
- 启动项目, 再观察 RabbitMQ 管控台
 点击交换机 directExchange, 查看绑定情况
点击交换机 directExchange, 查看绑定情况
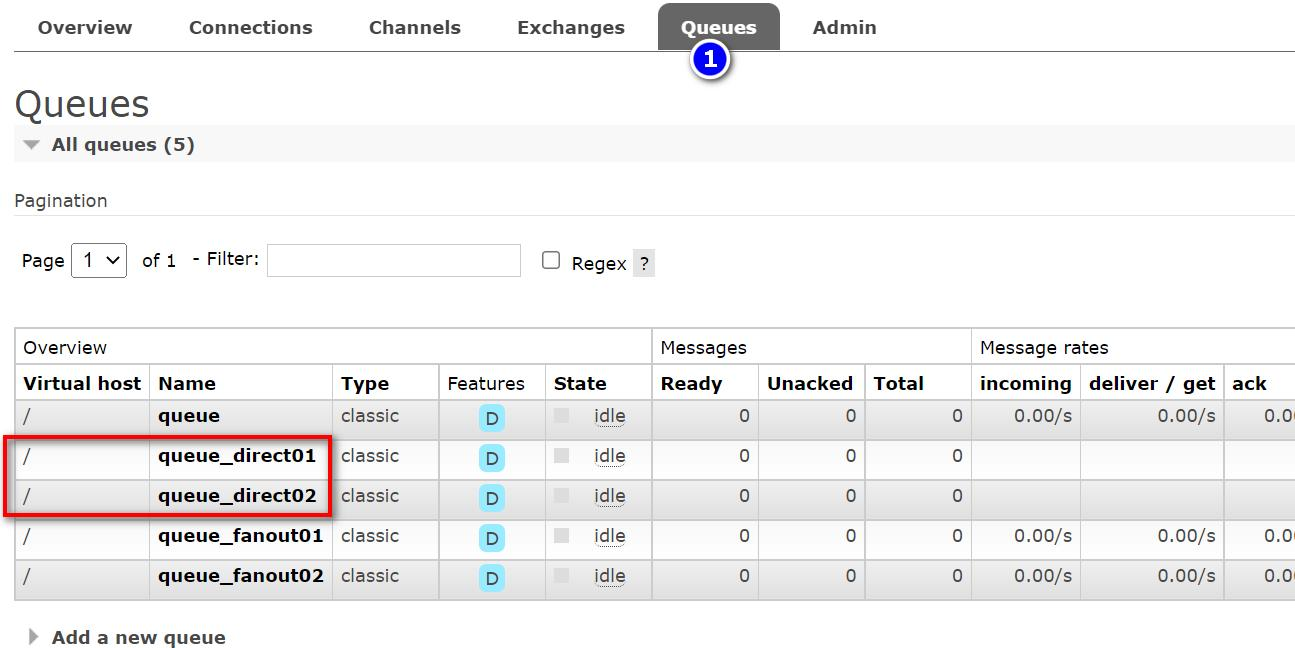
查看控制台数据情况
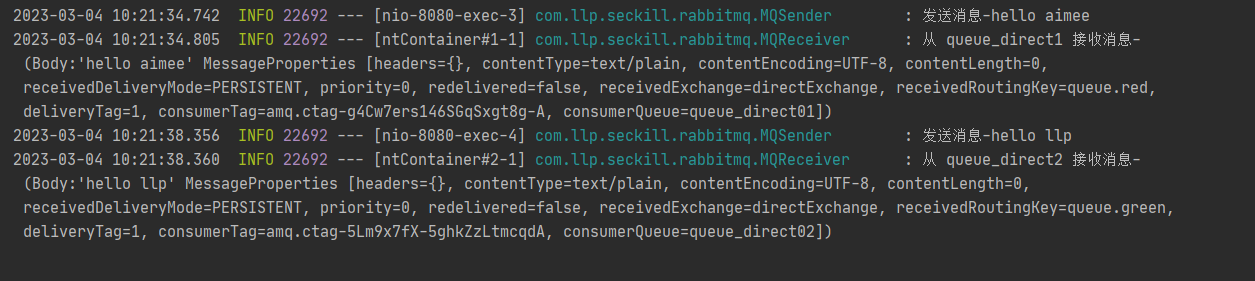
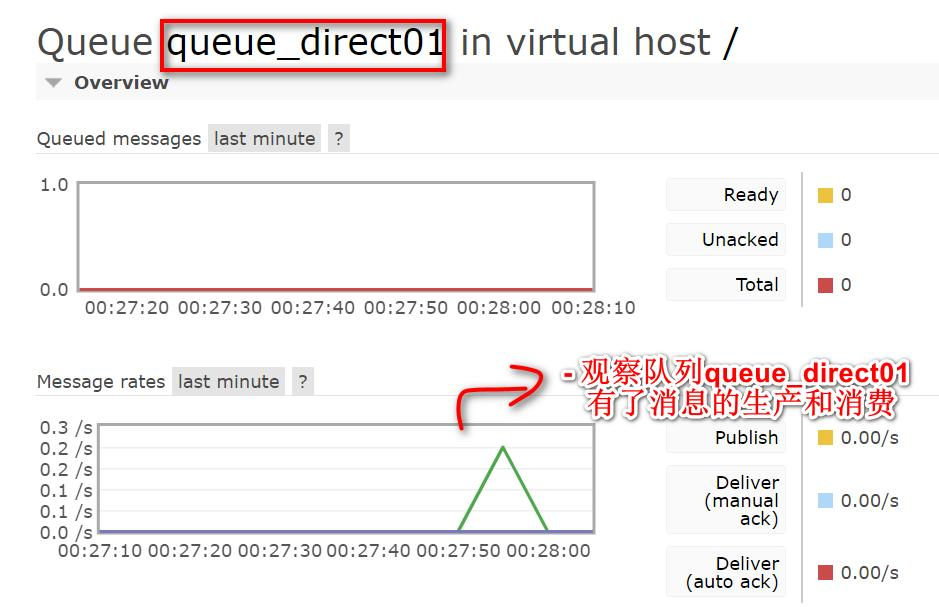
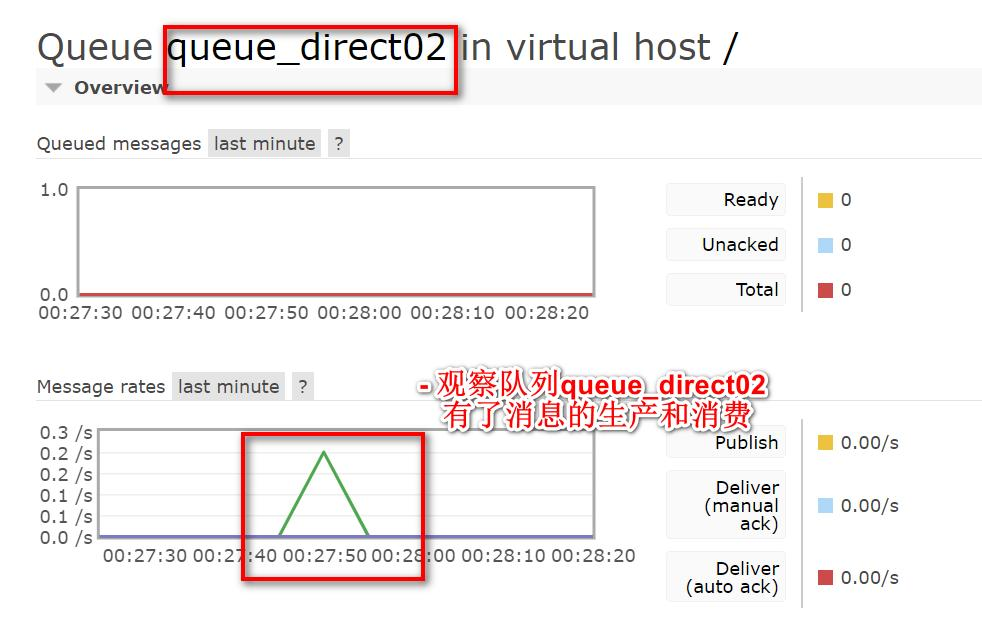
点击相应的队列, 观察队列已经有了消息变化, (提示:发送消息后就观察, 因为是实时刷新
的)
3.Topic主题模式
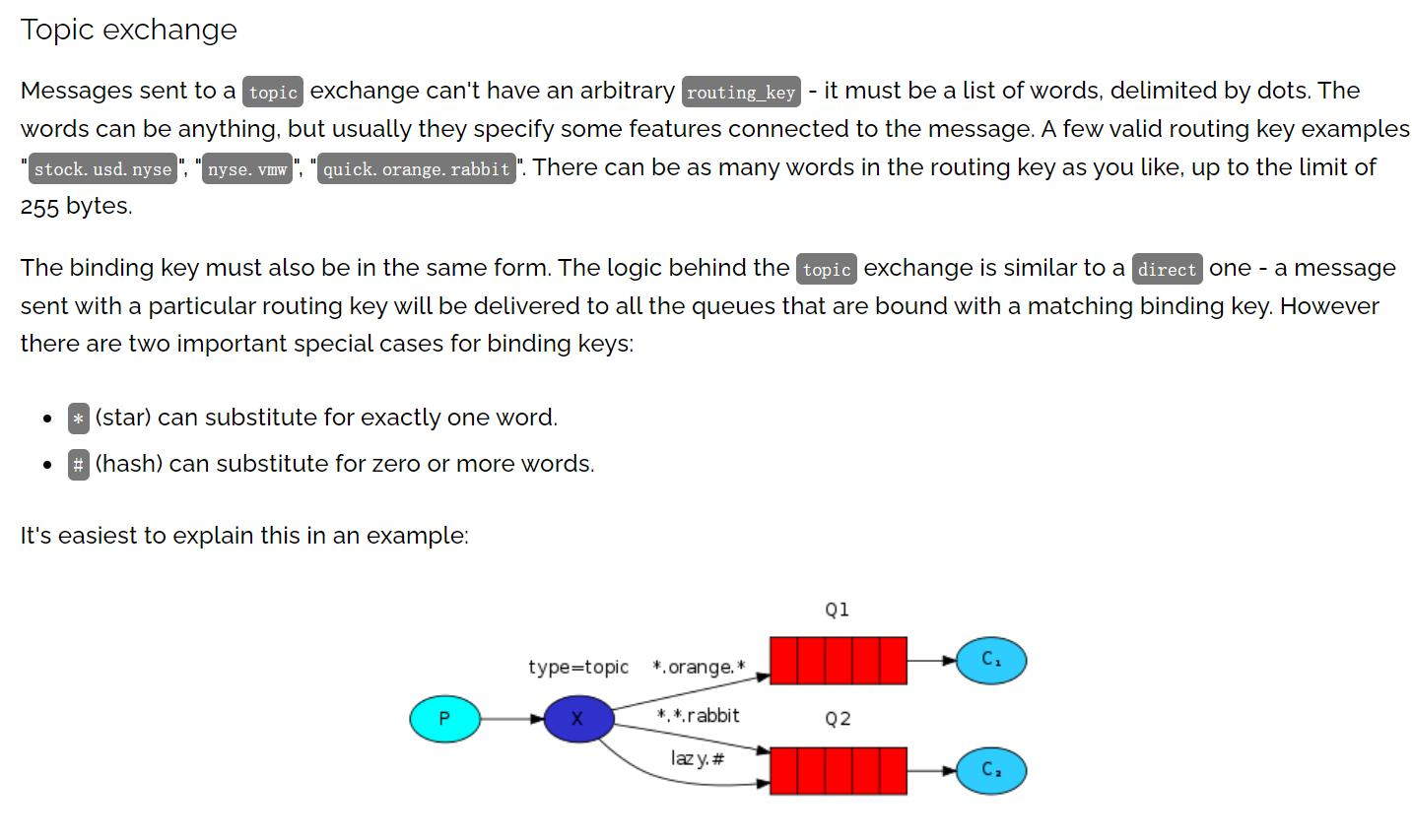
Topic 介绍
- direct 模式会造成路由 RoutingKey 太多, 而实际开发中往往是按照某个规则来进行路 由匹配的, RabbitMQ 提供了 Topic 模式/主题模式来适应这种需求.
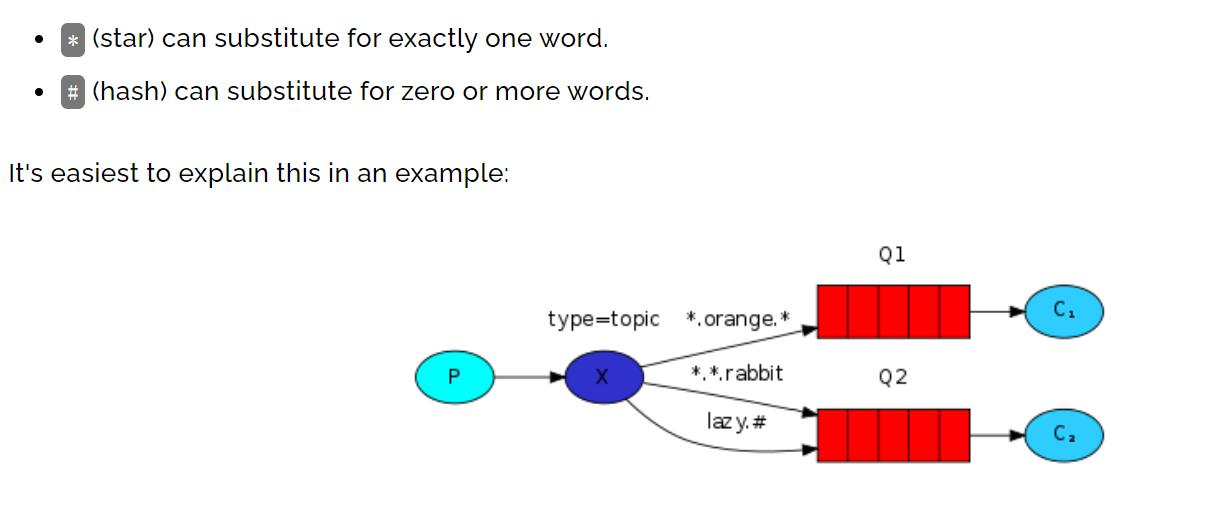
- Topic 模式是 direct 模式上的一种扩展/叠加, 扩展/叠加了模糊路由 RoutingKey 的模 式, 可以理解为是模糊的路由匹配模式
*(星号):可以(只能)匹配一个单词#(井号):可以匹配多个单词(或者零个)
示意图:
应用实例
- 需求说明/图解
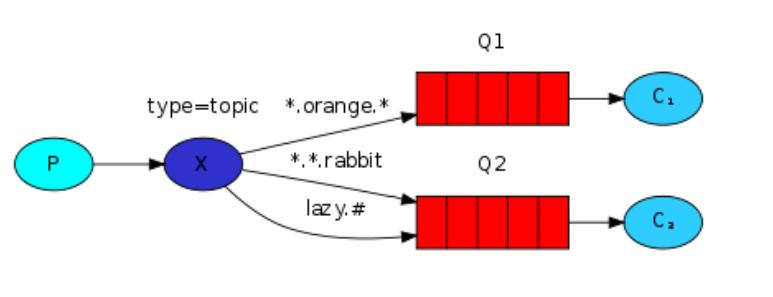
- 执行效果
代码实现
配置队列、交换机、路由
