引言
阅读顺序检测旨在捕获人类读者能够自然理解的单词序列。现有的OCR引擎通常按照从上到下、从左到右的方式排列识别到的文本行,但这并不适用于某些文档类型,如多栏模板、表格等。LayoutReader模型使用seq2seq模型捕获文本和布局信息,用于阅读顺序预测,在实验中表现出色,并显著提高了开源和商业OCR引擎在文本行排序方面的表现。
一、LayoutReader模型
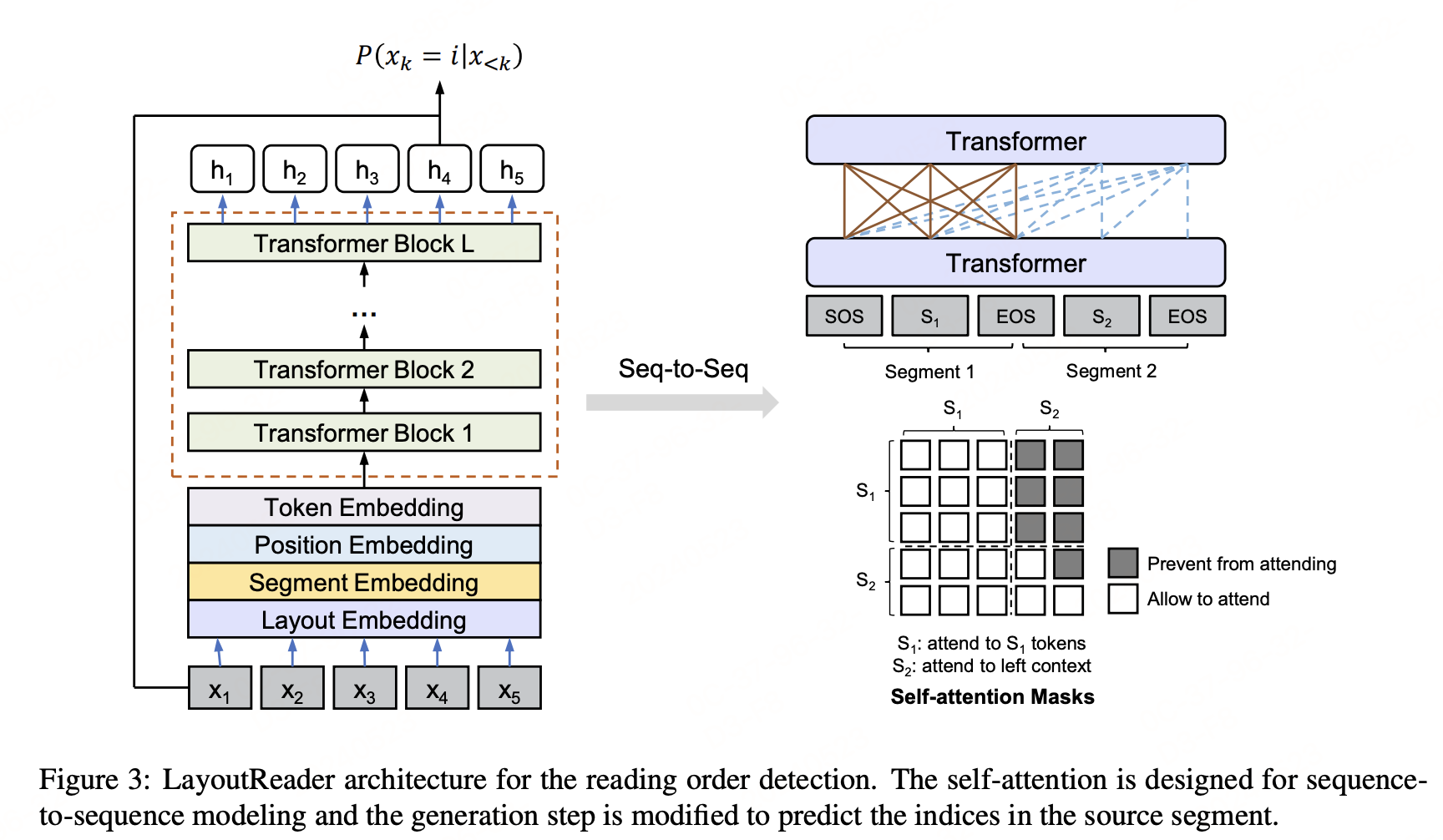
1.1 编码器(Encoder)
LayoutReader使用LayoutLM的布局模型作为编码器。在编码阶段,LayoutReader将源序列和目标序列打包成一个连续的输入序列,并设计了自注意力掩码来控制token之间的可见性。具体来说,LayoutReader允许源序列中的标记相互关注,同时阻止目标序列中的标记关注右侧上下文。
自注意力掩码
M
M
M的设计:
M
i
,
j
=
{
1
if
i
<
j
or
i
,
j
∈
src
0
otherwise
M_{i,j} = \begin{cases} 1 & \text{if } i < j \text{ or } i, j \in \text{src} \\ 0 & \text{otherwise} \end{cases}
Mi,j={10if i<j or i,j∈srcotherwise
其中,
i
i
i和
j
j
j是打包输入序列中的索引,可能来自源或目标序列;
i
,
j
∈
s
r
c
i, j ∈ src
i,j∈src表示两个标记都来自源序列。
1.2 解码器(Decoder)
在解码阶段,由于源序列和目标序列是重新排序的序列,预测候选可以被限制在源序列内。因此,模型被要求预测源序列中的索引。概率计算如下:

其中,
i
i
i是源序列中的索引;$e_i
和
和
和e_j
分别是源序列的第
分别是源序列的第
分别是源序列的第i
个和第
个和第
个和第j
个输入嵌入
(
i
n
p
u
t
e
m
b
e
d
d
i
n
g
s
)
;
个输入嵌入(input embeddings);
个输入嵌入(inputembeddings);h_k
是第
是第
是第k
步的隐藏状态
(
h
i
d
d
e
n
s
t
a
t
e
s
)
;
步的隐藏状态(hidden states);
步的隐藏状态(hiddenstates);b_k
是第
是第
是第k$步的偏置(bias)。
二、实验
进行了三个实验来评估LayoutReader在ReadingBank上的表现,包括阅读顺序检测、输入顺序研究和对OCR引擎的适应性



实验结果表明,LayoutReader在阅读顺序检测任务上超越了其他基线方法,并且可以显著提高OCR引擎的文本行排序。
三、非官方开源权重
- huggingface:https://huggingface.co/yujunhuinlp/LayoutReader-only-layout-large
- github code(only layout):https://github.com/yujunhuics/LayoutReader
- bbox排序
