上一节我们分析到了Execution的生成,然后调用taskManagerGateway.submitTask方法提交task,提交的时候会将executionVertex封装成TaskDeploymentDescriptor,task的提交与执行涉及到了flink多个组件的配合,之前没有详细讲过,可能有的小伙伴有点不太清楚,这里我们花点时间介绍一下。
1.Flink各个组件介绍
1.JobManager
在JobManager启动的时候会启动三个比较重要的组件:
**1. WebMonitorEndpoint: **里面有大约六七十个handler,如果客户端使用fink run的方式来提交一个job,最终会由WebMonitorEndpoint的submitJobHandler来处理。
**2. Dispatcher: **负责接收用户提交的jobGraph,然后启动Jobmaster。
**3. ResourceManager: **Flink集群的资源管理器,关于slot的管理和申请工作都由他负责。
2.TaskManager
TaskManager:是flink的worker节点,它是负责flink中本机slot资源的管理以及task的执行。TaskManager上基本的资源单位时slot,一个作业的task最终会在TaskManager上的slot上运行,TaskManager负责维护本地的slot资源列表,并和jobMaster进行通信。
2.TaskExecutor#submitTask
上节我们在execution中看到它调用了taskManagerGateway.submitTask方法提交task,taskManagerGateway是一个接口,我们点进它的子类RpcTaskManagerGateway中可以看到它调用了TaskExecutorGateway的submitTask方法。
TaskExecutorGateway也是一个接口,我们可以点进它的子类TaskExecutor,然后我们找到他的submitTask方法
@Override
public CompletableFuture<Acknowledge> submitTask(
TaskDeploymentDescriptor tdd,
JobMasterId jobMasterId,
Time timeout) {
try {
//获取jobid和尝试次数id
final JobID jobId = tdd.getJobId();
final ExecutionAttemptID executionAttemptID = tdd.getExecutionAttemptId();
//获取jobmanager的连接
final JobTable.Connection jobManagerConnection = jobTable.getConnection(jobId).orElseThrow(() -> {
final String message = "Could not submit task because there is no JobManager " +
"associated for the job " + jobId + '.';
log.debug(message);
return new TaskSubmissionException(message);
});
if (!Objects.equals(jobManagerConnection.getJobMasterId(), jobMasterId)) {
final String message = "Rejecting the task submission because the job manager leader id " +
jobMasterId + " does not match the expected job manager leader id " +
jobManagerConnection.getJobMasterId() + '.';
log.debug(message);
throw new TaskSubmissionException(message);
}
if (!taskSlotTable.tryMarkSlotActive(jobId, tdd.getAllocationId())) {
final String message = "No task slot allocated for job ID " + jobId +
" and allocation ID " + tdd.getAllocationId() + '.';
log.debug(message);
throw new TaskSubmissionException(message);
}
// re-integrate offloaded data:
try {
tdd.loadBigData(blobCacheService.getPermanentBlobService());
} catch (IOException | ClassNotFoundException e) {
throw new TaskSubmissionException("Could not re-integrate offloaded TaskDeploymentDescriptor data.", e);
}
// deserialize the pre-serialized information
final JobInformation jobInformation;
final TaskInformation taskInformation;
try {
//反序列化获取task信息和Job信息
jobInformation = tdd.getSerializedJobInformation().deserializeValue(getClass().getClassLoader());
taskInformation = tdd.getSerializedTaskInformation().deserializeValue(getClass().getClassLoader());
} catch (IOException | ClassNotFoundException e) {
throw new TaskSubmissionException("Could not deserialize the job or task information.", e);
}
if (!jobId.equals(jobInformation.getJobId())) {
throw new TaskSubmissionException(
"Inconsistent job ID information inside TaskDeploymentDescriptor (" +
tdd.getJobId() + " vs. " + jobInformation.getJobId() + ")");
}
//将task相关信息加入到taskMetricGroup
TaskMetricGroup taskMetricGroup = taskManagerMetricGroup.addTaskForJob(
jobInformation.getJobId(),
jobInformation.getJobName(),
