一、springboot的特性之一
基于springboot的特性 自动装配@Configuretion 注解
二、springboot内置Tomcat步骤
直接看SpringApplication方法的代码块
总纲:
1、在SpringApplication.run 初始化了一个上下文ConfigurableApplicationContext configurableApplicationContext = AnnotationConfigServletWebServerApplicationContext,这里是通过Class.forName获取到的。
2、在调用AbstartApplicationContext中调用了onRefresh()方法。
3、继承onRefresh()有5个子类
...
ServletWebServerApplicationContext
..
4、为什么说是在ServletWebServerApplicationContext实现的呢。
5、可以去查看AnnotationConfigServletWebServerApplicationContext这个类是继承那个类。可以看到,这个类继承了ServletWebServerApplicationContext,而onRefresh()方法在ServletWebServerApplicationContext实现了。衔接
6、在这个createWebServer()方法中。获取一个ServletWebServerFactory,创建一个服务生成工厂;而这里就比较有意思。这里是通过自动装配,ServletWebServerFactoryAutoConfiguretion;在这里创建了具体服务的工厂。
7、而我们引入spring-boot-starter的时候,依赖的spring-boot-starter-web中依赖的spring-boot-starter-tomcat; 所以在自动装配创建的TomcatServletWebServiceFactory;在这里个工厂中创建WebServer,也就是Tomcat;
8、既然Tomcat已经创建了,那么怎么跟SpringMvc中的DispatherServlet进行关联呢?第三章。
// 1、第一步从SpringAppplicaton.run开始
/**
* Static helper that can be used to run a {@link SpringApplication} from the
* specified source using default settings.
* @param primarySource the primary source to load
* @param args the application arguments (usually passed from a Java main method)
* @return the running {@link ApplicationContext}
*/
public static ConfigurableApplicationContext run(Class<?> primarySource, String... args) {
return run(new Class<?>[] { primarySource }, args);
}
// ....中间的就省略
// 第二步
try {
ApplicationArguments applicationArguments = new DefaultApplicationArguments(args);
ConfigurableEnvironment environment = prepareEnvironment(listeners, applicationArguments);
configureIgnoreBeanInfo(environment);
Banner printedBanner = printBanner(environment);
context = createApplicationContext();
exceptionReporters = getSpringFactoriesInstances(SpringBootExceptionReporter.class,
new Class[] { ConfigurableApplicationContext.class }, context);
prepareContext(context, environment, listeners, applicationArguments, printedBanner);
// 从这里进入
refreshContext(context);
afterRefresh(context, applicationArguments);
stopWatch.stop();
if (this.logStartupInfo) {
new StartupInfoLogger(this.mainApplicationClass).logStarted(getApplicationLog(), stopWatch);
}
listeners.started(context);
callRunners(context, applicationArguments);
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
handleRunFailure(context, ex, exceptionReporters, listeners);
throw new IllegalStateException(ex);
}
// 第三步
private void refreshContext(ConfigurableApplicationContext context) {
// 看这里
refresh(context);
if (this.registerShutdownHook) {
try {
context.registerShutdownHook();
}
catch (AccessControlException ex) {
// Not allowed in some environments.
}
}
}
查看refresh(context) 在使用ApplicationContext 类贯彻整条启动的链路 AbstratApplicationContext
而AnnotationConfigServletWebServerApplicationContext继承了SerlvetWebServerApplicationContext
所以在onRefresh(), 是使用SerlvetWebServerApplicationContext
try {
// Allows post-processing of the bean factory in context subclasses.
postProcessBeanFactory(beanFactory);
// Invoke factory processors registered as beans in the context.
invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(beanFactory);
// Register bean processors that intercept bean creation.
registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory);
// Initialize message source for this context.
initMessageSource();
// Initialize event multicaster for this context.
initApplicationEventMulticaster();
// Initialize other special beans in specific context subclasses.
// 在这里做内置Tomcat的内置,及加载到spring容器中。
// 在这里实现一些自定义的实现。
onRefresh();
// Check for listener beans and register them.
registerListeners();
// Instantiate all remaining (non-lazy-init) singletons.
finishBeanFactoryInitialization(beanFactory);
// Last step: publish corresponding event.
finishRefresh();
}
// 父类什么都没有?
