说明:我们今天要分享的是依赖注入(DI)通过自动装配的注解方式@Autowird注解方法的作用和实现原理以及实现机制。
前言:在分享之前,我们先来回顾一下说明是依赖注入,依赖注入中手动注入和自动装配的几种方式,以便于提高大家对本篇文章的理解。
一、依赖注入的方式
对于spring配置一个bean时,如果需要给该bean提供一些初始化参数,则需要通过依赖注入方式,所谓的依赖注入就是通过spring将bean所需要的一些参数传递到bean实例对象的过程(将依赖关系注入到对象中)
1)手动注入
①使用属性的setter方法注入 ,这是最常用的方式:
**要求: **属性注入要求Bean提供一个默认的构造函数,并为需要注入的属性提供对应的Setter方法。Spring先调用Bean的默认构造函数实例化Bean对象,然后通过反射的方式调用Setter方法注入属性值。
② 构造器注入
使用方式:
第一,在类中,不用为属性设置setter方法(但是可以有),但是需要生成该类带参的构造方法。
第二,在配置文件中配置该类的bean,并配置构造器,在配置构造器中用到了<constructor-arg>节点,该节点有四个属性:
· index是索引,指定注入的属性位置,从0开始;
· type是指该属性所对应的类型;
· ref 是指引用的依赖对象;
· value 当注入的不是依赖对象,而是基本数据类型时,就用value;
2)自动装配
**XML方式进行自动装配 **
大家可以看到用xml装配bean是一件很繁琐的事情,而且我们还要找到对应类型的bean才能装配。
创建应用对象之间协作关系的行为称为装配。也就是说当一个对象的属性是另一个对象时,实例化时,需要为这个对象属性进行实例化,这就是装配。
如果一个对象只通过接口来表明依赖关系,那么这种依赖就能够在对象本身毫不知情的情况下,用不同的具体实现进行切换。但是这样会存在一个问题,在传统的依赖注入配置中,我们必须要明确要给属性装配哪一个bean的引用,一旦bean很多,就不好维护了。基于这样的场景,spring使用注解来进行自动装配,解决这个问题。自动装配就是开发人员不必知道具体要装配哪个bean的引用,这个识别的工作会由spring来完成。
在sping框架中共有5种自动装配 :
- no:默认的方式是不进行自动装配的,通过手工设置ref属性来进行装配bean。
- byName:通过bean的名称进行自动装配,如果一个bean的 property 与另一bean 的name 相同,就进行自动装配。
- byType:通过参数的数据类型进行自动装配。
- constructor:利用构造函数进行装配,并且构造函数的参数通过byType进行装配。
- autodetect:自动探测,如果有构造方法,通过 construct的方式自动装配,否则使用 byType的方式自动装配。
上面所有方式的applicationContext.xml配置文件如下:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/context https://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd">
<!-- 使用注解前的配置 -->
<context:annotation-config></context:annotation-config>
<!-- 扫描 -->
<context:component-scan base-package="com.ape.pojo"></context:component-scan>
<!-- 手动注入 -->
<!-- set注入 -->
<bean id="Student" class="com.ape.pojo.Student">
<property name="sid" value="1"></property>
<property name="sname" value="张三"></property>
<property name="smoney" value="100.00"></property>
<property name="cat" ref="cat"></property>
</bean>
<!-- 构造器注入construct -->
<bean id="Student" class="com.ape.pojo.Student">
<constructor-arg name="sid" value="1"></constructor-arg>
<constructor-arg name="sname" value="张三"></constructor-arg>
<constructor-arg name="smoney" value="100.00"></constructor-arg>
<constructor-arg name="cat" ref="cat"></constructor-arg>
</bean>
<bean id="Student" class="com.ape.pojo.Student">
<constructor-arg type="int" value="1"></constructor-arg>
<constructor-arg type="java.lang.String" value="张三"></constructor-arg>
<constructor-arg type="double" value="100.00"></constructor-arg>
<constructor-arg type="com.ape.pojo.Cat" ref="cat"></constructor-arg>
</bean>
<bean id="Student" class="com.ape.pojo.Student">
<constructor-arg index="0" value="1"></constructor-arg>
<constructor-arg index="1" value="张三"></constructor-arg>
<constructor-arg index="2" value="100.00"></constructor-arg>
<constructor-arg index="3" ref="cat"></constructor-arg>
</bean>
<!-- 自动装配 -->
<!-- xml -->