taskInformation.getJobVertexId(),
tdd.getExecutionAttemptId(),
taskInformation.getTaskName(),
tdd.getSubtaskIndex(),
tdd.getAttemptNumber());
InputSplitProvider inputSplitProvider = new RpcInputSplitProvider(
jobManagerConnection.getJobManagerGateway(),
taskInformation.getJobVertexId(),
tdd.getExecutionAttemptId(),
taskManagerConfiguration.getTimeout());
final TaskOperatorEventGateway taskOperatorEventGateway = new RpcTaskOperatorEventGateway(
jobManagerConnection.getJobManagerGateway(),
executionAttemptID,
(t) -> runAsync(() -> failTask(executionAttemptID, t)));
TaskManagerActions taskManagerActions = jobManagerConnection.getTaskManagerActions();
CheckpointResponder checkpointResponder = jobManagerConnection.getCheckpointResponder();
GlobalAggregateManager aggregateManager = jobManagerConnection.getGlobalAggregateManager();
LibraryCacheManager.ClassLoaderHandle classLoaderHandle = jobManagerConnection.getClassLoaderHandle();
ResultPartitionConsumableNotifier resultPartitionConsumableNotifier = jobManagerConnection.getResultPartitionConsumableNotifier();
PartitionProducerStateChecker partitionStateChecker = jobManagerConnection.getPartitionStateChecker();
//本地状态存储
final TaskLocalStateStore localStateStore = localStateStoresManager.localStateStoreForSubtask(
jobId,
tdd.getAllocationId(),
taskInformation.getJobVertexId(),
tdd.getSubtaskIndex());
final JobManagerTaskRestore taskRestore = tdd.getTaskRestore();
final TaskStateManager taskStateManager = new TaskStateManagerImpl(
jobId,
tdd.getExecutionAttemptId(),
localStateStore,
taskRestore,
checkpointResponder);
MemoryManager memoryManager;
try {
memoryManager = taskSlotTable.getTaskMemoryManager(tdd.getAllocationId());
} catch (SlotNotFoundException e) {
throw new TaskSubmissionException("Could not submit task.", e);
}
//在实例化方法中构造InputGate和ResultPartition
Task task = new Task(
jobInformation,
taskInformation,
tdd.getExecutionAttemptId(),
tdd.getAllocationId(),
tdd.getSubtaskIndex(),
tdd.getAttemptNumber(),
tdd.getProducedPartitions(),
tdd.getInputGates(),
tdd.getTargetSlotNumber(),
memoryManager,
taskExecutorServices.getIOManager(),
taskExecutorServices.getShuffleEnvironment(),
taskExecutorServices.getKvStateService(),
taskExecutorServices.getBroadcastVariableManager(),
taskExecutorServices.getTaskEventDispatcher(),
externalResourceInfoProvider,
taskStateManager,
taskManagerActions,
inputSplitProvider,
checkpointResponder,
taskOperatorEventGateway,
aggregateManager,
classLoaderHandle,
fileCache,
taskManagerConfiguration,
taskMetricGroup,
resultPartitionConsumableNotifier,
partitionStateChecker,
getRpcService().getExecutor());
taskMetricGroup.gauge(MetricNames.IS_BACKPRESSURED, task::isBackPressured);
log.info("Received task {} ({}), deploy into slot with allocation id {}.",
task.getTaskInfo().getTaskNameWithSubtasks(), tdd.getExecutionAttemptId(), tdd.getAllocationId());
boolean taskAdded;
try {
taskAdded = taskSlotTable.addTask(task);
} catch (SlotNotFoundException | SlotNotActiveException e) {
throw new TaskSubmissionException("Could not submit task.", e);
}
if (taskAdded) {
task.startTaskThread();
setupResultPartitionBookkeeping(
tdd.getJobId(),
tdd.getProducedPartitions(),