// 那就看下父类有哪些实现了? 但这里是怎么实现在子类实现的?
// 子类里面是怎么关联到tomcat上的?
// 在
// 这里描述下为什么选择SerlvetWebServerApplicationContext
// 那是因为在启动创建spring的上下文的,AnnotationConfigServletWebServerApplicationContext
// 而AnnotationConfigServletWebServerApplicationContext继承了SerlvetWebServerApplicationContext
// 所以在onRefresh(), 是使用SerlvetWebServerApplicationContext
protected ConfigurableApplicationContext createApplicationContext() {
Class<?> contextClass = this.applicationContextClass;
if (contextClass == null) {
try {
switch (this.webApplicationType) {
case SERVLET:
// 这里创建的是org.springframework.boot.web.servlet.context.AnnotationConfigServletWebServerApplicationContext
contextClass = Class.forName(DEFAULT_SERVLET_WEB_CONTEXT_CLASS);
break;
case REACTIVE:
contextClass = Class.forName(DEFAULT_REACTIVE_WEB_CONTEXT_CLASS);
break;
default:
contextClass = Class.forName(DEFAULT_CONTEXT_CLASS);
}
}
catch (ClassNotFoundException ex) {
throw new IllegalStateException(
"Unable create a default ApplicationContext, please specify an ApplicationContextClass", ex);
}
}
return (ConfigurableApplicationContext) BeanUtils.instantiateClass(contextClass);
}
在SerlvetWebServerApplicationContext实现了onRefresh()方法
@Override
protected void onRefresh() {
super.onRefresh();
try {
// 在这里创建一个web服务,先看代码
createWebServer();
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
throw new ApplicationContextException("Unable to start web server", ex);
}
}
// 创建web服务
private void createWebServer() {
WebServer webServer = this.webServer;
ServletContext servletContext = getServletContext();
// 如果已经创建为了web服务,这里就不在创建,但是服务刚启动,肯定都是==null
if (webServer == null && servletContext == null) {
// 这里获取一个创建服务的工厂。这里就很有意思。这里用的springboot自动装配
ServletWebServerFactory factory = getWebServerFactory();
this.webServer = factory.getWebServer(getSelfInitializer());
}
else if (servletContext != null) {
try {
getSelfInitializer().onStartup(servletContext);
}
catch (ServletException ex) {
throw new ApplicationContextException("Cannot initialize servlet context", ex);
}
}
initPropertySources();
}
// 在容器中获取ServletWebServerFactory。 而这个类的子类是有三个
// 1、TomcatServletWebServerFactory (默认spring-boot-starter-web,依赖spring-boot-starter-tomcat)
// 2、JettyServletWebServerFactory
// 3、UndertowServletWebServerFactory
/**
* Returns the {@link ServletWebServerFactory} that should be used to create the
* embedded {@link WebServer}. By default this method searches for a suitable bean in
* the context itself.
* @return a {@link ServletWebServerFactory} (never {@code null})
*/
protected ServletWebServerFactory getWebServerFactory() {
// Use bean names so that we don't consider the hierarchy
String[] beanNames = getBeanFactory().getBeanNamesForType(ServletWebServerFactory.class);
if (beanNames.length == 0) {
throw new ApplicationContextException("Unable to start ServletWebServerApplicationContext due to missing "
+ "ServletWebServerFactory bean.");
}
if (beanNames.length > 1) {
throw new ApplicationContextException("Unable to start ServletWebServerApplicationContext due to multiple "
+ "ServletWebServerFactory beans : " + StringUtils.arrayToCommaDelimitedString(beanNames));
}
return getBeanFactory().getBean(beanNames[0], ServletWebServerFactory.class);
}
// 从头看起,我们在第一章的时候也说明了。这里用到springboot的自动装配。
// 这里要从@EnableAutoConfiguration ; 而这个注解是在@SpringBootApplication中引用
// 自动装备会读取starter注解下spring-factory中加载。
// 而创建服务工厂是ServletWebServerFactoryAutoConfiguration这个配置类
/**
* {@link EnableAutoConfiguration Auto-configuration} for servlet web servers.
