Linux shell脚本的调试方法比较多,上次我们探讨和测试了shell内建命令set所提供的一些调试选项,其实 shell 本身也提供了一些调试选项。我们以bash为例来看看。
1 bash 的命令行帮助信息(bash --help)
purleEndurer @ csdn ~ $ bash --help
GNU bash, version 4.2.46(2)-release-(x86_64-redhat-linux-gnu)
Usage: bash [GNU long option] [option] ...
bash [GNU long option] [option] script-file ...
GNU long options:
--debug
--debugger
--dump-po-strings
--dump-strings
--help
--init-file
--login
--noediting
--noprofile
--norc
--posix
--protected
--rcfile
--rpm-requires
--restricted
--verbose
--version
Shell options:
-irsD or -c command or -O shopt_option (invocation only)
-abefhkmnptuvxBCHP or -o option
Typebash -c "help set"' for more information about shell options. Typebash -c help' for more information about shell builtin commands.
purleEndurer @ csdn ~ $
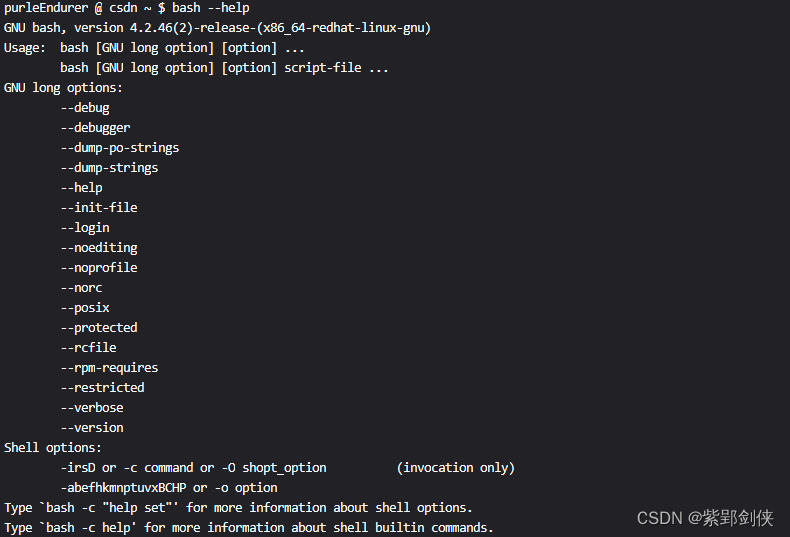
可以看到,bash命令有很多参数和选项。
使用
bash
命令加上特定的选项可以在运行Shell脚本时改变其行为,帮助我们诊断问题。
2 bash 的内置命令set提供的选项(bash -c "help set" )
我们可以使用命令 bash -c "help set" 查看 bash 内置命令set提供的选项。
purpleEndurer @ cdu ~ $ bash -c "help set"
set: set [-abefhkmnptuvxBCHP] [-o option-name] [--] [arg ...]
