文章目录
📚实验目的
倒排索引(Inverted Index)被用来存储在全文搜索下某个单词在一个文档或者一组文档中的存储位置的映射,是目前几乎所有支持全文索引的搜索引擎都需要依赖的一个数据结构。通过对倒排索引的编程实现,熟练掌握 MapReduce 程序在集群上的提交与执行过程,加深对 MapReduce 编程框架的理解。
📚实验平台
- 操作系统:Linux
- Hadoop 版本:3.2.2
- JDK 版本:1.8
- Java IDE:Eclipse
📚实验内容
关于倒排索引
🐇在本地编写程序和调试
在本地 eclipse 上编写带词频属性的对英文文档的文档倒排索引程序,要求程序能够实现对 stop-words(如 a,an,the,in,of 等词)的去除,能够统计单词在每篇文档中出现的频率。文档数据和停词表可在此链接上下载,在伪分布式环境下完成程序的编写和调试。
🥕代码框架思路
- Map():对输入的Text切分为多个word。这里的
Map()包含setup()和map()。每一次map都伴随着一次setup,进行停词,筛选那些不需要统计的。 - Combine():将Map输出的中间结果
相同key部分的value累加,减少向Reduce节点传输的数据量。 - Partition():为了
将同一个word的键值对发送到同一个Reduce节点,对key进行临时处理。将原key的(word, filename)临时拆开,使Partitioner只按照word值进行选择Reduce节点。基于哈希值的分片方法。 - Reduce():利用每个Reducer接收到的键值对中,word是排好序的,来进行最后的整合。将word#filename拆分开,
将filename与累加和拼到一起,存在str中。每次比较当前的word和上一次的word是否相同,若相同则将filename和累加和附加到str中,否则输出:key:word,value:str,并将新的word作为key继续。 - 上述reduce()只会在遇到新word时,处理并输出前一个word,故对于最后一个word还需要额外的处理。
重载cleanup(),处理最后一个word并输出
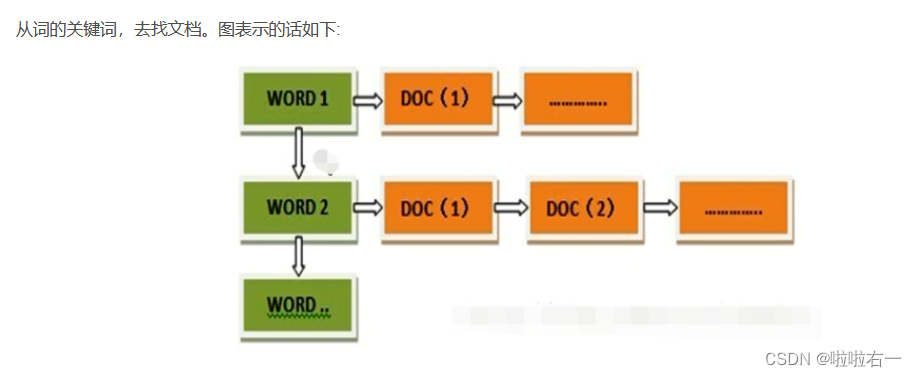
倒排索引的Map、Combiner、Partitioner部分就和上图一样
- 一个Map对应一个Combiner,借助Combiner对Map输出进行一次初始整合
- 一个Combiner又对应一个Partitioner,Partitioner将同一个word的键值对发送到同一个Reduce节点
🥕代码实现
(关注本地路径)
packageindex;importjava.io.BufferedReader;importjava.io.IOException;importjava.io.InputStreamReader;importjava.util.StringTokenizer;importjava.util.Vector;importorg.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Mapper;importorg.apache.hadoop.conf.Configuration;importorg.apache.hadoop.fs.FileSystem;importorg.apache.hadoop.fs.Path;importorg.apache.hadoop.io.IntWritable;importorg.apache.hadoop.io.Text;importorg.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.output.FileOutputFormat;importorg.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.partition.HashPartitioner;importorg.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Job;importorg.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Reducer;importorg.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.input.FileInputFormat;importorg.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.input.FileSplit;publicclass index
{publicstaticclassMapextendsMapper<Object,Text,Text,IntWritable>{/**
* setup():读取停词表到vector stop_words中
*/Vector<String> stop_words;//停词表protectedvoidsetup(Context context)throwsIOException{
