
作者|Rickyの水果摊
时间|2022年6月27日
文章目录
实验目的
了解Linux系统,熟悉Linux常用命令
实验原理
1.Linux文件系统
Linux 文件系统是树状结构,系统中每个分区都是一个文件系统,都有自己的目录层。Linux 会将这些分属不同分区的、单独的文件系统按照树状的方式形成一个系统的总目录层次结构。目录提供了一个管理文件方便而有效的途径,最上层是根目录,其它所有目录都是从根目录出发而生成的,如下图所示。
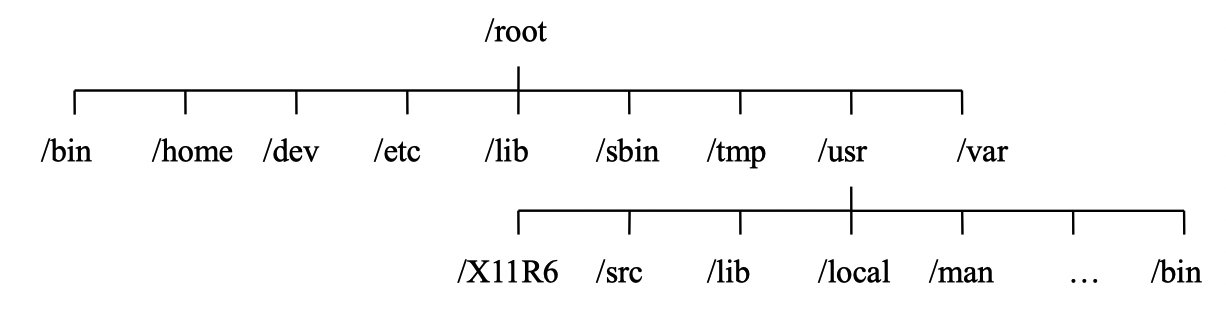
/root
:根目录,该目录下一般只存放目录,不存放文件。
/bin
:存放可执行二进制文件的目录,如常用命令
ls
、
mv
、
cat
等。
/home
:为用户设置的目录,如用户 user 的主目录就是
/home/user
/dev
:系统硬件设备目录(device)。Linux系统所有的硬件都通过文件表示,访问该目录下某个文件,相当于访问某个设备,比如
/dev/cdrom
是光驱。
/etc
:存放系统配置文件的目录,比如:
/ect/passwd
用于存储用户信息的文件。
/lib
:存放根文件系统程序运行所需要的共享库及内核模块。共享库又叫作动态链接共享库,作用类似Windows里的.dll文件,存放了根文件系统程序运行所需的共享文件。
/sbin
:放置系统管理员使用的可执行命令, 如
fdisk
、
shutdown
等。与/bin 不同的是,这几个目录是给系统管理员 root 使用的命令,一般用户只能"查看"而不能设置和使用。
/tmp
:临时文件目录,用于存放各种临时文件,是公用的临时文件存储点,系统重启后不会被保存。
/usr
:应用程序存放目录(unix system resource),
/usr/bin
存放应用程序,
/usr/share
存放共享数据,
/usr/lib
存放一些函数库文件等。
/var
:存放运行时需要改变数据的文件, 如随时更改的日志文件
/var/log
。
/mnt
:系统管理员安装临时文件系统的安装点,系统提供这个目录是让用户临时挂载其他的文件系统。
/boot
:放置 Linux 系统启动时用到的一些文件,如Linux 的内核文件、引导程序等。
/opt
:给主机额外安装软件所摆放的目录。
/proc
:内存映射目录,该目录可以查看系统的相关信息。操作系统运行时,进程信息及内核信息(比如cpu、硬盘分区、内存信息等)存放在这里。
2.Linux存储位置
- /bin
- /sbin
- /usr/bin
- /usr/sbin
常用命令存放位置
头文件存放位置
3.Linux常用命令
路径
pwd#print work/current directoryls#list filescd[directory_path]#enter directory_pathcd..#back to previous directorycd ~ #back to home directorycd / #back to root directoryexit#exit bash
目录
mkdir[new_directory]#create new_folder in work directoryrm-ri[directory_name]#remove directory with interactionrm-rf[directory_name]#remove directory without interactionrmdir[empty_directory]#remove empty_directory(not recommended)
文件
touch new.txt #create new.txt in work directoryecho"hello"> new.txt #create new.txt with content "hello"echo"world">> new.txt #append "world" to new.txtcat test.txt #show the content of test.txtcat> test.txt #create test.txt with new_content
new_content
⌃+D
cat>> test.txt #append new content to test.txt
new_content
⌃+D
vi test.txt #open "vi" to modify test.txtvim test.txt #open "vim" to modify test.txt
实验内容
1. Linux常用命令实践
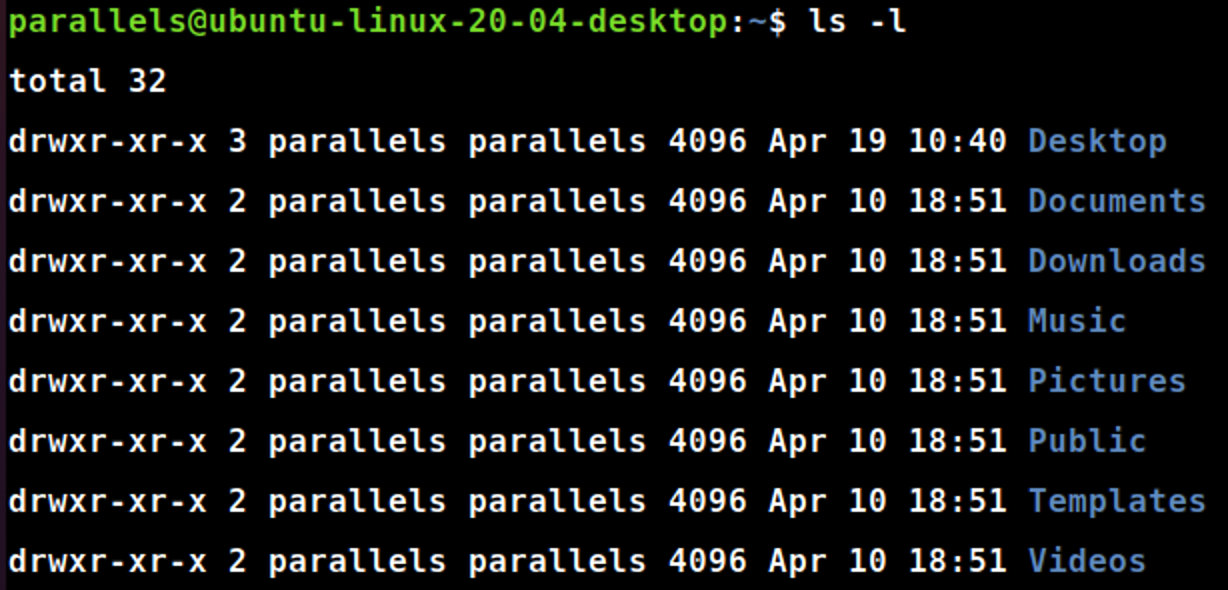
1.1 ls命令
ls → list directory contents
ls
ls

ls -l
ls-l#以长格式列出文件的详细信息
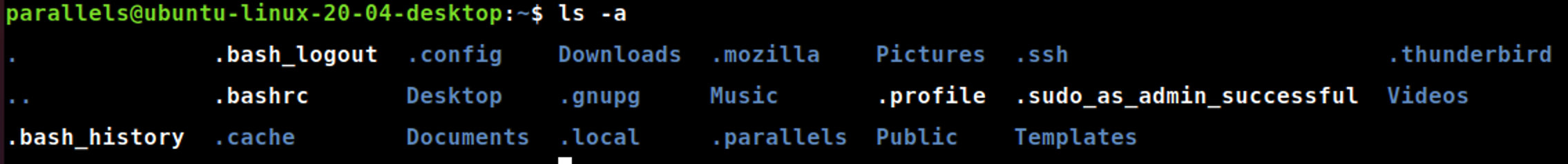
ls -a
ls-a#列出目录下的所有文件,包括以.开头的隐藏文件。
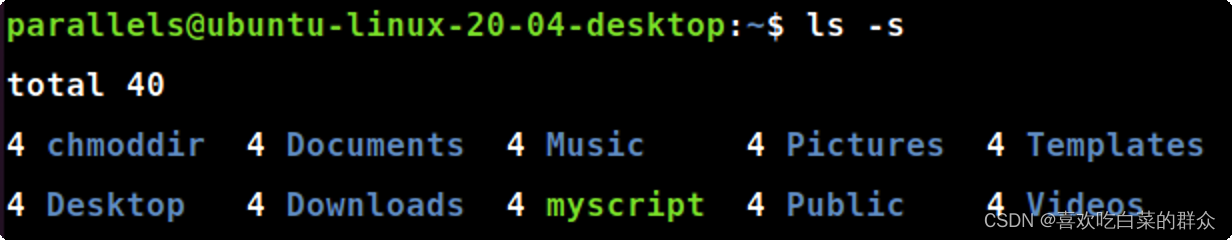
ls -s
ls-s#在每个文件名后输出该文件的大小。
1.2 cat命令
cat → concatenate and print files
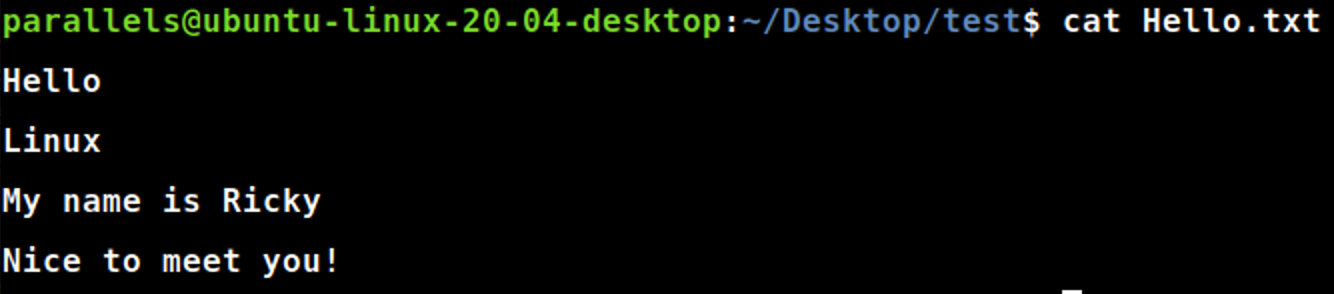
cat
cat file_name.txt #显示输出文档的内容
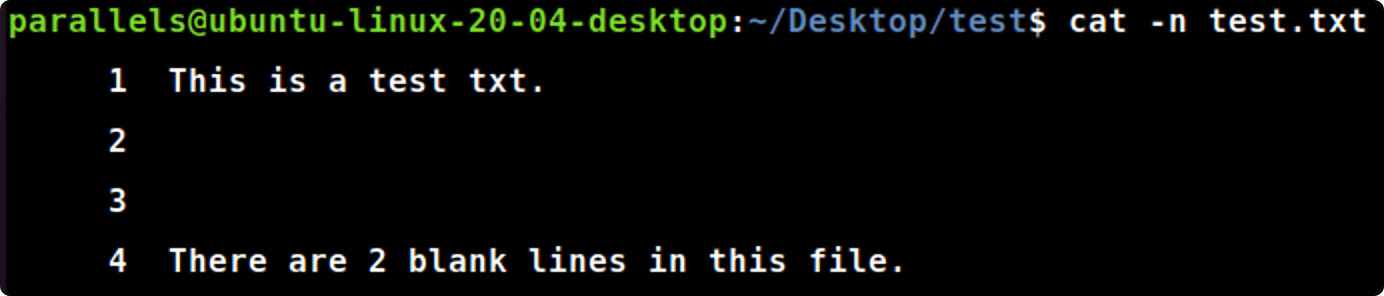
cat -n
cat-n file_name.txt #显示输出文档时,对输出文档的行数进行编号,从1开始
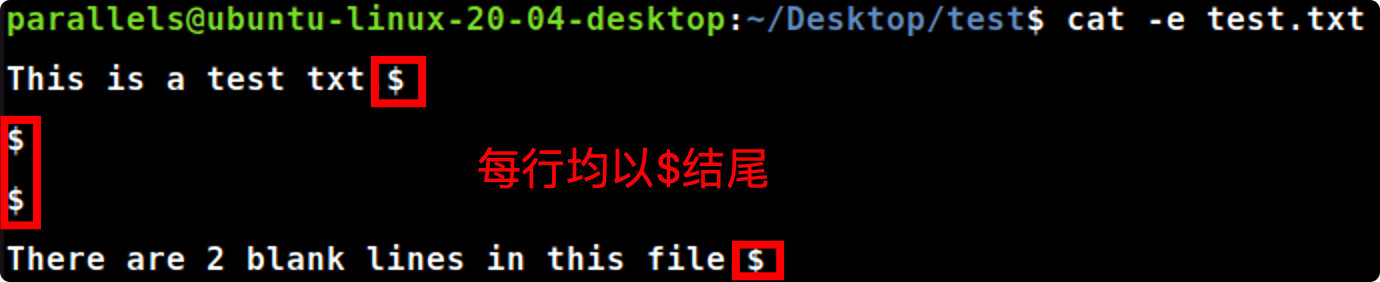
cat -b
cat-b file_name.txt #显示输出文档时,对输出文档的非空行数进行编号,从1开始
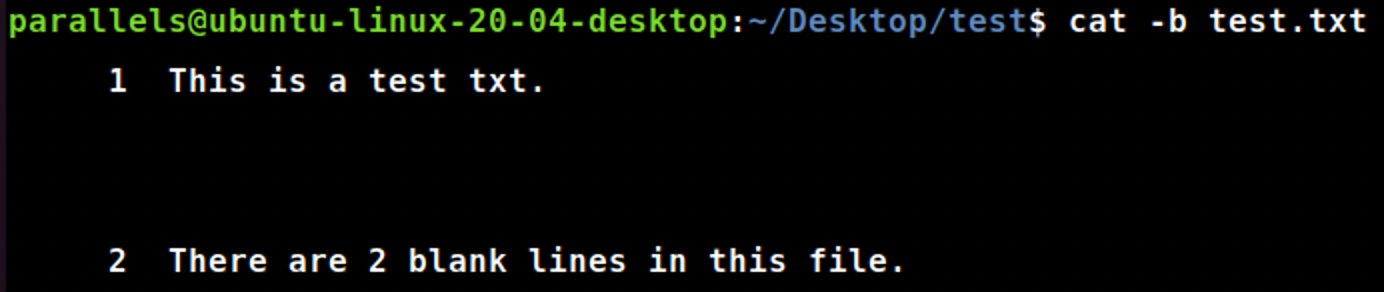
cat -s
cat-s file_name.txt #显示输出文档时,将输出文档的多行空格显示为一行空格
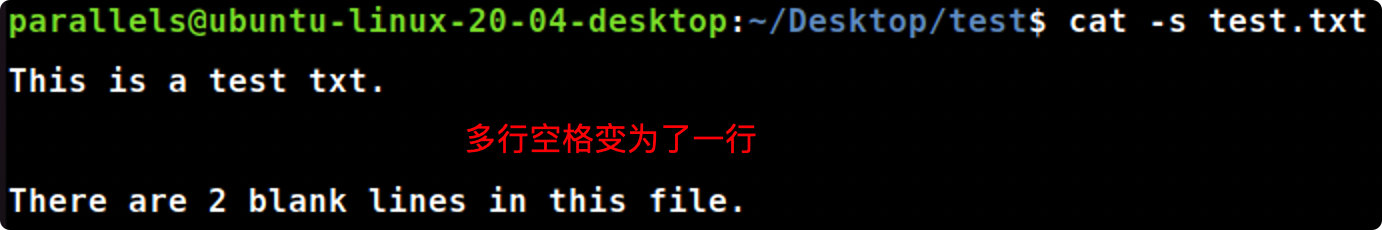
cat -e
cat-e file_name.txt #显示输出文档时,在每行结束处显示$
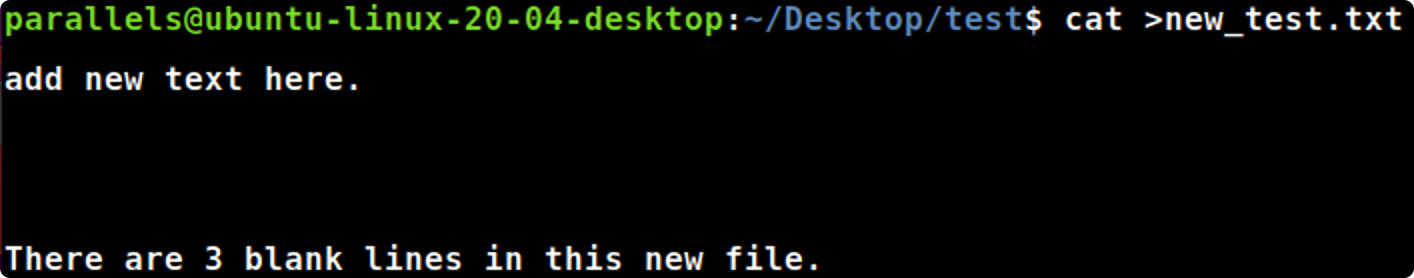
cat >
cat>new_test.txt #创建空白的new_test.txt文件,并且写入下面内容add new text here.
