1. 概述
通过了解springboot加载配置,可以更方便地封装自定义Starter。
在SpringBoot中,可以使用以下6种方式读取 yml、properties配置:
- 使用@Value注解:读取springboot全局配置文件单个配置。
- 使用Environment接口:通过Environment接口动态获取配置。(将yml全部数据封装到Environment对象)
- 使用@ConfigurationProperties注解:在配置类上使用@ConfigurationProperties注解并指定加载配置项的前缀,就可以批量读取配置注入自定义类的成员变量中。(自定义类需要提供setter方法)
- 使用PropertySource注解:加载properties文件配置,然后在字段上使用@Value获取配置。
- 配置PropertySourcesPlaceholderConfigurer的Bean加载自定义yml文件,然后在字段上使用@Value获取配置。
- Java原生方式获取配置。(IO流)
环境准备:
1、创建maven项目(不需要任何archetype模板构建)
2、引入依赖:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?><projectxmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0"xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd"><modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion><groupId>cn.aopmin</groupId><artifactId>springboot-loadconfig</artifactId><version>1.0.0</version><!--父工程--><parent><groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId><artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId><version>2.4.5</version><relativePath/><!-- lookup parent from repository --></parent><properties><maven.compiler.source>8</maven.compiler.source><maven.compiler.target>8</maven.compiler.target><project.build.sourceEncoding>UTF-8</project.build.sourceEncoding></properties><dependencies><!-- SpringBoot配置元数据的注解处理器,可以让自定义配置实现自动补全和校验功能 --><dependency><groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId><artifactId>spring-boot-configuration-processor</artifactId><optional>true</optional></dependency><!