stop_words =newVector<String>();//初始化停词表Configuration conf = context.getConfiguration();//读取停词表文件BufferedReader reader =newBufferedReader(newInputStreamReader(FileSystem.get(conf).open(newPath("hdfs://localhost:9000/user/hadoop/input/stop_words_eng.txt"))));String line;while((line = reader.readLine())!=null){//按行处理StringTokenizer itr=newStringTokenizer(line);while(itr.hasMoreTokens()){//遍历词,存入vector
stop_words.add(itr.nextToken());}}
reader.close();}/**
* map():对输入的Text切分为多个word
* 输入:key:当前行偏移位置 value:当前行内容
* 输出:key:word#filename value:1
*/protectedvoidmap(Object key,Text value,Context context)throwsIOException,InterruptedException{FileSplit fileSplit =(FileSplit) context.getInputSplit();String fileName = fileSplit.getPath().getName();//获取文件名,转换为小写String line = value.toString().toLowerCase();//将行内容全部转为小写字母//只保留数字和字母String new_line="";for(int i =0; i < line.length(); i ++){if((line.charAt(i)>=48&& line.charAt(i)<=57)||(line.charAt(i)>=97&& line.charAt(i)<=122)){//按行处理
new_line += line.charAt(i);}else{//其他字符保存为空格
new_line +=" ";}}
line = new_line.trim();//去掉开头和结尾的空格StringTokenizer strToken=newStringTokenizer(line);//按照空格拆分while(strToken.hasMoreTokens()){String str = strToken.nextToken();if(!stop_words.contains(str)){//不是停词则输出key-value对
context.write(newText(str+"#"+fileName),newIntWritable(1));}}}}publicstaticclassCombineextendsReducer<Text,IntWritable,Text,IntWritable>{/**
* 将Map输出的中间结果相同key部分的value累加,减少向Reduce节点传输的数据量
* 输入:key:word#filename value:1
* 输出:key:word#filename value:累加和(词频)
*/protectedvoidreduce(Text key,Iterable<IntWritable> values,Context context)throwsIOException,InterruptedException{int sum =0;for(IntWritable val : values){
sum ++;}
context.write(key,newIntWritable(sum));}}publicstaticclassPartitionextendsHashPartitioner<Text,IntWritable>{/**
* 为了将同一个word的键值对发送到同一个Reduce节点,对key进行临时处理
* 将原key的(word, filename)临时拆开,使Partitioner只按照word值进行选择Reduce节点
* 基于哈希值的分片方法
*/publicintgetPartition(Text key,IntWritable value,int numReduceTasks){//第三个参数numPartitions表示每个Mapper的分片数,也就是Reducer的个数String term = key.toString().split("#")[0];//获取word#filename中的wordreturnsuper.getPartition(newText(term), value, numReduceTasks);//按照word分配reduce节点 }}publicstaticclassReduceextendsReducer<Text,IntWritable,Text,Text>{/**
* Reduce():利用每个Reducer接收到的键值对中,word是排好序的,来进行最后的整合
* 将word#filename拆分开,将filename与累加和拼到一起,存在str中
* 每次比较当前的word和上一次的word是否相同,若相同则将filename和累加和附加到str中,否则输出:key:word,value:str,并将新的word作为key继续
* 输入:
* key value
* word1#filename 1 [num1,num2,...]
* word1#filename 2 [num1,num2,...]
* word2#filename 1 [num1,num2,...]