task.getTerminationFuture());
return CompletableFuture.completedFuture(Acknowledge.get());
} else {
final String message = "TaskManager already contains a task for id " +
task.getExecutionId() + '.';
log.debug(message);
throw new TaskSubmissionException(message);
}
} catch (TaskSubmissionException e) {
return FutureUtils.completedExceptionally(e);
}
}
这个方法体很长,里面做了很多工作,但其中最重要的有两部分:
1.Task的实例化,在task实例化的过程中创建了InputGate和ResultPartition
2.Task线程的启动,task线程启动后,会将inputGate和ResultPartition拉起来,使用inputGate接入数据,buffer pool用来缓存数据
3.Task的实例化
这个是task的构造方法,里面有很多东西,我们也不需要全都看懂,我们只要看对我们来说比较重要的就好了
public Task(
JobInformation jobInformation,
TaskInformation taskInformation,
ExecutionAttemptID executionAttemptID,
AllocationID slotAllocationId,
int subtaskIndex,
int attemptNumber,
List<ResultPartitionDeploymentDescriptor> resultPartitionDeploymentDescriptors,
List<InputGateDeploymentDescriptor> inputGateDeploymentDescriptors,
int targetSlotNumber,
MemoryManager memManager,
IOManager ioManager,
ShuffleEnvironment<?, ?> shuffleEnvironment,
KvStateService kvStateService,
BroadcastVariableManager bcVarManager,
TaskEventDispatcher taskEventDispatcher,
ExternalResourceInfoProvider externalResourceInfoProvider,
TaskStateManager taskStateManager,
TaskManagerActions taskManagerActions,
InputSplitProvider inputSplitProvider,
CheckpointResponder checkpointResponder,
TaskOperatorEventGateway operatorCoordinatorEventGateway,
GlobalAggregateManager aggregateManager,
LibraryCacheManager.ClassLoaderHandle classLoaderHandle,
FileCache fileCache,
TaskManagerRuntimeInfo taskManagerConfig,
@Nonnull TaskMetricGroup metricGroup,
ResultPartitionConsumableNotifier resultPartitionConsumableNotifier,
PartitionProducerStateChecker partitionProducerStateChecker,
Executor executor) {
Preconditions.checkNotNull(jobInformation);
Preconditions.checkNotNull(taskInformation);
Preconditions.checkArgument(0 <= subtaskIndex, "The subtask index must be positive.");
Preconditions.checkArgument(0 <= attemptNumber, "The attempt number must be positive.");
Preconditions.checkArgument(0 <= targetSlotNumber, "The target slot number must be positive.");
this.taskInfo = new TaskInfo(
taskInformation.getTaskName(),
taskInformation.getMaxNumberOfSubtasks(),
subtaskIndex,
taskInformation.getNumberOfSubtasks(),
attemptNumber,
String.valueOf(slotAllocationId));
this.jobId = jobInformation.getJobId();
this.vertexId = taskInformation.getJobVertexId();
this.executionId = Preconditions.checkNotNull(executionAttemptID);
this.allocationId = Preconditions.checkNotNull(slotAllocationId);
this.taskNameWithSubtask = taskInfo.getTaskNameWithSubtasks();
this.jobConfiguration = jobInformation.getJobConfiguration();
this.taskConfiguration = taskInformation.getTaskConfiguration();
this.requiredJarFiles = jobInformation.getRequiredJarFileBlobKeys();
this.requiredClasspaths = jobInformation.getRequiredClasspathURLs();
this.nameOfInvokableClass = taskInformation.getInvokableClassName();
this.serializedExecutionConfig = jobInformation.getSerializedExecutionConfig();
Configuration tmConfig = taskManagerConfig.getConfiguration();
this.taskCancellationInterval = tmConfig.getLong(TaskManagerOptions.TASK_CANCELLATION_INTERVAL);