-- web起步依赖 --><dependency><groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId><artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId></dependency><!-- junit --><dependency><groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId><artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId><scope>test</scope></dependency><!-- lombok --><dependency><groupId>org.projectlombok</groupId><artifactId>lombok</artifactId></dependency></dependencies><build><plugins><plugin><groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId><artifactId>spring-boot-maven-plugin</artifactId><configuration><excludes><exclude><groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId><artifactId>spring-boot-configuration-processor</artifactId></exclude></excludes></configuration></plugin></plugins></build></project>
3、编写启动类:
packagecn.aopmin;importorg.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;importorg.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;@SpringBootApplicationpublicclassLoadConfigApplication{publicstaticvoidmain(String[] args){SpringApplication.run(LoadConfigApplication.class, args);}}
2. 使用@Value注解读取单个配置
1、编写application.yml文件配置:
student:name: jack
age:20
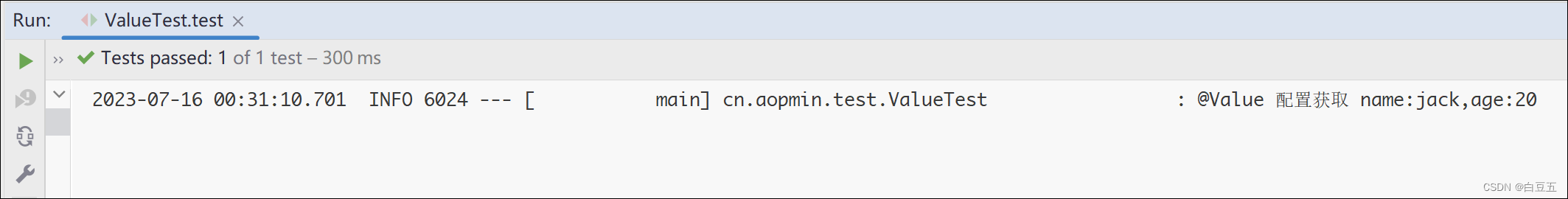
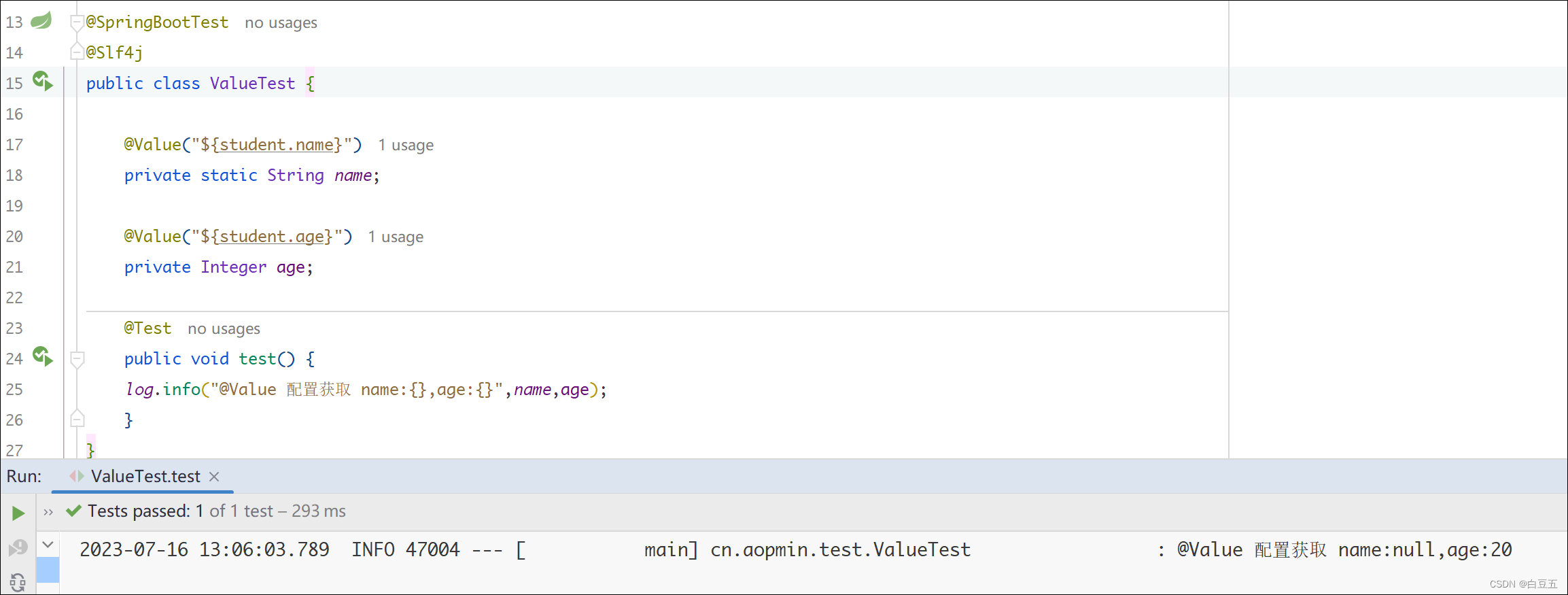
2、使用@Value读取配置:
@SpringBootTest@Slf4jpublicclassValueTest{@Value("${student.name}")privateString name;@Value("${student.age}")privateInteger age;@Testpublicvoidtest(){
log.info("@Value 配置获取 name:{},age:{}",name,age);}}
@Value注意事项:
①
@Value
注解只能读取单个配置进行赋值,无法读取整个配置文件批量赋值。当使用@Value注解读取配置时,确保配置在yml中存在,否则启动程序时就会报错。注解中属性名引用方式如下:
@Value("${一级属性名.二级属性名...}")