* 输出:
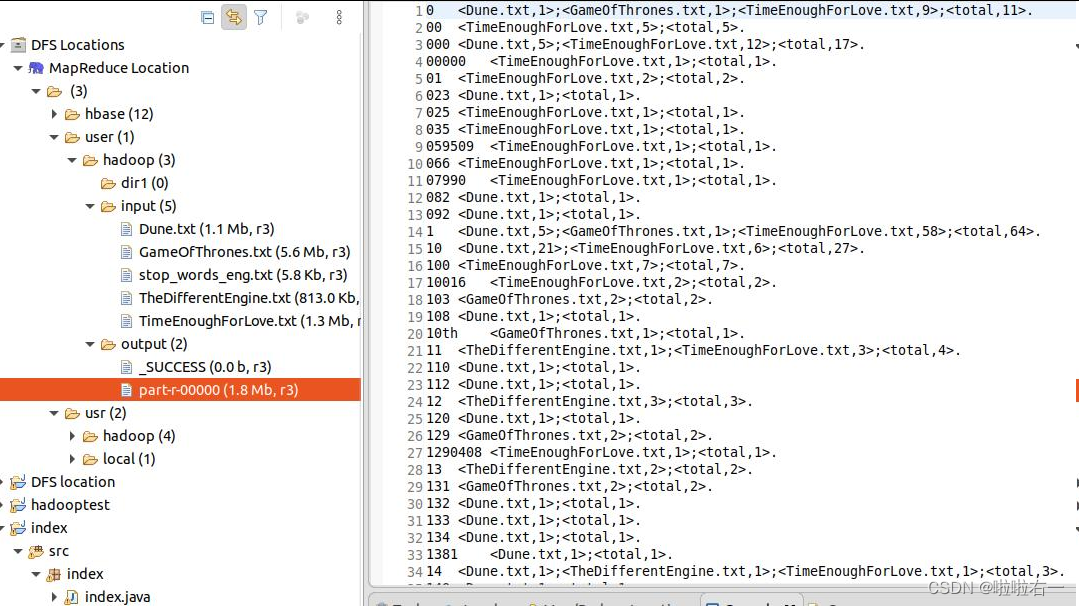
* key:word value:<filename1,词频><filename2,词频>...<total,总词频>
*/privateString lastfile =null;//存储上一个filenameprivateString lastword =null;//存储上一个wordprivateString str ="";//存储要输出的value内容privateint count =0;privateint totalcount =0;protectedvoidreduce(Text key,Iterable<IntWritable> values,Context context)throwsIOException,InterruptedException{String[] tokens = key.toString().split("#");//将word和filename存在tokens数组中if(lastword ==null){
lastword = tokens[0];}if(lastfile ==null){
lastfile = tokens[1];}if(!tokens[0].equals(lastword)){//此次word与上次不一样,则将上次的word进行处理并输出
str +="<"+lastfile+","+count+">;<total,"+totalcount+">.";
context.write(newText(lastword),newText(str));//value部分拼接后输出
lastword = tokens[0];//更新word
lastfile = tokens[1];//更新filename
count =0;
str="";for(IntWritable val : values){//累加相同word和filename中出现次数
count += val.get();//转为int}
totalcount = count;return;}if(!tokens[1].equals(lastfile)){//新的文档
str +="<"+lastfile+","+count+">;";
lastfile = tokens[1];//更新文档名
count =0;//重设count值for(IntWritable value : values){//计数
count += value.get();//转为int}
totalcount += count;return;}//其他情况,只计算总数即可for(IntWritable val : values){
count += val.get();
totalcount += val.get();}}/**
* 上述reduce()只会在遇到新word时,处理并输出前一个word,故对于最后一个word还需要额外的处理
* 重载cleanup(),处理最后一个word并输出
*/publicvoidcleanup(Context context)throwsIOException,InterruptedException{
str +="<"+lastfile+","+count+">;<total,"+totalcount+">.";