There are 3 blank lines in this new file.
#输入control+D来结束输入
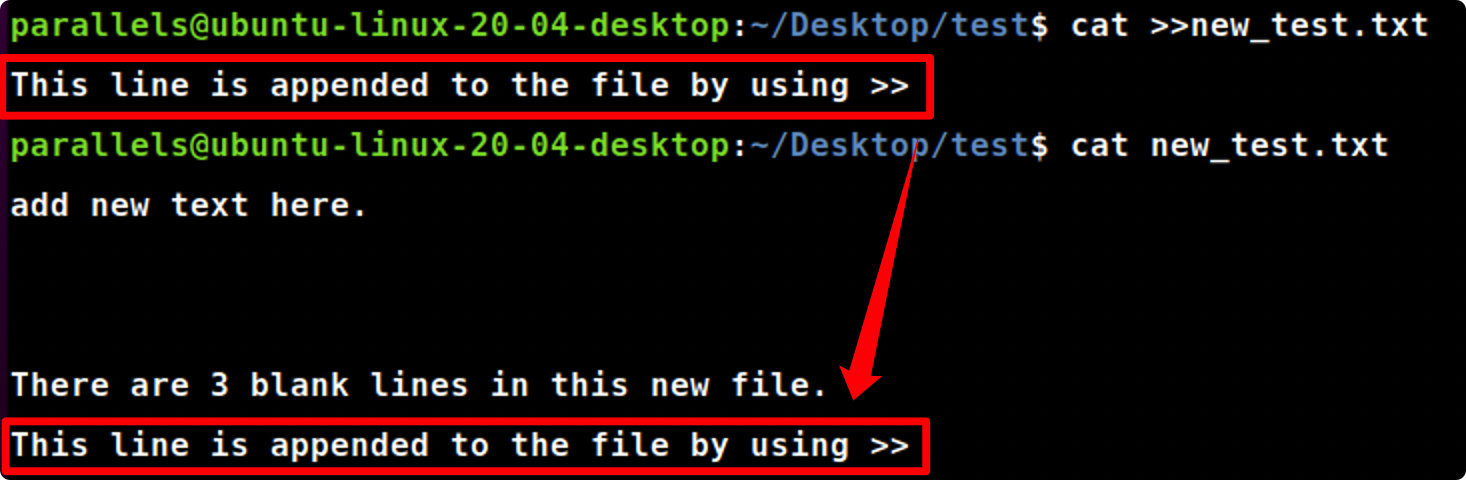
cat >>
cat>>new_test.txt #向new_test.txt文件中追加内容
This line is appended to the file by using >>#输入control+D来结束输入
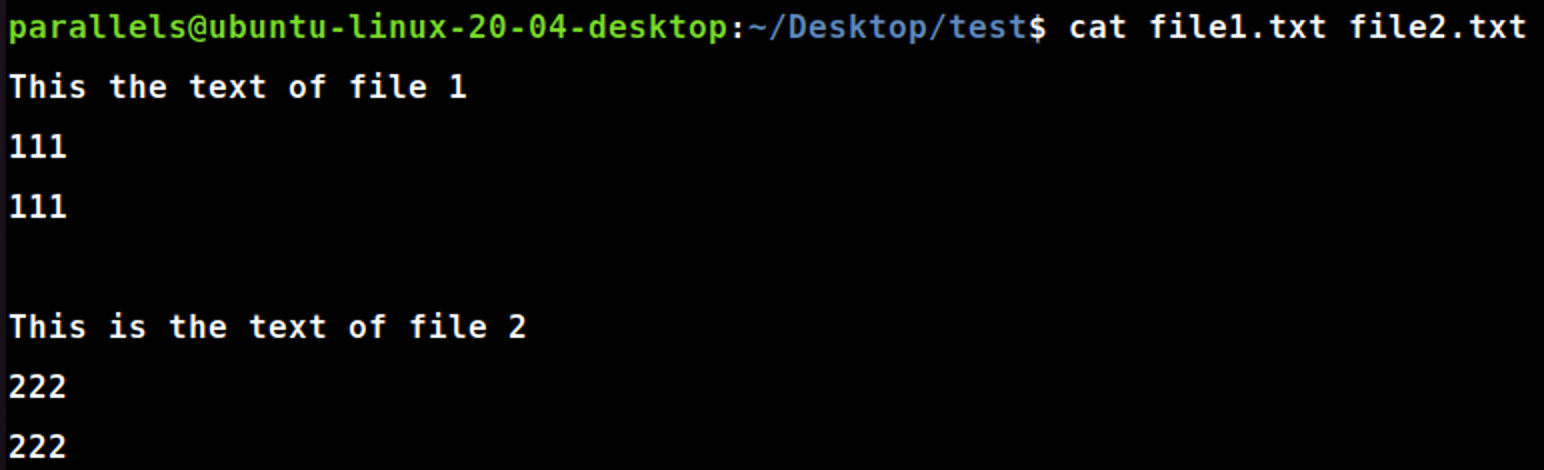
cat [file1] [file2]
cat file1.txt file2.txt #将file1与file2内容连接起来并显示(不改变原file1,file2内容)
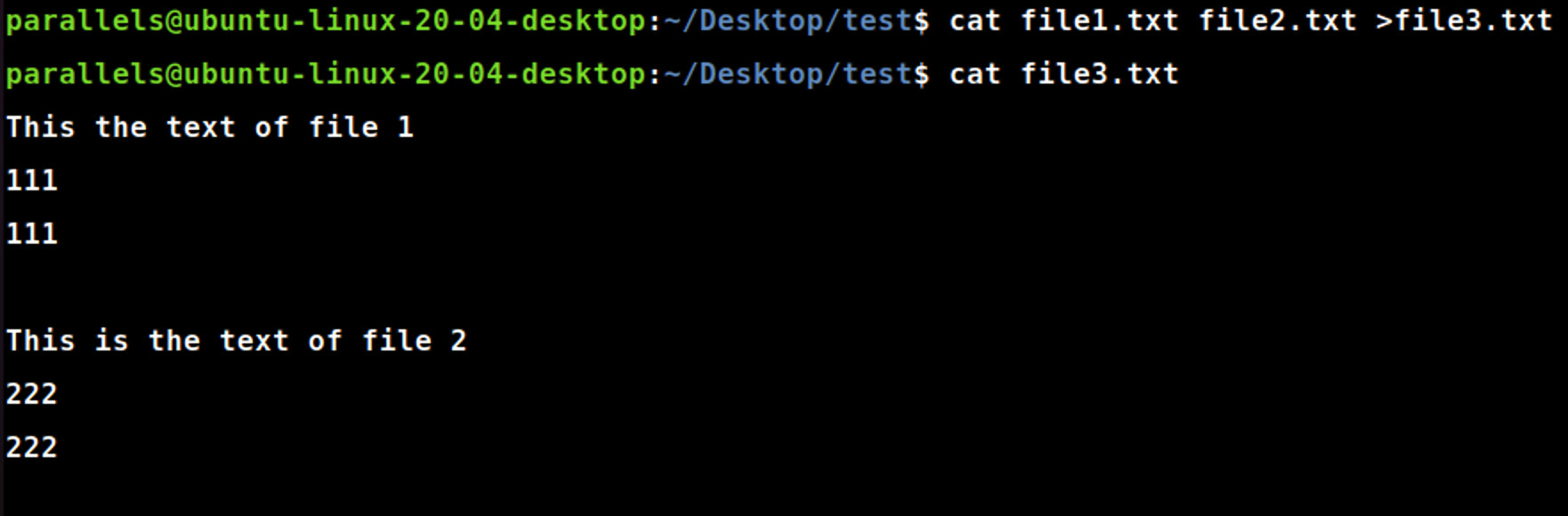
cat [file1] [file2] >[file3]
cat file1.txt file2.txt >file3.txt #创建file3,将file1与file2内容连接起来并且写入file3中
1.3 chmod命令
chmod → change file mode bits
ll [file]
ll file1.txt #查看指定文档的权限
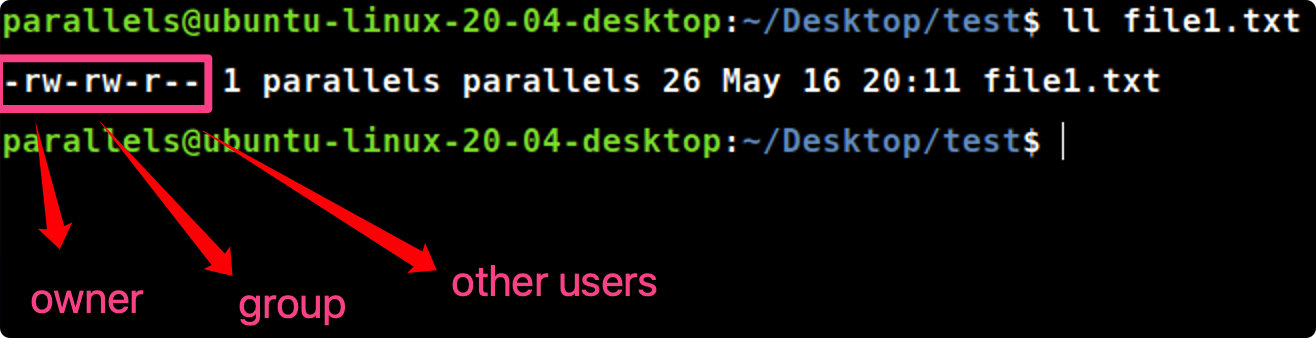
chmod [user_type] [+/-] [r/w/x] [file]
chmod u-w file1.txt #删除owner的写入权限
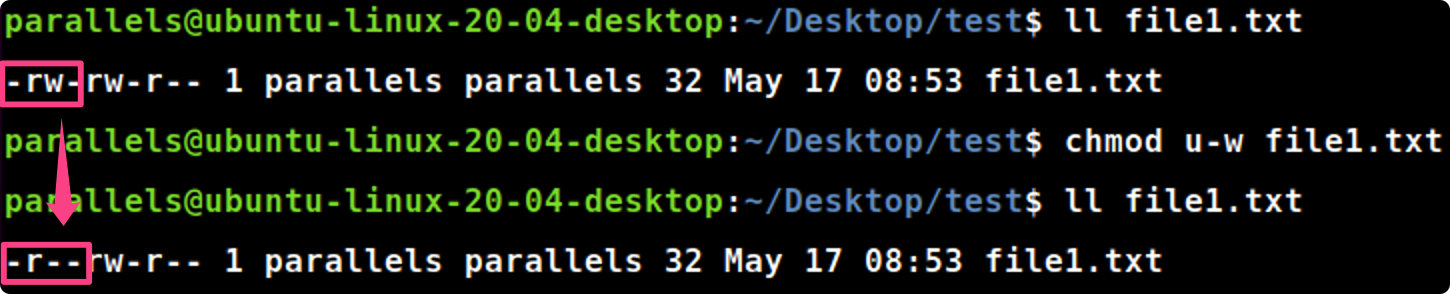
chmod-w file1.txt #删除file1.txt的写入权限chmod +w file1.txt #添加file1.txt的写入权限
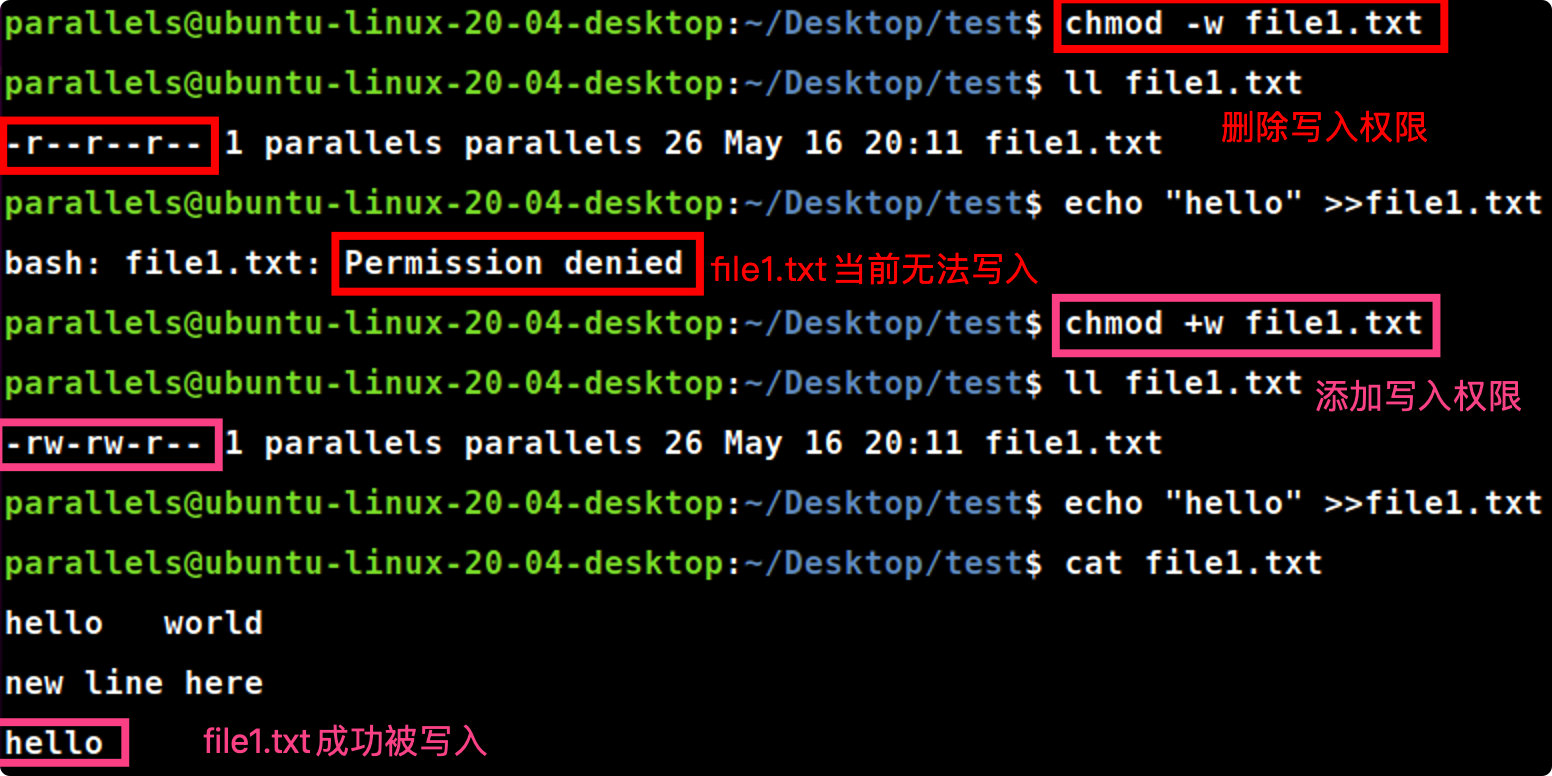