② 当使用
@Value
注解引用属性时,可以在属性名称后面使用冒号(:
default-value
)的形式添加默认值。这样,如果在配置文件中找不到对应的属性,就会使用默认值。如果在配置文件中找到了属性,其值将会覆盖默认值。
//可以使用各种类型的默认值,包括字符串、数字、布尔值等@Value("${student.name:aopmin}")privateString name;@Value("${student.age:18}")privateInteger age;
//表示一个空字符串作为默认值@Value("${student.name:}")privateString name;
③
@Value
注解只能用于被Spring管理的Bean中使用,,如使用
@Component
、
@Service
、
@Controller
等注解修饰的类,或者使用Java配置编写的
@Configuration
类中。
④
@Value
注解可以用于字段、构造函数参数、方法参数和方法上。当将它放在方法上时,Spring容器初始化时会调用该方法,并将配置属性的值作为方法的参数传递进去。
@ComponentpublicclassMyBean{privateString myProperty;@AutowiredpublicMyBean(@Value("${my.property}")String myProperty){this.myProperty = myProperty;}@Value("${another.property}")publicvoidsetAnotherProperty(String anotherProperty){// do something with anotherProperty...}@Value("${yet.another.property}")publicvoidprocessValue(String value){// do something with value...}}/*
@Value注解被用于构造函数参数、setter方法和普通方法上。容器初始化时,会将配置属性的值作为参数传递到构造函数、setter方法和普通方法中。
*/
⑤
@Value
注解不能在
static
修饰的字段上使用。因为@Value注解是通过访问Spring容器中的上下文来解析属性值并注入到目标字段中的。由于static字段不属于对象实例,无法通过实例访问容器,所以在静态字段上使用@Value注解是无效的。
3. 使用@ConfigurationProperties注解批量绑定
1、编写application.yml文件配置:
student:name: jack
age:20
2、使用@ConfigurationProperties批量绑定:
packagecn.aopmin.pojo;importlombok.Data;importorg.springframework.boot.context.properties.ConfigurationProperties;importorg.springframework.stereotype.Component;/**
* 参数配置类 (需要提供setter方法)
*
* @author 白豆五
* @version 2023/07/16
* @since JDK8
*/@Component@Data//将这个类与配置文件前缀为student的配置绑定,然后把yml、properties中关于student的配置信息注入到当前类的成员变量中@ConfigurationProperties(prefix ="student")publicclassStudentProperties{privateString name;}