this.taskCancellationTimeout = tmConfig.getLong(TaskManagerOptions.TASK_CANCELLATION_TIMEOUT);
this.memoryManager = Preconditions.checkNotNull(memManager);
this.ioManager = Preconditions.checkNotNull(ioManager);
this.broadcastVariableManager = Preconditions.checkNotNull(bcVarManager);
this.taskEventDispatcher = Preconditions.checkNotNull(taskEventDispatcher);
this.taskStateManager = Preconditions.checkNotNull(taskStateManager);
this.accumulatorRegistry = new AccumulatorRegistry(jobId, executionId);
this.inputSplitProvider = Preconditions.checkNotNull(inputSplitProvider);
this.checkpointResponder = Preconditions.checkNotNull(checkpointResponder);
this.operatorCoordinatorEventGateway = Preconditions.checkNotNull(operatorCoordinatorEventGateway);
this.aggregateManager = Preconditions.checkNotNull(aggregateManager);
this.taskManagerActions = checkNotNull(taskManagerActions);
this.externalResourceInfoProvider = checkNotNull(externalResourceInfoProvider);
this.classLoaderHandle = Preconditions.checkNotNull(classLoaderHandle);
this.fileCache = Preconditions.checkNotNull(fileCache);
this.kvStateService = Preconditions.checkNotNull(kvStateService);
this.taskManagerConfig = Preconditions.checkNotNull(taskManagerConfig);
this.metrics = metricGroup;
this.partitionProducerStateChecker = Preconditions.checkNotNull(partitionProducerStateChecker);
this.executor = Preconditions.checkNotNull(executor);
// create the reader and writer structures
final String taskNameWithSubtaskAndId = taskNameWithSubtask + " (" + executionId + ')';
final ShuffleIOOwnerContext taskShuffleContext = shuffleEnvironment
.createShuffleIOOwnerContext(taskNameWithSubtaskAndId, executionId, metrics.getIOMetricGroup());
// produced intermediate result partitions
//创建ResultPartitionWriter
final ResultPartitionWriter[] resultPartitionWriters = shuffleEnvironment.createResultPartitionWriters(
taskShuffleContext,
resultPartitionDeploymentDescriptors).toArray(new ResultPartitionWriter[] {});
this.consumableNotifyingPartitionWriters = ConsumableNotifyingResultPartitionWriterDecorator.decorate(
resultPartitionDeploymentDescriptors,
resultPartitionWriters,
this,
jobId,
resultPartitionConsumableNotifier);
// consumed intermediate result partitions
//创建inputGate
final IndexedInputGate[] gates = shuffleEnvironment.createInputGates(
taskShuffleContext,
this,
inputGateDeploymentDescriptors)
.toArray(new IndexedInputGate[0]);
this.inputGates = new IndexedInputGate[gates.length];
int counter = 0;
for (IndexedInputGate gate : gates) {
inputGates[counter++] = new InputGateWithMetrics(gate, metrics.getIOMetricGroup().getNumBytesInCounter());
}
if (shuffleEnvironment instanceof NettyShuffleEnvironment) {
//noinspection deprecation
((NettyShuffleEnvironment) shuffleEnvironment)
.registerLegacyNetworkMetrics(metrics.getIOMetricGroup(), resultPartitionWriters, gates);
}
invokableHasBeenCanceled = new AtomicBoolean(false);
// finally, create the executing thread, but do not start it
executingThread = new Thread(TASK_THREADS_GROUP, this, taskNameWithSubtask);
}
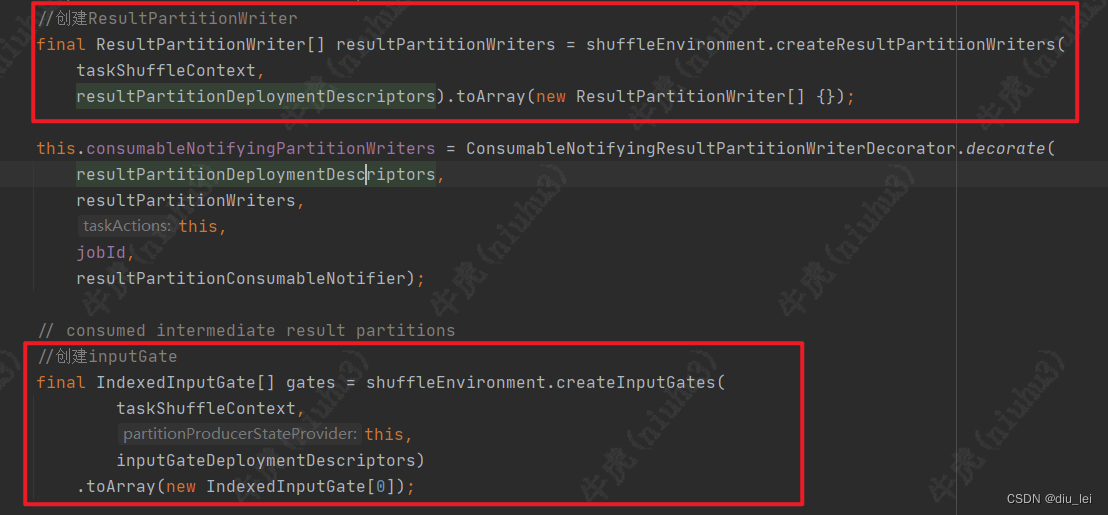
这个方法体里面有3个部分比较重要:
1.ResultPartitionWriter和InputGate的创建
2.创建一个执行线程,后面启动的task线程就是这个

4.Task线程的启动