用户类型
who用户类型说明uowner文件所有者ggroup文件所有者所在组oother users所有其他用户aall所有用户,相当于ugo
Linux/Unix的文件调用权限分为三级 : 文件所有者(Owner)、用户组(Group)、其它用户(Other Users)
操作符号
Operator说明+添加指定用户类型的权限-删除指定用户类型的权限=设置指定用户权限的设置,即将用户类型的所有权限重新设置
权限符号
operator说明r读取w写入x执行
1.4 cp命令
cp → copy files or directories
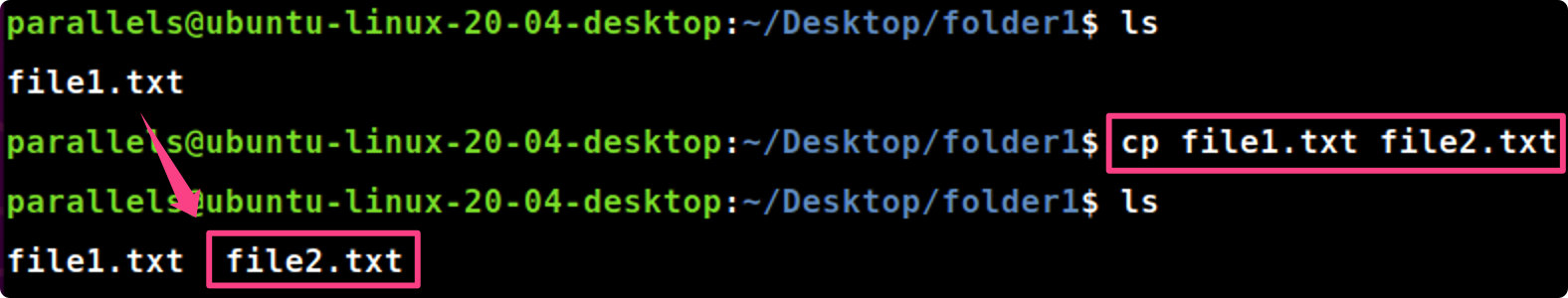
cp [file1] [file2]
cp file1.txt file2.txt #将file1.txt复制到file2.txt
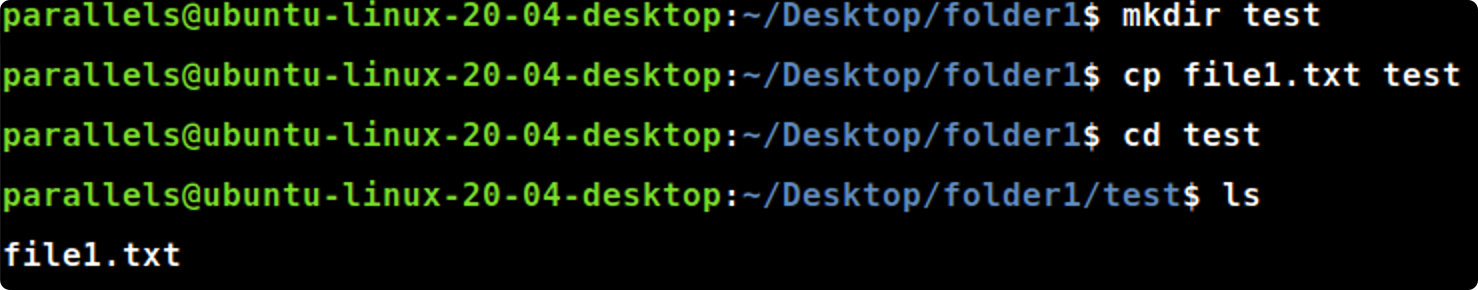
cp [file] [folder]
cp file1.txt test#将file1.txt复制到test文件夹中
1.5 mv命令
mv → move(rename) files
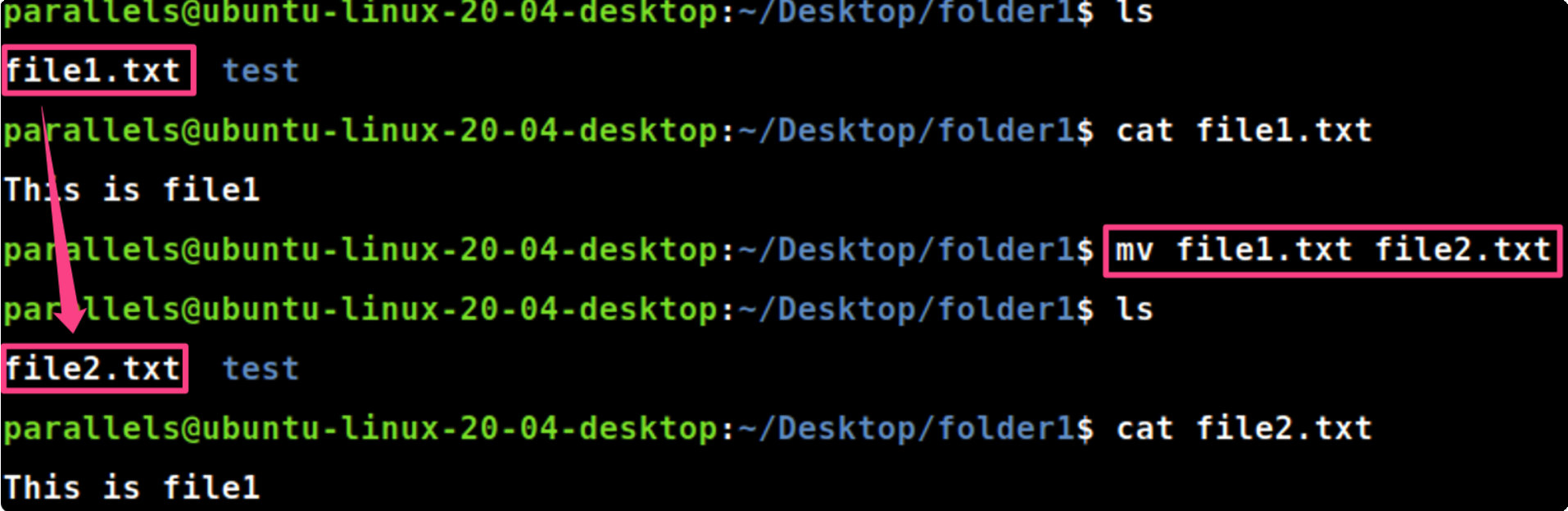
mv [file1] [file2]
mv file1.txt file2.txt #将当前目录下的文件 file1 更名为 file2
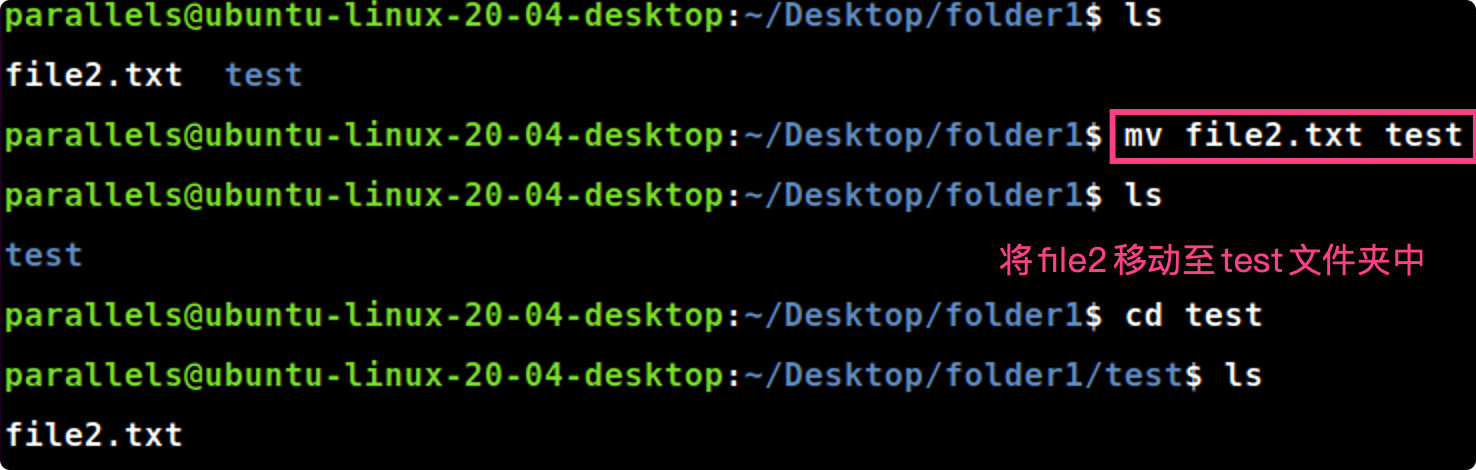
mv [file] [folder]
mv file2.txt test#将file2.txt移动至同一目录下的test文件夹中
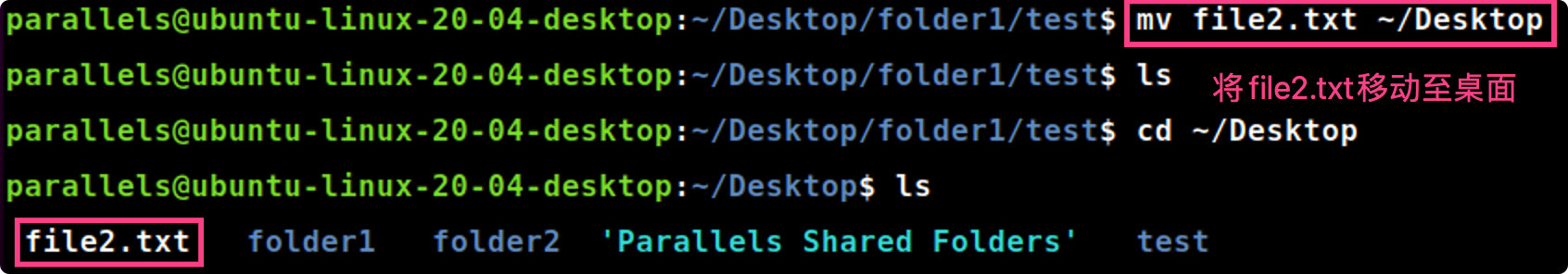
mv file2.txt ~/Desktop #将file2.txt移动至桌面
mv [file] ..