importorg.springframework.amqp.core.Binding;importorg.springframework.amqp.core.BindingBuilder;importorg.springframework.amqp.core.Queue;importorg.springframework.amqp.core.TopicExchange;importorg.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;importorg.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;@ConfigurationpublicclassRabbitMQTopicConfig{//topic主题模式privatestaticfinalString QUEUE_TOPIC1 ="queue_topic01";privatestaticfinalString QUEUE_TOPIC2 ="queue_topic02";privatestaticfinalString EXCHANGE_TOPIC ="topicExchange";//路由privatestaticfinalString routing_key01 ="#.queue.#";privatestaticfinalString routing_key02 ="*.queue.#";@BeanpublicQueuequeue_topic01(){returnnewQueue(QUEUE_TOPIC1);}@BeanpublicQueuequeue_topic02(){returnnewQueue(QUEUE_TOPIC2);}@BeanpublicTopicExchangetopicExchange(){returnnewTopicExchange(EXCHANGE_TOPIC);}@BeanpublicBindingbinding_topic1(){//将队列queue1和交换机进行绑定returnBindingBuilder.bind(queue_topic01()).to(topicExchange()).with(routing_key01);}@BeanpublicBindingbinding_topic2(){//将队列queue1和交换机进行绑定returnBindingBuilder.bind(queue_topic02()).to(topicExchange()).with(routing_key02);}}
消息发送者
/**
* 消息发送者
*/@Slf4j@ServicepublicclassMQSender{@ResourceprivateRabbitTemplate rabbitTemplate;publicvoidsendTopic1(Object msg){
log.info("发送消息-"+ msg);
rabbitTemplate.convertAndSend("topicExchange","queue.red.message", msg);}publicvoidsendTopic2(Object msg){
log.info("发送消息-"+ msg);
rabbitTemplate.convertAndSend("topicExchange","green.queue.green.message", msg);}}
消息接收者
/**
* 消息接收者
*/@Service@Slf4jpublicclassMQReceiver{-@RabbitListener(queues ="queue_topic01")publicvoidqueue_topic1(Object msg){