task线程启动后会去调用自己的run方法,我们再run方法中可以看到run方法又调用了doRun方法
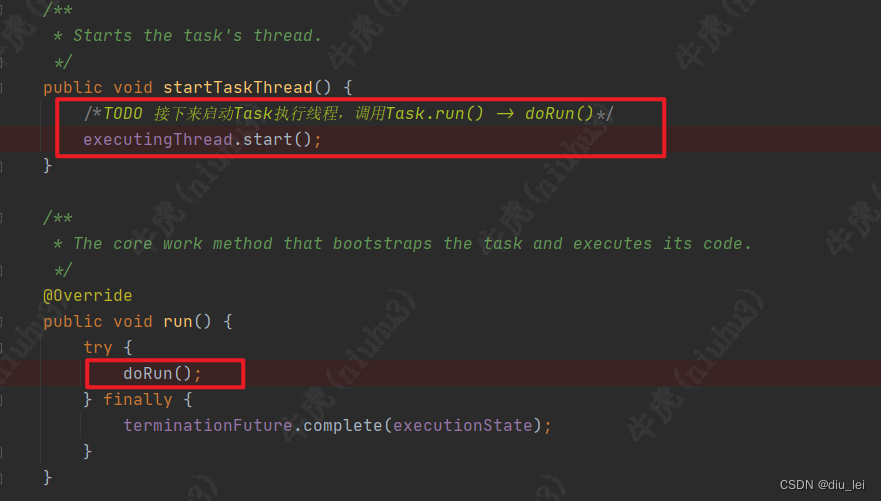
doRun方法的方法体也是很长,我们还是只找重点,前面无非就是变更状态
private void doRun() {
// ----------------------------
// Initial State transition
// ----------------------------
while (true) {
ExecutionState current = this.executionState;
if (current == ExecutionState.CREATED) {
if (transitionState(ExecutionState.CREATED, ExecutionState.DEPLOYING)) {
// success, we can start our work
break;
}
}
else if (current == ExecutionState.FAILED) {
// we were immediately failed. tell the TaskManager that we reached our final state
notifyFinalState();
if (metrics != null) {
metrics.close();
}
return;
}
else if (current == ExecutionState.CANCELING) {
if (transitionState(ExecutionState.CANCELING, ExecutionState.CANCELED)) {
// we were immediately canceled. tell the TaskManager that we reached our final state
notifyFinalState();
if (metrics != null) {
metrics.close();
}
return;
}
}
else {
if (metrics != null) {
metrics.close();
}
throw new IllegalStateException("Invalid state for beginning of operation of task " + this + '.');
}
}
// all resource acquisitions and registrations from here on
// need to be undone in the end
Map<String, Future<Path>> distributedCacheEntries = new HashMap<>();
AbstractInvokable invokable = null;
try {
// ----------------------------
// Task Bootstrap - We periodically
// check for canceling as a shortcut
// ----------------------------
// activate safety net for task thread
LOG.debug("Creating FileSystem stream leak safety net for task {}", this);
FileSystemSafetyNet.initializeSafetyNetForThread();
// first of all, get a user-code classloader
// this may involve downloading the job's JAR files and/or classes
LOG.info("Loading JAR files for task {}.", this);
userCodeClassLoader = createUserCodeClassloader();
final ExecutionConfig executionConfig = serializedExecutionConfig.deserializeValue(userCodeClassLoader.asClassLoader());
if (executionConfig.getTaskCancellationInterval() >= 0) {
// override task cancellation interval from Flink config if set in ExecutionConfig
taskCancellationInterval = executionConfig.getTaskCancellationInterval();
}
if (executionConfig.getTaskCancellationTimeout() >= 0) {
// override task cancellation timeout from Flink config if set in ExecutionConfig
taskCancellationTimeout = executionConfig.getTaskCancellationTimeout();
}
if (isCanceledOrFailed()) {
throw new CancelTaskException();
}
// ----------------------------------------------------------------
// register the task with the network stack
// this operation may fail if the system does not have enough
// memory to run the necessary data exchanges
// the registration must also strictly be undone
// ----------------------------------------------------------------
LOG.info("Registering task at network: {}.", this);
//设置resultPartition和inputGate
setupPartitionsAndGates(consumableNotifyingPartitionWriters, inputGates);
for (ResultPartitionWriter partitionWriter : consumableNotifyingPartitionWriters) {
taskEventDispatcher.registerPartition(partitionWriter.getPartitionId());
}
// next, kick off the background copying of files for the distributed cache
try {
for (Map.Entry<String, DistributedCache.DistributedCacheEntry> entry :