mv file1.txt ..#将file1.txt移动至上一级目录中
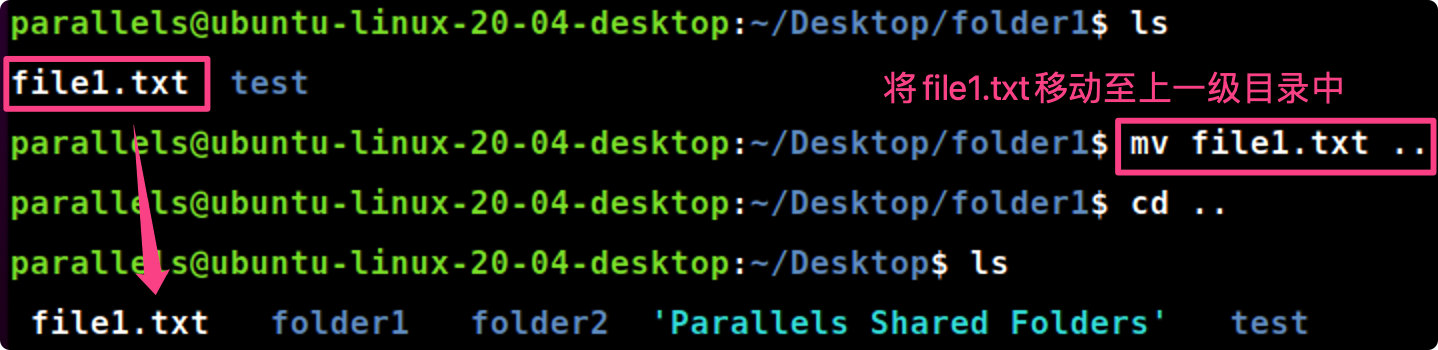
1.6 rm命令
rm → remove files or directories
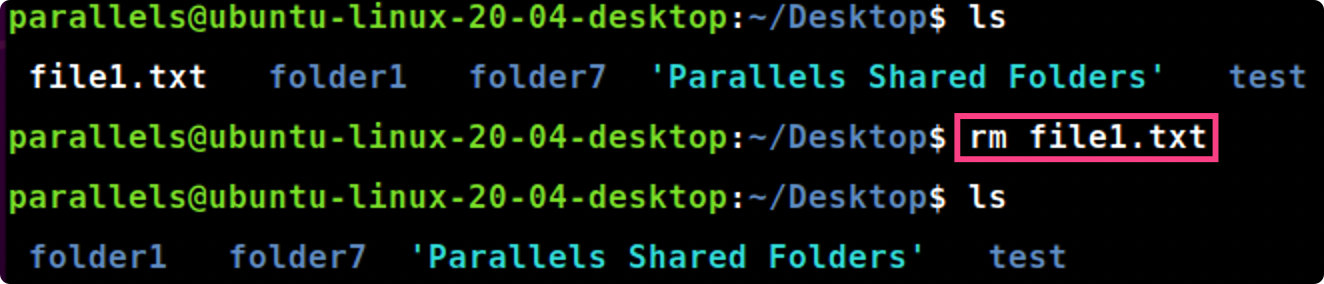
rm [file]
rm file1.txt #删除file1.txt
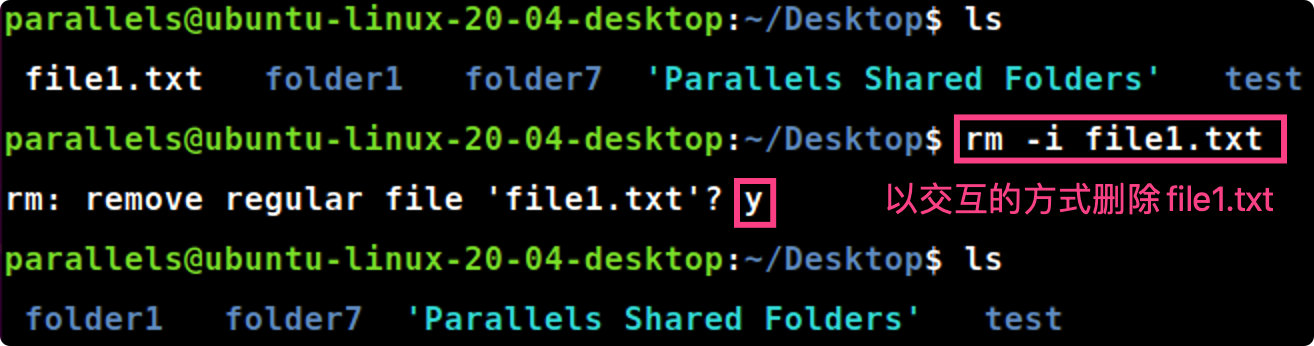
rm -i [file]
rm-i file1.txt #以交互的方式删除file1.txt
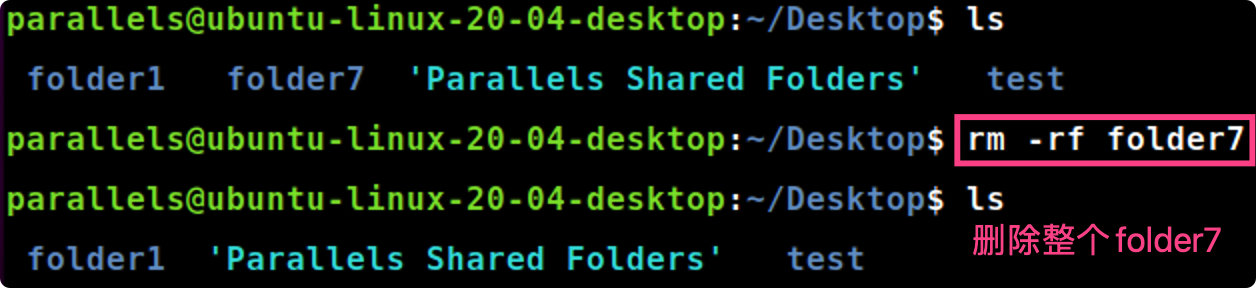
rm -rf [folder]
rm-rf folder7 #删除整个folder7目录,无交互
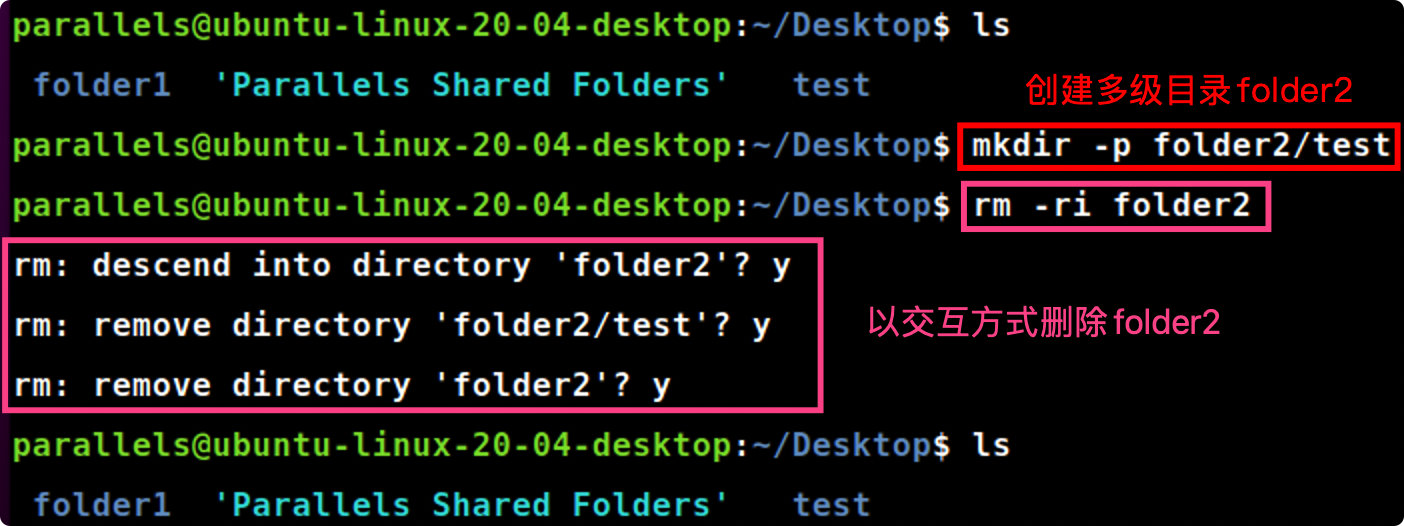
rm -ri [folder]
rm-ri folder2 #删除整个folder7目录,有交互
1.7 mkdir命令
mk → make directories
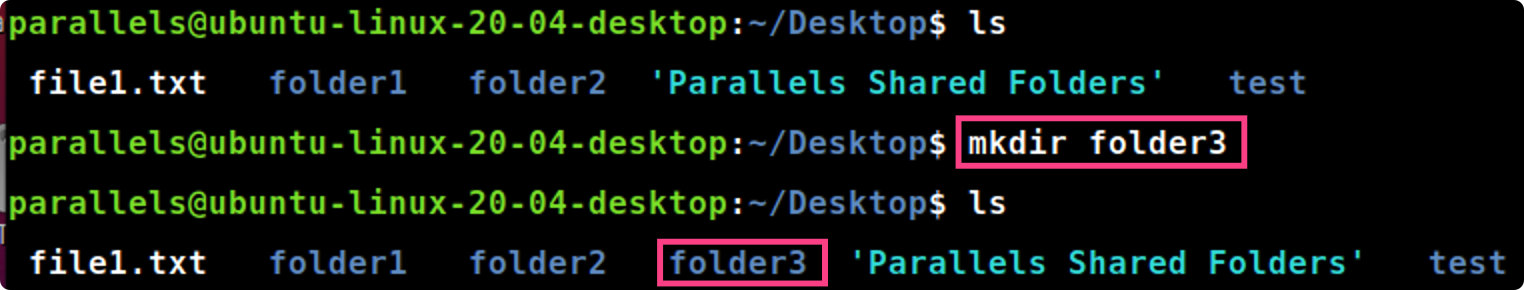
mkdir [folder]
mkdir folder #在当前工作目录中创建新的目录folder
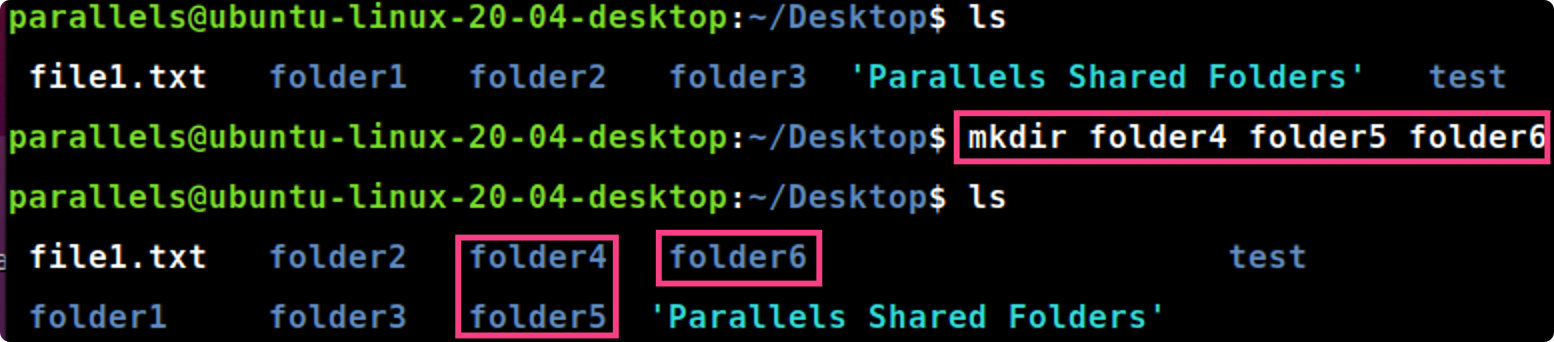
mkdir [folder1 folder2 folder3]
mkdir folder4 folder5 folder6 #在当前工作目录中创建新的目录folder
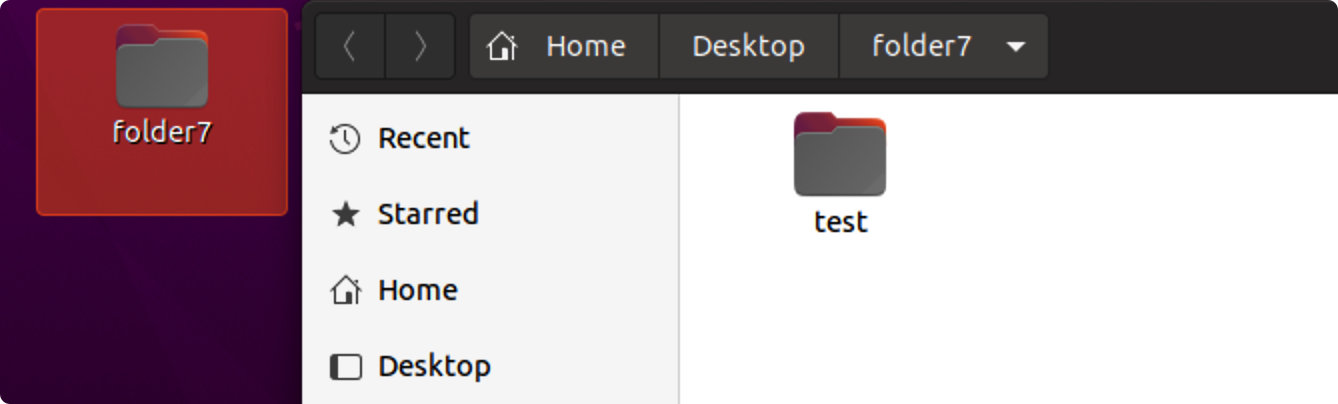
mkdir -p [folder/subfolder]
mkdir-p folder7/test #在当前工作目录中创建带有子目录的目录
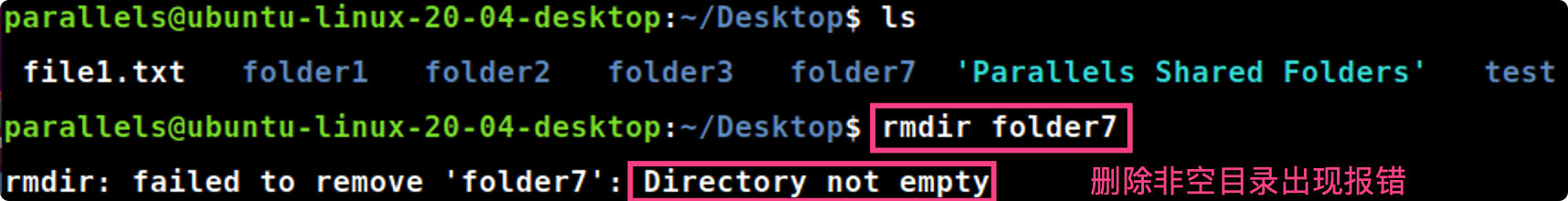
1.8 rmdir命令
rmdir → remove empty directories
rmdir [folder]
rmdir folder6 folder5 folder4 #删除空目录folder6/5/4
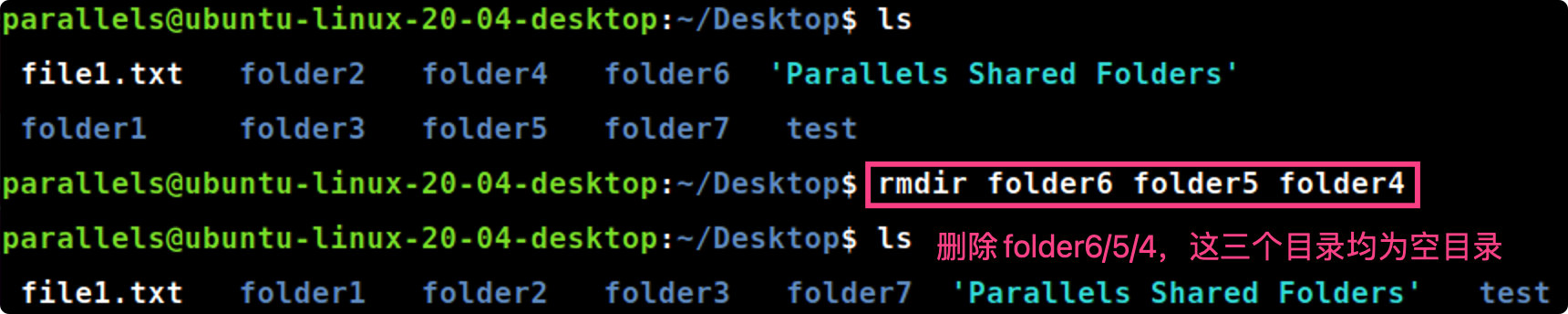
注意点:rmdir命令仅支持删除空目录,若选择的目录是非空目录,则会报错。
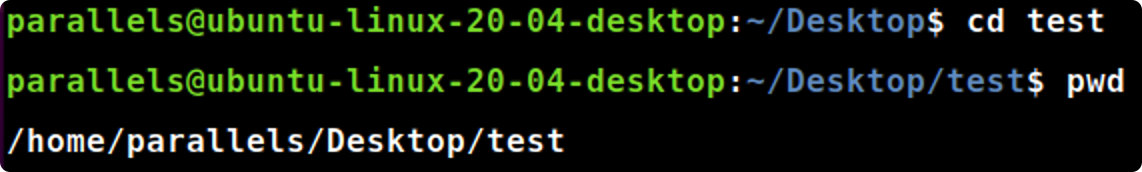
1.9 cd命令
cd [directory]
cdtest#切换至指定目录
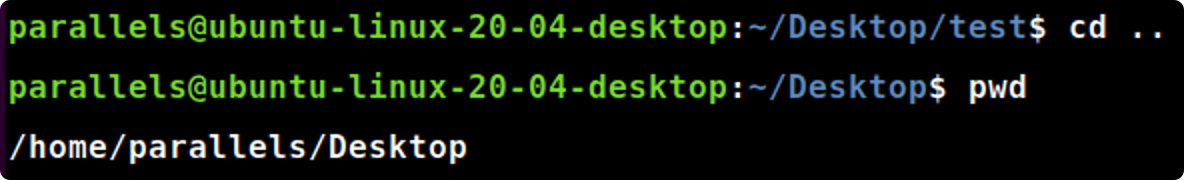
cd ..
cd..#返回上一级目录
cd ~
cd ~ #进入用户主目录
cd /
cd / #进入根目录
1.10 pwd命令
pwd → print name of current/working directory
pwd
pwd#显示当前工作目录的绝对路径

2. Linux其他命令实践
2.1 date命令
