重点表示
登录用户数据,用户信息的获取,以及Srping Security为什么把用户信息放到SecurityContextHolder中的,又是如何做的。
多线程下,在Spring Security是如何获取到用户信息的?
匿名访问!
用户数据
获取登录成功后的数据,
用户数据存在Authenticatiion,这里就是我在配置中的Authentication。
存在threadLocal中,是线程级别。
Authentication authentication =SecurityContextHolder.getContext().getAuthentication();
点进去看一下:SecurityContextHolder,简单解释一下,根据源码逻辑,不指定strategyName的情况下,就是空的,默认给一个MODE_THREADLOCAL。
privatestaticvoidinitializeStrategy(){if("MODE_PRE_INITIALIZED".equals(strategyName)){Assert.state(strategy !=null,"When using MODE_PRE_INITIALIZED, setContextHolderStrategy must be called with the fully constructed strategy");}else{if(!StringUtils.hasText(strategyName)){
strategyName ="MODE_THREADLOCAL";}if(strategyName.equals("MODE_THREADLOCAL")){
strategy =newThreadLocalSecurityContextHolderStrategy();}elseif(strategyName.equals("MODE_INHERITABLETHREADLOCAL")){
strategy =newInheritableThreadLocalSecurityContextHolderStrategy();}elseif(strategyName.equals("MODE_GLOBAL")){
strategy =newGlobalSecurityContextHolderStrategy();}else{try{Class<?> clazz =Class.forName(strategyName);Constructor<?> customStrategy = clazz.getConstructor();
strategy =(SecurityContextHolderStrategy)customStrategy.newInstance();}catch(Exception var2){ReflectionUtils.handleReflectionException(var2);}}}}
这里有一点要注意,在我们的Web工程中,登陆之后,Tomcat从线程池中拿出一个线程处理,new 一个新线程的情况下,就拿不到用户信息了。
我们进入源码看一下,实际上,这块就是在SecurityContextHolderFilter里面,我们看它的doFilter方法。
privatevoiddoFilter(HttpServletRequest request,HttpServletResponse response,FilterChain chain)throwsServletException,IOException{if(request.getAttribute(FILTER_APPLIED)!=null){
chain.doFilter(request, response);}else{