DistributedCache.readFileInfoFromConfig(jobConfiguration)) {
LOG.info("Obtaining local cache file for '{}'.", entry.getKey());
Future<Path> cp = fileCache.createTmpFile(entry.getKey(), entry.getValue(), jobId, executionId);
distributedCacheEntries.put(entry.getKey(), cp);
}
}
catch (Exception e) {
throw new Exception(
String.format("Exception while adding files to distributed cache of task %s (%s).", taskNameWithSubtask, executionId), e);
}
if (isCanceledOrFailed()) {
throw new CancelTaskException();
}
// ----------------------------------------------------------------
// call the user code initialization methods
// ----------------------------------------------------------------
TaskKvStateRegistry kvStateRegistry = kvStateService.createKvStateTaskRegistry(jobId, getJobVertexId());
Environment env = new RuntimeEnvironment(
jobId,
vertexId,
executionId,
executionConfig,
taskInfo,
jobConfiguration,
taskConfiguration,
userCodeClassLoader,
memoryManager,
ioManager,
broadcastVariableManager,
taskStateManager,
aggregateManager,
accumulatorRegistry,
kvStateRegistry,
inputSplitProvider,
distributedCacheEntries,
consumableNotifyingPartitionWriters,
inputGates,
taskEventDispatcher,
checkpointResponder,
operatorCoordinatorEventGateway,
taskManagerConfig,
metrics,
this,
externalResourceInfoProvider);
// Make sure the user code classloader is accessible thread-locally.
// We are setting the correct context class loader before instantiating the invokable
// so that it is available to the invokable during its entire lifetime.
executingThread.setContextClassLoader(userCodeClassLoader.asClassLoader());
// now load and instantiate the task's invokable code
/*TODO 加载和实例化task的可执行代码*/
invokable = loadAndInstantiateInvokable(userCodeClassLoader.asClassLoader(), nameOfInvokableClass, env);
// ----------------------------------------------------------------
// actual task core work
// ----------------------------------------------------------------
// we must make strictly sure that the invokable is accessible to the cancel() call
// by the time we switched to running.
this.invokable = invokable;
// switch to the RUNNING state, if that fails, we have been canceled/failed in the meantime
if (!transitionState(ExecutionState.DEPLOYING, ExecutionState.RUNNING)) {
throw new CancelTaskException();
}
// notify everyone that we switched to running
taskManagerActions.updateTaskExecutionState(new TaskExecutionState(jobId, executionId, ExecutionState.RUNNING));
// make sure the user code classloader is accessible thread-locally
executingThread.setContextClassLoader(userCodeClassLoader.asClassLoader());
// run the invokable
/*TODO 执行代码( invokable即为operator对象实例,比如 StreamTask里)*/
invokable.invoke();
// make sure, we enter the catch block if the task leaves the invoke() method due
// to the fact that it has been canceled
if (isCanceledOrFailed()) {
throw new CancelTaskException();
}
// ----------------------------------------------------------------
// finalization of a successful execution
// ----------------------------------------------------------------
// finish the produced partitions. if this fails, we consider the execution failed.