log.info("从 queue_topic01 接收消息-"+ msg);}@RabbitListener(queues ="queue_topic02")publicvoidqueue_topic2(Object msg){
log.info("从 queue_topic02 接收消息-"+ msg);}}
编写controller层测试方法
@ControllerpublicclassRabbitMQHandler{//装配MQSender@ResourceprivateMQSender mqSender;//topic 模式@GetMapping("/mq/topic01")@ResponseBodypublicvoidtopic01(){
mqSender.sendDirect1("hello aimee topic");}//topic 模式@GetMapping("/mq/topic02")@ResponseBodypublicvoidtopic02(){
mqSender.sendDirect2("hello llp topic");}}
完成测试
- 启动项目, 再观察 RabbitMQ 管控台
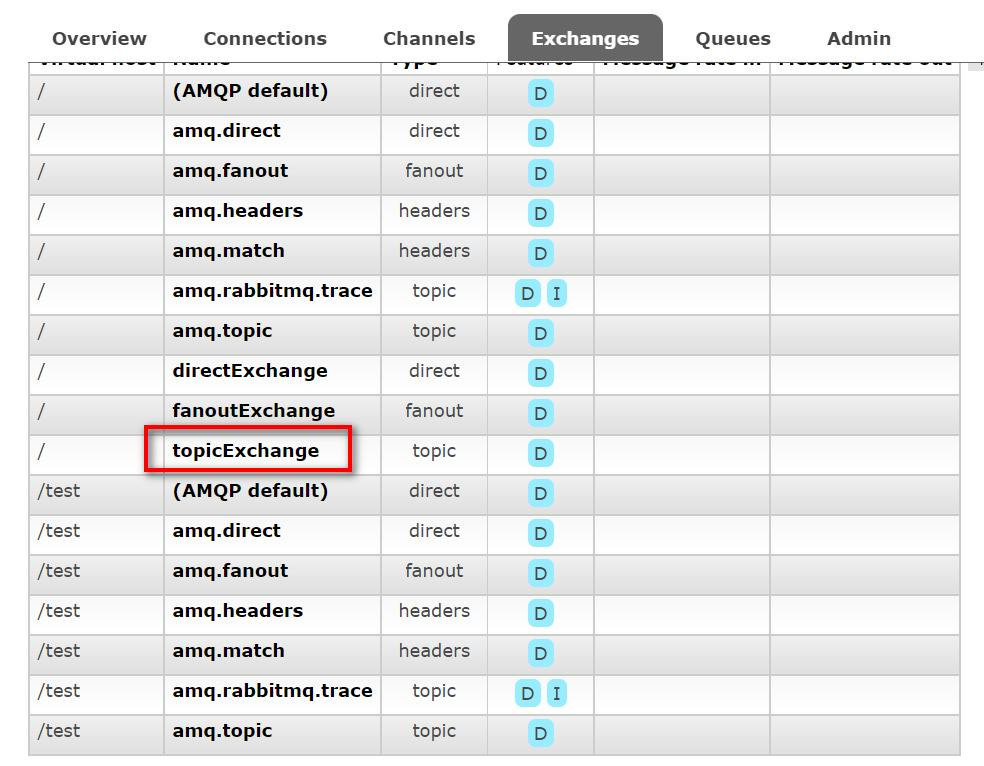
点击交换机 topicExchange, 查看绑定情况
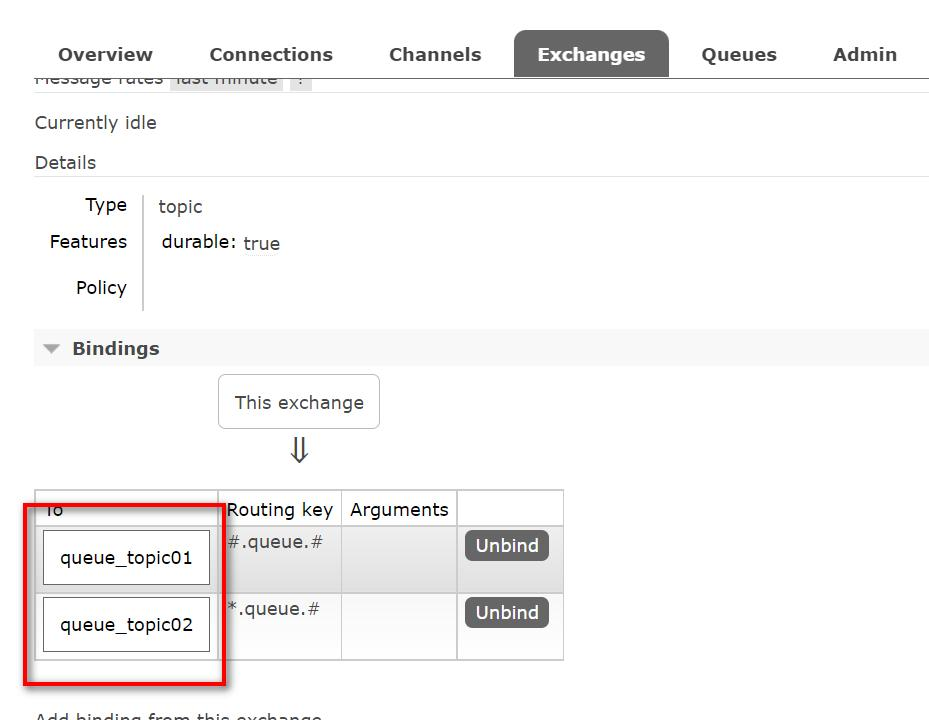
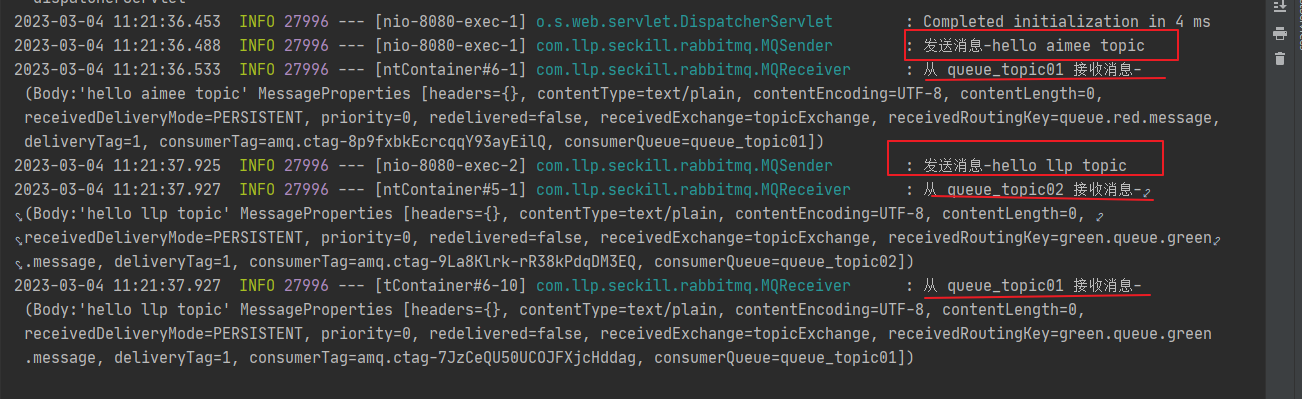
观察后台输出
queue.red.message
green.queue.green.message
#.queue.#
*.queue.#
调用topic1, queue.red.message匹配到的路由是#.queue.#