Set or unset values of shell options and positional parameters.Change the value of shell attributes and positional parameters, or display the names and values of shell variables. Options: -a Mark variables which are modified or created for export. -b Notify of job termination immediately. -e Exit immediately if a command exits with a non-zero status. -f Disable file name generation (globbing). -h Remember the location of commands as they are looked up. -k All assignment arguments are placed in the environment for a command, not just those that precede the command name. -m Job control is enabled. -n Read commands but do not execute them. -o option-name Set the variable corresponding to option-name: allexport same as -a braceexpand same as -B emacs use an emacs-style line editing interface errexit same as -e errtrace same as -E functrace same as -T hashall same as -h histexpand same as -H history enable command history ignoreeof the shell will not exit upon reading EOF interactive-comments allow comments to appear in interactive commands keyword same as -k monitor same as -m noclobber same as -C noexec same as -n noglob same as -f nolog currently accepted but ignored notify same as -b nounset same as -u onecmd same as -t physical same as -P pipefail the return value of a pipeline is the status of the last command to exit with a non-zero status, or zero if no command exited with a non-zero status posix change the behavior of bash where the default operation differs from the Posix standard to match the standard privileged same as -p verbose same as -v vi use a vi-style line editing interface xtrace same as -x -p Turned on whenever the real and effective user ids do not match. Disables processing of the $ENV file and importing of shell functions. Turning this option off causes the effective uid and gid to be set to the real uid and gid. -t Exit after reading and executing one command. -u Treat unset variables as an error when substituting. -v Print shell input lines as they are read. -x Print commands and their arguments as they are executed. -B the shell will perform brace expansion -C If set, disallow existing regular files to be overwritten by redirection of output. -E If set, the ERR trap is inherited by shell functions. -H Enable ! style history substitution. This flag is on by default when the shell is interactive. -P If set, do not follow symbolic links when executing commands such as cd which change the current directory. -T If set, the DEBUG trap is inherited by shell functions. -- Assign any remaining arguments to the positional parameters. If there are no remaining arguments, the positional parameters are unset. - Assign any remaining arguments to the positional parameters. The -x and -v options are turned off. Using + rather than - causes these flags to be turned off. The flags can also be used upon invocation of the shell. The current set of flags may be found in $-. The remaining n ARGs are positional parameters and are assigned, in order, to $1, $2, .. $n. If no ARGs are given, all shell variables are printed. Exit Status: Returns success unless an invalid option is given.purpleEndurer @ cdu ~ $
这个信息与
Linux shell编程学习笔记28:脚本调试 set命令https://blog.csdn.net/Purpleendurer/article/details/134506337?spm=1001.2014.3001.5501中set --help命令显示的帮助信息是一致的。
3 查看bash内置的命令:bash -c help
purpleEndurer @ csdn ~ $ bash -c help
GNU bash, version 4.2.46(2)-release (x86_64-redhat-linux-gnu)
These shell commands are defined internally. Typehelp' to see this list. Typehelp name' to find out more about the functionname'. Useinfo bash' to find out more about the shell in general.
Useman -k' orinfo' to find out more about commands not in this list.A star (*) next to a name means that the command is disabled.
job_spec [&] history [-c] [-d offset] [n] or hist>
(( expression )) if COMMANDS; then COMMANDS; [ elif C>
. filename [arguments] jobs [-lnprs] [jobspec ...] or jobs >
: kill [-s sigspec | -n signum | -sigs>
[ arg... ] let arg [arg ...]
[[ expression ]] local [option] name[=value] ...
alias [-p] [name[=value] ... ] logout [n]
bg [job_spec ...] mapfile [-n count] [-O origin] [-s c>
bind [-lpvsPVS] [-m keymap] [-f filen> popd [-n] [+N | -N]
break [n] printf [-v var] format [arguments]
builtin [shell-builtin [arg ...]] pushd [-n] [+N | -N | dir]
caller [expr] pwd [-LP]
case WORD in [PATTERN [| PATTERN]...)> read [-ers] [-a array] [-d delim] [->
cd [-L|[-P [-e]]] [dir] readarray [-n count] [-O origin] [-s>
command [-pVv] command [arg ...] readonly [-aAf] [name[=value] ...] o>
compgen [-abcdefgjksuv] [-o option] > return [n]
complete [-abcdefgjksuv] [-pr] [-DE] > select NAME [in WORDS ... ;] do COMM>
compopt [-o|+o option] [-DE] [name ..> set [-abefhkmnptuvxBCHP] [-o option->
continue [n] shift [n]
coproc [NAME] command [redirections] shopt [-pqsu] [-o] [optname ...]
declare [-aAfFgilrtux] [-p] [name[=va> source filename [arguments]
dirs [-clpv] [+N] [-N] suspend [-f]
disown [-h] [-ar] [jobspec ...] test [expr]
echo [-neE] [arg ...] time [-p] pipeline
enable [-a] [-dnps] [-f filename] [na> times
eval [arg ...] trap [-lp] [[arg] signal_spec ...]
exec [-cl] [-a name] [command [argume> true
exit [n] type [-afptP] name [name ...]