<bean id="Student" class="com.ape.pojo.Student" autowire="no">
<property name="sid" value="1"></property>
<property name="sname" value="张三"></property>
<property name="smoney" value="100.00"></property>
<property name="cat" ref="cat"></property>
</bean>
<bean id="Student" class="com.ape.pojo.Student" autowire="byName">
</bean>
<bean id="Student" class="com.ape.pojo.Student" autowire="byType">
</bean>
<bean id="Student" class="com.ape.pojo.Student" autowire="constructor">
</bean>
<bean id="Student" class="com.ape.pojo.Student" autowire="default">
</bean>
</beans>
二、注解@Autowired的自动装配原理
1)@Autowired自动装配过程
使用@Autowired注解来自动装配指定的bean。在使用@Autowired注解之前需要在Spring配置文件进行配置<context:annotation-config />。
在启动spring IoC时,容器自动装载了一个AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor后置处理器,当容器扫描到@Autowied、@Resource或@Inject时,就会在IOC容器自动查找需要的bean,并装配给该对象的属性。在使用@Autowired时,首先在容器中查询对应类型的bean:
如果查询结果刚好为一个,就将该bean装配给@Autowired指定的数据;
如果查询的结果不止一个,那么@Autowired会根据名称来查找;
如果上述查找的结果为空,那么会抛出异常。解决方法时,使用required=false。
2) 实现原理
①首先看看spring的源代码定义
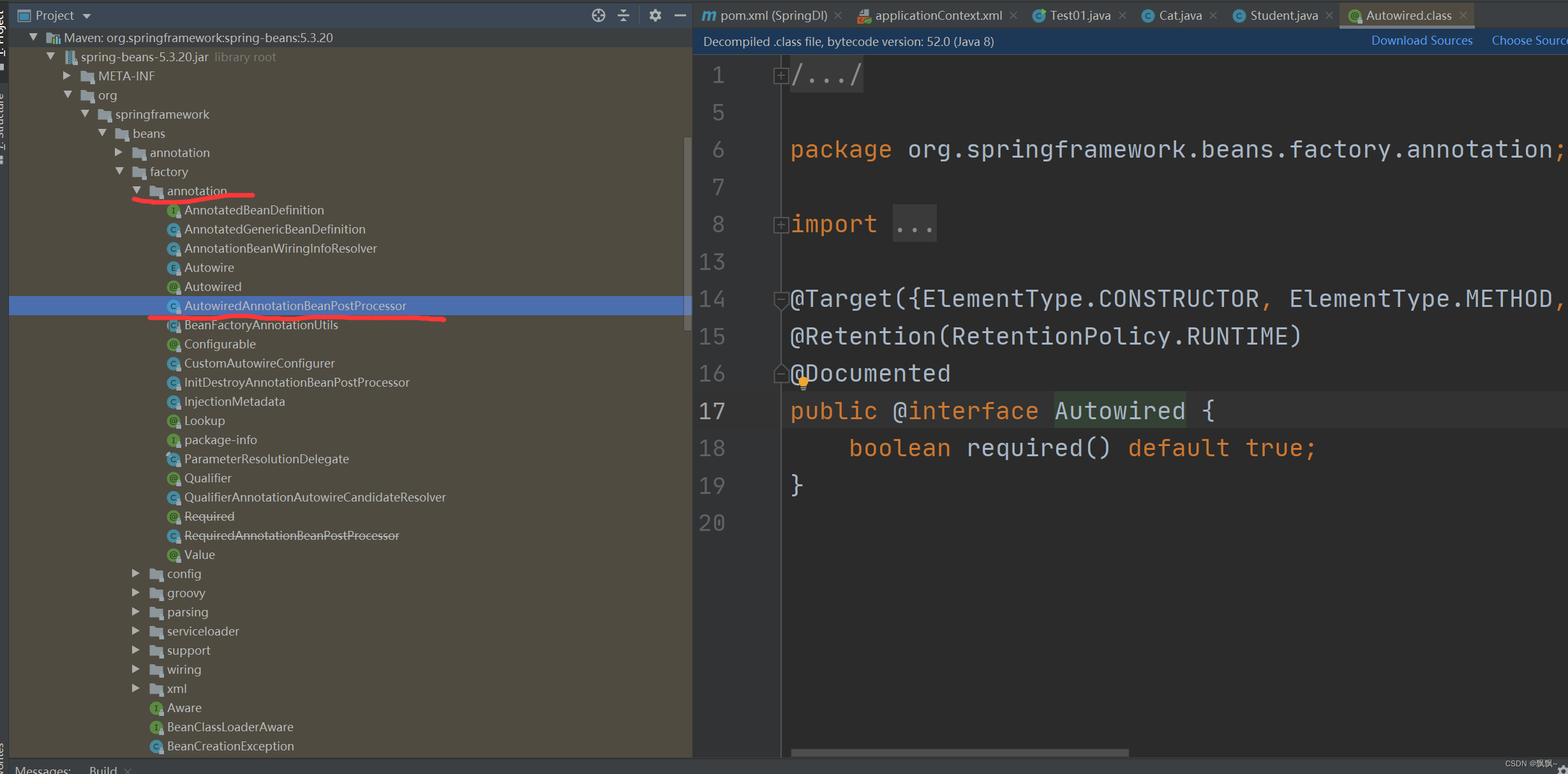
阅读代码我们可以看到,Autowired注解可以应用在构造方法,普通方法,参数,字段,以及注解这五种类型的地方,它的保留策略是在运行时。在Spring源代码当中,Autowired注解位于包org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation之中,如上图。
②核心逻辑在buildAutowiringMetadata中
通过反射获取该类的每一个字段和方法,并且分别用 findAutowiredAnnotation方法遍历每一个字段和方法,如果有@Autowired注解修饰,则返回注解相关属性。最后这个方法返回的就是包含所有带有autowire注解修饰的一个InjectionMetadata集合。
private InjectionMetadata buildAutowiringMetadata(Class<?> clazz) {
if (!AnnotationUtils.isCandidateClass(clazz, this.autowiredAnnotationTypes)) {
return InjectionMetadata.EMPTY;
} else {
List<InjectedElement> elements = new ArrayList();
Class targetClass = clazz;
do {
List<InjectedElement> currElements = new ArrayList();
ReflectionUtils.doWithLocalFields(targetClass, (field) -> {
MergedAnnotation<?> ann = this.findAutowiredAnnotation(field);
if (ann != null) {
if (Modifier.isStatic(field.getModifiers())) {
if (this.logger.isInfoEnabled()) {
this.logger.info("Autowired annotation is not supported on static fields: " + field);
}
return;
}
boolean required = this.determineRequiredStatus(ann);
currElements.add(new AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor.AutowiredFieldElement(field, required));
}
});
ReflectionUtils.doWithLocalMethods(targetClass, (method) -> {
Method bridgedMethod = BridgeMethodResolver.findBridgedMethod(method);
if (BridgeMethodResolver.isVisibilityBridgeMethodPair(method, bridgedMethod)) {
MergedAnnotation<?> ann = this.findAutowiredAnnotation(bridgedMethod);
if (ann != null && method.equals(ClassUtils.getMostSpecificMethod(method, clazz))) {
if (Modifier.isStatic(method.getModifiers())) {
if (this.logger.isInfoEnabled()) {
this.logger.info("Autowired annotation is not supported on static methods: " + method);