date → print or set the system date and time
date
date#显示当前日期信息

2.2 echo命令
echo → display a line of text
echo
echo"hello\tworld"#显示字符串,一般起到提示的作用

echo -e
echo-e"hello\tworld"#显示字符串,转义字符生效

echo -n
echo-n"hello\tworld"#显示字符串,结尾不换行

echo string > file1
echo-e"hello\tworld">file1.txt #将"hello world"覆盖至file1.txt中
echo string >> file1
echo-e"hello\tworld">>file1.txt #将"hello world"追加至file1.txt中
echo “\033[xxm……\033[0m”
echo-e"\033[33mhello\tworld\033[0m"#显示彩色字体

#彩色字体参数表\033[30m 黑色字 \033[0m
\033[31m 红色字 \033[0m
\033[32m 绿色字 \033[0m
\033[33m 黄色字 \033[0m
\033[34m 蓝色字 \033[0m
\033[35m 紫色字 \033[0m
\033[36m 天蓝字 \033[0m
\033[37m 白色字 \033[0m
\033[40;37m 黑底白字 \033[0m
\033[41;37m 红底白字 \033[0m
\033[42;37m 绿底白字 \033[0m
\033[43;37m 黄底白字 \033[0m
\033[44;37m 蓝底白字 \033[0m
\033[45;37m 紫底白字 \033[0m
\033[46;37m 天蓝底白字 \033[0m
\033[47;30m 白底黑字 \033[0m
2.3 cal命令
cal → calendar
cal
cal#显示当前月份日历
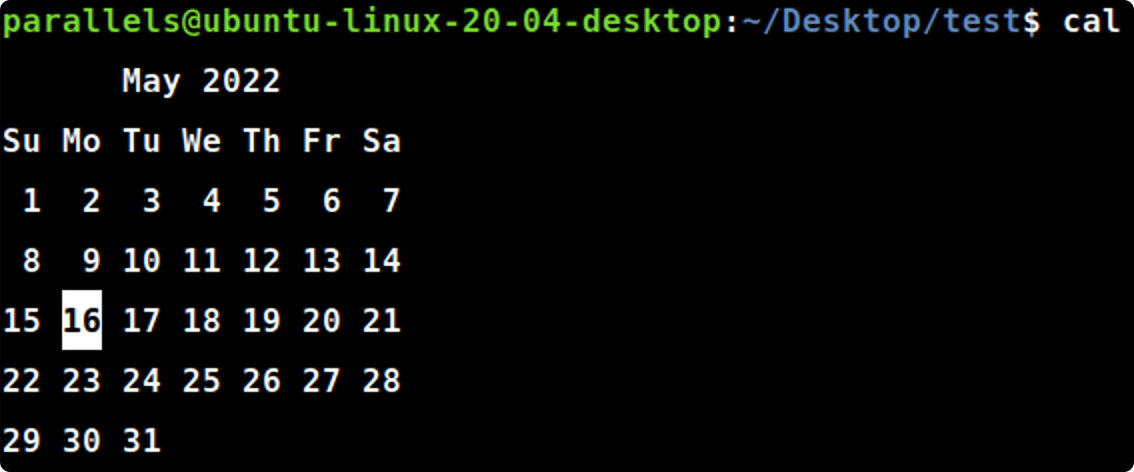
cal month year
cal102022#显示指定月份日历
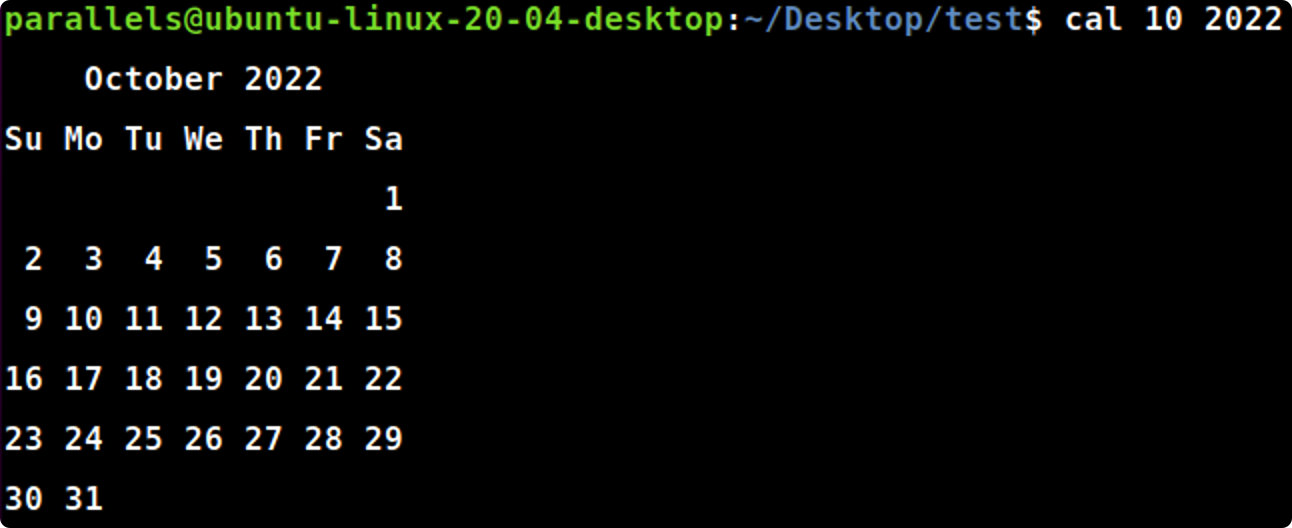
cal -j
cal-j#显示自1月1日起的总天数
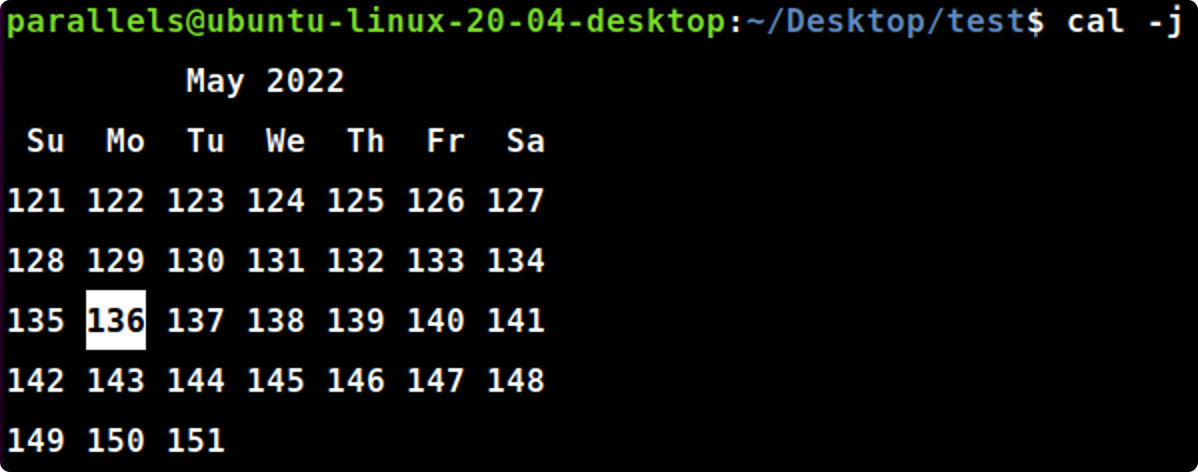
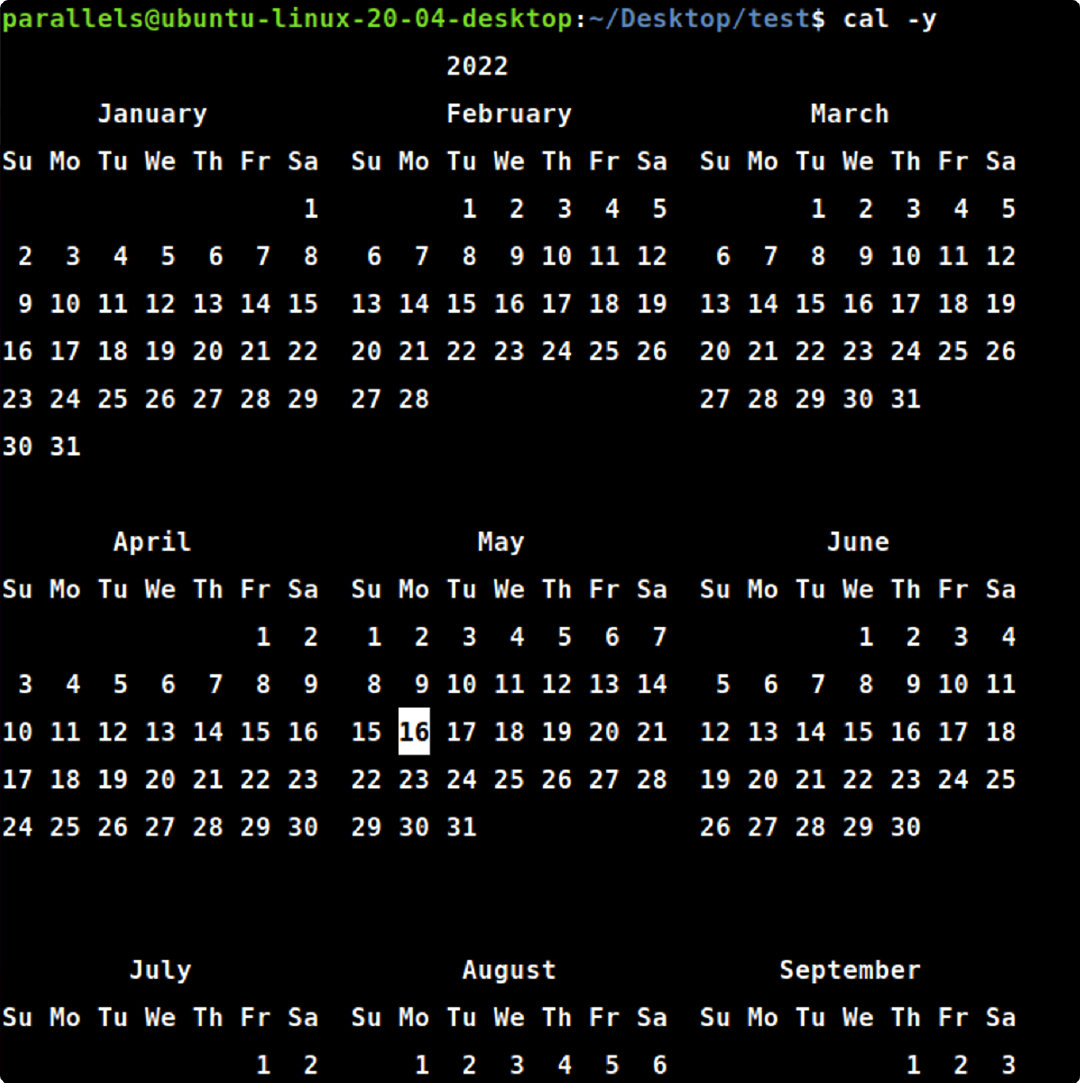
cal -y
cal-y#显示当前年历
2.4 clear命令
clear → clear the terminal screen
clear
clear#使终端显示页向后翻一页,实现清屏
2.5 ps命令
ps → report a snapshot of the current processes
ps -l
ps-l#较长、较详细的将属于本次登入用户的进程列出来
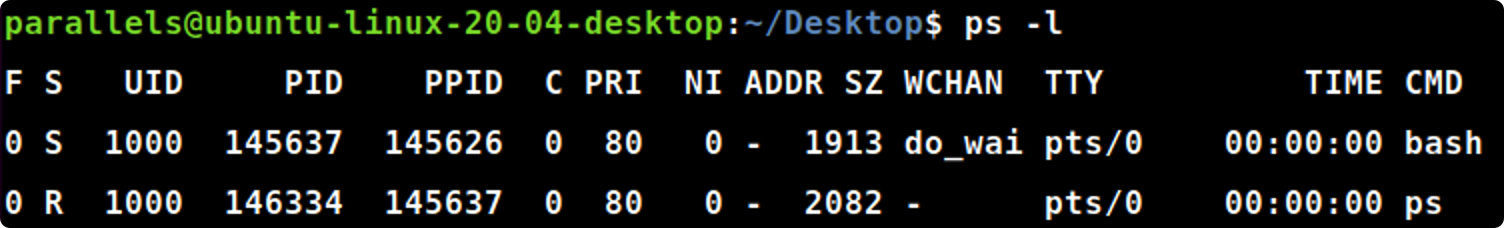
各个表头的含义为:
- F:代表这个进程的flag,如果是4,则代表使用者为 super user