export [-fn] [name[=value] ...] or ex> typeset [-aAfFgilrtux] [-p] name[=va>
false ulimit [-SHacdefilmnpqrstuvx] [limit>
fc [-e ename] [-lnr] [first] [last] o> umask [-p] [-S] [mode]
fg [job_spec] unalias [-a] name [name ...]
for NAME [in WORDS ... ] ; do COMMAND> unset [-f] [-v] [name ...]
for (( exp1; exp2; exp3 )); do COMMAN> until COMMANDS; do COMMANDS; done
function name { COMMANDS ; } or name > variables - Names and meanings of so>
getopts optstring name [arg] wait [id]
hash [-lr] [-p pathname] [-dt] [name > while COMMANDS; do COMMANDS; done
help [-dms] [pattern ...] { COMMANDS ; }
purpleEndurer @ csdn ~ $
2 bash 命令行常用调试选项说明和演示
下面我们就bash命令行中的一些常用的调试选项逐一进行说明和演示。
2.1 echo $-:显示当前已启动的选项
purpleEndurer @ cdu ~ $ echo $-
himBHpurpleEndurer @ cdu ~ $
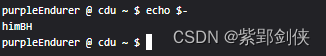
可以看到,当前启用的选项有h、i、m、B和H这几个选项处于启动状态。
2.2 bash -n 脚本文件名说明符:不执行脚本,仅检查错误
-n 选项的功能是:读一遍脚本中的命令但不执行,用于检查脚本中的语法等错误。
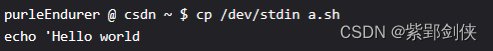
2.2.1 创建测试脚本文件a.sh
我们用 cp 命令来创建 ,文件内容是: echo 'Hello world
为了测试,我们故意漏了命令行末尾配对的单引号。
purleEndurer @ csdn ~ $ cp /dev/stdin a.sh
echo 'Hello world
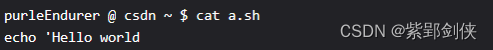
2.2.2 查看测试脚本文件a.sh内容
purleEndurer @ csdn ~ $ cat a.sh
echo 'Hello world
2.2.3 检查脚本语法错误
purleEndurer @ csdn ~ $ bash -n a.sh
a.sh: line 1: unexpected EOF while looking for matching `''
a.sh: line 2: syntax error: unexpected end of file
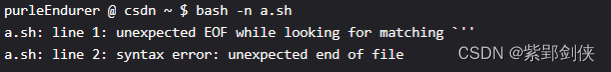
可以看到,bash检查出a.sh存在两个错误。
第1个错误出现在第1行:寻找匹配的 ''' 时出现意外的 EOF,即单引号未配对。
第2个错误出现在第2行:语法错误:意外的文件结尾。
2.3 bash -x 脚本文件说明符:先显示命令及参数(不显示注释),再显示执行结果
bash命令的-x选项与set 命令中的-x选项功能相同,都是打开echo模式,执行命令后,会先显示该命令及所带的参数,再显示命令执行的结果:
2.3.1 创建测试脚本文件a.sh
我们用 cp 命令来创建 a.sh,文件内容如下:
purleEndurer @ csdn ~ $ cp /dev/stdin a.sh
echo -n Enter your name please: # 提示用户输入名字
read n # 将用户输入的名字保存到变量n
echo Your name is $n # 显示用户输入的名字
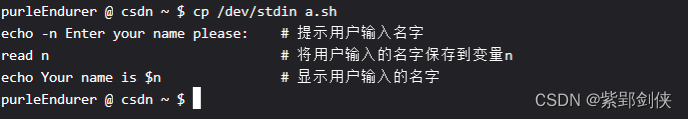
#号后的内容是对命令功能的说明。
2.3.2 执行脚本文件a.sh
