Spark Map 和 FlatMap 的比较
本节将介绍Spark中
map(func)
和
flatMap(func)
两个函数的区别和基本使用。
函数原型
map(func)
将原数据的每个元素传给函数func进行格式化,返回一个新的分布式数据集。
flatMap(func)
跟
map(func)
类似,但是每个输入项和成为0个或多个输出项,所以func函数应该返回的是一个序列化的数据而不是单个数据项。
使用说明
在使用时map会将一个长度为N的RDD转换为另一个长度为N的RDD;而flatMap会将一个长度为N的RDD转换成一个N个元素的集合,然后再把这N个元素合成到一个单个RDD的结果集。
比如一个包含三行内容的数据文件“README.md”。
a b c
d
经过以下转换过程
val textFile = sc.textFile("README.md")
textFile.flatMap(_.split(" "))
其实就是经历了以下转换
["a b c", "", "d"] => [["a","b","c"],[],["d"]] => ["a","b","c","d"]
在这个示例中,flatMap就把包含多行数据的RDD,即
["a b c", "", "d"]
,转换为了一个包含多个单词的集合。实际上,flatMap相对于map多的是
[["a","b","c"],[],["d"]] => ["a","b","c","d"]
这一步。
区别对比
map(func)
函数会对每一条输入进行指定的func操作,然后为每一条输入返回一个对象;而
flatMap(func)
也会对每一条输入进行执行的func操作,然后每一条输入返回一个相对,但是最后会将所有的对象再合成为一个对象;从返回的结果的数量上来讲,map返回的数据对象的个数和原来的输入数据是相同的,而flatMap返回的个数则是不同的。参考下图进行理解: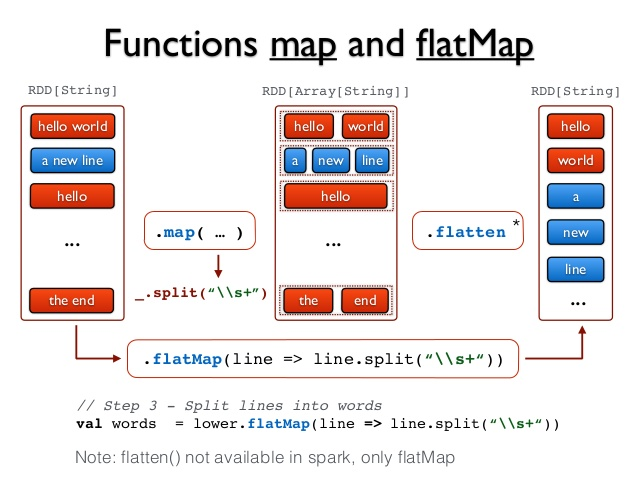
通过上图可以看出,flatMap其实比map多的就是flatten操作。
示例验证
接下来,我们用一个例子来进行比较,首先在HDFS里写入了这样内容的一个文件:
C:\WINDOWS\system32>hadoop fs -cat hdfs://localhost:9000/user/input/wordcount.txt
word in text
hello spark
the third line
C:\WINDOWS\system32>
然后再spark里进行测试,如下
scala> var textFile =sc.textFile("hdfs://localhost:9000/user/input/wordcount.txt")
textFile: org.apache.spark.rdd.RDD[String] = hdfs://localhost:9000/user/input/wordcount.txt MapPartitionsRDD[1] at textFile at <console>:27
map的结果
scala> var mapResult = textFile.map(line => line.split("\\s+"))
mapResult: org.apache.spark.rdd.RDD[Array[String]] = MapPartitionsRDD[2] at map at <console>:29
scala> mapResult.collect
res0: Array[Array[String]] = Array(Array(word, in, text), Array(hello, spark), Array(the, third, line))
flatMap的结果
scala> var flatMapResult = textFile.flatMap(line => line.split("\\s+"))
flatMapResult: org.apache.spark.rdd.RDD[String] = MapPartitionsRDD[3] at flatMap at <console>:29
scala> flatMapResult.collect
res1: Array[String] = Array(word, in, text, hello, spark, the, third, line)
版权归原作者 不二人生 所有, 如有侵权,请联系我们删除。