💕“生命不在于相信奇迹,而在于创造奇迹。”——朱学恒💕
🐼作者:不能再留遗憾了🐼
🎆专栏:MySQL学习🎆
🚗本文章主要内容:MySQL对表操作进阶。数据库约束、表的设计、新增,后续会更新进阶表的查询🚗
文章目录
前言
前面我们已经介绍过初识MySQL以及MySQL对库和对表操作(初阶),那么今天我将为大家分享MySQL对表操作(进阶)。如果大家觉得对你有帮助的话。记得点个赞哦。😊
1.数据库约束
NULL约束
指定某列不能存储NULL值。
在之前我们创建一个表的时候,我们会发现除了我们指定的表名、列名和列名对应的数据类型外,还会额外展现其他的信息,那么这些信息代表什么意思呢?我将会为大家一一介绍。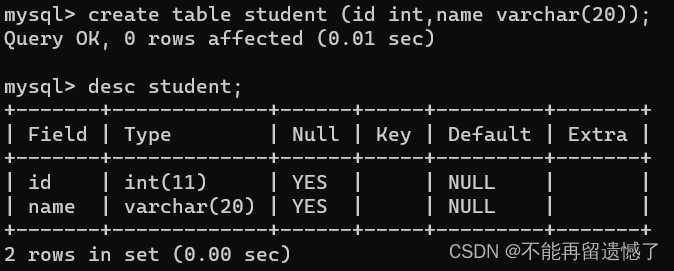
NULL这一列的YES说明,该列内容可以为null,那么如果我们不想让该列出现null该怎么办呢?
NOT NULL 使得指定列的内容不能为null。
createtable 表名 (列名 类型 notnull);
createtable student (id intnotnull,name varchar(20));desc student;insertinto student values(1,'张三');insertinto student values(null,'李四');
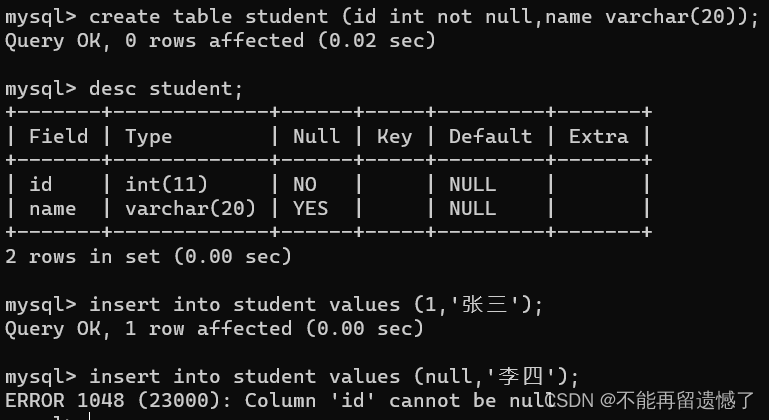
当我们使用 NOT NULL 约束了列之后,如果插入该列的内是null就会报错
UNIQUE:唯一约束