- S:代表这个进程的状态stat
- UID:代表执行者的userId
- PID:进程的id
- PPID:父进程的id
- C:占用CPU资源的百分比
- PRI:指进程的执行优先级(Priority的简写),其值越小越早被执行
- NI:代表进程的nice值,其表示进程可被执行的优先级的修正数值
- ADDR:代表进程的地址,它指出该进程在内存的哪个部分,如果是个正在运行的程序,一般都是"-"
- SZ:占用的内存大小
- WCHAN:判断当前进程是否正在运行,若为"-",则代表正在运行;若该进程处于休眠状态,该值就是它在内核中的地址
- TTY:该进程是在那个终端机上面运行,若与终端机无关,则显示?,另外,tty1-tty6 是本机上面的登入者程序,若为 pts/0 等等的,则表示为由网络连接进主机的程序。
- TIME:占用CPU的时间
- CMD:所下达的指令名称
ps -aux
ps-aux#显示后台运行的进程
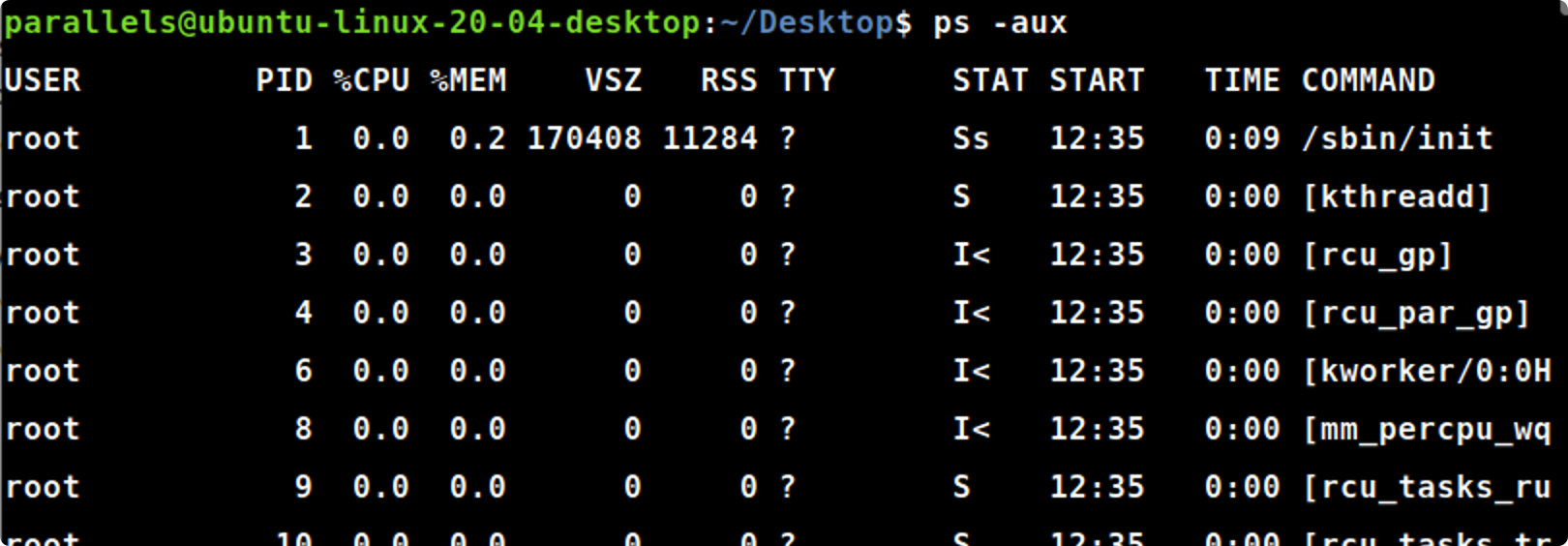
各个表头的含义为:
- USER:表示该进程属于哪个用户
- PID:进程id
- %CPU:该进程占用CPU资源的百分比
- %MEM:该进程占用内存的百分比
- VSZ:该进程使用掉的虚拟内存量 (Kbytes)
- RSS:该进程占用的固定的内存量 (Kbytes)
- TTY:该进程是在那个终端机上面运行,若与终端机无关,则显示?,另外,tty1-tty6 是本机上面的登入者程序,若为 pts/0 等等的,则表示为由网络连接进主机的程序。
- STAT:代表该进程目前的状态,主要的状态有: - R:该进程正在运行- S:该进程正在休眠,但可被某些信号(signal)唤醒- D:无法中断的休眠状态(通常为IO进程)- T:该进程已经停止- Z:僵死状态,该进程应该已经终止,但是其父进程却无法正常的终止它,造成zombie(疆尸)程序的状态- W:等待状态,等待内存的分配- <:高优先级的进程- N:低优先级的进程
- START:该进程被触发启动的时间
- COMMAND:该进程的实际指令
ps -u
ps-u#显示属于自己的进程
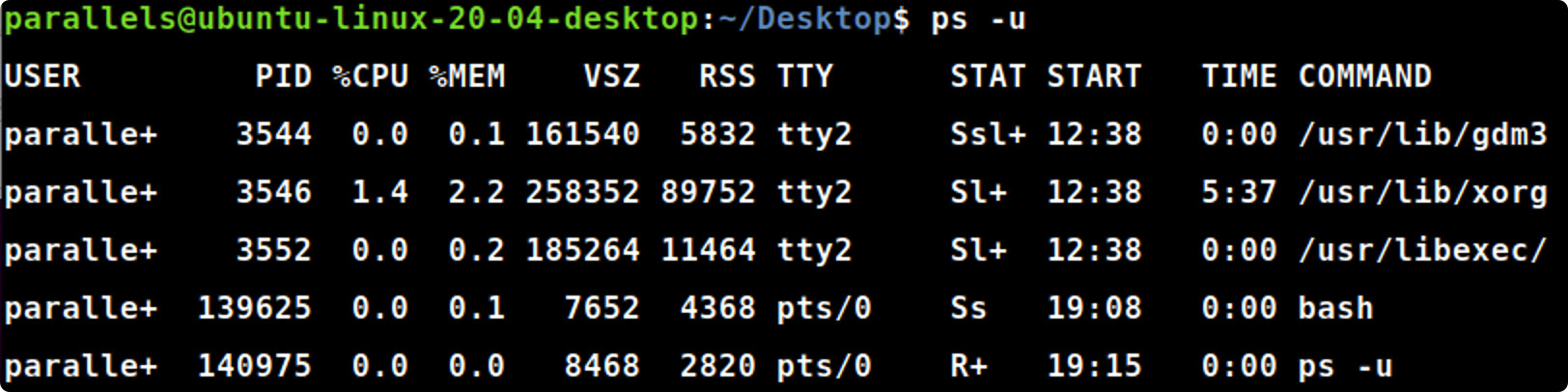
ps -ef | grep [xxx]
ps-ef|grepjava#查看指定进程,如关于java的进程

2.6 kill命令
kill → send a signal to a process
kill -l
kill-l#显示所有信号名称
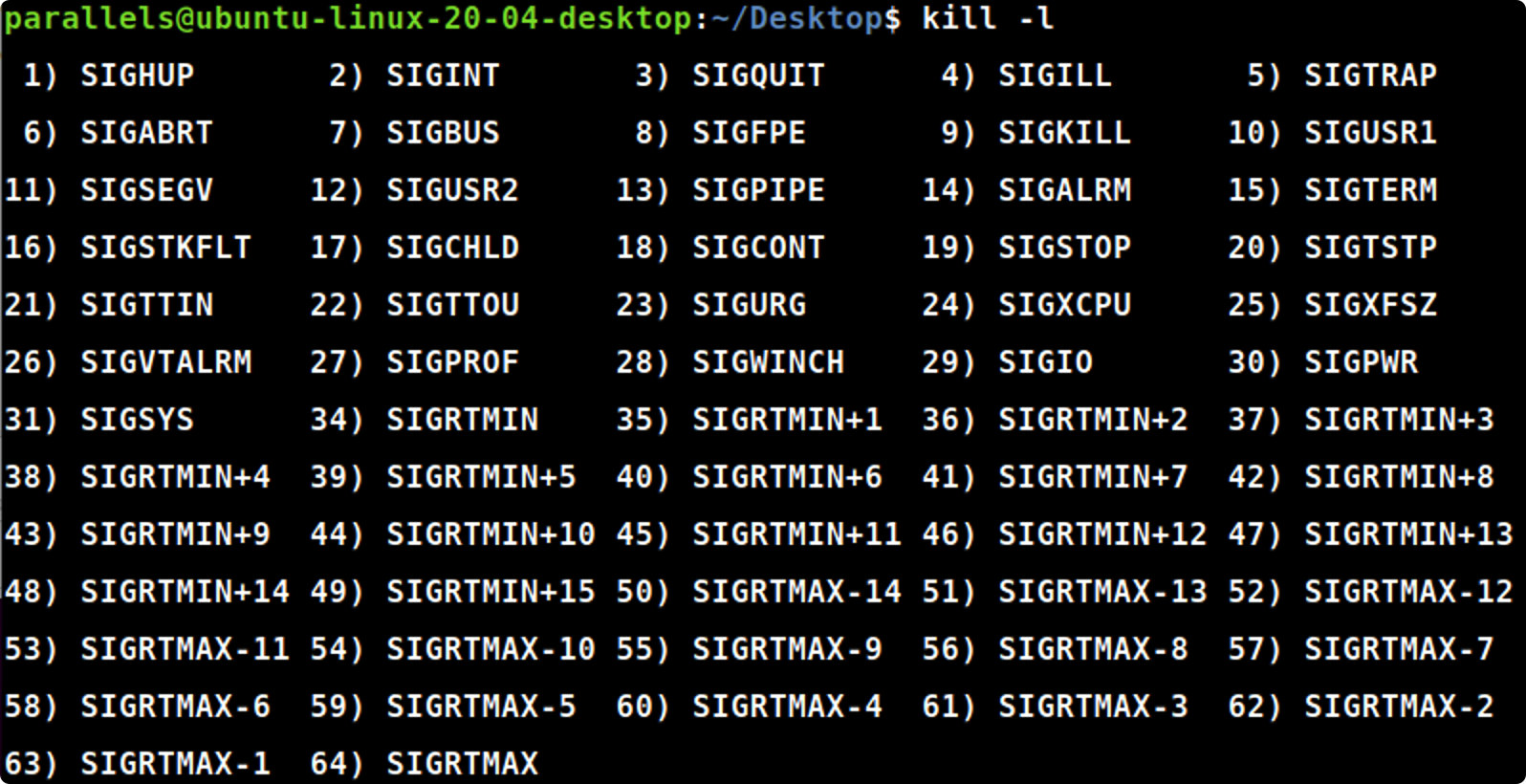
只有第9种信号 “强制退出” (SIGKILL)才可以无条件终止进程,其他信号进程都有权利忽略。
kill -9 [PID]
#先筛选出相关进程>ps-ef|grepjava
root 1693410 Feb25 ? 00:18:13 java-jar demo.jar
#彻底杀死该进程>kill-916934
2.7 who命令
who → show who is logged on