for (ResultPartitionWriter partitionWriter : consumableNotifyingPartitionWriters) {
if (partitionWriter != null) {
partitionWriter.finish();
}
}
// try to mark the task as finished
// if that fails, the task was canceled/failed in the meantime
if (!transitionState(ExecutionState.RUNNING, ExecutionState.FINISHED)) {
throw new CancelTaskException();
}
}
catch (Throwable t) {
// unwrap wrapped exceptions to make stack traces more compact
if (t instanceof WrappingRuntimeException) {
t = ((WrappingRuntimeException) t).unwrap();
}
// ----------------------------------------------------------------
// the execution failed. either the invokable code properly failed, or
// an exception was thrown as a side effect of cancelling
// ----------------------------------------------------------------
TaskManagerExceptionUtils.tryEnrichTaskManagerError(t);
try {
// check if the exception is unrecoverable
if (ExceptionUtils.isJvmFatalError(t) ||
(t instanceof OutOfMemoryError && taskManagerConfig.shouldExitJvmOnOutOfMemoryError())) {
// terminate the JVM immediately
// don't attempt a clean shutdown, because we cannot expect the clean shutdown to complete
try {
LOG.error("Encountered fatal error {} - terminating the JVM", t.getClass().getName(), t);
} finally {
Runtime.getRuntime().halt(-1);
}
}
// transition into our final state. we should be either in DEPLOYING, RUNNING, CANCELING, or FAILED
// loop for multiple retries during concurrent state changes via calls to cancel() or
// to failExternally()
while (true) {
ExecutionState current = this.executionState;
if (current == ExecutionState.RUNNING || current == ExecutionState.DEPLOYING) {
if (t instanceof CancelTaskException) {
if (transitionState(current, ExecutionState.CANCELED)) {
cancelInvokable(invokable);
break;
}
}
else {
if (transitionState(current, ExecutionState.FAILED, t)) {
// proper failure of the task. record the exception as the root cause
failureCause = t;
cancelInvokable(invokable);
break;
}
}
}
else if (current == ExecutionState.CANCELING) {
if (transitionState(current, ExecutionState.CANCELED)) {
break;
}
}
else if (current == ExecutionState.FAILED) {
// in state failed already, no transition necessary any more
break;
}
// unexpected state, go to failed
else if (transitionState(current, ExecutionState.FAILED, t)) {
LOG.error("Unexpected state in task {} ({}) during an exception: {}.", taskNameWithSubtask, executionId, current);
break;
}
// else fall through the loop and
}
}
catch (Throwable tt) {
String message = String.format("FATAL - exception in exception handler of task %s (%s).", taskNameWithSubtask, executionId);
LOG.error(message, tt);
notifyFatalError(message, tt);
}
}
finally {
try {
LOG.info("Freeing task resources for {} ({}).", taskNameWithSubtask, executionId);
// clear the reference to the invokable. this helps guard against holding references