调用topic2, green.queue.green.message匹配到的路由是*.queue.#和#.queue.#
* 有且仅有一个
# 可以有多个也可以没有
4.Headers模式
Headers 介绍
- headers 模式/headers 头路由模式 使用比较少
- headers 交换机是一种比较复杂且少见的交换机,不同于 direct 和 topic,它不关心路由 key 是否匹配,而只关心 header 中的 key-value 对是否匹配(这里的匹配为精确匹配,包含键和值都必须匹配), 有点类似于 http 中的请求头。
- headers 头路由模型中,消息是根据 prop 即请求头中 key-value 来匹配的。
- 绑定的队列(也可以理解成消费方) 指定的 headers 中必须包含一个"x-match"的键
- 键"x-match"的值有 2 个:all 和 any。 all:表示绑定的队列/消费方 指定的所有 key-value 都必须在消息 header 中出现并匹配 any:表示绑定的队列/消费方 指定的 key-value 至少有一个在消息 header 中出现并匹配即可
应用实例
- 需求说明/图解
- 给 headers 交换机发送消息 hello ABC, 让 QUEUE01 和 QUEUE02 两个队列都接收
- 给 headers 交换机发送消息 hello llp, 让 QUEUE01 队列都接收
- 适应 headers 模式完成
代码实现
创建队列、交换机
@ConfigurationpublicclassRabbitMQHeadersConfig{privatestaticfinalString QUEUE01 ="queue_header01";privatestaticfinalString