*
* @author Phillip Webb
* @author Dave Syer
* @author Ivan Sopov
* @author Brian Clozel
* @author Stephane Nicoll
* @since 2.0.0
*/
@Configuration(proxyBeanMethods = false)
@AutoConfigureOrder(Ordered.HIGHEST_PRECEDENCE)
// 这个配置类生效,必须是有ServletRequest这个类
@ConditionalOnClass(ServletRequest.class)
@ConditionalOnWebApplication(type = Type.SERVLET)
// 注入ServerProperties属性进来, 这是server服务的配置项。
// 端口。超时情况。在第四会详情介绍Tomcat配置详解。
@EnableConfigurationProperties(ServerProperties.class)
// 导入如下配置
@Import({ ServletWebServerFactoryAutoConfiguration.BeanPostProcessorsRegistrar.class,
// 嵌入tomcat
ServletWebServerFactoryConfiguration.EmbeddedTomcat.class,
// 嵌入Jetty
ServletWebServerFactoryConfiguration.EmbeddedJetty.class,
// 嵌入Undertow,netty
ServletWebServerFactoryConfiguration.EmbeddedUndertow.class })
public class ServletWebServerFactoryAutoConfiguration {
}
// 来看下嵌入的这些代码都干了什么?
// 先来看下EmbeddedTomcat这个类
// 初始化TomcatServletWebServerFactory是前提条件Servlet,Tomcat等类是要存在才生效
// 而我们spring-boot-web-starter主键里面默认是引入了spring-boot-starter-tomcat。
// 这些类是存在,反之我们看jetty的。
@Configuration(proxyBeanMethods = false)
@ConditionalOnClass({ Servlet.class, Tomcat.class, UpgradeProtocol.class })
@ConditionalOnMissingBean(value = ServletWebServerFactory.class, search = SearchStrategy.CURRENT)
static class EmbeddedTomcat {
@Bean
TomcatServletWebServerFactory tomcatServletWebServerFactory(
ObjectProvider<TomcatConnectorCustomizer> connectorCustomizers,
ObjectProvider<TomcatContextCustomizer> contextCustomizers,
ObjectProvider<TomcatProtocolHandlerCustomizer<?>> protocolHandlerCustomizers) {
TomcatServletWebServerFactory factory = new TomcatServletWebServerFactory();
factory.getTomcatConnectorCustomizers()
.addAll(connectorCustomizers.orderedStream().collect(Collectors.toList()));
factory.getTomcatContextCustomizers()
.addAll(contextCustomizers.orderedStream().collect(Collectors.toList()));
factory.getTomcatProtocolHandlerCustomizers()
.addAll(protocolHandlerCustomizers.orderedStream().collect(Collectors.toList()));
return factory;
}
}
// 反观jetty的初始化Factory。这里是server都是标红了。
@Configuration(proxyBeanMethods = false)
@ConditionalOnClass({ Servlet.class, Server.class, Loader.class, WebAppContext.class })
@ConditionalOnMissingBean(value = ServletWebServerFactory.class, search = SearchStrategy.CURRENT)
static class EmbeddedJetty {
@Bean
JettyServletWebServerFactory JettyServletWebServerFactory(
ObjectProvider<JettyServerCustomizer> serverCustomizers) {
JettyServletWebServerFactory factory = new JettyServletWebServerFactory();
factory.getServerCustomizers().addAll(serverCustomizers.orderedStream().collect(Collectors.toList()));
return factory;
}
}
// 获取到了WebServer在操作Tomcat操作。
如图:

来查看下TomcatServletWebSeverFactory下创建WebServer
@Override
public WebServer getWebServer(ServletContextInitializer... initializers) {
if (this.disableMBeanRegistry) {
Registry.disableRegistry();
}
// 创建一个Tomcat服务,这里的就是apache的代码块了。
// 如下图Tomcat的结果图进行对比代码。
// 这里就是一个Server
// 这里默认的一个Service是StandardService