purleEndurer @ csdn ~ $ bash -x a.sh
- echo -n Enter your name please:
Enter your name please:+ read n
purpleEndurer- echo Your name is purpleEndurer
Your name is purpleEndurer
purleEndurer @ csdn ~ $

bash会将以+开头,将执行的命令显示出来,然后再显示命令执行的结果。
2.3.3 使用环境变量PS4定制显示格式
其实我们在使用bash的 -x选项来显示命令和参数时前面加的 + 是环境变量PS4 保存的。
purpleEndurer @csdn ~ $ set | grep PS4
PS4='+ '

因此,我们可以通过修改环境变量PS4的值来设置 bash的 -x选项显示命令和参数时的格式。
例如:我们对显示的命令和参数以 > 开头,然后引入${BASH_SOURCE} 显示脚本文件名,${LINENO}显示行号,${FUNCNAME[0]}显示正在执行的函数的名字:
purpleEndurer @csdn ~ $ PS1="\e[35mpurpleEndurer\e[0m @csdn \w $ "
purpleEndurer @csdn ~ $ export PS4='>${BASH_SOURCE} [${LINENO}]${FUNCNAME[0]}: '
purpleEndurer @csdn ~ $ bash -x a.sha.sh [1] : echo -n Enter your name please:
Enter your name please:>a.sh [2] : read n
abc
a.sh [3] : echo Your name is abc
Your name is abc
purpleEndurer @csdn ~ $
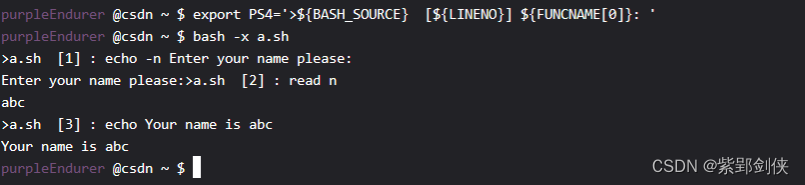
如果觉得字符太多,不容易辨别的话,我们还可以分别给它们加上颜色:
purpleEndurer @csdn ~ $ export PS4='\e[35m>${BASH_SOURCE} \e[0m \e[33m [${LINENO}]\e[0m \e[31m ${FUNCNAME[0]}: \e[0m'
purpleEndurer @csdn ~ $ bash -x a.sha.sh [1] : echo -n Enter your name please:
Enter your name please:>a.sh [2] : read n
abc
a.sh [3] : echo Your name is abc
Your name is abc
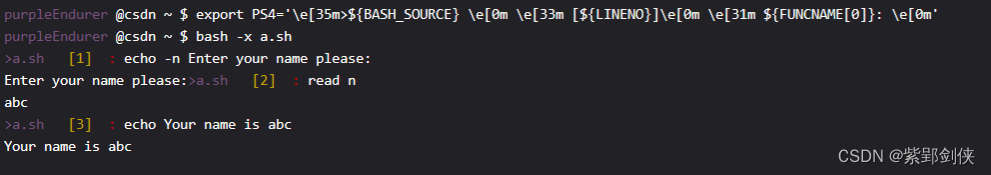
这里我们使用了
Linux shell编程学习笔记4:修改命令行提示符格式(内容和颜色)https://blog.csdn.net/Purpleendurer/article/details/133416124?spm=1001.2014.3001.5501中介绍的知识,让脚本文件名以紫色显示,行号以黄色显示,正在执行的函数的名字以红色显示。
2.4 bash -v 脚本文件说明符:一边执行脚本,一边将执行过的脚本命令打印到标准输出(包括注释)
purpleEndurer @csdn ~ $ export PS4='\e[35m>${BASH_SOURCE} \e[0m \e[33m [${LINENO}]\e[0m \e[31m ${FUNCNAME[0]}: \e[0m'
purpleEndurer @csdn ~ $ bash -v a.sh
echo -n Enter your name please: # 提示用户输入名字
Enter your name please:read n # 将用户输入的名字保存到变量n
abc
echo Your name is $n # 显示用户输入的名字
Your name is abc
purpleEndurer @csdn ~ $

可以看到,-v选项显示所执行的命令不受环境变量PS4的影响,而且会连脚本文件中的注释一并显示。
版权归原作者 紫郢剑侠 所有, 如有侵权,请联系我们删除。