在日常很多情况下,我们会要求数据的唯一性,也就是说不出现重复的数据,而在MySQL中也可以对表操作保证数据的唯一性。
createtable 表名 (列名 类型 unique);
UNIQUE唯一约束会在插入数据之前检测列中的数据是否已经存在,如果存在就不能插入,不存在就允许插入。
createtable student (id intunique,name varchar(20));desc student;insertinto student values(1,'张三');insertinto student values(1,'李四');
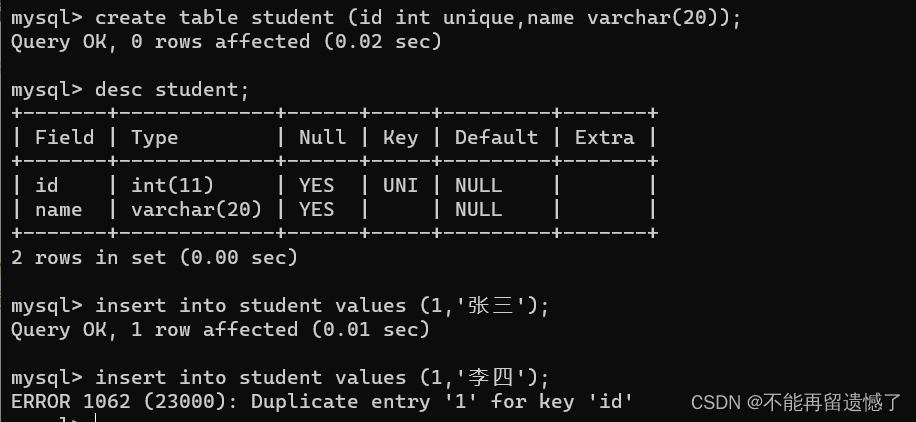
key中的UNI表示该列存在UNIQUE唯一约束,该列不能出现重复数据。
DEFALUT:默认值约束
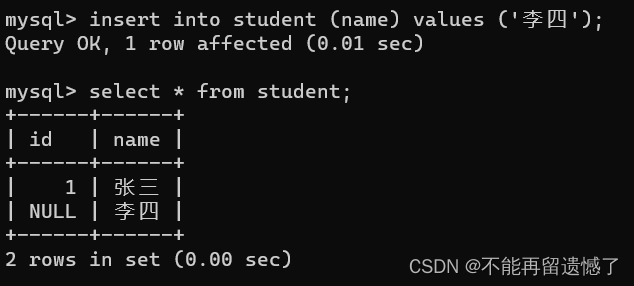
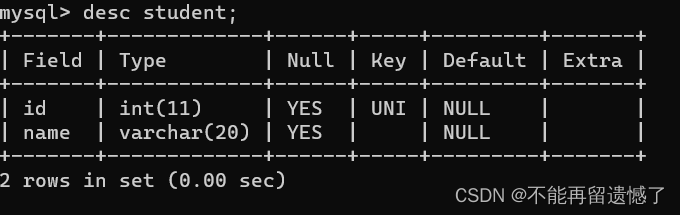
当进行指定列插入的时候,那么那些未插入数据的列的内容将会被默认DEFAULT为null,如果我们不想默认值为null怎么办呢?
createtable 表名 (列名 类型 default 默认值);
DEFAULT设置默认值
createtable student (id int,name varchar(20)default'无名氏');desc student;insertinto student (id)values(1);select*from student;
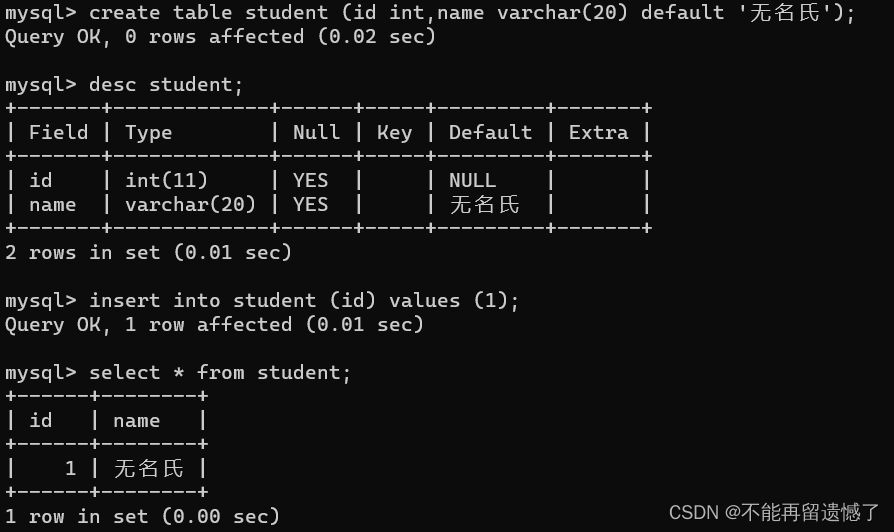