Tomcat tomcat = new Tomcat();
// 文件的路径,这里要获取jar文件目录,部署的目录。
File baseDir = (this.baseDirectory != null) ? this.baseDirectory : createTempDir("tomcat");
tomcat.setBaseDir(baseDir.getAbsolutePath());
// 创建一个连接协议,这里传入的HttpNioProtocol
// 一个Server可以有多个Connector。一种协议只能有一个Connector。
Connector connector = new Connector(this.protocol);
connector.setThrowOnFailure(true);
tomcat.getService().addConnector(connector);
customizeConnector(connector);
tomcat.setConnector(connector);
// 设置host,如果有新的web应用进来,可以自动发布应用。
tomcat.getHost().setAutoDeploy(false);
// StandardEngine
configureEngine(tomcat.getEngine());
// 这里可以自定义连接协议,比如非http等;
for (Connector additionalConnector : this.additionalTomcatConnectors) {
tomcat.getService().addConnector(additionalConnector);
}
prepareContext(tomcat.getHost(), initializers);
return getTomcatWebServer(tomcat);
}
1、Tomcat回归
- 一个Tomcat只会有一个Server
- 一个Server有多个service
- 一个Service有多个Connector连接协议,有http,https,ajp等协议。
- 一个Service只有一个Engine(引擎)
- 一个Engine,可以有多个Host,每个Host代表一个虚拟主机,他可以包含多个Web应用。
- 每一个context表示运行在Tomcat的web应用
2、Tomcat的结构图

三、SpringMvc的DispatcherServlet关联Tomcat
还是原汁原味自动装配。
总纲:
1、还是回到@EnableAutoConfiguration这个注解,会自动装配一个叫 @DispatcherServletAutoConfiguration;
2、这个配置类会初始化1:DispatherServlet
初始2:DispatcherServletRegistrationConfiguration,在这里面初始化了DispatcherServletRegistrationBean,来看看这个类都继承了什么。
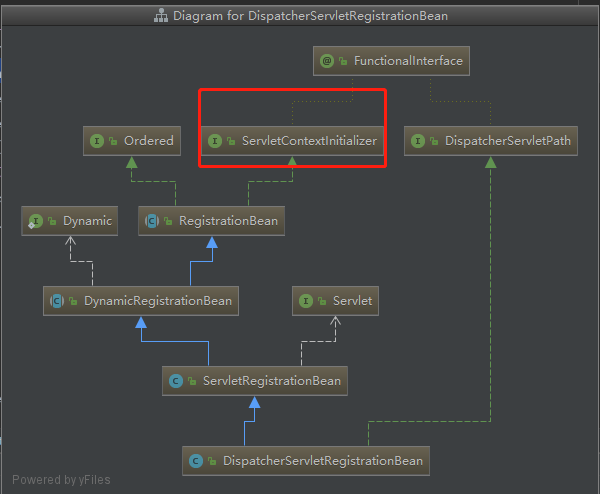
这个类很熟悉了吧。在初始化Tomcat。屡次出现;
这个类就能拿到ServletContext上下文了。在看看Tomcat的结构图。是不是就能对得起一些东西了。
3、DispatcherServletRegistrationBean从这个类来往上翻,看在那一层上实现了ServletContextInitializer,最终是RegistrationBean类实现ServletContextInitializer的onStartUp(),
在DynamicRegistrationBean上实现RegistrationBean的register功能。
4、直接上代码流程
代码如下:
// 先看自动装配
@Configuration(proxyBeanMethods = false)
@Conditional(DefaultDispatcherServletCondition.class)
@ConditionalOnClass(ServletRegistration.class)
@EnableConfigurationProperties({ HttpProperties.class, WebMvcProperties.class })
protected static class DispatcherServletConfiguration {
@Bean(name = DEFAULT_DISPATCHER_SERVLET_BEAN_NAME)
public DispatcherServlet dispatcherServlet(HttpProperties httpProperties, WebMvcProperties webMvcProperties) {
DispatcherServlet dispatcherServlet = new DispatcherServlet();
dispatcherServlet.setDispatchOptionsRequest(webMvcProperties.isDispatchOptionsRequest());
dispatcherServlet.setDispatchTraceRequest(webMvcProperties.isDispatchTraceRequest());
dispatcherServlet.setThrowExceptionIfNoHandlerFound(webMvcProperties.isThrowExceptionIfNoHandlerFound());
dispatcherServlet.setPublishEvents(webMvcProperties.isPublishRequestHandledEvents());
dispatcherServlet.setEnableLoggingRequestDetails(httpProperties.isLogRequestDetails());
return dispatcherServlet;
}
@Bean
@ConditionalOnBean(MultipartResolver.class)
@ConditionalOnMissingBean(name = DispatcherServlet.MULTIPART_RESOLVER_BEAN_NAME)
public MultipartResolver multipartResolver(MultipartResolver resolver) {
// Detect if the user has created a MultipartResolver but named it incorrectly
return resolver;
}
}