QUEUE02 ="queue_header02";privatestaticfinalString EXCHANGE ="headersExchange";@BeanpublicQueuequeue_header01(){returnnewQueue(QUEUE01);}@BeanpublicQueuequeue_header02(){returnnewQueue(QUEUE02);}@BeanpublicHeadersExchangeheadersExchange(){returnnewHeadersExchange(EXCHANGE);}@BeanpublicBindingbinding_header01(){Map<String,Object> map =newHashMap<>();
map.put("color","red");
map.put("speed","low");System.out.println("yy="+headersExchange().hashCode());//whereAny(map): 只要发送的消息的属性 MessageProperties 有任意一个k-v匹配就 OKreturnBindingBuilder.bind(queue_header01()).to(headersExchange()).whereAny(map).match();}@BeanpublicBindingbinding_header02(){Map<String,Object> map =newHashMap<>();
map.put("color","red");
map.put("speed","fast");System.out.println("xx="+headersExchange().hashCode());//whereAll(map): 发送的消息的属性 MessageProperties 要全部匹配才 OKreturnBindingBuilder.bind(queue_header02()).to(headersExchange()).whereAll(map).match();}}
消息发送者
@Slf4j@ServicepublicclassMQSender{@ResourceprivateRabbitTemplate rabbitTemplate;publicvoidsendHeader1(String msg){MessageProperties properties =newMessageProperties();
properties.setHeader("color","red");
properties.setHeader("speed","fast");Message message =newMessage(msg.getBytes(), properties);
rabbitTemplate.convertAndSend("headersExchange","",message);}publicvoidsendHeader2(String msg){MessageProperties properties =newMessageProperties();
properties.setHeader("color","red");
properties.setHeader("speed","normal");Message message =newMessage(msg.getBytes(), properties);
rabbitTemplate.convertAndSend("headersExchange","",message);}}