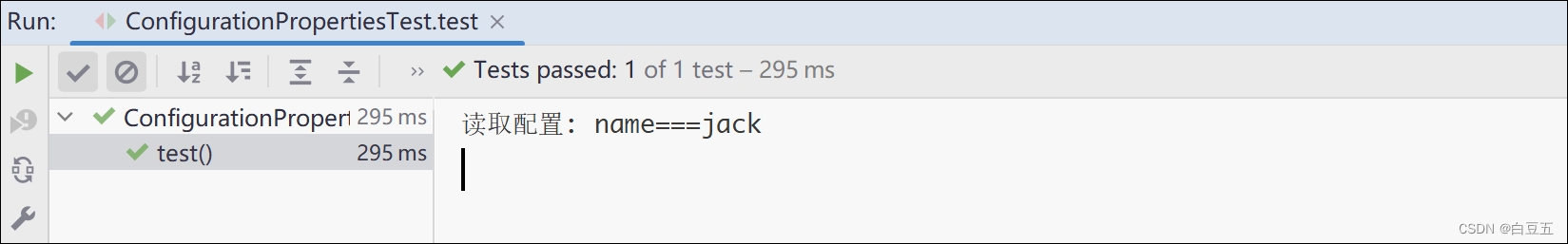
3、测试
@SpringBootTestpublicclassConfigurationPropertiesTest{@AutowiredprivateStudentProperties studentProperties;@Testpublicvoidtest(){System.out.println("读取配置: name==="+studentProperties.getName());}}
@ConfigurationProperties注意事项:
- 确保添加了@EnableConfigurationProperties注解:为了使@ConfigurationProperties生效,需要在主配置类上添加@EnableConfigurationProperties(value=xxxxProperties.class)注解,开启@ConfigurationProperties注解自动装配功能。
- 配置文件中的属性名与类字段名的映射规则:默认情况下,@ConfigurationProperties会将配置文件中的属性名与类字段名进行映射。例如,配置文件中的属性student.name会自动映射到类字段name上。如果配置文件中的属性名与类字段名不一致,可以使用@Value注解或通过setter方法来指定映射关系。
- 类必须是Spring管理的Bean:被@ConfigurationProperties注解标记的类必须是由Spring容器管理的Bean,因此需要确保该类被@Component或其他相关注解标记,以便Spring能够扫描并创建该类的实例。
- 支持类型转换:@ConfigurationProperties支持自动类型转换,将配置文件中的字符串值转换为目标字段的类型。例如,将字符串转换为整数、布尔值等。如果无法进行类型转换,会抛出异常。
- 默认值和可选属性:可以为@ConfigurationProperties注解的字段设置默认值,以防止配置文件中缺少对应的属性。可以使用":“符号指定默认值,例如@Value(”${my.property:default-value}")。另外,可以使用required属性来指定某个属性是否为必需的。
- 配置项的验证和校验:可以使用JSR-303/349规范的注解对@ConfigurationProperties注解的字段进行验证和校验。例如,使用@NotBlank、@Min、@Max等注解来限制属性值的有效性。
4. 使用Environment动态获取配置
1、编写application.yml文件配置:
student:name: jack
age:20
2、使用Environment动态获取配置:(将Environment对象自动装配,然后调用getProperty()方法获取指定属性值)
packagecn.aopmin.test;importlombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;importorg.junit.jupiter.api.Test;importorg.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;importorg.springframework.core.env.Environment;importjavax.annotation.Resource;/**