@Configuration(proxyBeanMethods = false)
@Conditional(DispatcherServletRegistrationCondition.class)
@ConditionalOnClass(ServletRegistration.class)
@EnableConfigurationProperties(WebMvcProperties.class)
@Import(DispatcherServletConfiguration.class)
protected static class DispatcherServletRegistrationConfiguration {
@Bean(name = DEFAULT_DISPATCHER_SERVLET_REGISTRATION_BEAN_NAME)
@ConditionalOnBean(value = DispatcherServlet.class, name = DEFAULT_DISPATCHER_SERVLET_BEAN_NAME)
public DispatcherServletRegistrationBean dispatcherServletRegistration(DispatcherServlet dispatcherServlet,
WebMvcProperties webMvcProperties, ObjectProvider<MultipartConfigElement> multipartConfig) {
DispatcherServletRegistrationBean registration = new DispatcherServletRegistrationBean(dispatcherServlet,
webMvcProperties.getServlet().getPath());
registration.setName(DEFAULT_DISPATCHER_SERVLET_BEAN_NAME);
registration.setLoadOnStartup(webMvcProperties.getServlet().getLoadOnStartup());
multipartConfig.ifAvailable(registration::setMultipartConfig);
return registration;
}
}
// 在看这个DispatcherServletRegistrationBean的族谱,上图已经明了,会继承到ServletContextInitializer
// 实现onStartup()
@Override
public final void onStartup(ServletContext servletContext) throws ServletException {
String description = getDescription();
if (!isEnabled()) {
logger.info(StringUtils.capitalize(description) + " was not registered (disabled)");
return;
}
register(description, servletContext);
}
@Override
protected final void register(String description, ServletContext servletContext) {
//servlet注册在这里完成 该方法由子类ServletRegistrationBean实现
//servlet注册完后会返回一个registration对象,用于完成servlet-mapping的配置
D registration = addRegistration(description, servletContext);
if (registration == null) {
logger.info(StringUtils.capitalize(description) + " was not registered (possibly already registered?)");
return;
}
// servlet的mapping配置在这里完成 该方法由子类ServletRegistrationBean实现
configure(registration);
}
四、SpringBoot的Tomcat及access配置项
Tomcat配置类:ServerProperties,以server开头。这个类在ServletWebServerFactoryAutoConfiguration中开启注入进来。
直接撸代码,在代码做注释
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "server", ignoreUnknownFields = true)
public class ServerProperties {
// 这里就好解释,就是端口咯
private Integer port;
// 绑定网络ip,填写这个了,那么访问只能这个ip才能访问,亲测可以的;当然也是随便填写服务的ip,
// 这个属性目前不是很明确要做什么,服务私有? 而且不是本机的ip,会报错的。
private InetAddress address;
// 配置爆出Exception后,跳转到指定的报错页面 -> BasicErrorController (这个类也是springboot实现的)
// 尝试了下,没起作用,就放弃,现在更多的都是前后端分离,都使用@ControllerAdice
// 具体放在yml中注明
@NestedConfigurationProperty
private final ErrorProperties error = new ErrorProperties();
// 看着意思是设置转发头部策略,好像这个不建议使用,没有尝试过
// 有三种Native framework none
private ForwardHeadersStrategy forwardHeadersStrategy;
//
private String serverHeader;
// 请求头部最大的size设置,默认8Kb
private DataSize maxHttpHeaderSize = DataSize.ofKilobytes(8);
// 连接器在关闭连接之前等待另一个HTTP请求的时间。不设置无效等待
// 好像也什么用了。
private Duration connectionTimeout;
// 请求https-ssl证书加密,这个也没有用过,没尝试过
@NestedConfigurationProperty
private Ssl ssl;