primary key:主键约束
primary key主键约束就类似于我们的身份证和学生证,是每个人所特有的,也就是说primary key是每行的关键数据,它不可为null,也不可重复。 一个表中只能有一个主键
createtable 表名 (列名 类型 primarykey);
createtable student (id intprimarykey,name varchar(20));desc student;insertinto student values(null,'张三');insertinto student values(1,'张三');insertinto student values(1,'李四');
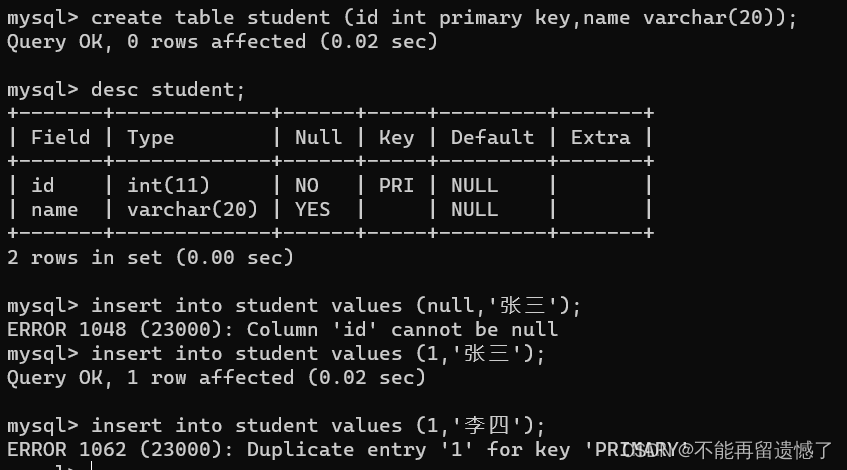
primary key 通常搭配着 auto_increment 使用,表示自增主键。如果我们想要使用自增主键,只需要在插入数据的时候插入的内容是null就行了。
createtable student (id intprimarykeyauto_increment,name varchar(20));desc student;insertinto student values(null,'张三');insertinto student values(null,'李四');select*from student;
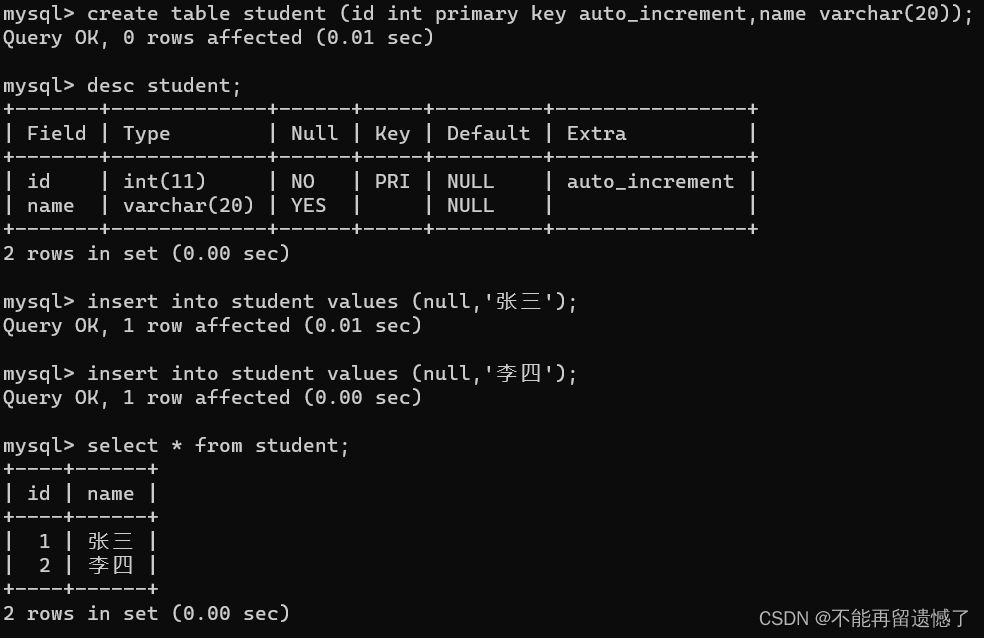
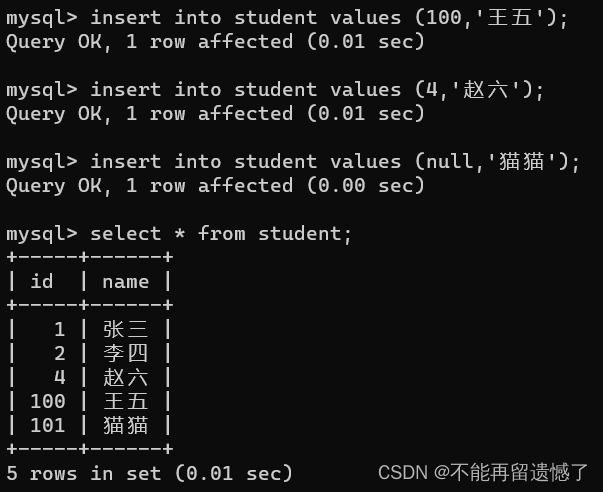