* Environment是springboot核心的环境配置接口,它提供了一些方法用于访问应用程序配置属性。
* 包括系统属性、操作系统环境变量、命令行参数、以及配置文件中定义的属性等等
*
* @author 白豆五
* @version 2023/07/16
* @since JDK8
*/@Slf4j@SpringBootTestpublicclassEnvironmentTest{@ResourceprivateEnvironment env;@Testpublicvoidtest(){String name = env.getProperty("student.name");// 逻辑处理...(也可以控制某一个bean是否生效)
log.info("Environment配置读取: name:{}", name);}}
除了自动装配方式,也可以从spring容器中获取bean:
@Slf4j@SpringBootTestpublicclassEnvironmentTest2implementsEnvironmentAware{privateEnvironment env;@Testpublicvoidtest(){String name = env.getProperty("student.name");
log.info("Environment配置读取: name:{}", name);}@OverridepublicvoidsetEnvironment(Environment environment){// 逻辑处理...(也可以控制某一个bean是否生效)this.env = environment;}}
Aware是Spring框架提供的一组特殊接口,可以让Bean从Spring容器中拿到一些资源信息。
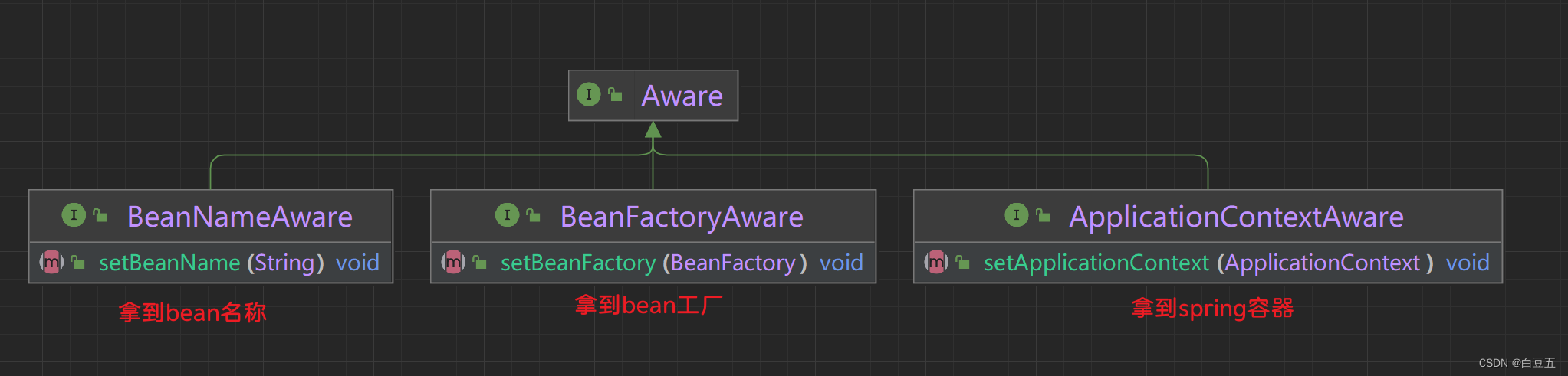
Aware接口是一种回调机制,当Bean被实例化并注册到Spring容器中时,容器会自动调用Bean中实现了特定Aware接口的方法,将相应的资源或信息传递给Bean。
以下是几个常用的Aware接口:
- ApplicationContextAware:通过实现该接口,Bean可以访问ApplicationContext对象,从而获取Spring容器的相关信息。
- BeanFactoryAware:通过实现该接口,Bean可以访问BeanFactory对象,从而获取Bean在容器中的相关信息。
- EnvironmentAware:通过实现该接口,Bean可以访问Environment对象,从而获取环境相关的配置属性,比如系统属性、环境变量等。
- ResourceLoaderAware:通过实现该接口,Bean可以访问ResourceLoader对象,从而获取资源加载器,用于加载类路径下的资源文件。
- MessageSourceAware:通过实现该接口,Bean可以访问MessageSource对象,从而获取国际化消息。
5.使用@PropertySources注解获取外部配置
前3种都是从springboot全局配置文件中获取配置,如果获取外部自定义文件就不可以啦,我们可以通过@PropertySources注解获取==.properties==文件配置。
1、在resources目录下创建student.properties文件:
student.id=1001
student.name=白豆五
2、在配置类中使用@PropertySources注解绑定配置:
packagecn.aopmin.pojo;importlombok.Data;importorg.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value;importorg.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;importorg.springframework.context.annotation.PropertySource;/**
* 绑定自定义properties配置
*
* @author 白豆五
* @version 2023/07/16
* @since JDK8
*/@Data@Configuration@PropertySource(value ="classpath:student.properties", encoding ="UTF-8")publicclassPropertySourcesConf{@Value("${student.id}")privateInteger id;@Value("${student.name}")privateString name;}
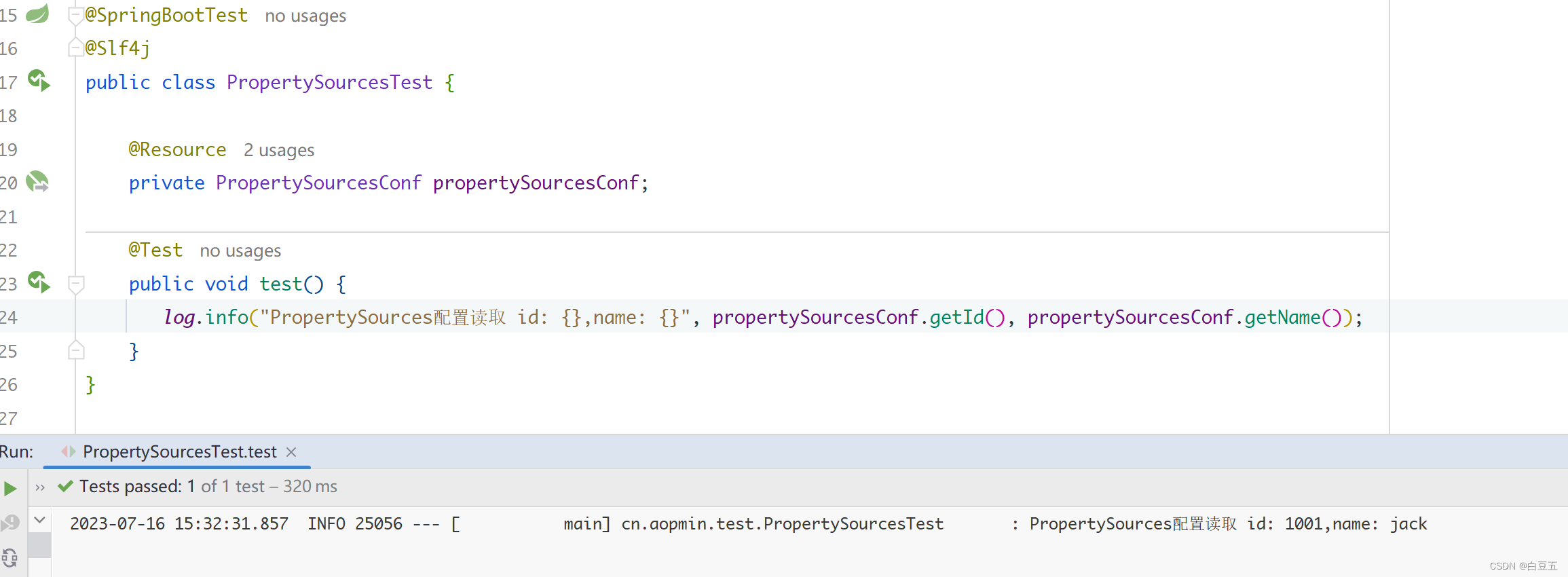
3、测试
@SpringBootTest@Slf4jpublicclassPropertySourcesTest{@ResourceprivatePropertySourcesConf propertySourcesConf;@Testpublicvoidtest(){
log.info("PropertySources配置读取 id: {}", propertySourcesConf.getId());
log.info("name: {}", propertySourcesConf.getName());}}
6. 配置PropertySourcesPlaceholderConfigurer的Bean获取外部配置
1、编写student.yml配置:
file:type: 自定义yaml文件配置
2、 配置PropertySourcesPlaceholderConfigurer获取自定义yml文件配置:
packagecn.aopmin.config;importorg.springframework.beans.factory.config.YamlPropertiesFactoryBean;importorg.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;importorg.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;importorg.springframework.context.support.PropertySourcesPlaceholderConfigurer;importorg.springframework.core.io.ClassPathResource;importjava.util.Objects;/**
* 配置PropertySourcesPlaceholderConfigurer读取yml配置
* @author 白豆五
* @version 2023/07/16
* @since JDK8
*/@ConfigurationpublicclassMyYamlConfig{@BeanpublicstaticPropertySourcesPlaceholderConfigureryamlConfigurer(){PropertySourcesPlaceholderConfigurer configurer =newPropertySourcesPlaceholderConfigurer();YamlPropertiesFactoryBean yaml =newYamlPropertiesFactoryBean();