import torchfrom model import LayoutLMv3ForBboxClassificationfrom collections import defaultdictCLS_TOKEN_ID =0UNK_TOKEN_ID =3EOS_TOKEN_ID =2defBboxesMasks(boxes): bbox =[[0,0,0,0]]+ boxes +[[0,0,0,0]] input_ids =[CLS_TOKEN_ID]+[UNK_TOKEN_ID]*len(boxes)+[EOS_TOKEN_ID] attention_mask =[1]+[1]*len(boxes)+[1]return{"bbox": torch.tensor([bbox]),"attention_mask": torch.tensor([attention_mask]),"input_ids": torch.tensor([input_ids]),}defdecode(logits, length): logits = logits[1: length +1,:length] orders = logits.argsort(descending=False).tolist() ret =[o.pop()for o in orders]whileTrue: order_to_idxes = defaultdict(list)for idx, order inenumerate(ret): order_to_idxes[order].append(idx) order_to_idxes ={k: v for k, v in order_to_idxes.items()iflen(v)>1}ifnot order_to_idxes:breakfor order, idxes in order_to_idxes.items(): idxes_to_logit ={}for idx in idxes: idxes_to_logit[idx]= logits[idx, order] idxes_to_logit =sorted( idxes_to_logit.items(), key=lambda x: x[1], reverse=True)for idx, _ in idxes_to_logit[1:]: ret[idx]= orders[idx].pop()return retdeflayoutreader(bboxes): inputs = BboxesMasks(bboxes) logits = model(**inputs).logits.cpu().squeeze(0) orders = decode(logits,len(bboxes))return ordersif __name__ =='__main__': bboxes =[[584,0,595,1],[35,120,89,133],[35,140,75,152]] model_path ="" model = LayoutLMv3ForBboxClassification.from_pretrained()print(layoutreader(bboxes))# [1, 2, 0] - 效果样例
参考文献
- paper:LayoutReader: Pre-training of Text and Layout for Reading Order Detection,https://arxiv.org/pdf/2108.11591
- Official code:https://github.com/microsoft/unilm/tree/master/layoutreader
版权归原作者 余俊晖 所有, 如有侵权,请联系我们删除。