}
return;
}
if (method.getParameterCount() == 0 && this.logger.isInfoEnabled()) {
this.logger.info("Autowired annotation should only be used on methods with parameters: " + method);
}
boolean required = this.determineRequiredStatus(ann);
PropertyDescriptor pd = BeanUtils.findPropertyForMethod(bridgedMethod, clazz);
currElements.add(new AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor.AutowiredMethodElement(method, required, pd));
}
}
});
elements.addAll(0, currElements);
targetClass = targetClass.getSuperclass();
} while(targetClass != null && targetClass != Object.class);
return InjectionMetadata.forElements(elements, clazz);
}
}
③InjectionMetadata类
这个类由两部分组成: targetClass目标类和我们要获得的injectedElements集合。
public InjectionMetadata(Class<?> targetClass, Collection<InjectionMetadata.InjectedElement> elements) {
this.targetClass = targetClass;
this.injectedElements = elements;
}
④ 实现注入逻辑
调用InjectionMetadata中的公共inject方法遍历调用protect的inject方法
public PropertyValues postProcessProperties(PropertyValues pvs, Object bean, String beanName) {
InjectionMetadata metadata = this.findAutowiringMetadata(beanName, bean.getClass(), pvs);
try {
metadata.inject(bean, beanName, pvs);
return pvs;
} catch (BeanCreationException var6) {
throw var6;
} catch (Throwable var7) {
throw new BeanCreationException(beanName, "Injection of autowired dependencies failed", var7);
}
}
⑤调用InjectionMetadata中的公共inject
public void inject(Object target, @Nullable String beanName, @Nullable PropertyValues pvs) throws Throwable {
Collection<InjectionMetadata.InjectedElement> checkedElements = this.checkedElements;
Collection<InjectionMetadata.InjectedElement> elementsToIterate = checkedElements != null ? checkedElements : this.injectedElements;
if (!((Collection)elementsToIterate).isEmpty()) {
Iterator var6 = ((Collection)elementsToIterate).iterator();
while(var6.hasNext()) {
InjectionMetadata.InjectedElement element = (InjectionMetadata.InjectedElement)var6.next();
element.inject(target, beanName, pvs);
}
}
}
⑥遍历调用protect的inject方法
protected void inject(Object target, @Nullable String requestingBeanName, @Nullable PropertyValues pvs) throws Throwable {
if (this.isField) {
Field field = (Field)this.member;
ReflectionUtils.makeAccessible(field);
field.set(target, this.getResourceToInject(target, requestingBeanName));
} else {
if (this.checkPropertySkipping(pvs)) {
return;
}
try {
Method method = (Method)this.member;
ReflectionUtils.makeAccessible(method);
method.invoke(target, this.getResourceToInject(target, requestingBeanName));
} catch (InvocationTargetException var5) {
throw var5.getTargetException();
}
}
}
实质就是inject也使用了反射技术并且依然是分成字段和方法去处理的。
博主也是第一次分享源码,确实在写本篇博客过程中收获颇丰,所以,建议有java基础的小伙伴,在后面的学习中,遇到新知识,可以自己通过阅读源码的方式进行相关技术的学习。

版权归原作者 飘飘~ 所有, 如有侵权,请联系我们删除。