who
who#显示当前登录系统的用户
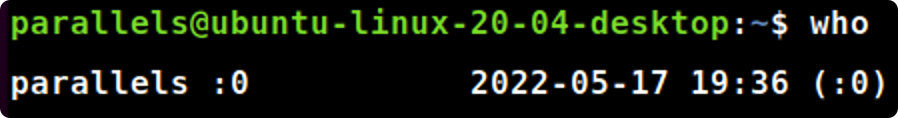
who --version
who--version#查看当前版本
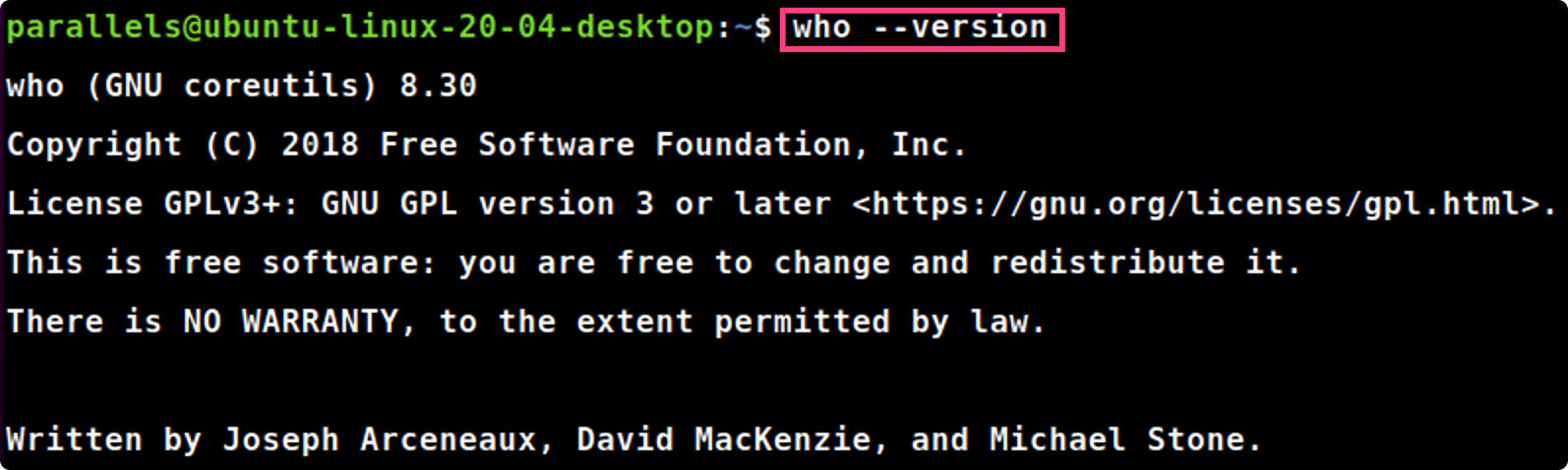
whoami
whoami#显示当前登录的用户名
2.8 reboot命令
reboot → halt, power-off or reboot the machine
reboot
reboot#重新启动计算机,它的使用权限是系统管理者。
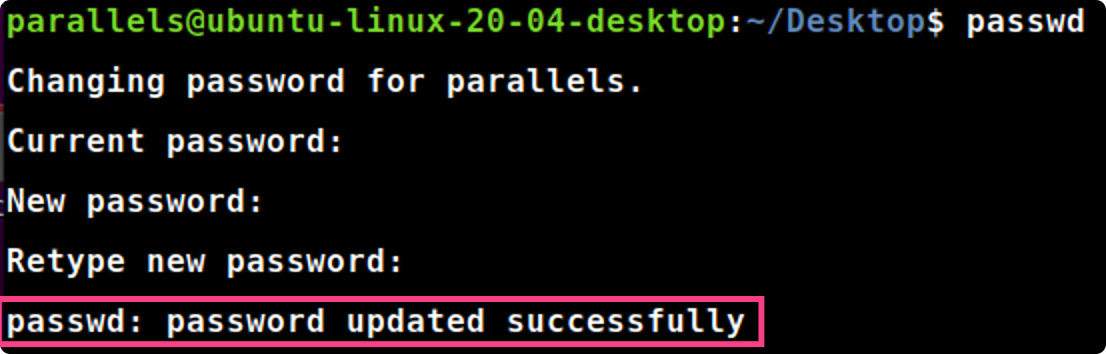
2.9 passwd命令
passwd → change user password
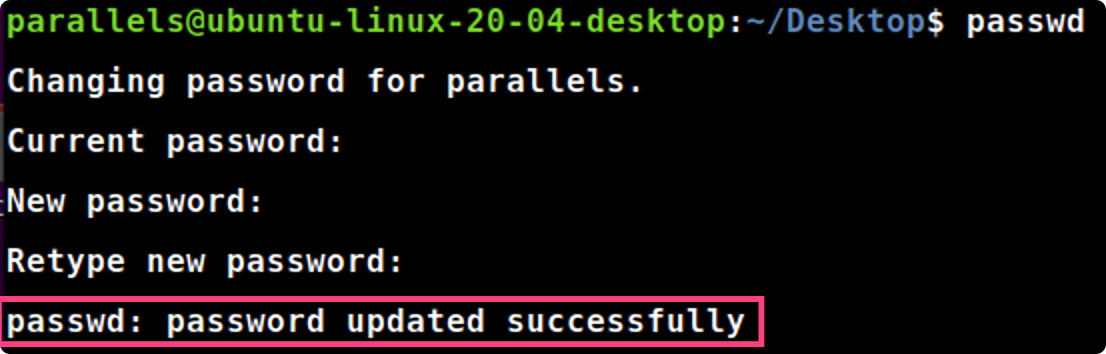
passwd
passwd#修改当前用户登陆密码
passwd -d [user]
passwd-d parallels #删除用户parallels的密码
2.10 su命令
su → run a command with substitute user and group ID
cat
>whoami #显示当前用户
ricky
>pwd #显示当前目录
/home/ricky
>su root #切换到root用户
密码:
>whoami #显示当前用户
root
2.11 man命令
man → an interface to the system reference manuals
man
manls#显示ls命令的使用指南
实验作业
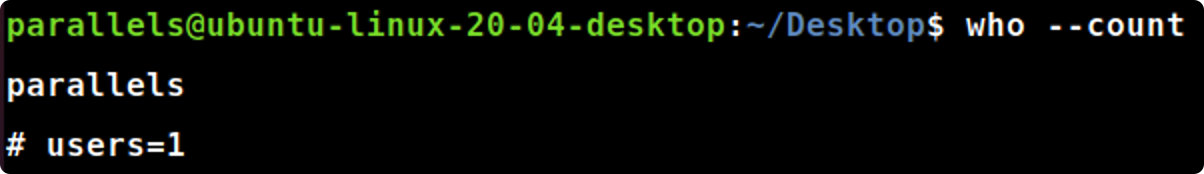
1.who 命令
- 有多少用户正在使用你的Linux系统?给出显示的结果
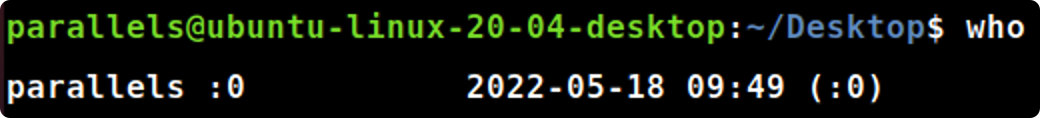
- 哪个用户登录的时间最长?给出该用户登录的时间和日期。
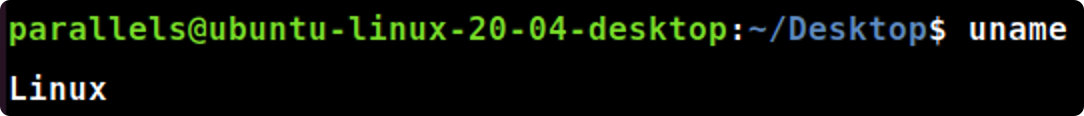
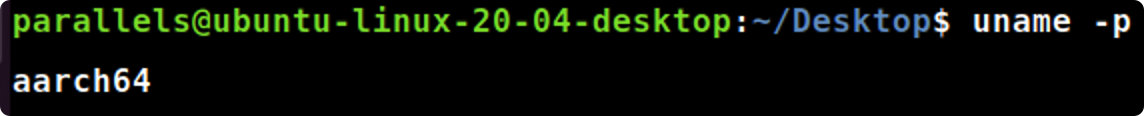
2.uname 命令
使用下面的命令显示有关你计算机系统信息:uname(显示操作系统的名称), uname –n(显示系统域名),uname –p(显示系统的CPU名称)
- 你的操作系统名字是什么?
- 你计算机系统的域名是什么?

- 你计算机系统的CPU名字是什么?
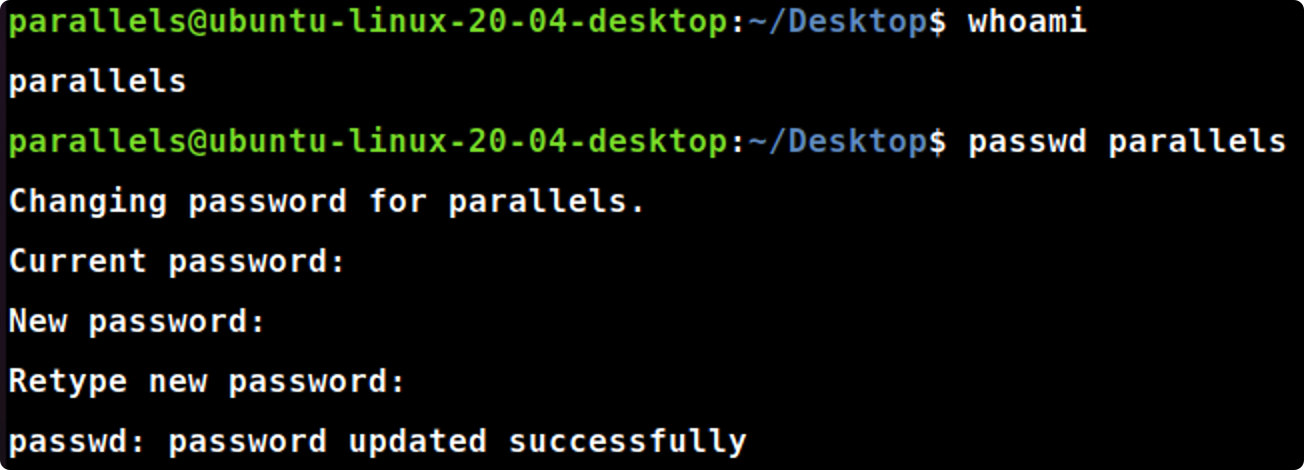
3.passwd命令
- 使用passwd命令修改你用whoami命令找到的用户的密码。
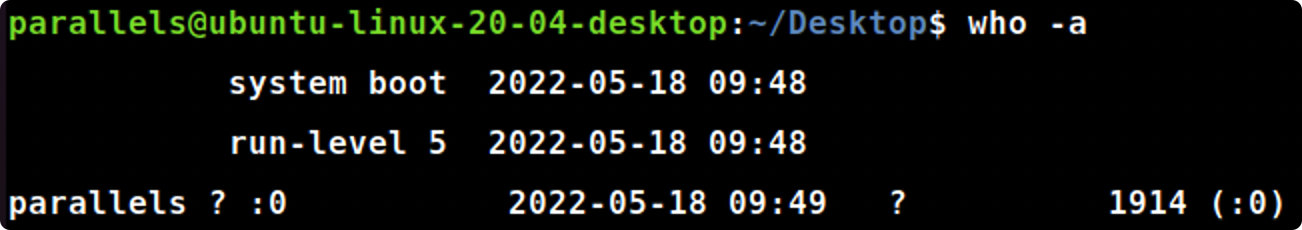
- 然后使用who -a命令来看看你的用户名和同一系统其他用户的登录密码。
4.PS1提示符
- 在shell提示符后,输入echo $PS1并按回车键,系统怎样回答?

PS1为shell命令行界面的主提示符。
- 在shell提示符后,输入PS1=%并按回车键,显示屏有什么变化?