// to the invokable and its structures in cases where this Task object is still referenced
this.invokable = null;
// free the network resources
releaseResources();
// free memory resources
if (invokable != null) {
memoryManager.releaseAll(invokable);
}
// remove all of the tasks resources
fileCache.releaseJob(jobId, executionId);
// close and de-activate safety net for task thread
LOG.debug("Ensuring all FileSystem streams are closed for task {}", this);
FileSystemSafetyNet.closeSafetyNetAndGuardedResourcesForThread();
notifyFinalState();
}
catch (Throwable t) {
// an error in the resource cleanup is fatal
String message = String.format("FATAL - exception in resource cleanup of task %s (%s).", taskNameWithSubtask, executionId);
LOG.error(message, t);
notifyFatalError(message, t);
}
// un-register the metrics at the end so that the task may already be
// counted as finished when this happens
// errors here will only be logged
try {
metrics.close();
}
catch (Throwable t) {
LOG.error("Error during metrics de-registration of task {} ({}).", taskNameWithSubtask, executionId, t);
}
}
}
638行有一句代码比较重要,就是拉起我们之前创建的InputGate和ResultPartition
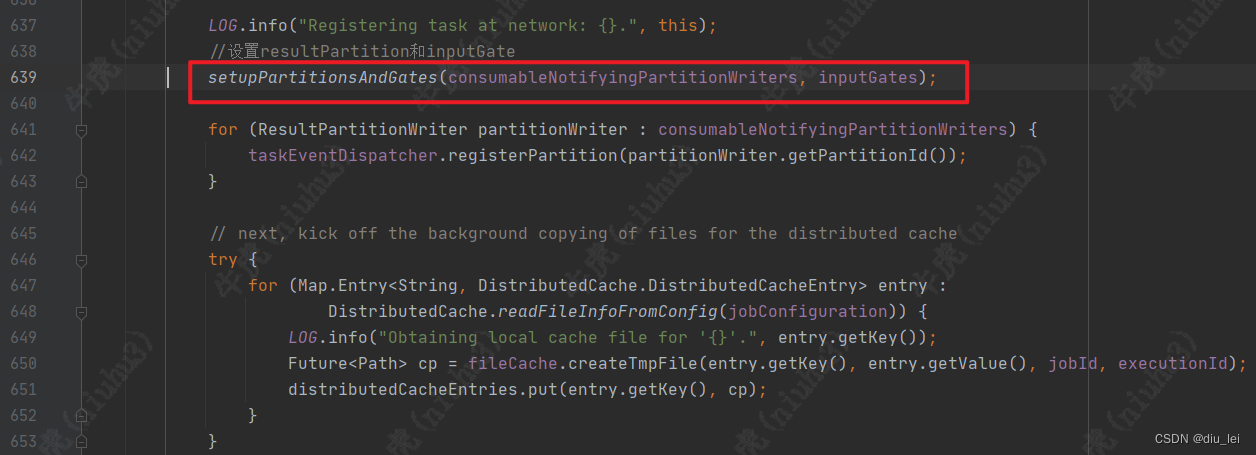
这些准备工作做好之后,就是开始加载和实例化task的可执行代码
上面代码调用了loadAndInstantiateInvokable方法,在这个方法中利用反射获取他的构造方法并创建实例,到这里可能有的兄弟就有点晕了,不知道接下来该往哪里跳了
private static AbstractInvokable loadAndInstantiateInvokable(
ClassLoader classLoader,
String className,
Environment environment) throws Throwable {
final Class<? extends AbstractInvokable> invokableClass;
try {
//反射获取主类
invokableClass = Class.forName(className, true, classLoader)
.asSubclass(AbstractInvokable.class);
} catch (Throwable t) {
throw new Exception("Could not load the task's invokable class.", t);
}
Constructor<? extends AbstractInvokable> statelessCtor;
try {
//获取该反射类的构造方法
statelessCtor = invokableClass.getConstructor(Environment.class);
} catch (NoSuchMethodException ee) {
throw new FlinkException("Task misses proper constructor", ee);
}
// instantiate the class
try {
//noinspection ConstantConditions --> cannot happen
//实例化构造方法
return statelessCtor.newInstance(environment);
} catch (InvocationTargetException e) {
// directly forward exceptions from the eager initialization
throw e.getTargetException();
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new FlinkException("Could not instantiate the task's invokable class.", e);
}
}
其实在构建StreamGraph的时候就指定了invokableClass ,在生成 StreamNode 的时候,会通过
OpearatorFactory 执行判断,如果该 StreamOperator 是 StreamSource 的话,就会指定该
StreamTask 的 invokableClass 为 SourceStreamTask, 否则为 (OneInputStreamTask,
TwoInputStreamTask, StreamTask)。核心代码是:
StreamGraph.addOperator(....){
invokableClass = operatorFactory.isStreamSource() ? SourceStreamTask.class :
OneInputStreamTask.class;
}
后面我们就可以根据具体的task类型点进对应的构造方法中去看对应的实际逻辑。
版权归原作者 diu_lei 所有, 如有侵权,请联系我们删除。