@NestedConfigurationProperty
private final Compression compression = new Compression();
@NestedConfigurationProperty
private final Http2 http2 = new Http2();
// servlet配置,结构图可以参照下Tomcat结构图
private final Servlet servlet = new Servlet();
// tomcat配置类, 在yml上署名,这里重点说明下Tomcat配置。
private final Tomcat tomcat = new Tomcat();
// jetty配置类, 在yml上署名
private final Jetty jetty = new Jetty();
// netty配置类, 在yml上署名
private final Netty netty = new Netty();
// Undertow配置类, 在yml上署名
private final Undertow undertow = new Undertow();
// 这里是Servlet配置。
public static class Servlet {
// Servlet参数
private final Map<String, String> contextParameters = new HashMap<>();
// 路径 例如:/tk 请求路径http://xx:xx/tk/xx
private String contextPath;
// Servlet应用名称
private String applicationDisplayName = "application";
// jsp属性,这里都不展示,因为现在的框架基本都是前后端分离
@NestedConfigurationProperty
private final Jsp jsp = new Jsp();
// session会话配置
@NestedConfigurationProperty
private final Session session = new Session();
}
/**
* Tomcat配置项
*/
public static class Tomcat {
// tomcat的accesslog配置,这里在下面具体配置上说明
private final Accesslog accesslog = new Accesslog();
/**
* Regular expression that matches proxies that are to be trusted.
*/
private String internalProxies = "10\\.\\d{1,3}\\.\\d{1,3}\\.\\d{1,3}|" // 10/8
+ "192\\.168\\.\\d{1,3}\\.\\d{1,3}|" // 192.168/16
+ "169\\.254\\.\\d{1,3}\\.\\d{1,3}|" // 169.254/16
+ "127\\.\\d{1,3}\\.\\d{1,3}\\.\\d{1,3}|" // 127/8
+ "172\\.1[6-9]{1}\\.\\d{1,3}\\.\\d{1,3}|" // 172.16/12
+ "172\\.2[0-9]{1}\\.\\d{1,3}\\.\\d{1,3}|172\\.3[0-1]{1}\\.\\d{1,3}\\.\\d{1,3}|" //
+ "0:0:0:0:0:0:0:1|::1";
/**
* Header that holds the incoming protocol, usually named "X-Forwarded-Proto".
*/
// 看着是协议请求头设置
private String protocolHeader;
private String protocolHeaderHttpsValue = "https";
// 端口请求头
private String portHeader = "X-Forwarded-Port";
/**
* Name of the HTTP header from which the remote IP is extracted. For instance,
* `X-FORWARDED-FOR`.
*/
private String remoteIpHeader;
/**
* Name of the HTTP header from which the remote host is extracted.
*/
private String hostHeader = "X-Forwarded-Host";
/**
* Tomcat base directory. If not specified, a temporary directory is used.
*/
// 根目录,存放一些日志使用的,一般就是 ".", 根目录
private File basedir;
/**
* Delay between the invocation of backgroundProcess methods. If a duration suffix
* is not specified, seconds will be used.
*/
@DurationUnit(ChronoUnit.SECONDS)
private Duration backgroundProcessorDelay = Duration.ofSeconds(10);
/**
* Maximum amount of worker threads.
*/
// 最大线程数,默认是200,可以任务是临时工,有活来了,就要干。
private int maxThreads = 200;
// 最小工作线程,可以认为这是正式工,每天都要干活
private int minSpareThreads = 10;
// post请求,最大报文大小,默认2M
private DataSize maxHttpFormPostSize = DataSize.ofMegabytes(2);
// 最大正文大小。这里说明下。这里跟spring里面也有一个文件大小设置的
// 这两个是没有什么上下关系
private DataSize maxSwallowSize = DataSize.ofMegabytes(2);
private Boolean redirectContextRoot = true;
private boolean useRelativeRedirects;
// unicode设置
private Charset uriEncoding = StandardCharsets.UTF_8;
// 提问:Tomcat最大能承接多少连接?