消息接收者
/**
* 消息接收者
*/@Service@Slf4jpublicclassMQReceiver{@RabbitListener(queues ="queue_header01")publicvoidqueue_header1(Message message){
log.info("queue_header01 接收消息 message 对象"+ message);
log.info("queue_header01 接收消息"+newString(message.getBody()));}@RabbitListener(queues ="queue_header02")publicvoidqueue_header2(Message message){
log.info("queue_header2 接收消息 message 对象"+ message);
log.info("queue_header2 接收消息"+newString(message.getBody()));}}
完成测试
- 启动项目, 再观察 RabbitMQ 管控台
点击交换机 headersExchange, 查看绑定情况
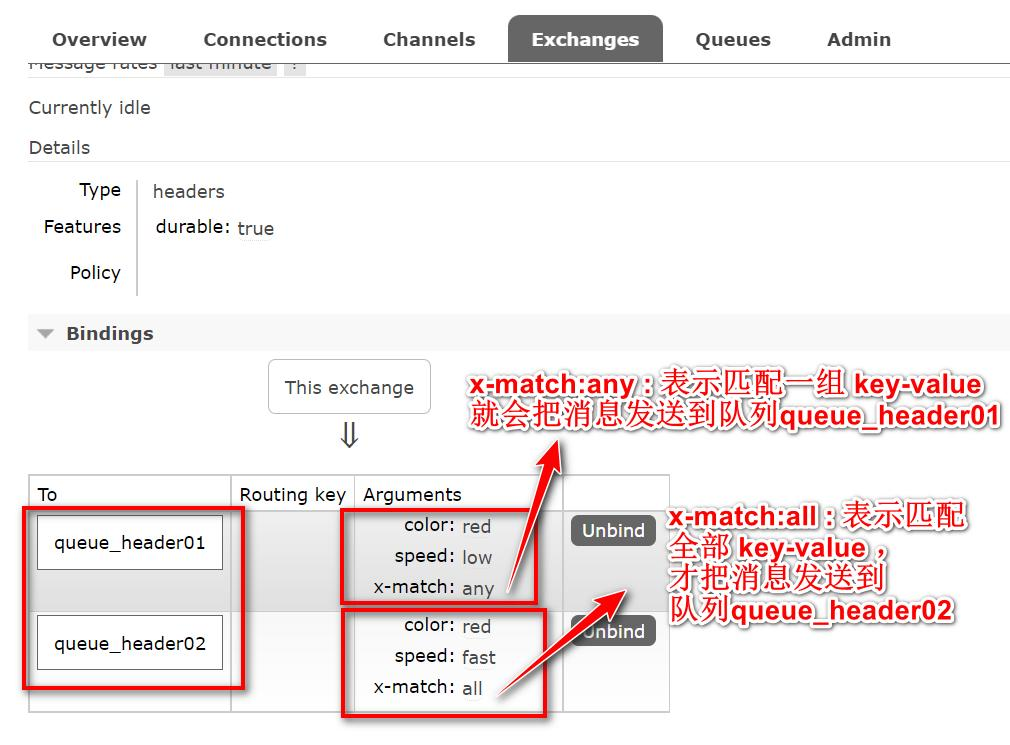
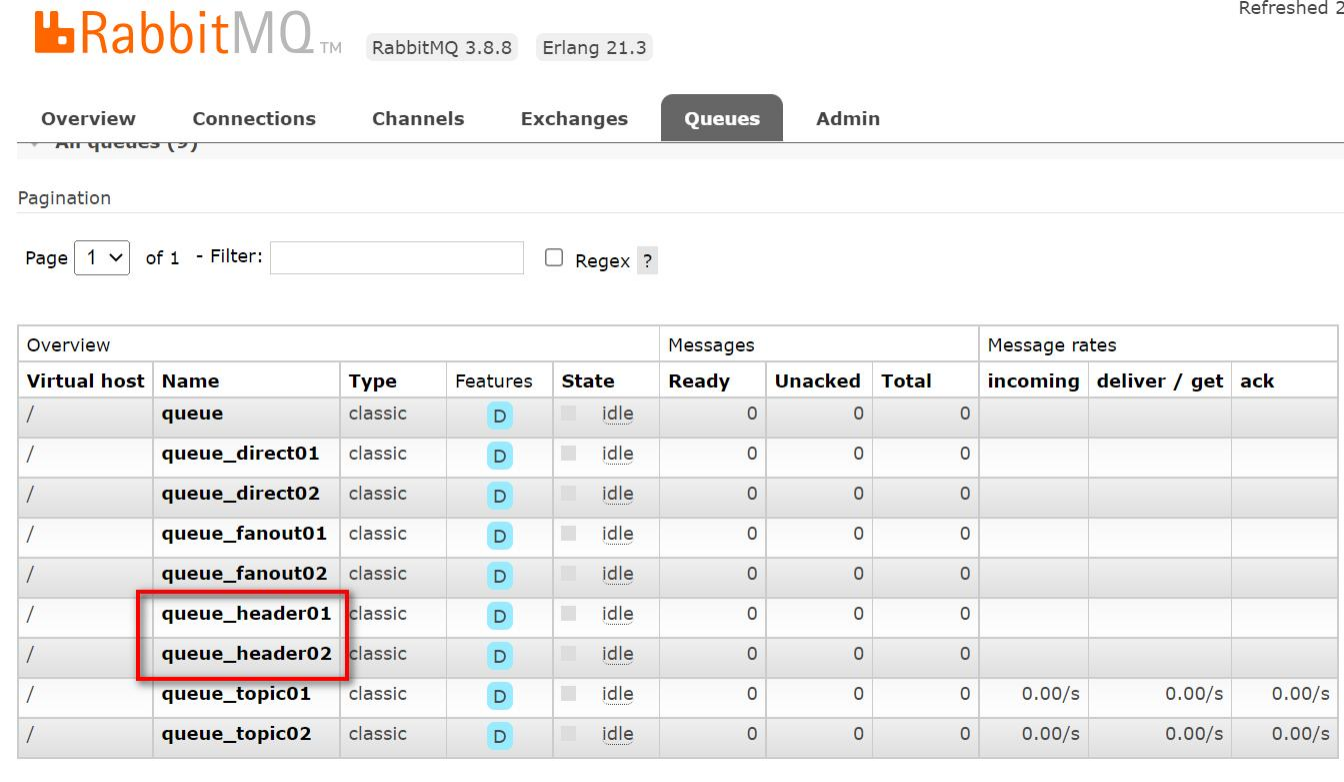
调用header1,队列1和队列2都能接收
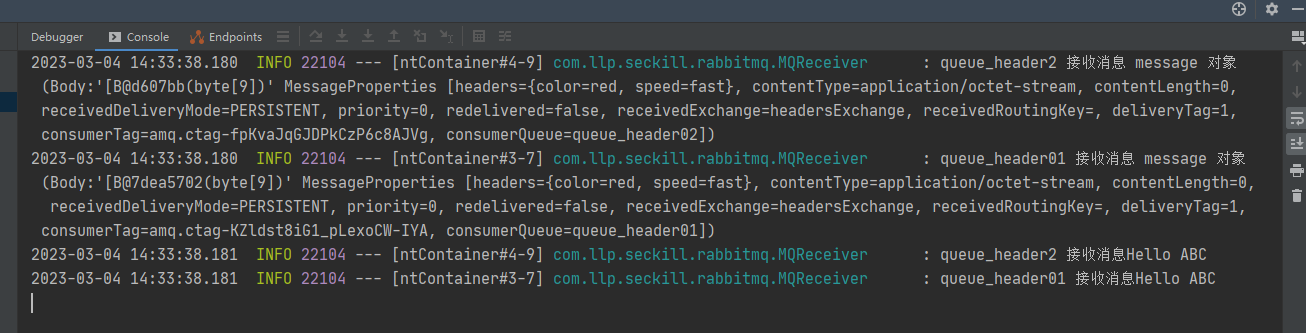
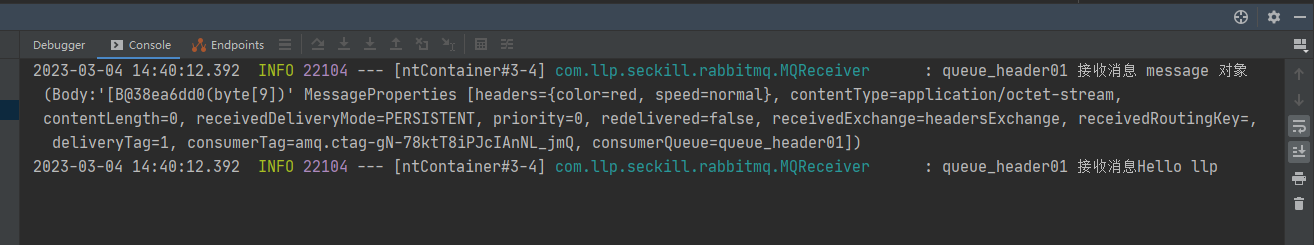
调用header2,header头并不完全匹配,因此只有队列1能够接收到消息
版权归原作者 llp1110 所有, 如有侵权,请联系我们删除。