primary key auto_increment 自增的规律是:当前面数据都为null时,从1开始自增,当前面有数据不为null时,从前面数据的最大值开始自增。
insertinto student values(100,'王五');insertinto student values(4,'赵六');insertinto student values(null,'猫猫');
foreign key:外键约束
在学校中,我们都知道每个学生都有对应的班级,同样在MySQL中也可以将这种类似的关系体现出来。
外键用于关联其他表的主键或唯一键
createtable 表名 (列名 类型 foreignkey(列名)references 另一个表名(关联的列名));
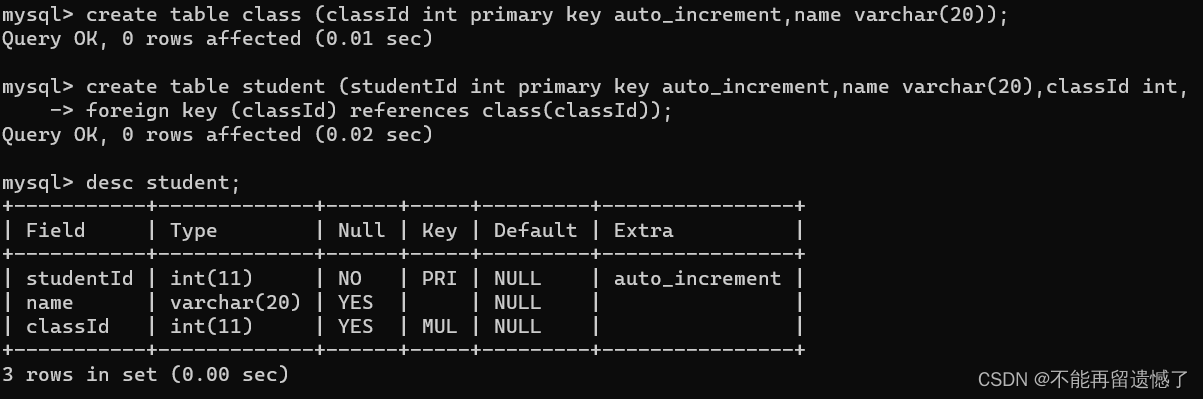
createtable class (classId intprimarykeyauto_increment,name varchar(20));createtable student (studentId intprimarykeyauto_increment,name varchar(20),classId int,foreignkey(classId)references class(classId));desc student;
既然是学生,那么肯定要先有班级然后学生才能进入班级,并且学生不能进入不存在的班级。
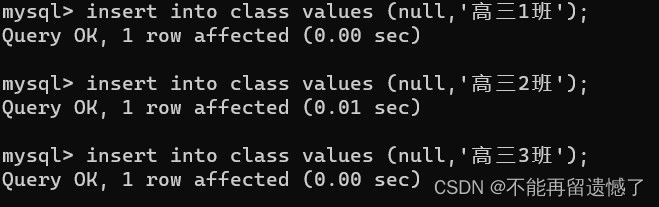