yaml.setResources(newClassPathResource("student.yml"));//自定义yml文件//Objects.requireNonNull()方法的作用是如果对象为空,则抛出空指针异常,否则返回对象本身。
configurer.setProperties(Objects.requireNonNull(yaml.getObject()));return configurer;}}
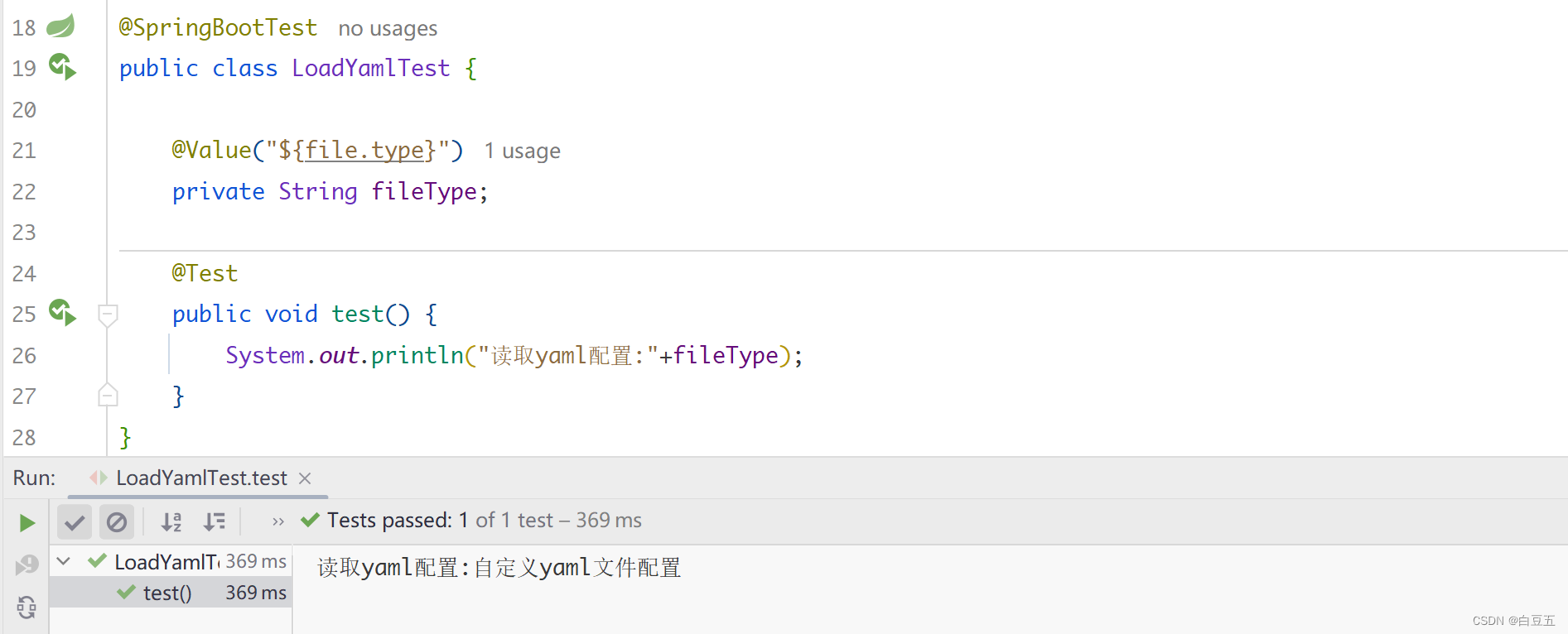
3、测试
@SpringBootTestpublicclassLoadYamlTest{@Value("${file.type}")privateString fileType;@Testpublicvoidtest(){System.out.println("读取yaml配置:"+fileType);}}
7. Java原生方式获取配置
通过IO流读取配置,然后放入propertis配置对象中。
packagecn.aopmin.test;importorg.junit.jupiter.api.Test;importorg.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;importjava.io.IOException;importjava.io.InputStream;importjava.io.InputStreamReader;importjava.nio.charset.StandardCharsets;importjava.util.Properties;/**
* @author 白豆五
* @version 2023/07/16
* @since JDK8
*/@SpringBootTestpublicclassCustomTest{@Testpublicvoidtest(){// 配置对象Properties props =newProperties();InputStreamReader input =null;try{// 输入流 (字节流转字符流)
input =newInputStreamReader(this.getClass().getClassLoader().getResourceAsStream("student.properties"),//通过类加载器来获取指定路径下的资源文件,并返回一个InputStream对象StandardCharsets.UTF_8);//指定编码格式// 加载配置
props.load(input);}catch(IOException e){thrownewRuntimeException(e);}finally{if(input!=null)try{
input.close();}catch(IOException e){
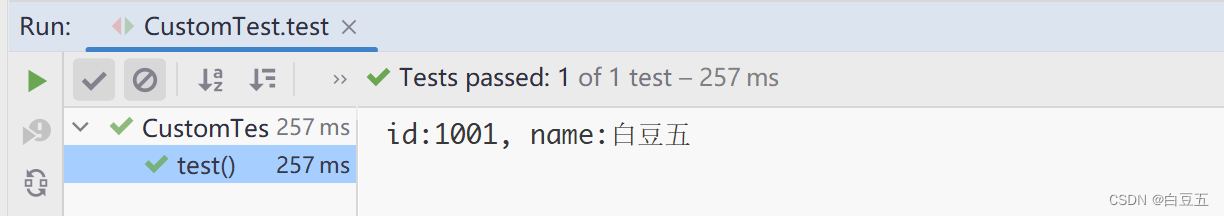
e.printStackTrace();}}// 获取配置System.out.println("id:"+ props.getProperty("student.id")+", name:"+ props.getProperty("student.name"));}}
版权归原作者 白豆五 所有, 如有侵权,请联系我们删除。