context.write(newText(lastword),newText(str));super.cleanup(context);}}publicstaticvoidmain(String args[])throwsException{Configuration conf =newConfiguration();
conf.set("fs.defaultFS","hdfs://localhost:9000");if(args.length !=2){System.err.println("Usage: Relation <in> <out>");System.exit(2);}Job job =Job.getInstance(conf,"InvertedIndex");//设置环境参数
job.setJarByClass(index.class);//设置整个程序的类名
job.setMapperClass(Map.class);//设置Mapper类
job.setCombinerClass(Combine.class);//设置combiner类
job.setPartitionerClass(Partition.class);//设置Partitioner类
job.setReducerClass(Reduce.class);//设置reducer类
job.setOutputKeyClass(Text.class);//设置Mapper输出key类型
job.setOutputValueClass(IntWritable.class);//设置Mapper输出value类型FileInputFormat.addInputPath(job,newPath(args[0]));//输入文件目录FileOutputFormat.setOutputPath(job,newPath(args[1]));//输出文件目录System.exit(job.waitForCompletion(true)?0:1);//参数true表示检查并打印 Job 和 Task 的运行状况}}
⭐补充:当我们新建一个Package和Class后运行时,可能会出现如下报错(主要是在MapReduce编程输入输出里会遇到)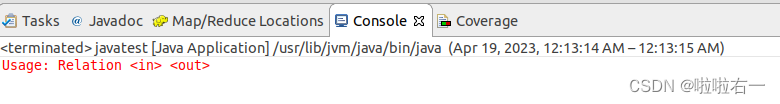
⭐解决办法:
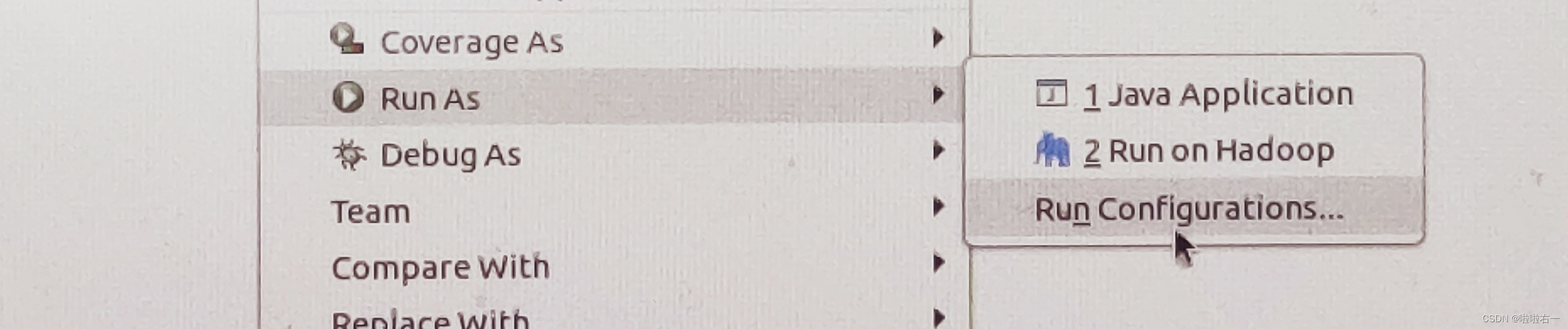
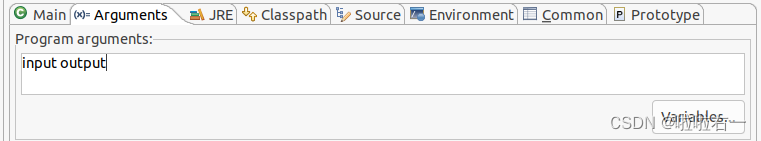
- “Run As”选中“Run Configurations…”

- 然后在“Arguments”里输入
input output,然后再run就行了。
🐇在集群上提交作业并执行
集群的服务器地址为 10.102.0.198,用户主目录为/home/用户名,hdfs 目录为/user/用户名。集群上的实验文档存放目录为 hdfs://10.102.0.198:9000/input/. 英文停词表文件存放位置为hdfs://10.102.0.198:9000/stop_words/stop_words_eng.txt。
🥕在集群上提交作业并执行,同本地执行相比即需修改路径。

🥕修改后通过expoet,导出jar包,关注 Main-Class 的设置!