insertinto class (null,'高三1班');insertinto class values(null,'高三2班');insertinto class values(null,'高三3班');insertinto student values(null,'张三',1);insertinto student values(null,'李四',4);
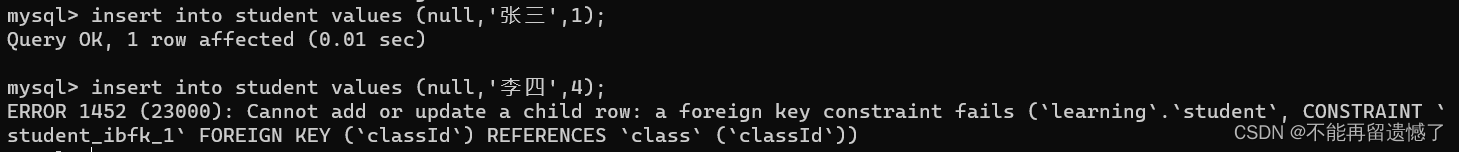
当插入的数据在外键对应的列中不含有时,就会报错。并且在以上的外键关系中,class为父表,student为子表,子表的插入和删除都受到父表的约束,同时父表的删除也受到子表的约束。
update student set classId =5;deletefrom class where classId =1;
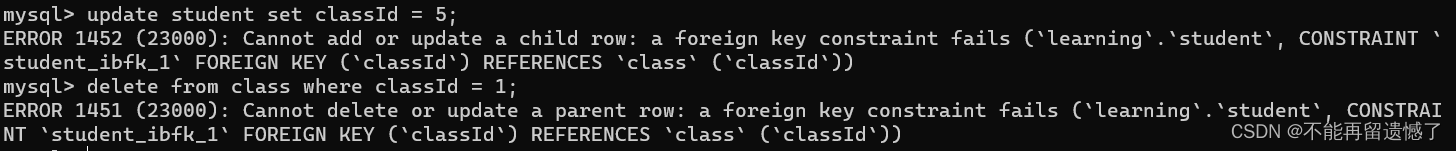
子表的修改,对应的列修改后的数据还是需要在父表中存在。父表删除的时候,如果子表与其有关联,那么就删除不了,只能先删除掉子表的对应行,然后再删除父表。
check约束
check约束在本篇文章就不过多解释了,大家有兴趣的话,可以自己去了解了解哦。
2.表的设计
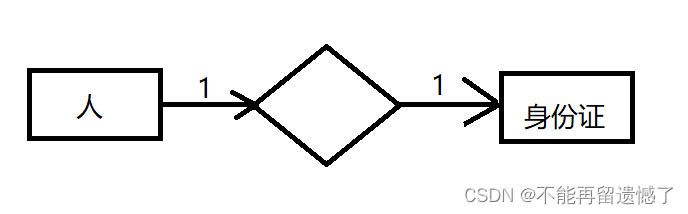
一对一
两者之间是一对一的关系
一对多
一个人可以拥有多个宠物,但是一个宠物不可以有多个主人。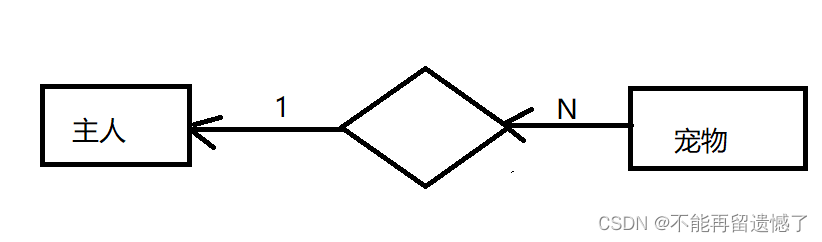
多对多
两者之间除了他们之间有关系外,他们还可以与其他的事物具有其他关系。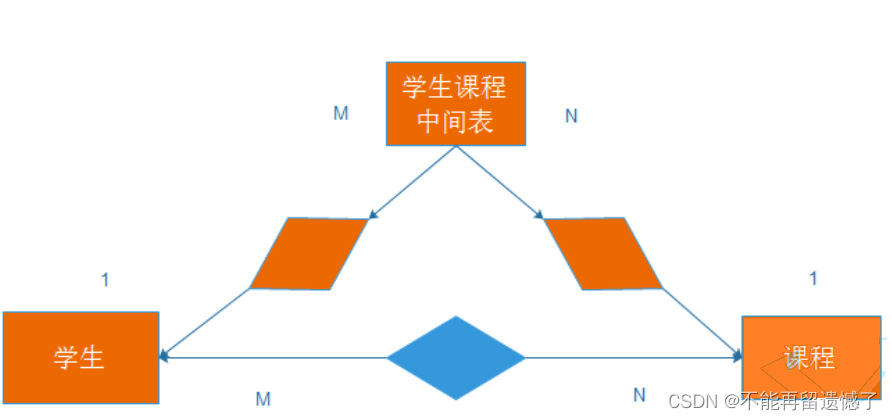