// 最大的请求连接设置
private int maxConnections = 8192;
// 如果请求数量超过了最大的请求连接,就会把连接存放在队列中。
private int acceptCount = 100;
// 所以Tomcat最大能承接的连接是 maxConnections + acceptCount - 连接使用完的。
private int processorCache = 200;
private List<String> additionalTldSkipPatterns = new ArrayList<>();
/**
* Comma-separated list of additional unencoded characters that should be allowed
* in URI paths. Only "< > [ \ ] ^ ` { | }" are allowed.
*/
private List<Character> relaxedPathChars = new ArrayList<>();
/**
* Comma-separated list of additional unencoded characters that should be allowed
* in URI query strings. Only "< > [ \ ] ^ ` { | }" are allowed.
*/
private List<Character> relaxedQueryChars = new ArrayList<>();
// 连接超时时间,如果不设置,或者设置-1,那么就会无限时间连接。
private Duration connectionTimeout;
private final Resource resource = new Resource();
private final Mbeanregistry mbeanregistry = new Mbeanregistry();
// Tomcat的accesslog设置
public static class Accesslog {
// 是否开启accesslog日志,默认不开启
private boolean enabled = false;
// # 在Servlet.getAttribute("token"),存在的时候才输出日志, 这里不在输出,一般应该不会选择这个。
private String conditionIf;
// ServletRequest.getAttribute(conditionUnless) 是否存在整个class输出
private String conditionUnless;
// 内容输出正则配置
// "%{yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss.SSS}t %h %A %l %user \"%r\" %s %b %D"
// 这里的正则与logback差不多一致
private String pattern = "common";
// tomcat日志目录
private String directory = "logs";
// 文件输出前缀
protected String prefix = "access_log";
// 文件输出后缀
private String suffix = ".log";
//
private String encoding;
/**
* Locale used to format timestamps in log entries and in log file name
* suffix. Default to the default locale of the Java process.
*/
private String locale;
// 检查日志文件是否存在,存在是否重新创建;
private boolean checkExists = false;
// 是否开启根据时间轮转日志,比如今天access.2023-06-14.log,明天access.2023-06-15.log
private boolean rotate = true;
// 是否推迟在文件名上加上时间;等轮转到第二天的时候,在加上;
private boolean renameOnRotate = false;
// 日志文件天数多少天删除
private int maxDays = -1;
// 文件名格式化时间戳
private String fileDateFormat = ".yyyy-MM-dd";
private boolean ipv6Canonical = false;
// 请求是否带上request的属性,ip,端口,协议等
private boolean requestAttributesEnabled = false;
// 是否启用缓存,定时刷新到日志文件中
private boolean buffered = true;
}
更直观的通yml在展示下;
server:
# 端口设置
port: 5051
# 绑定网络ip,填写这个了,那么访问只能这个ip才能访问,亲测可以的;当然也是随便填写服务的ip,
# 这个属性目前不是很明确要做什么,服务私有?而且不是本机的ip,会报错的。
address: 127.0.0.1
# 开启设置请求content-type支持类型比如application/json;text/html;application/xml等
compression:
enabled: true
# 设置context-path,http://localhost:5051/tk/test/get
servlet:
context-path: /tk
# 设置会话,这块就不在做说什么。
# session:
# cookie:
# comment:
# 指定报错后,跳转/error页面,/error的实现Controller -> BasicErrorController
# 没有尝试,好像没什么用。不过前后端都分离,更多都是用@ControllerAdice
error:
path: /error
include-exception: true
whitelabel:
enabled: true
# 重定向请求头部使用策略。没有对比过
# forward-headers-strategy: native
# 头部最大size,这里是kb
max-http-header-size: 8KB
# 连接器最大超时时间,这里是指connector这个连接器
connection-timeout: 100s
tomcat:
# 存放一些日志等的目录,一般都是设置根目录,当然也不一定是
basedir: .