- 选中index.java右键Export。
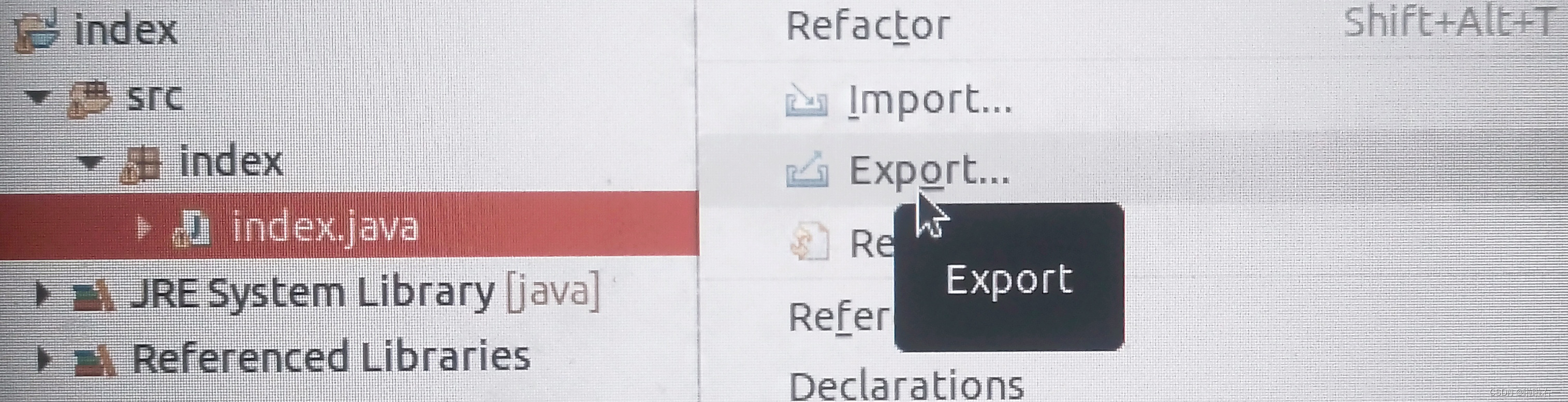
- 如下图选中
JAR file后点Next。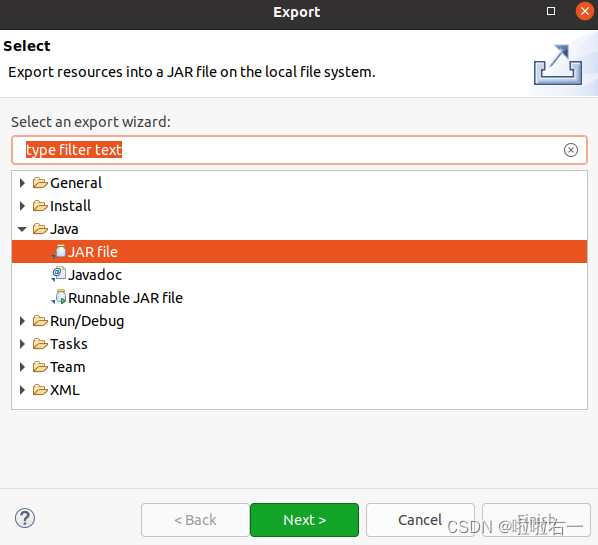
- 确认选中index及其src,
JAR的命名要和class名一样,比如这里是index.java,就是class index,也就是index.jar。然后点Next。
- 到如下页面,再点Next。
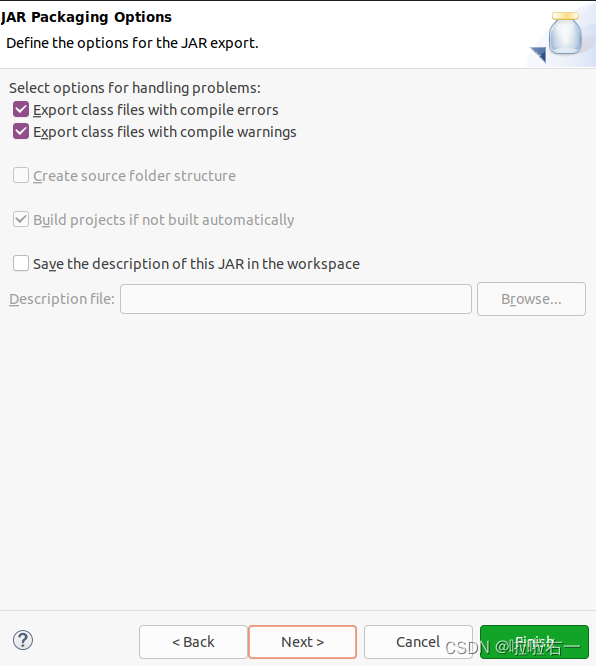
- 在
Main class那点Browse,选中index。
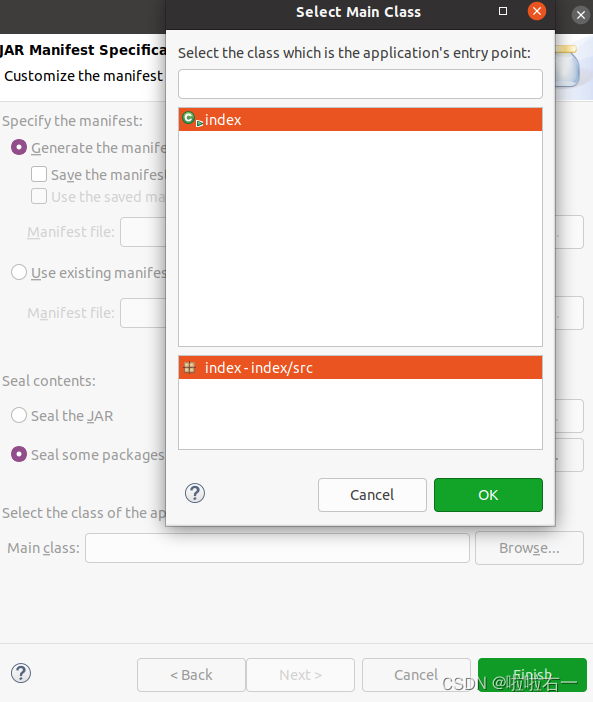
- 如下图。
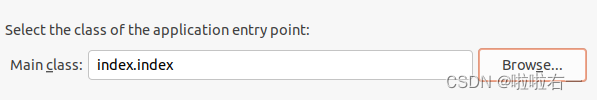
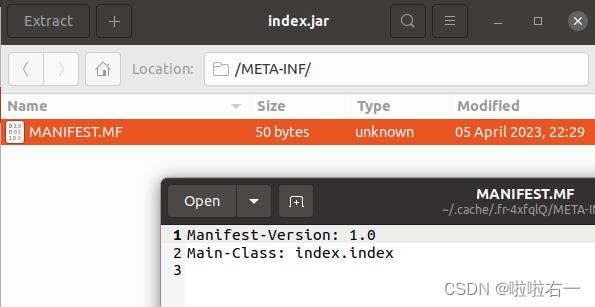
- 最后点finish完成导出,可在文件夹里找到index.jar。双击index.jar,在它的
METS-INT里头查看Main-Class是否设置成功。
🥕在终端依次输入以下指令,完成提交
- 使用