3.新增
如果我们想要从将一个表中的数据复制到另一个类型相同的表当中,我们可以在查询的同时就插入数据,这样就极大地提高了效率。
insertinto 表名 select(列名)from 另一个表名;
需要注意的是,当从一个表中向另一个表中插入数据时,表的结构应该相同或兼容。也就是说,目标表中的所有列都应该存在于源表中,并且具有相似的数据类型和长度,否则插入将会失败。
🙌 整列复制插入
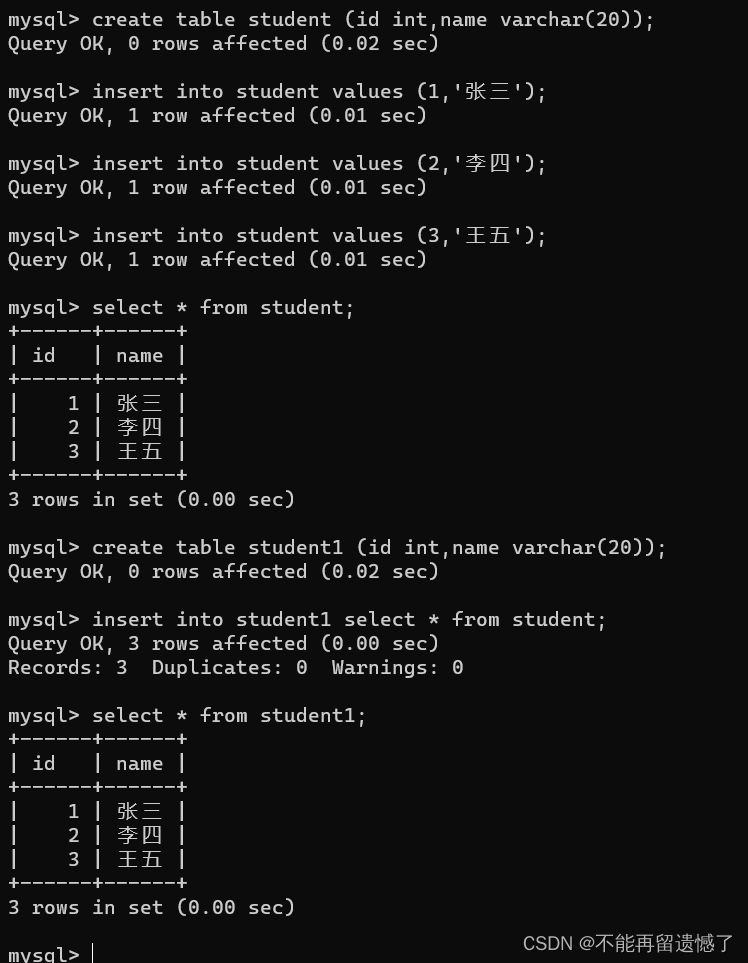
createtable student (id int,name varchar(20));insertinto student values(1,'张三');insertinto student values(2,'李四');insertinto student values(3,'王五');select*from student;createtable student1 (id int,name varchar(20));insertinto student1 select*from student;select*from student1;
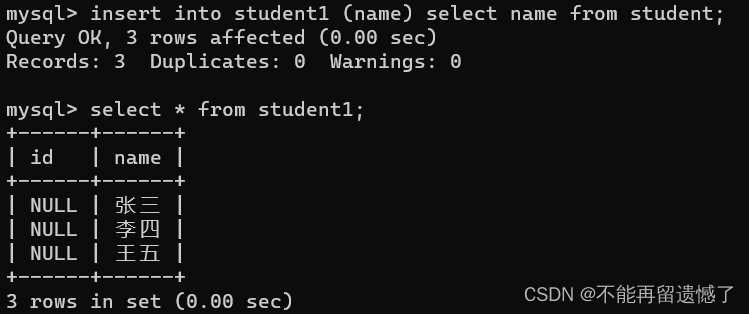
🙌指定列复制插入
insertinto student1 (name)select name from student;select*from student1;
版权归原作者 不能再留遗憾了 所有, 如有侵权,请联系我们删除。