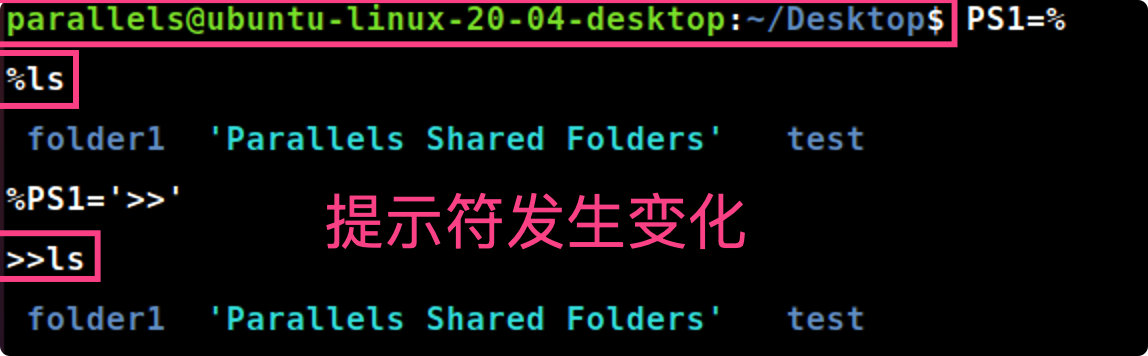
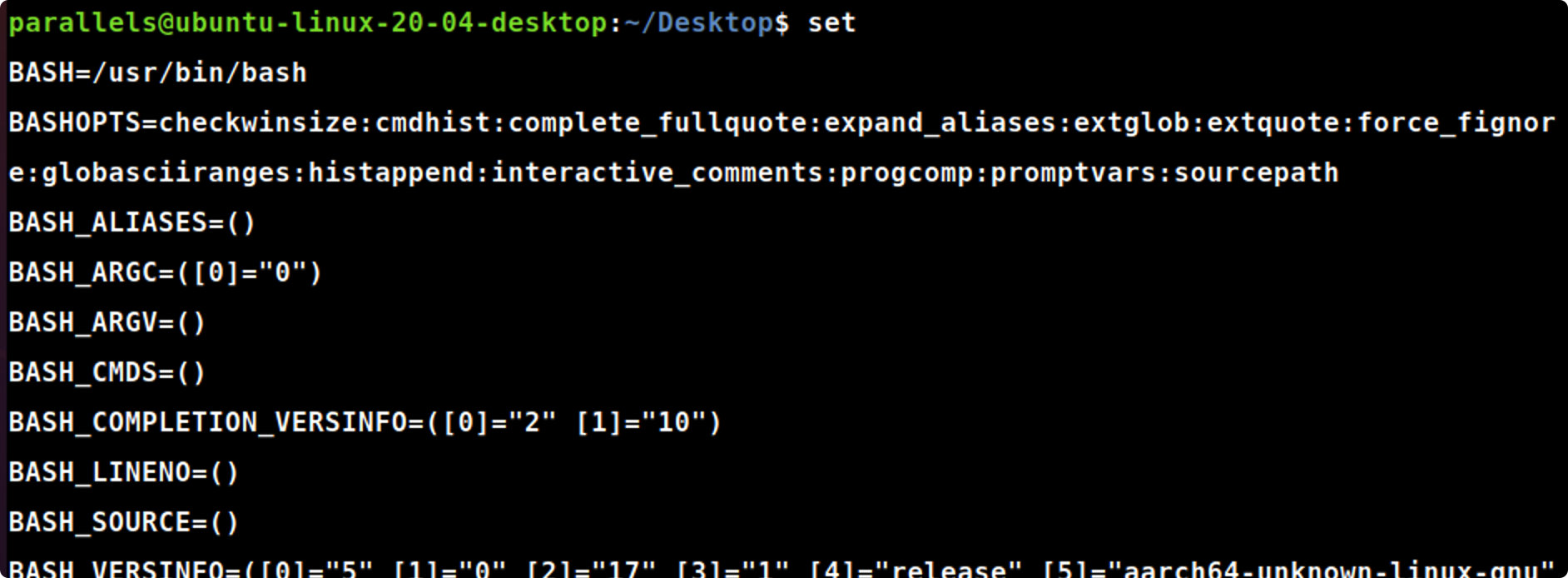
- 在shell提示符后,输入set 并按回车键,系统显示环境变量。给出你系统中的环境变量和它的值。
5.综合实践
本实验用到的命令还有:date、cal、pwd、write、uptime、man等。
- 登录你的Linux系统。
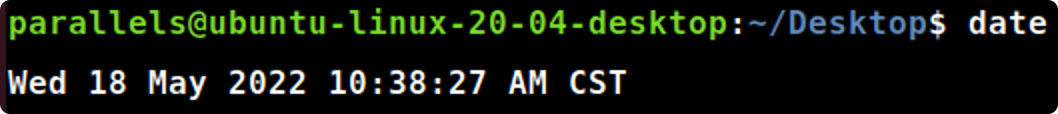
- 用命令date显示当前的时间,给出显示的结果。
date
- 用cal命令显示下列年份的日历:4、52、1752、1952、2005、2006
a) 给出你显示以上年份年历的命令
cal4cal52cal1752cal1952cal2005cal2006
b) 1752年有几天,为什么?
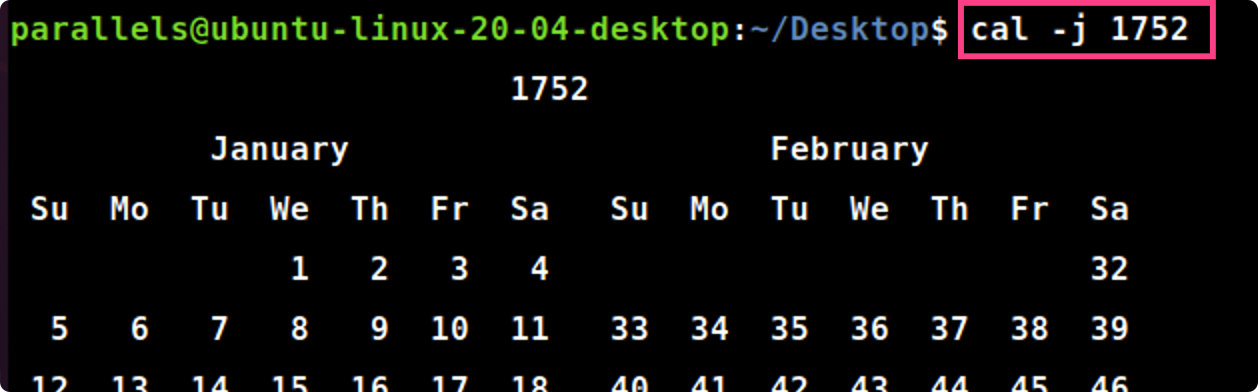
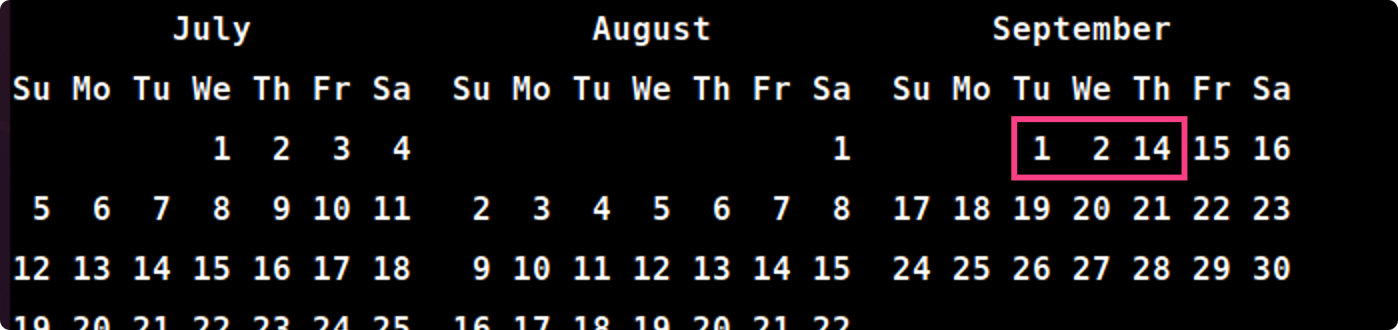
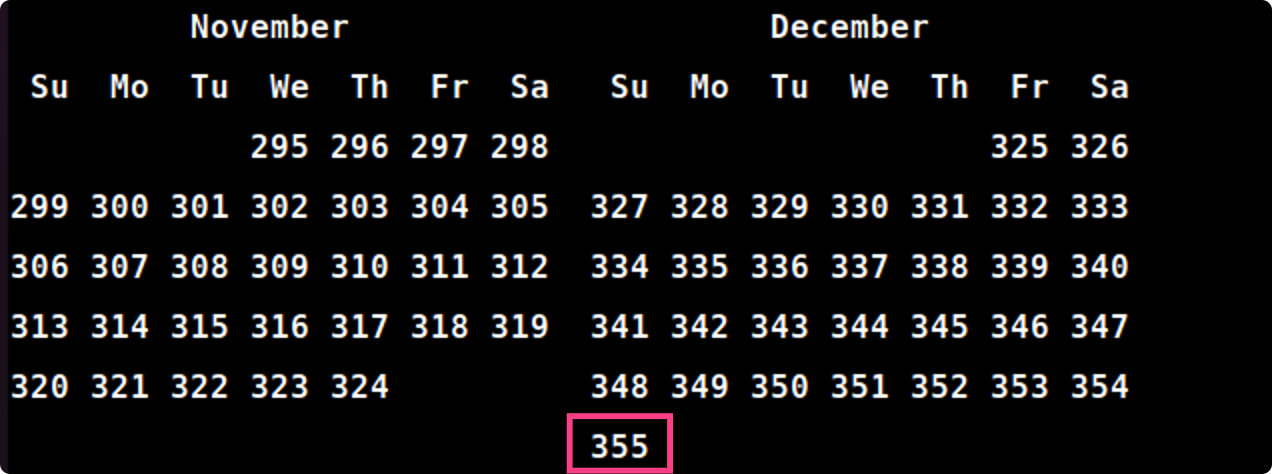
1752年由于某些历史原因,在9月份少了11天,全年仅有355天。
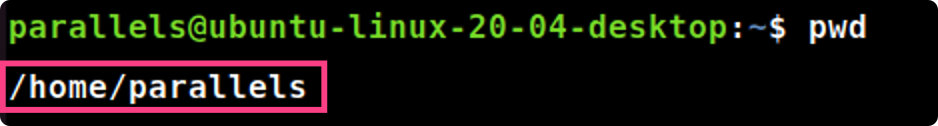
- 用pwd显示你的主目录(home directory)名字,给出pwd显示的结果。
pwd
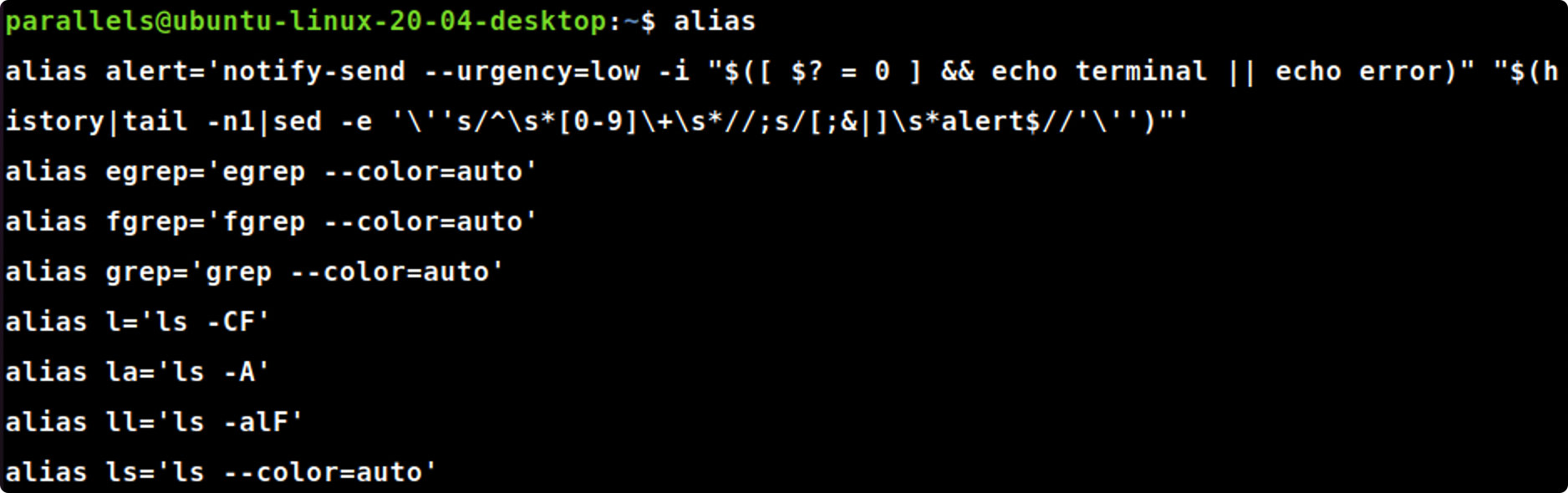
- 使用alias 命令显示系统中的命令的别名,给出显示的结果。
alias
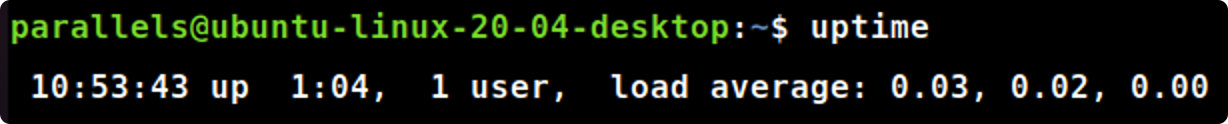
- 使用uptime命令判断系统已启动运行的时间和当前系统中有多少登录用户,给出显示的结果。
uptime
- 通过因特网或 Linux的man命令得到下面的shell命令、系统调用和库函数功能描述及每个命令使用例子:
CommandShort DescriptionUse Exampletouchupdate the access and modification times of each FILE to the current timetouch [file]cpcopy files and directoriescp [file] [dir]mvmove (rename) filesmv [file] [dir]rmremove files or directoriesrm -rf [dir]mkdirmake directoriesmkdir [dir]rmdirremove empty directoriesrmdir [dir]lslist directory contentslscdchange directorycd [dir]pwdprint name of current/working directorypwdopenopen, openat, creat - open and possibly create a fileint fd=open(“./file”,O_RDONLY)readread from a file descriptorread -p “prompt” [input]writesend a message to another usern=write(fp, p1+len, 3)closeclose a file descriptorint close(int fd)pipecreate pipeint pipe(int pipefd[2]); #fd[0]为读端,fd[1] 为写端socketcreate an endpoint for communicationint socket(int domain,int type,int protocol)mkfifomake FIFOs (named pipes)int mkfifo(const char* pathname, mode_t mode)systemexecute a shell commandint system(const char *command)printfformat and print dataprintf [format] [arguments]
版权归原作者 Rickyの水果摊 所有, 如有侵权,请联系我们删除。