scp InvertedIndex.jar 用户名@10.102.0.198:/home/用户名命令将本地程序提交到 Hadoop 集群 - 通过
ssh 用户名@10.102.0.198命令远程登录到 Hadoop 集群进行操作; - 使用
hadoop jar InvertedIndex.jar /input /user/用户名/output命令在集群上运行 Hadoop 作业,指定输出目录为自己 hdfs 目录下的 output。 - 使用
diff 命令判断自己的输出结果与标准输出的差异
scp index.jar bigdata_学号@10.102.0.198:/home/bigdata_学号
ssh bigdata_学号@10.102.0.198
hadoop jar index.jar /input /user/bigdata_学号/output
diff<(hdfs dfs -cat /output/part-r-00000)<(hdfs dfs -cat /user/bigdata_学号/output/part-r-00000)
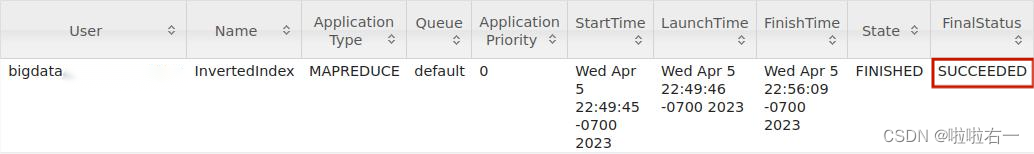
在浏览器中打开 http://10.102.0.198:8088,可以查看集群上作业的基本执行情况。
版权归原作者 啦啦右一 所有, 如有侵权,请联系我们删除。