request.setAttribute(FILTER_APPLIED,Boolean.TRUE);Supplier<SecurityContext> deferredContext =this.securityContextRepository.loadDeferredContext(request);try{this.securityContextHolderStrategy.setDeferredContext(deferredContext);
chain.doFilter(request, response);}finally{this.securityContextHolderStrategy.clearContext();
request.removeAttribute(FILTER_APPLIED);}}}
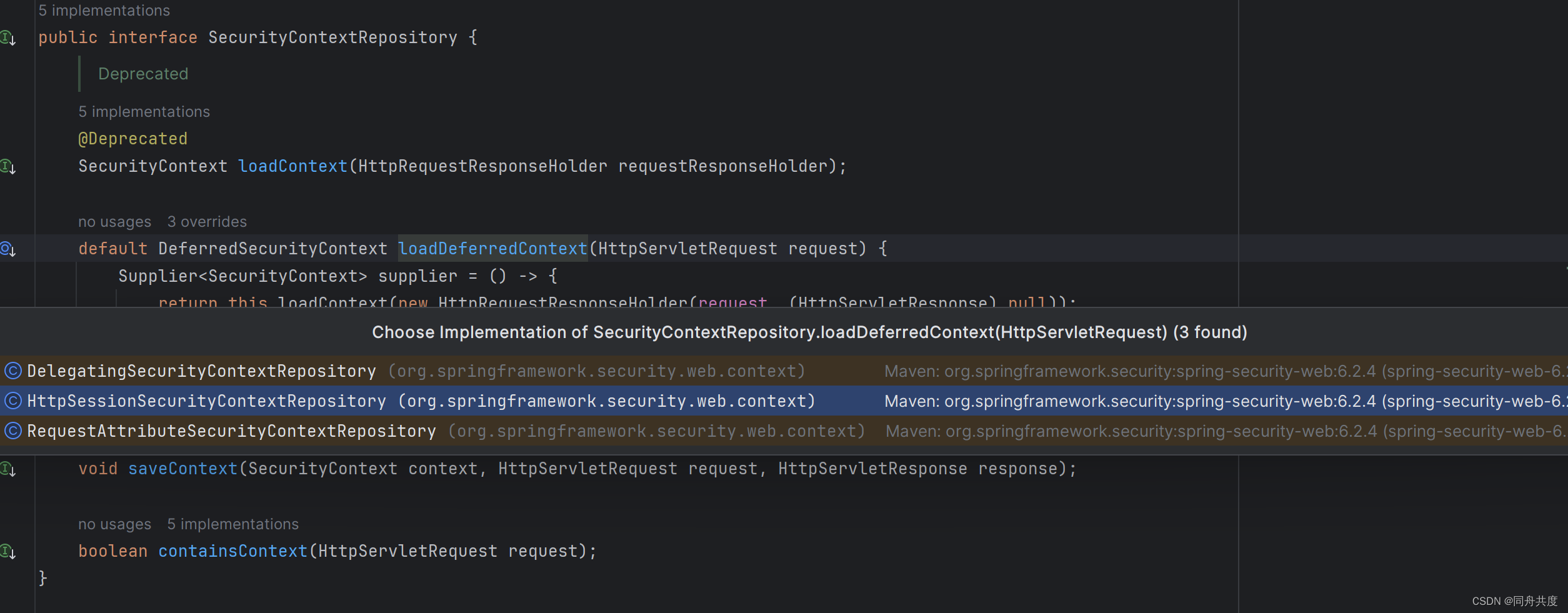
这里简单解释一下:
使用Http Session,从session里面拿到值,然后存到ContextHolder中,最后请求结束的时候,又清理掉。
那为什么要这么弄呢,为什么不直接放在Http Session中呢,这是因为有些场景下,Http Session并不是那么容易获取的,甚至在一些场景中,根本就没用到Http Session,比如说
Service要获取到用户信息,那没有Http session,就要注入session,比较麻烦,最关键的是,在一些前后端分离登录中,可能服务端生成jwt,存在redis,不用session,所以,Spring Security一开始就替我们考虑到了这样的场景,直接存到SecurityContextHolder中,更灵活。
看一下从session中怎么拿:
@GetMapping("/hello")publicStringhello(HttpSession httpSession){Authentication authentication =SecurityContextHolder.getContext().getAuthentication();SecurityContext securityContext =(SecurityContext)httpSession.getAttribute(HttpSessionSecurityContextRepository.SPRING_SECURITY_CONTEXT_KEY);Authentication authentication1 = securityContext.getAuthentication();System.out.println(authentication1 == authentication);return"hello";}
那如果一定要在子线程中获取到用户信息呢,Security也提供了相关的配置,如下
publicstaticvoidmain(String[] args){System.setProperty("spring.security.strategy",SecurityContextHolder.MODE_GLOBAL);SpringApplication.run(Security02DemoApplication.class, args);}
@GetMapping("/hello")publicStringhello(HttpSession httpSession){Authentication authentication =SecurityContextHolder.getContext().getAuthentication();SecurityContext securityContext =(SecurityContext)httpSession.getAttribute(HttpSessionSecurityContextRepository.SPRING_SECURITY_CONTEXT_KEY);Authentication authentication1 = securityContext.getAuthentication();System.out.println(authentication1 == authentication);newThread(newRunnable(){@Overridepublicvoidrun(){Authentication authentication =SecurityContextHolder.getContext().getAuthentication();System.out.println(authentication.getPrincipal());}}).start();return"hello";}
就是在启动类前,加上这个全局配置,存到 private static SecurityContext contextHolder;这里面去,相当于静态变量保存,自然和线程就没啥关系了,不过这种方式是不推荐的。
还有一种获取Authentication和Principal的方法,直接放在参数中,可以直接拿到。
/**
* 这两个参数默认会被解析,类似于HttpSession,HttpServletRequest
* @param authentication
* @param principal
*/@GetMapping("/user")publicvoiduser(Authentication authentication,Principal principal){}
还可以通过HttpServletRequest,来获取,如下
@GetMapping("/hello2")publicvoidhello2(HttpServletRequest request){//本质上也是从ContextHolder里面拿的,所以子线程也是获取不到//这里是说,获取用户名String remoteUser = request.getRemoteUser();//是否具备admin角色boolean admin = request.isUserInRole("admin");//当前用户登陆对象Principal userPrincipal = request.getUserPrincipal();}
我们可以进去看一下,
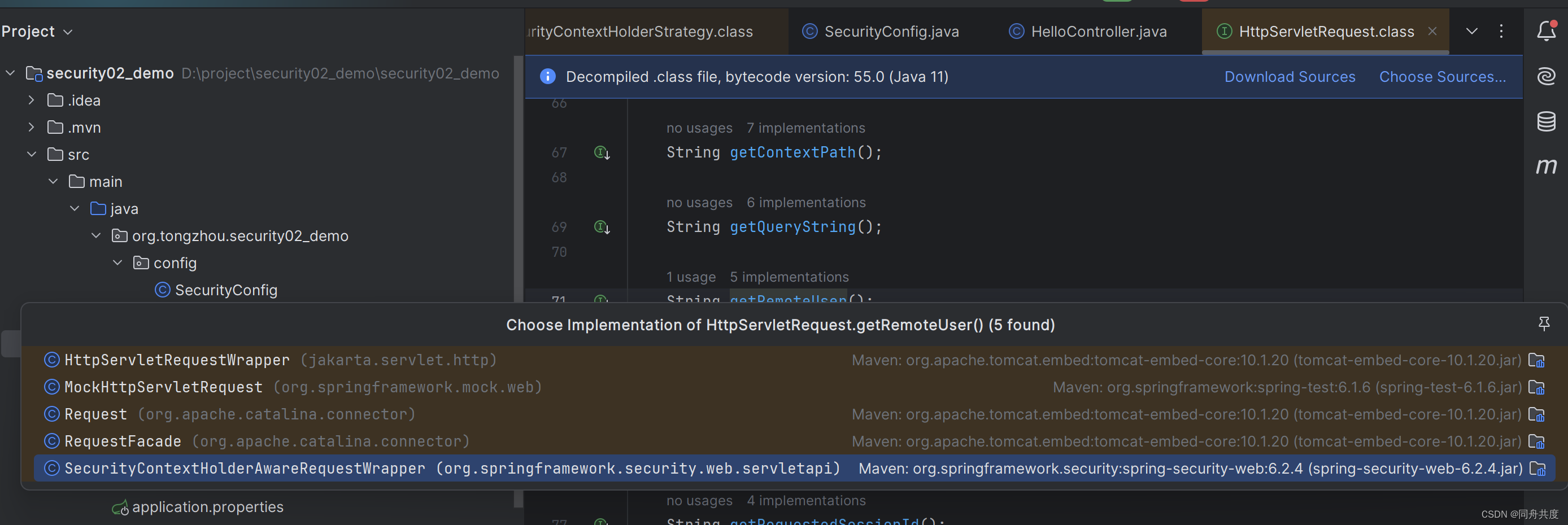
进入到SecurityContextHolderAwareRequestWrapper ,这里我们可以看到 this.securityContextHolderStrategy = SecurityContextHolder.getContextHolderStrategy();,这样就拿到了,本质上还是从ContextHolder中获取的。
匿名访问
//适用于静态页面放行,不会走security过滤器链,从contextHolder取不到值@BeanWebSecurityCustomizerwebSecurityCustomizer(){return web -> web.ignoring().requestMatchers("/hello");}/**
* 可以在这里修改过滤器
* @param httpSecurity 所有过滤器都可以通过这个来配置。保存的默认的过滤器
* @return
*/@BeanSecurityFilterChainsecurityFilterChain(HttpSecurity httpSecurity)throwsException{//所有请求,都要登陆后才能访问
httpSecurity.authorizeRequests(a -> a
//登陆或不登陆都可以访问.requestMatchers("/hello").permitAll()//只能未认证访问.requestMatchers("/hello").anonymous().anyRequest().authenticated())
这就是他们的区别,这一点一定要注意。
结语
攀登的过程,注定艰辛!
版权归原作者 同舟共度 所有, 如有侵权,请联系我们删除。