# 服务的接受和处理最大的连接数,默认:8192,如果超过这个数据,那么就会进入队列,accept-count
# 这里很容易被面试,Tomcat最大能承接连接数???
max-connections: 8192
# 当请求的连接都接受和处理,那么传入进来的连接就会进入队列,这个是设置队列使用
accept-count: 100
# 最大工作线程数,默认200;并不是所有的服务线程都是使用 8191
max-threads: 200
# 最小的工作线程数,默认10
min-spare-threads: 10
# url解码字符编码,默认utf-8
uri-encoding: utf-8
# post请求最大内容大小设置,默认2M,如果设置-1,则不限制post请求大小
max-http-form-post-size: 2MB
# 可吞下的请求正文的最大数量,默认2MB
max-swallow-size: 2MB
# 请求连接的最大超时时间
connection-timeout: 60000ms
# tomcat的accesslog配置
accesslog:
# 是否开启accesslog设置
enabled: true
# 是否把请求日志缓存起来,在定时缓存刷新,这里应该要设置false,为什么要设置false,这里不做讨论
buffered: false
# 存在日志文件夹下
directory: logs
# 放置文件拼接的文件名
file-date-format: .yyyy-MM-dd
# 格式化格式
pattern: "%{yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss.SSS}t %h %A %l %user \"%r\" %s %b %D"
# 文件名前缀
prefix: access
# 文件名后缀
suffix: .log
# 是否推迟文件名中包含时间戳,知道轮换时间;意思就是先不在文件名上加时间,知道日志做分割的时候在做;
rename-on-rotate: false
# 请求是否带上request的请求属性,比如ip,端口,主机名等
request-attributes-enabled: true
# 是否启用日志分割; 未看到按照日志文件大小分割。这里应该按照时间来分割。随时间进行新建文件
# 设置为true,比如今天是access.2023-06-14.log 明天就是access.2023-06-15.log;
# 设置为false,那么就只会有一个文件
rotate: true
# 在Servlet.getAttribute("token"),存在的时候才输出日志, 这里不在输出,一般应该不会选择这个。
condition-if: token
# 删除日志保留文件前N天的accesslog日志,-1,不删除; 默认不删除
max-days: -1
# 检查日志文件是否存在,要是存在,是否重建;设置true就重建;设置false就不重建。
check-exists: false
五、SpringBoot的Tomcat的优化建议
从第四章的tomcat配置了解到
能接收到连接数是通过server.tomcat.max-connections和accept-count来控制;
而处理这些连接线程控制是:server.tomcat.max-threads 和 server.tomcat.min-spare-threads
总结:
假设1:把连接数max-connections和accept-count设置过大;但是线程数max-threads不变情况;
但是功能可能处理过慢,线程数处理连接就过慢(硬件资源等问题)所以连接就会积压;要是连接上限触发connection-timeout;假设1:连接数设置过大,线程数处理不过来;第一:这里的线程数跟硬件资源;比如cpu。第二:跟代码程序原因;
假设2:把连接数max-connections和accept-count设置小;线程数设置大;
如果请求量大,所以就会触发连接数上限后,就触发连接拒绝;所以支撑不了更多的请求量。
总结:
1、设置最小工作线程:
最小工作线程:server.tomcat.min-spare-threads
这个本上是跟硬件资源有关,比如多少核,算力更快;4核,8核的;都不一样;所以这里建议是不做变更或者设置到10-50之间即可
2、设置最大线程数:
最大工作线程:server.tomcat.max-threads
这个跟上面的也是一样的意思;一般都是跟硬件和代码本身相关;比如程序需要耗费很多cpu资源等;需要很多算力的资源;所以这里就不能设置过大,一般是server.tomcat.min-spare-threads 的20倍左右,也就是在200-1000的左右。
3、设置最大连接数:
这个就没什么可讲的,一般现在做分布式集群服务,基本很满足业务;默认即可;
版权归原作者 wang1989cs 所有, 如有侵权,请联系我们删除。